freeswitch APR-UTIL库线程池实现分析

概述
freeswitch的核心源代码是基于apr库开发的,在不同的系统上有很好的移植性。
APR库在之前的文章中已经介绍过了,APR-UTIL库是和APR并列的工具库,它们都是由APACHE开源出来的跨平台可移植库,不同点在于库中实现的功能接口有区别。
在应用的开发过程中,多线程并发是提高效率的常用方案,但是多线程管理并不好做。
在很多大型应用中,都会引入线程池的框架。线程池是一个线程集合,有统一的管理,当有一个新的任务下发,线程池管理会按照一定的策略将任务分配给空闲的线程。当任务积压较多时,线程池会创建新的线程来加快处理效率。
APR-UTIL库中就提供了一套线程池接口。
我对几个问题比较好奇,线程池如何管理?线程池什么情况要增加线程?什么情况会减少线程?线程池线程数目如何设置才有最优的效率?
下面我们对apr-util库的线程池实现做一个介绍。
环境
centos:CentOS release 7.0 (Final)或以上版本
APR-UTIL:1.6.1
GCC:4.8.5
本来要使用freeswitch1.8.7中带的apr-util库源代码来梳理,但是很遗憾的是这个apr-util库版本是1.2.8,里面没有apr_thread_pool接口。。。所以从APR官网上下载了最新的1.6.1版本来做分析。
数据结构
apr线程池源文件:
apr-util-1.6.1\include\apr_thread_pool.h
apr-util-1.6.1\misc\apr_thread_pool.c
号码池数据结构定义在apr_thread_pool.c中
typedef struct apr_thread_pool_task
{
APR_RING_ENTRY(apr_thread_pool_task) link;
apr_thread_start_t func;
void *param;
void *owner;
union
{
apr_byte_t priority;
apr_time_t time;
} dispatch;
} apr_thread_pool_task_t;
APR_RING_HEAD(apr_thread_pool_tasks, apr_thread_pool_task);
struct apr_thread_list_elt
{
APR_RING_ENTRY(apr_thread_list_elt) link;
apr_thread_t *thd;
volatile void *current_owner;
volatile enum { TH_RUN, TH_STOP, TH_PROBATION } state;
};
APR_RING_HEAD(apr_thread_list, apr_thread_list_elt);
struct apr_thread_pool
{
apr_pool_t *pool;
volatile apr_size_t thd_max;
volatile apr_size_t idle_max;
volatile apr_interval_time_t idle_wait;
volatile apr_size_t thd_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t idle_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t task_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t scheduled_task_cnt;
volatile apr_size_t threshold;
volatile apr_size_t tasks_run;
volatile apr_size_t tasks_high;
volatile apr_size_t thd_high;
volatile apr_size_t thd_timed_out;
struct apr_thread_pool_tasks *tasks;
struct apr_thread_pool_tasks *scheduled_tasks;
struct apr_thread_list *busy_thds;
struct apr_thread_list *idle_thds;
apr_thread_mutex_t *lock;
apr_thread_cond_t *cond;
volatile int terminated;
struct apr_thread_pool_tasks *recycled_tasks;
struct apr_thread_list *recycled_thds;
apr_thread_pool_task_t *task_idx[TASK_PRIORITY_SEGS];
};
线程池内存模型总图,线程池,任务队列,线程队列。
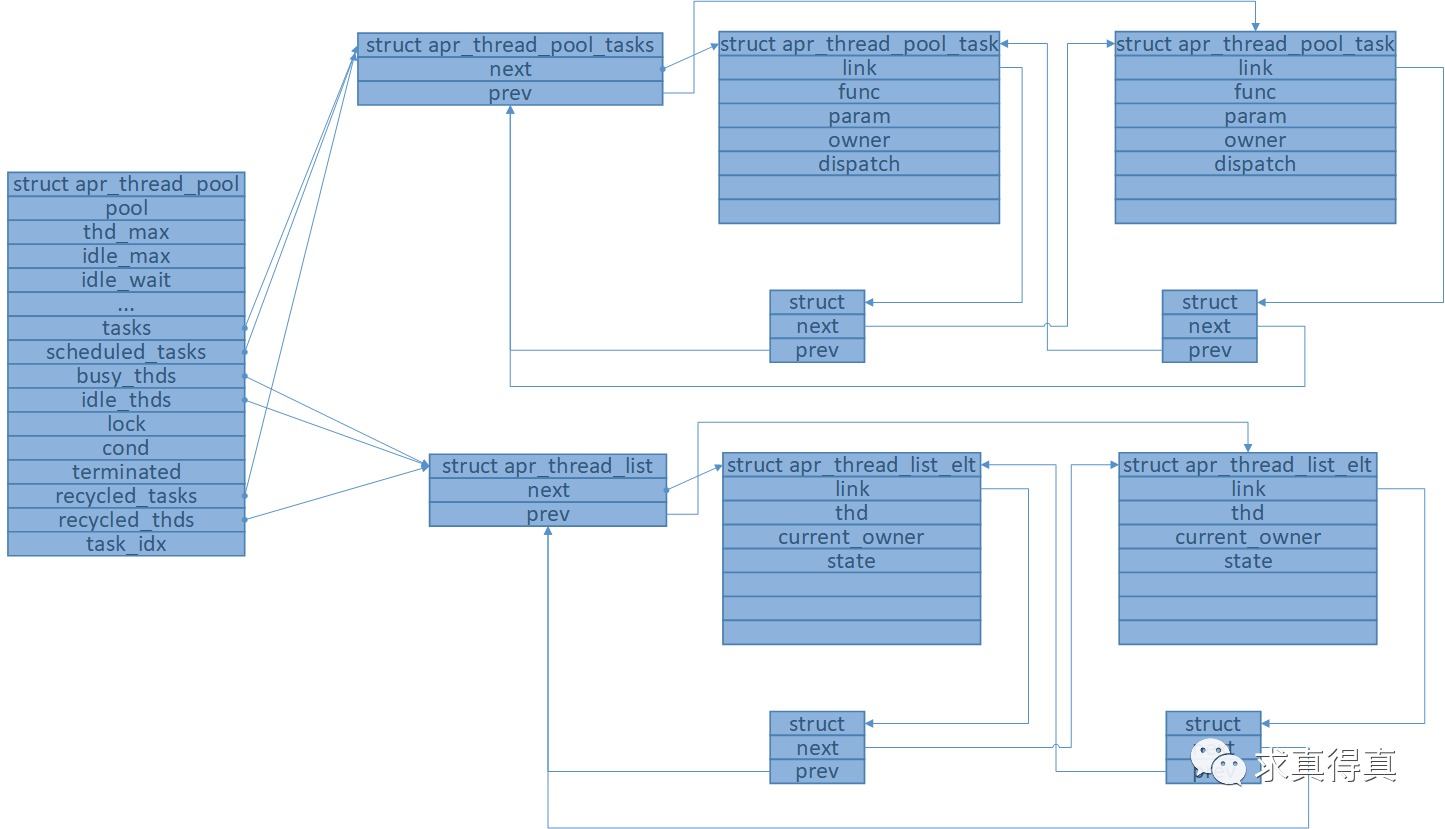
常用函数
常用函数接口
apr_thread_pool_create //Create a thread pool
apr_thread_pool_destroy //Destroy the thread pool and stop all the threads
apr_thread_pool_push //Schedule a task to the bottom of the tasks of same priority.
apr_thread_pool_schedule //Schedule a task to be run after a delay
apr_thread_pool_top //Schedule a task to the top of the tasks of same priority.
apr_thread_pool_tasks_cancel //Cancel tasks submitted by the owner. If there is any task from the owner that is currently running, the function will spin until the task finished.
apr_thread_pool_tasks_count //Get the current number of tasks waiting in the queue
apr_thread_pool_scheduled_tasks_count //Get the current number of scheduled tasks waiting in the queue
apr_thread_pool_threads_count //Get the current number of threads
apr_thread_pool_busy_count //Get the current number of busy threads
apr_thread_pool_idle_count //Get the current number of idle threads
apr_thread_pool_idle_max_set //Access function for the maximum number of idle threads. Number of current idle threads will be reduced to the new limit.
apr_thread_pool_tasks_run_count //Get number of tasks that have run
apr_thread_pool_tasks_high_count //Get high water mark of the number of tasks waiting to run
apr_thread_pool_threads_high_count //Get high water mark of the number of threads
apr_thread_pool_threads_idle_timeout_count //Get the number of idle threads that were destroyed after timing out
apr_thread_pool_idle_max_get //Access function for the maximum number of idle threads
apr_thread_pool_thread_max_set //Access function for the maximum number of threads.
apr_thread_pool_idle_wait_set //Access function for the maximum wait time (in microseconds) of an idling thread that exceeds the maximum number of idling threads. A non-zero value allows for the reaping of idling threads to shrink over time. Which helps reduce thrashing.
apr_thread_pool_idle_wait_get //Access function for the maximum wait time (in microseconds) of an idling thread that exceeds the maximum number of idling threads
apr_thread_pool_thread_max_get //Access function for the maximum number of threads
apr_thread_pool_threshold_set //Access function for the threshold of tasks in queue to trigger a new thread.
apr_thread_pool_threshold_get //Access function for the threshold of tasks in queue to trigger a new thread.
apr_thread_pool_task_owner_get //Get owner of the task currently been executed by the thread.
apr_thread_pool_create创建
APU_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_thread_pool_create(apr_thread_pool_t ** me,
apr_size_t init_threads,
apr_size_t max_threads,
apr_pool_t * pool)
接口逻辑:
- 分配一块大小为apr_thread_pool_t的内存tp。
- 在传入的内存池pool中申请一个新的内存池tp->pool。
- 初始化线程池数据。
a) 线程池数据初始化。
b) 创建线程互斥锁me->lock。
c) 创建条件变量me->cond。
d) 在内存池pool上分配一块大小为“apr_thread_pool_tasks“的内存赋值给me->tasks。
e) 在内存池pool上分配一块大小为“apr_thread_pool_tasks“的内存赋值给me->scheduled_tasks。
f) 在内存池pool上分配一块大小为“apr_thread_pool_tasks“的内存赋值给me->recycled_tasks。
g) 在内存池pool上分配一块大小为“apr_thread_list“的内存赋值给me->busy_thds。
h) 在内存池pool上分配一块大小为“apr_thread_list“的内存赋值给me->idle_thds。
i) 在内存池pool上分配一块大小为“apr_thread_list“的内存赋值给me->recycled_thds。
j) 线程池数据初始化。
- 在内存池tp->pool中注册清理回调函数。
- 循环创建初始工作线程,并加入线程池的管理。工作线程的逻辑见“thread_pool_func工作线程”。
- 返回创建结果。
线程池初始化成功后,内存模型如图(工作线程启动未完成时)
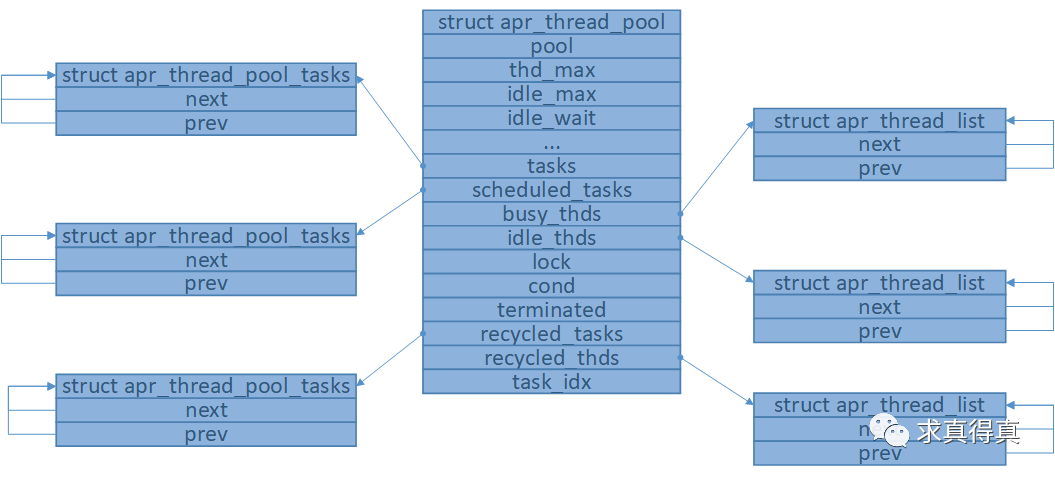
thread_pool_func工作线程
static void *APR_THREAD_FUNC thread_pool_func(apr_thread_t * t, void *param)
接口逻辑:
- 加锁me->lock
- 判断me->recycled_thds链表为空?为空则创建新的apr_thread_list_elt节点elt,不为空则获取recycled_thds中首节点elt并从recycled_thds中移除该节点。
- 循环处理。
a) 将elt节点加入me->busy_thds链表。
b) 获取一个新任务task。TODO
c) 循环处理。解锁me->lock。调用任务回调task->func。加锁me->lock。将task加入me->recycled_tasks链表。获取新任务task。线程状态置为TH_STOP时跳出循环。获取任务为空跳出循环。
d) 线程从busy到stop状态,将elt加入me->recycled_thds链表尾部,解锁me->lock,退出线程。
e) 线程从busy到idle状态,将elt节点从me->busy_thds链表中移除,将elt加入me->idle_thds链表尾部。
f) 检查是否有定时任务并获取任务执行等待时间。
g) 检查当前空闲线程数是否大于最大空闲数,获取空闲等待时间me->idle_wait,并设置当前线程状态为TH_PROBATION,下一轮循环中进入stop处理流程。
h) 线程阻塞,等待条件变量me->cond的通知或超时。
- 线程数me->thd_cnt自减。
- 解锁me->lock。
- 退出线程。
线程池初始化成功后,内存模型如图(工作线程启动完成时)
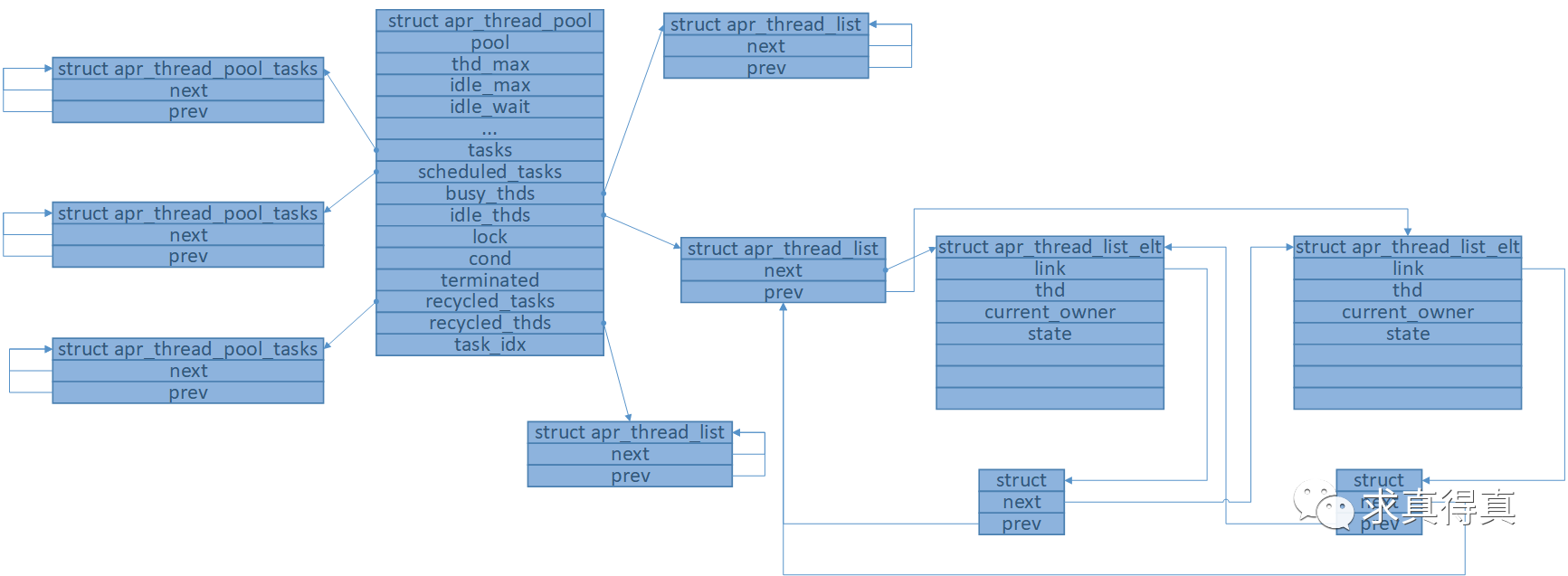
apr_thread_pool_push添加任务
APU_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_thread_pool_push(apr_thread_pool_t *me,
apr_thread_start_t func,
void *param,
apr_byte_t priority,
void *owner)
接口逻辑:
- 加锁me->lock。
- 检查me->recycled_tasks是否为空,为空则新建任务节点t,不为空则从me->recycled_tasks获取任务节点t。
- 任务节点t数据初始化。
- 计算任务优先级,根据优先级设置me->task_idx[seg]和me->tasks。
- 当前工作线程数为0时,或者空闲线程数为0并且当前线程数未达到最大并且当前任务数超过阈值等条件,动态创建新的工作线程。
- 对条件变量me->cond发通知。
- 解锁me->lock。
线程池添加任务后的内存模型图。

apr_thread_pool_tasks_cancel取消任务
APU_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_thread_pool_tasks_cancel(apr_thread_pool_t *me,
void *owner)
接口逻辑:
- 加锁me->lock。
- 如果当前任务数大于0,则清空owner的所有任务。
- 如果定时任务数大于0,则清空owner的所有定时任务。
- 解锁me->lock。
- 等待线程退出。
总结
APR线程池的几个关注点。
线程从busy到stop状态时,没有将elt节点从me->busy_thds链表中删除?
APR线程池没有内置的管理线程,根据当前线程数和任务数进行动态的调整,而是通过任务阈值、空闲线程最大值和超时时间等设置来控制线程数的增减,这一点和我开始想的不一样。
空空如常
求真得真
freeswitch APR-UTIL库线程池实现分析的更多相关文章
- [转]ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的分析和使用
1. 引言 合理利用线程池能够带来三个好处. 第一:降低资源消耗.通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗. 第二:提高响应速度.当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行. 第 ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的分析和使用
1. 引言 合理利用线程池能够带来三个好处. 第一:降低资源消耗.通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗. 第二:提高响应速度.当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行. 第 ...
- java并发包&线程池原理分析&锁的深度化
java并发包&线程池原理分析&锁的深度化 并发包 同步容器类 Vector与ArrayList区别 1.ArrayList是最常用的List实现类,内部是通过数组实现的, ...
- ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之SizeBlockingQueue
ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之SizeBlockingQueue 尽管前面写好几篇ES线程池分析的文章(见文末参考链接),但都不太满意.但从ES的线程池中了解到了不少JAVA线程池的使用 ...
- ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之 ExecutorScalingQueue
ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之 ExecutorScalingQueue 在ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之SizeBlockingQueue这篇文章中分析了ES的fixed ...
- ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之 ResizableBlockingQueue
ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之 ResizableBlockingQueue 在上一篇文章 ElasticSearch 线程池类型分析之 ExecutorScalingQueue的末尾, ...
- JAVA线程池的分析和使用
1. 引言 合理利用线程池能够带来三个好处.第一:降低资源消耗.通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗.第二:提高响应速度.当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行.第三:提 ...
- Java 线程池原理分析
1.简介 线程池可以简单看做是一组线程的集合,通过使用线程池,我们可以方便的复用线程,避免了频繁创建和销毁线程所带来的开销.在应用上,线程池可应用在后端相关服务中.比如 Web 服务器,数据库服务器等 ...
- 聊聊并发(三)Java线程池的分析和使用
1. 引言 合理利用线程池能够带来三个好处.第一:降低资源消耗.通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗.第二:提高响应速度.当任务到达时,任务可以不需要的等到线程创建就能立即执行. ...
随机推荐
- express系列(1)概述
在 Node.js 出现之前,前后端的开发必须使用不同的语言进行.为此你需要学习多种的语言和框架.有了 Node.js 之后,你就可以使用一门语言在前后端开发中自由切换,这是最吸引人的地方. 什么是 ...
- 在 Qualys SSL Labs SSL 测试中获得 A+ 评级的秘技 2021 版
本系列文章将阐述主流应用交付控制器和主流 Web 服务器如何运行 HTTP/2 和 TLSv1.3 协议,以及如何在 SSL Test 中获得 A+ 评级. 请访问原文链接:https://sysin ...
- supervise安装与使用
确认当前是否已经安装which supervise/usr/local/bin/supervise 软件下载安装-------------------------------------------- ...
- 添加用户的jsp页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %><!-- H ...
- Tomcat简单介绍
1.目录结构 在conf文件夹中修改了配置之后一定要重启Tomcat
- 使用matplotlib中的bar函数绘制柱状图
使用柱状图显示三日电影的票房信息 要显示的数据为2018年12月7日-9日四场电影的票房信息 四场电影分别为:无名之辈,狗十三,毒液:知名守卫者,憨豆特工3 2018年12月7日四场电影票房分别为:[ ...
- 从离线分析建模到稳健风控升级,为什么说顶象Dinsight实时风控引擎是对的选择?
随着金融业数字化程度进一步加深,互联网垂直电商.消费金融等领域与人们生活的深度融合,数字科技在安全风险控制上已经成为了重要的基石.如何主动防范化解风险,建立智能化的实时风险监测预警体系,加速业务模式转 ...
- (转)Zookeeper原理和作用
本周末学习zookeeper,原理和安装配置 本文参考: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-zookeeper/ http:/ ...
- python之异步编程
一.异步编程概述 异步编程是一种并发编程的模式,其关注点是通过调度不同任务之间的执行和等待时间,通过减少处理器的闲置时间来达到减少整个程序的执行时间:异步编程跟同步编程模型最大的不同就是其任务的切换, ...
- CF253A Boys and Girls 题解
Content 有 \(n\) 个男生.\(m\) 个女生坐在一排,请求出这样一种方案,使得相邻两个座位之间的人的性别不同的次数最多. 数据范围:\(1\leqslant n,m\leqslant 1 ...
