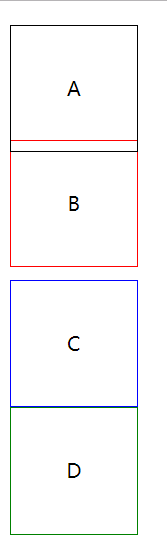
position定位及实际应用
position: static; 静态定位 / 常规定位 / 自然定位
忽略top/right/bottom/left/z-index的影响,使元素回到自然流中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.block{
width:100px;
height:100px;
line-height:100px;
text-align:center; position: relative;
top:10px;
}
.block:first-child{
border:1px solid;
}
.block:nth-child(2){
position: static;
border:1px solid red;
}
.block:nth-child(3){
border:1px solid blue;
}
.block:nth-child(4){
border:1px solid green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="block">A</div>
<div class="block">B</div>
<div class="block">C</div>
<div class="block">D</div>
</body>
</html>
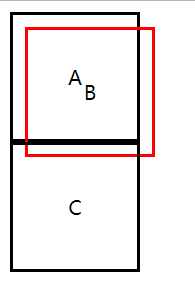
设置margin:auto为水平居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.block{
width:100px;
height:100px;
line-height:100px;
text-align:center; position: static;
margin:auto;
}
.block:first-child{
border:1px solid;
}
.block:nth-child(2){
border:1px solid red;
}
.block:nth-child(3){
border:1px solid blue;
}
.block:nth-child(4){
border:1px solid green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="block">A</div>
<div class="block">B</div>
<div class="block">C</div>
<div class="block">D</div>
</body>
</html>

position:relative 相对定位
相对于自己在常规流中的位置,进行偏移
原来的空间依然预留
可以使浮动元素发生偏移,并控制堆叠顺序
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.block{
width:100px;
height:100px;
line-height:100px;
text-align:center;
color:white; float:left;
position: relative; }
.block:first-child{
background:black;
z-index:2;
}
.block:nth-child(2){
background:red;
left:-50px;
z-index:1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="block">A</div>
<div class="block">B</div>
</body>
</html>

position:absolute;
参照物是最近定位的祖先元素
如果没有祖先元素被定位,则默认为body
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.block{
width:100px;
height:100px;
line-height:100px;
text-align:center;
border:2px solid; position: relative;
}
.block:nth-child(2){
border-color:red; position: absolute;
top:20px;
left:20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="block">A</div>
<div class="block">B</div>
<div class="block">C</div>
</body>
</html>
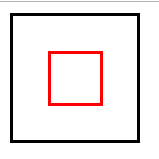
实现水平垂直居中定位:
1、给父元素设置:position: relative;
2、给子元素设置:
position: absolute;
top:0;
left:0;
right:0;
bottom:0;
margin:auto auto;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.parent{
width:100px;
height:100px;
border:2px solid; position: relative;
}
.child{
width:40px;
height:40px;
border:2px solid;
border-color:red; position: absolute;
top:0;
left:0;
right:0;
bottom:0;
margin:auto auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="child"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
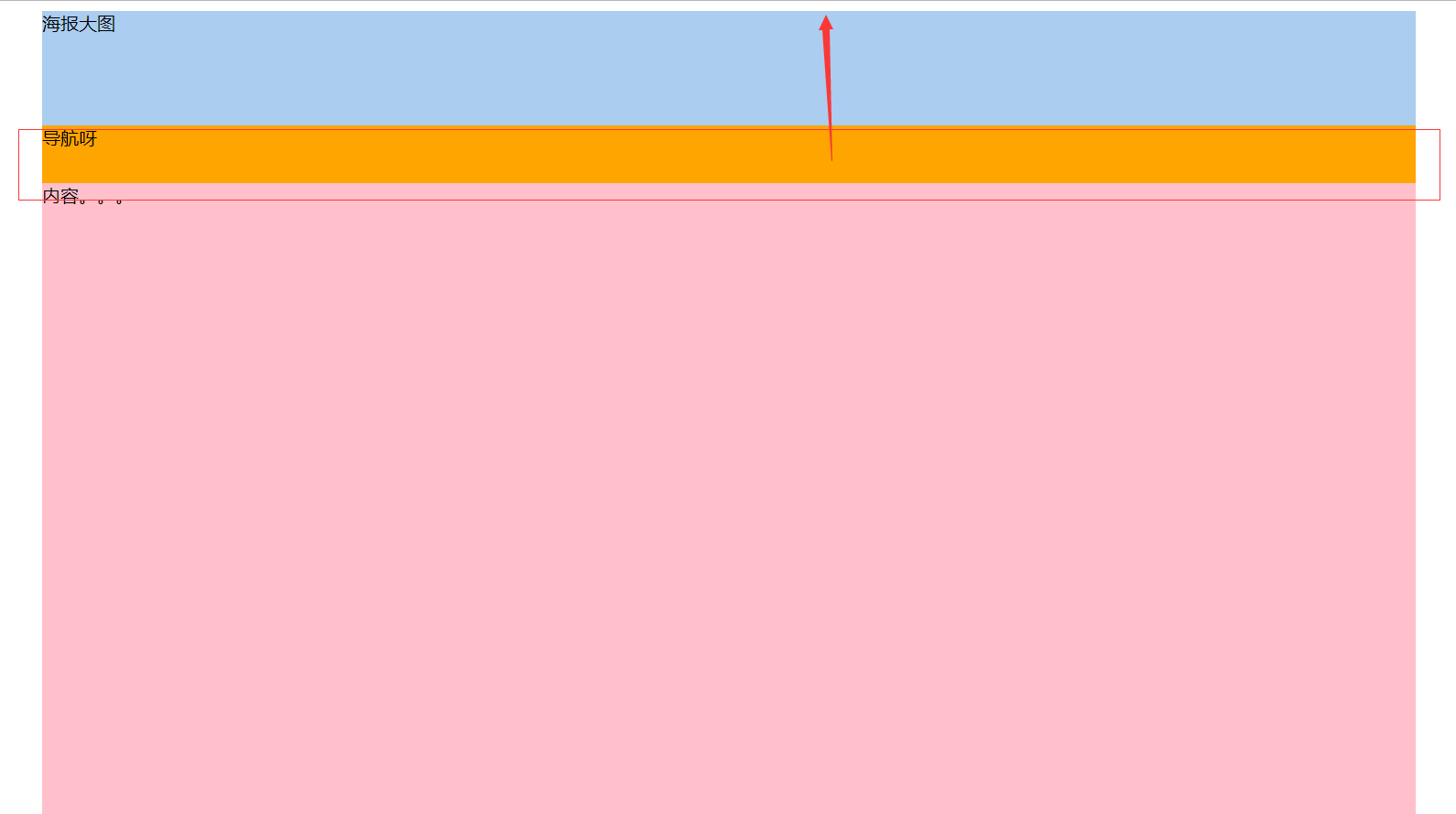
position:fixed;
继承position:absolute;的所有特征,区别是以视口做参照来定位
position:sticky;
与top偏移量结合使用
如果最近祖先元素有定位,则参考最近祖先元素;否则参考视口
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.banner{
width:1200px;
height:100px;
background:#abcdef;
margin:0 auto;
}
.nav{
width:1200px;
height:50px;
background:orange;
margin:0 auto;
position: sticky;
top:0;
}
.container{
width:1200px;
height:1000px;
background:pink;
margin:0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="banner">海报大图</div>
<div class="nav">导航呀</div>
<div class="container">内容。。。</div>
</body>
</html>

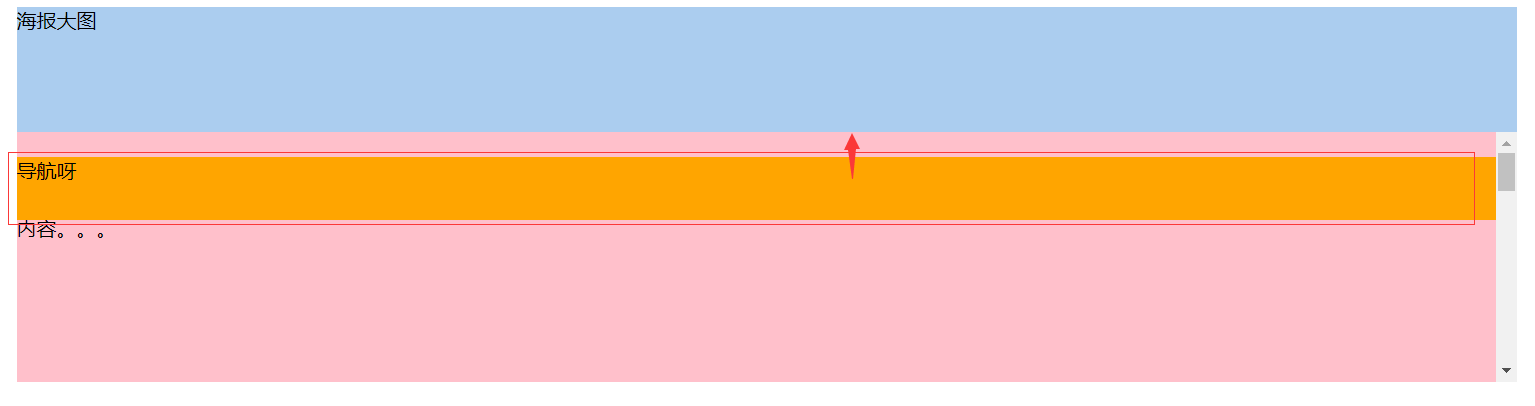
相对于最近定位的祖先元素做参考:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.banner{
width:1200px;
height:100px;
background:#abcdef;
margin:0 auto;
}
.nav{
width:1200px;
height:50px;
background:orange;
margin:0 auto;
position: sticky;
top:20px;
}
.container{
width:1200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
margin:0 auto;
position: relative;
overflow-y: scroll;
overflow-x: hidden; }
p{
height:1000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="banner">海报大图</div>
<div class="container">
<div class="nav">导航呀</div>
<p>内容。。。</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>

导航在居中位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.banner{
width:1200px;
height:100px;
background:#abcdef;
margin:0 auto;
}
.nav{
width:1200px;
height:50px;
background:orange;
margin:0 auto;
position: sticky;
top:20px;
}
.container{
width:1200px;
height:200px;
background:pink;
margin:0 auto;
position: relative;
overflow-y: scroll;
overflow-x: hidden; }
p{
height:1000px;
}
p:first-child{
height:50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="banner">海报大图</div>
<div class="container">
<p>内容。。。</p>
<div class="nav">居中导航呀</div>
<p>内容。。。</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
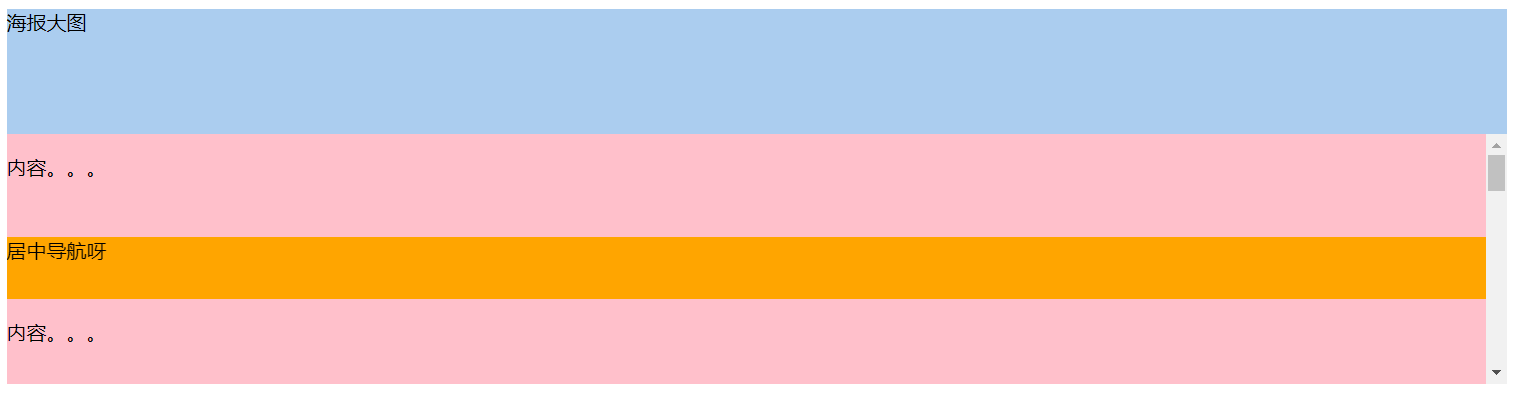
www.caniuse.com 检测浏览器兼容性
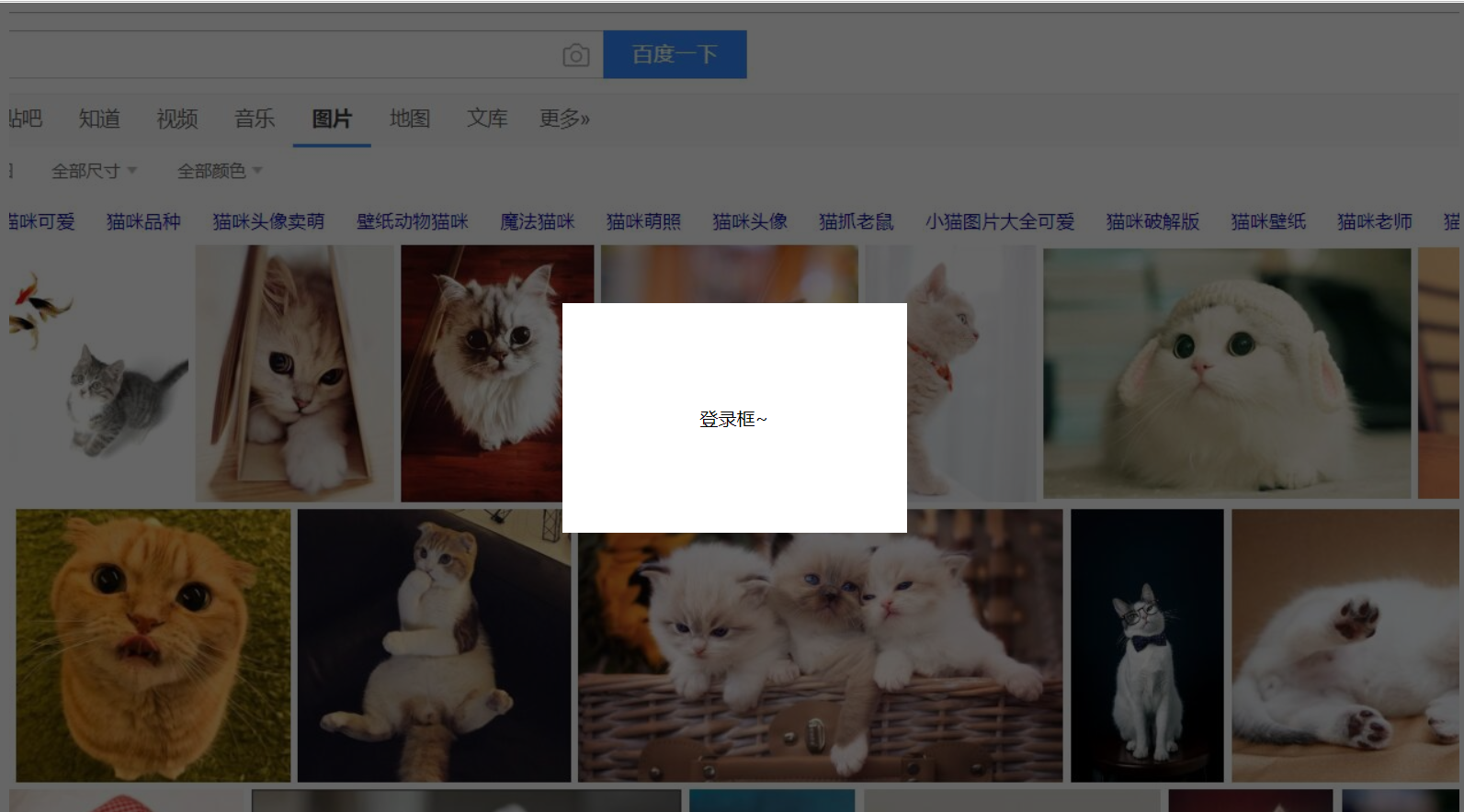
弹出层的简单实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.content{
width:100%;
height:1000px;
background:url(bg.jpg) top center no-repeat;
}
.opacity{
width:100%;
height:100%;
background-color:rgba(0,0,0,.6);
position: fixed;
top:0;
left:0;
}
.login{
width:300px;
height:200px;
text-align:center;
line-height:200px;
position: fixed;
background-color:#fff;
top:50%;
left:50%;
margin-top:-100px;
margin-left:-150px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content"></div>
<div class="opacity"></div>
<div class="login">登录框~</div>
</body>
</html>
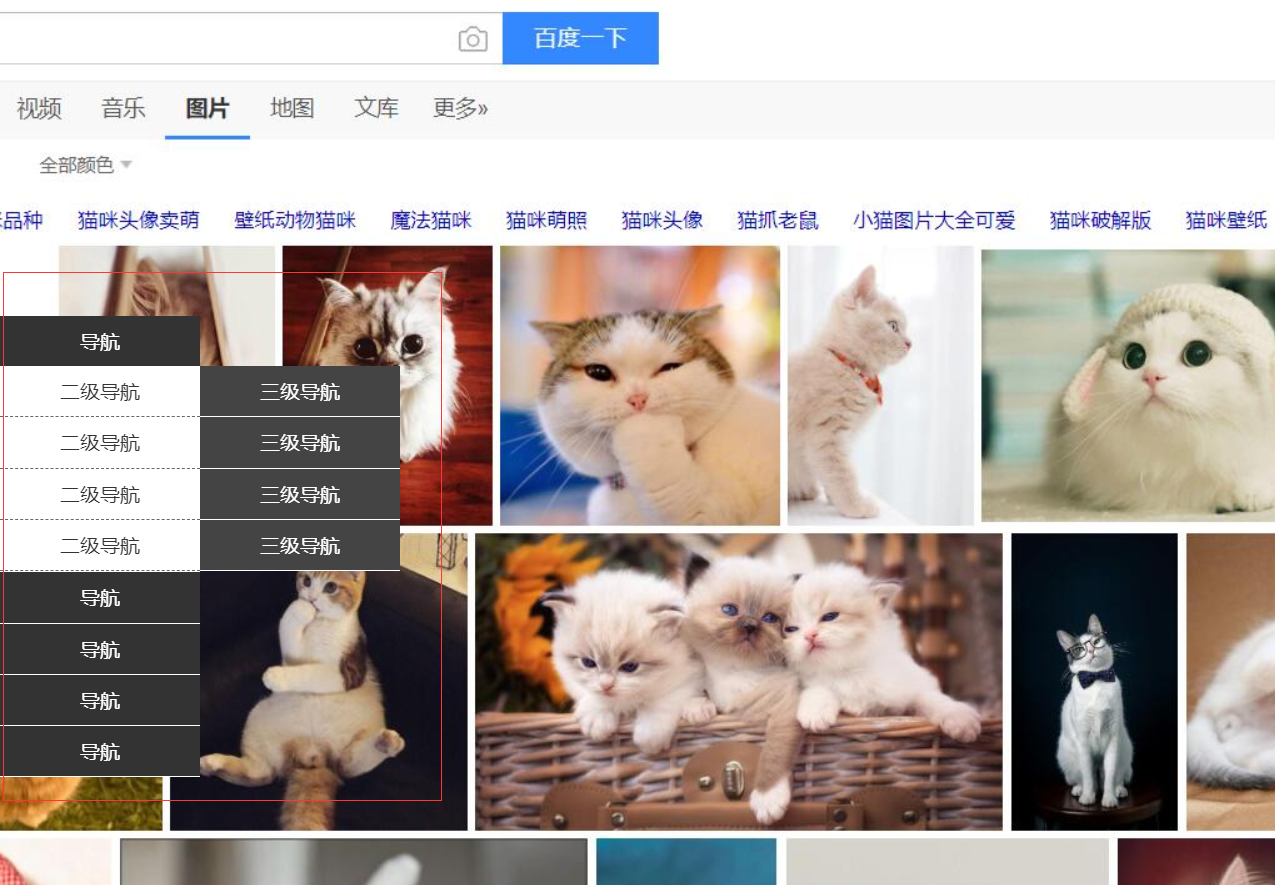
侧边栏导航实例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
margin:0;
padding:0;
} ul{
list-style:none;
} .content{
width:100%;
height:1000px;
background:url(bg.jpg) top center no-repeat;
} .nav{
width:160px;
height:205px;
position: fixed;
left:0;
top:50%;
margin-top:-102px;
} .nav-li{
width:160px;
height:auto;
line-height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #fff;
color:#fff;
background:#333;
text-align: center;
cursor:pointer;
} .tit{
width:160px;
height:40px;
} .nav-li ul{
width:160px;
height:auto;
background:#fff;
display: none;
} .nav-li:hover ul{
display: block
} .nav-li ul li{
width:160px;
height:40px;
color:#333;
border-bottom:1px dashed #666;
text-align: center;
line-height:40px;
position: relative;
} .nav-li ul li:hover .subnav{
display: block;
} .subnav{
position: absolute;
width:160px;
height:auto;
top:0;
left:160px;
background:#444;
display: none;
} .subnav-item{
width:160px;
height:40px;
border-bottom:1px solid #fff;
color:#fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="nav">
<div class="nav-li">
<div class="tit">导航</div>
<ul>
<li>
二级导航
<div class="subnav">
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>二级导航</li>
<li>二级导航</li>
<li>二级导航</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="nav-li">导航</div>
<div class="nav-li">导航</div>
<div class="nav-li">导航</div>
<div class="nav-li">
<div class="tit">导航</div>
<ul>
<li>
二级导航
<div class="subnav">
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
<div class="subnav-item">三级导航</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>二级导航</li>
<li>二级导航</li>
<li>二级导航</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
position定位及实际应用的更多相关文章
- CSS Position 定位属性
本篇文章主要介绍元素的Position属性,此属性可以设置元素在页面的定位方式. 目录 1. 介绍 position:介绍position的值以及辅助属性. 2. position 定位方式:介绍po ...
- position定位
CSS盒模型和定位的类型 为了搞清楚定位首先你得了解CSS盒模型.在上一句中的链接是我写在InstantShift 中的一篇关于盒模型的文章.我在那篇文章做了详细的讲解并会在这篇文章中做一个快速的总结 ...
- 浅析CSS——元素重叠及position定位的z-index顺序
多次在项目中遇到html页面元素的非期待重叠错误,多数还是position定位情况下z-index的问题.其实每次解决类似问题思路大致都是一样的,说到底还是对z-index的理解比较模糊,可以解决问题 ...
- position定位的小问题
css中position定位有四个属性,分别是:static.fixed.relative.absolute. 其中,static是默认值,未脱离文档流,元素的位置即按照文档结构的顺序进行定位排序: ...
- (转)Position定位:relative | absolute
原文:http://hi.baidu.com/zxc0420/item/9ada5110845ba1e89c778a08 Position定位:relative | absolute 定位一直是WEB ...
- 元素重叠及position定位的z-index顺序
元素位置重叠的背景常识 (x)html文档中的元素默认处于普通流(normal flow)中,也就是说其顺序由元素在文档中的先后位置决定,此时一般不会产生重叠(但指定负边距可能产生重叠).当我们用cs ...
- 盒子模型&position定位
有时候深深的感觉语文这门课程其实很有用, 至少以前学的时候没有感觉到 直到现在阅读大量的别人的资料文章的时候或者是看一些题目....... 总之:认真阅读小心品味 当然,前面的孤言自语和本文无关,只是 ...
- CSS定位:几种类型的position定位的元素
当人们刚接触布局的时候都比较倾向于使用定位的方式.因为定位的概念看起来好像比较容易掌握.表面上你确切地指定了一个块元素所处的位置那么它就会坐落于那里.可是定位比你刚看到的时候要稍微复杂一点.对于定位来 ...
- 归纳篇(一)CSS的position定位和float浮动
近期会更新一系列博客,对基础知识再度做个巩固和梳理. 一.position定位 (一):position的属性 1.absolute:生成绝对定位的元素,相对于最近一级定位不是static的父元素来进 ...
- (转)浅析CSS——元素重叠及position定位的z-index顺序
多次在项目中遇到html页面元素的非期待重叠错误,多数还是position定位情况下z-index的问题.其实每次解决类似问题思路大致都是一样的,说到底还是对z-index的理解比较模糊,可以解决问题 ...
随机推荐
- Leetcode 题目整理-8 Count and Say
38. Count and Say The count-and-say sequence is the sequence of integers beginning as follows: 1, 11 ...
- CenOS安装MySQL服务
说明:本教程是CenOS安装MySQL服务. 0. 预备知识: 什么是rpm RMP 是 LINUX 下的一种软件的可执行程序,你只要安装它就可以了.这种软件安装包通常是一个RPM包(Redha ...
- Android小记(整理一下自己犯过的错误)
时间:2019/12/20 如题,写这篇博客的原因主要是为了记录自己在Android编程中犯的一些低级的错误,以此警戒自己不要出现类似的错误. 1.在监听按钮的点击事件时,如果使用的是实现View.O ...
- 编译调试 .NET Core 5.0 Preview 并分析 Span 的实现原理
很久没有写过 .NET Core 相关的文章了,目前关店在家休息所以有些时间写一篇新的
- 使用IntelliJ IDEA创建Maven工程
1. 新建项目(点击“+ Create New Project”): 2. 选择Maven,不必选择项目骨架,直接点击Next 按钮即可: 3. 输入项目名称,选择项目位置,输入组织名称,模块名称,项 ...
- Codeforces_729_C
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/729/C 二分找最小容量,然后找符合的最小花费. #include<iostream> #include ...
- python之reload用法
一.python2和python3的区别 python2中可以直接使用reload().python3中需要从库中导入,有两种方法: >>> from imp import relo ...
- github三步走(init;add . ;commit -m "提交说明")
掌握以下几点就基本能满足你平时使用了.按这个顺序来1.git安装,已经好了,略 -到这里本地代码推送到远程已经结束了 2.git本地命令操作-shift+右键-git init:初始化git环境-新建 ...
- SpringBoot嵌入式Servlet配置原理
SpringBoot嵌入式Servlet配置原理 SpringBoot修改服务器配置 配置文件方式方式修改,实际修改的是ServerProperties文件中的值 server.servlet.con ...
- 小记centos7下将未使用的磁盘空间重新分区挂载使用
一块1TB的硬盘,用作samba共享,在安装系统时分区如下: /boot 2048M swap 512M / 229GB 剩下约 700GB左右未使用空间,在安装完系统后再使用 以下是详细操作,就几个 ...
