Matlab处理数据导出Paraview可读的vtk文件(一)
Paraview是一个开源的可视化软件。
用到matlab子程序从这里下载
或者到博客末尾复制粘贴
子程序名为 vtkwrite
示例1:
load mri
D = squeeze(D);
vtkwrite('mri.vtk', 'structured_points', 'mri', D)
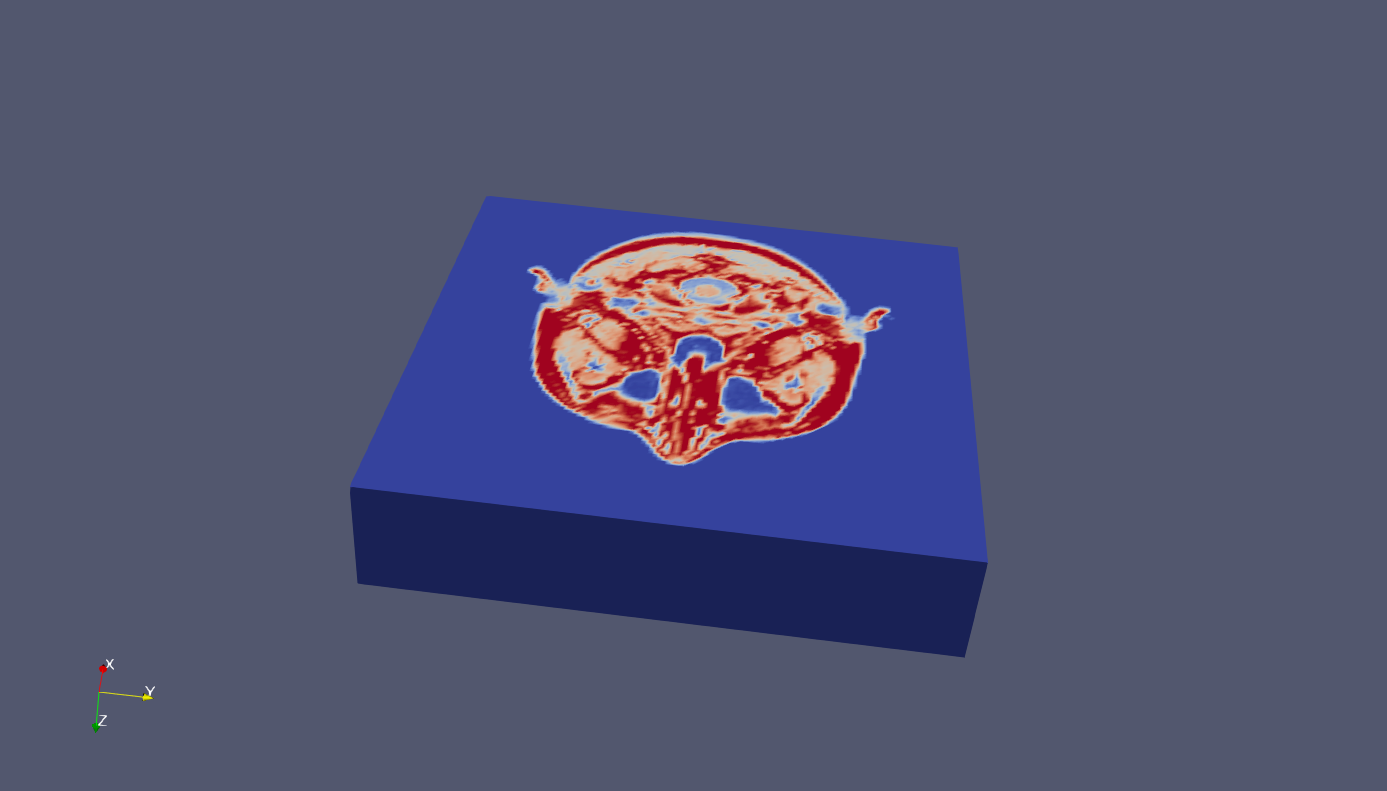
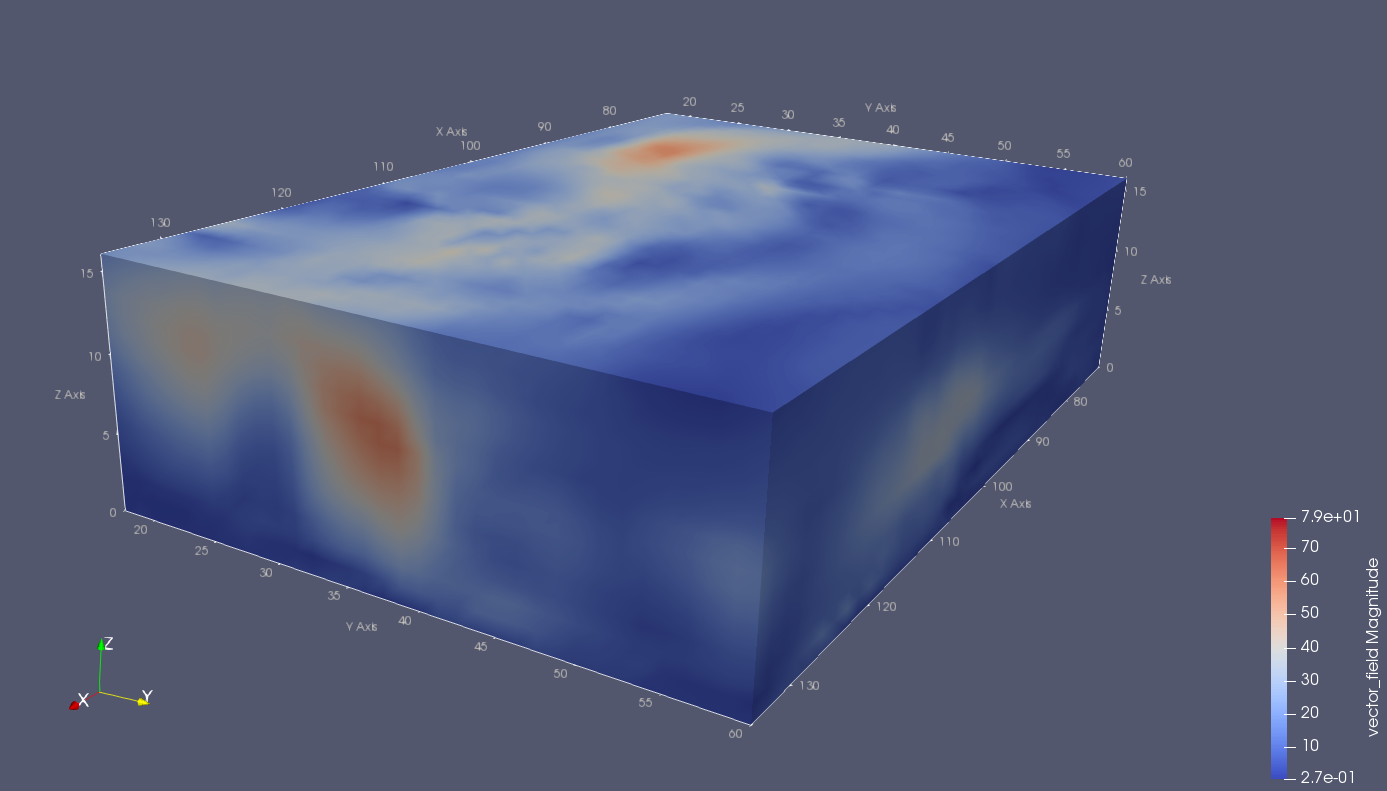
示例2:云图
load wind
[cu,cv,cw] = curl(x, y, z, u, v, w);
div = divergence(x, y, z, u, v, w);
vtkwrite('wind.vtk', 'structured_grid', x, y, z, ...
'vectors', 'vector_field', u, v, w, 'vectors', 'vorticity', cu, cv, cw, 'scalars', 'divergence', div);
示例3:二维曲线
x = :;
y = sin(x);
z = sqrt(x);
vtkwrite('execute','polydata','lines',x,y,z);
示例4:三角形
[x,y,z] = peaks();
z = .*z;
tri = delaunay(x,y);
vtkwrite('peaks.vtk','polydata','triangle',x,y,z,tri);
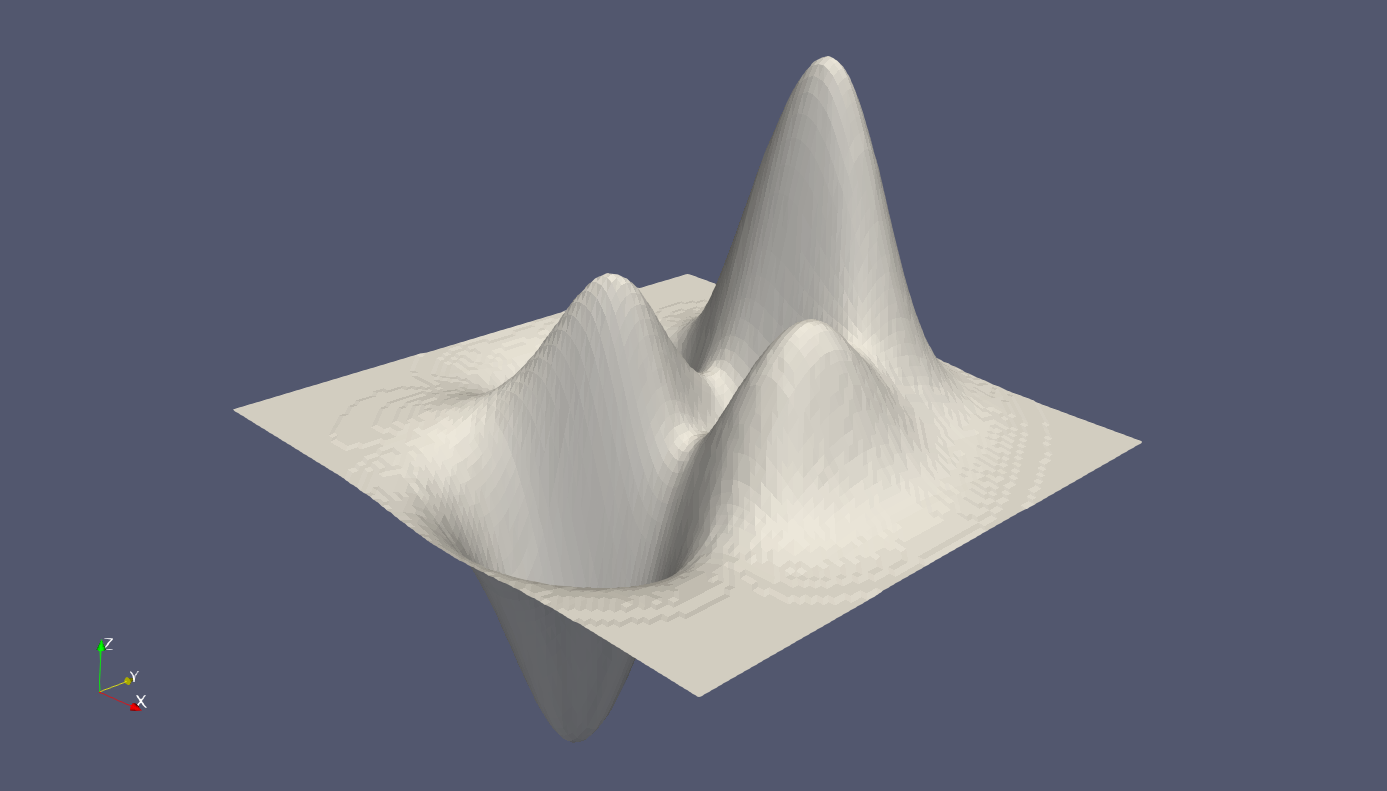
示例5:四面体
d = [- ];
[x, y, z] = meshgrid(d, d, d);
DT = delaunayTriangulation(x(:), y(:), z(:));
vtkwrite('execute', 'polydata','tetrahedron', x, y, z, DT.ConnectivityList);
vtkwrite
function vtkwrite( filename,dataType,varargin )
% VTKWRITE Writes 3D Matlab array into VTK file format.
% vtkwrite(filename,'structured_grid',x,y,z,'vectors',title,u,v,w) writes
% a structured 3D vector data into VTK file, with name specified by the string
% filename. (u,v,w) are the vector components at the points (x,y,z). x,y,z
% should be -D matrices like those generated by meshgrid, where
% point(ijk) is specified by x(i,j,k), y(i,j,k) and z(i,j,k).
% The matrices x,y,z,u,v,w must all be the same size and contain
% corrresponding position and vector component. The string title specifies
% the name of the vector field to be saved.
%
% vtkwrite(filename,'structured_grid',x,y,z,'scalars',title,r) writes a 3D
% scalar data into VTK file whose name is specified by the string
% filename. r is the scalar value at the points (x,y,z). The matrices
% x,y,z,r must all be the same size and contain the corresponding position
% and scalar values.
%
% vtkwrite(filename,'structured_grid',x,y,z,'vectors',title,u,v,w,'scalars',
% title2,r) writes a 3D structured grid that contains both vector and scalar values.
% x,y,z,u,v,w,r must all be the same size and contain the corresponding
% positon, vector and scalar values.
%
% vtkwrite(filename, 'structured_points', title, m) saves matrix m (could
% be 1D, 2D or 3D array) into vtk as structured points.
%
% vtkwrite(filename, 'structured_points', title, m, 'spacing', sx, sy, sz)
% allows user to specify spacing. (default: , , ). This is the aspect
% ratio of a single voxel.
%
% vtkwrite(filename, 'structured_points', title, m, 'origin', ox, oy, oz)
% allows user to speicify origin of dataset. (default: , , ).
%
% vtkwrite(filename,'unstructured_grid',x,y,z,'vectors',title,u,v,w,'scalars',
% title2,r) writes a 3D unstructured grid that contains both vector and scalar values.
% x,y,z,u,v,w,r must all be the same size and contain the corresponding
% positon, vector and scalar values.
%
% vtkwrite(filename, 'polydata', 'lines', x, y, z) exports a 3D line where
% x,y,z are coordinates of the points that make the line. x, y, z are
% vectors containing the coordinates of points of the line, where point(n)
% is specified by x(n), y(n) and z(n).
%
% vtkwrite(filename,'polydata','lines',x,y,z,'Precision',n) allows you to
% specify precision of the exported number up to n digits after decimal
% point. Default precision is digits.
%
% vtkwrite(filename,'polydata','triangle',x,y,z,tri) exports a list of
% triangles where x,y,z are the coordinates of the points and tri is an
% m* matrix whose rows denote the points of the individual triangles.
%
% vtkwrite(filename,'polydata','tetrahedron',x,y,z,tetra) exports a list
% of tetrahedrons where x,y,z are the coordinates of the points
% and tetra is an m* matrix whose rows denote the points of individual
% tetrahedrons.
%
% vtkwrite('execute','polydata','lines',x,y,z) will save data with default
% filename ''matlab_export.vtk' and automatically loads data into
% ParaView.
%
% Version 2.3
% Copyright, Chaoyuan Yeh,
% Codes are modified from William Thielicke and David Gingras's submission. if strcmpi(filename,'execute'), filename = 'matlab_export.vtk'; end
fid = fopen(filename, 'w');
% VTK files contain five major parts
% . VTK DataFile Version
fprintf(fid, '# vtk DataFile Version 2.0\n');
% . Title
fprintf(fid, 'VTK from Matlab\n'); binaryflag = any(strcmpi(varargin, 'BINARY'));
if any(strcmpi(varargin, 'PRECISION'))
precision = num2str(varargin{find(strcmpi(vin, 'PRECISION'))+});
else
precision = '';
end switch upper(dataType)
case 'STRUCTURED_POINTS'
title = varargin{};
m = varargin{};
if any(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))
sx = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))+};
sy = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))+};
sz = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'spacing'))+};
else
sx = ;
sy = ;
sz = ;
end
if any(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))
ox = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))+};
oy = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))+};
oz = varargin{find(strcmpi(varargin, 'origin'))+};
else
ox = ;
oy = ;
oz = ;
end
[nx, ny, nz] = size(m);
setdataformat(fid, binaryflag); fprintf(fid, 'DATASET STRUCTURED_POINTS\n');
fprintf(fid, 'DIMENSIONS %d %d %d\n', nx, ny, nz);
fprintf(fid, ['SPACING ', num2str(sx), ' ', num2str(sy), ' ',...
num2str(sz), '\n']);
fprintf(fid, ['ORIGIN ', num2str(ox), ' ', num2str(oy), ' ',...
num2str(oz), '\n']);
fprintf(fid, 'POINT_DATA %d\n', nx*ny*nz);
fprintf(fid, ['SCALARS ', title, ' float 1\n']);
fprintf(fid,'LOOKUP_TABLE default\n');
if ~binaryflag
spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f '];
fprintf(fid, spec, m(:)');
else
fwrite(fid, m(:)', 'float', 'b');
end case {'STRUCTURED_GRID','UNSTRUCTURED_GRID'}
% . The format data proper is saved in (ASCII or Binary). Use
% fprintf to write data in the case of ASCII and fwrite for binary.
if numel(varargin)<, error('Not enough input arguments'); end
setdataformat(fid, binaryflag);
% fprintf(fid, 'BINARY\n');
x = varargin{};
y = varargin{};
z = varargin{};
if sum(size(x)==size(y) & size(y)==size(z))~=length(size(x))
error('Input dimesions do not match')
end
n_elements = numel(x);
% . Type of Dataset ( can be STRUCTURED_POINTS, STRUCTURED_GRID,
% UNSTRUCTURED_GRID, POLYDATA, RECTILINEAR_GRID or FIELD )
% This part, dataset structure, begins with a line containing the
% keyword 'DATASET' followed by a keyword describing the type of dataset.
% Then the geomettry part describes geometry and topology of the dataset.
if strcmpi(dataType,'STRUCTURED_GRID')
fprintf(fid, 'DATASET STRUCTURED_GRID\n');
fprintf(fid, 'DIMENSIONS %d %d %d\n', size(x,), size(x,), size(x,));
else
fprintf(fid, 'DATASET UNSTRUCTURED_GRID\n');
end
fprintf(fid, ['POINTS ' num2str(n_elements) ' float\n']);
output = [x(:)'; y(:)'; z(:)']; if ~binaryflag
spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f '];
fprintf(fid, spec, output);
else
fwrite(fid, output, 'float', 'b');
end
% .This final part describe the dataset attributes and begins with the
% keywords 'POINT_DATA' or 'CELL_DATA', followed by an integer number
% specifying the number of points of cells. Other keyword/data combination
% then define the actual dataset attribute values.
fprintf(fid, ['\nPOINT_DATA ' num2str(n_elements)]);
% Parse remaining argument.
vidx = find(strcmpi(varargin,'VECTORS'));
sidx = find(strcmpi(varargin,'SCALARS'));
if vidx~=
for ii = :length(vidx)
title = varargin{vidx(ii)+};
% Data enteries begin with a keyword specifying data type
% and numeric format.
fprintf(fid, ['\nVECTORS ', title,' float\n']);
output = [varargin{ vidx(ii) + }(:)';...
varargin{ vidx(ii) + }(:)';...
varargin{ vidx(ii) + }(:)']; if ~binaryflag
spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f '];
fprintf(fid, spec, output);
else
fwrite(fid, output, 'float', 'b');
end
% fwrite(fid, [reshape(varargin{vidx(ii)+},,n_elements);...
% reshape(varargin{vidx(ii)+},,n_elements);...
% reshape(varargin{vidx(ii)+},,n_elements)],'float','b');
end
end
if sidx~=
for ii = :length(sidx)
title = varargin{sidx(ii)+};
fprintf(fid, ['\nSCALARS ', title,' float\n']);
fprintf(fid, 'LOOKUP_TABLE default\n');
if ~binaryflag
spec = ['%0.', precision, 'f '];
fprintf(fid, spec, varargin{ sidx(ii) + });
else
fwrite(fid, varargin{ sidx(ii) + }, 'float', 'b');
end
% fwrite(fid, reshape(varargin{sidx(ii)+},,n_elements),'float','b');
end
end case 'POLYDATA' fprintf(fid, 'ASCII\n');
if numel(varargin)<, error('Not enough input arguments'); end
x = varargin{}(:);
y = varargin{}(:);
z = varargin{}(:);
if numel(varargin)<, error('Not enough input arguments'); end
if sum(size(x)==size(y) & size(y)==size(z))~= length(size(x))
error('Input dimesions do not match')
end
n_elements = numel(x);
fprintf(fid, 'DATASET POLYDATA\n');
if mod(n_elements,)==
x(n_elements+:n_elements+,)=[;];
y(n_elements+:n_elements+,)=[;];
z(n_elements+:n_elements+,)=[;];
elseif mod(n_elements,)==
x(n_elements+,)=;
y(n_elements+,)=;
z(n_elements+,)=;
end
nbpoint = numel(x);
fprintf(fid, ['POINTS ' num2str(nbpoint) ' float\n']); spec = [repmat(['%0.', precision, 'f '], , ), '\n']; output = [x(::end-), y(::end-), z(::end-),...
x(::end-), y(::end-), z(::end-),...
x(::end), y(::end), z(::end)]'; fprintf(fid, spec, output); switch upper(varargin{})
case 'LINES'
if mod(n_elements,)==
nbLine = *n_elements-;
else
nbLine = *(n_elements-);
end
conn1 = zeros(nbLine,);
conn2 = zeros(nbLine,);
conn2(:nbLine/) = :nbLine/;
conn1(:nbLine/) = conn2(:nbLine/)-;
conn1(nbLine/+:end) = :nbLine/;
conn2(nbLine/+:end) = conn1(nbLine/+:end)-;
fprintf(fid,'\nLINES %d %d\n',nbLine,*nbLine);
fprintf(fid,'2 %d %d\n',[conn1';conn2']);
case 'TRIANGLE'
ntri = length(varargin{});
fprintf(fid,'\nPOLYGONS %d %d\n',ntri,*ntri);
fprintf(fid,'3 %d %d %d\n',(varargin{}-)');
case 'TETRAHEDRON'
ntetra = length(varargin{});
fprintf(fid,'\nPOLYGONS %d %d\n',ntetra,*ntetra);
fprintf(fid,'4 %d %d %d %d\n',(varargin{}-)');
end
end
fclose(fid);
if strcmpi(filename,'matlab_export.vtk')
switch computer
case {'PCWIN','PCWIN64'}
!paraview.exe --data='matlab_export.vtk' &
% Exclamation point character is a shell escape, the rest of the
% input line will be sent to operating system. It can not take
% variables, though. The & at the end of line will return control to
% Matlab even when the outside process is still running.
case {'GLNXA64','MACI64'}
!paraview --data='matlab_export.vtk' &
end
end
end function setdataformat(fid, binaryflag) if ~binaryflag
fprintf(fid, 'ASCII\n');
else
fprintf(fid, 'BINARY\n');
end
end
Matlab处理数据导出Paraview可读的vtk文件(一)的更多相关文章
- Matlab处理数据导出Paraview可读的vtk文件(二)
由于我在用SPH方法仿真时用的是FORTRAN语言,并且没有找到直接输出vtk文件的代码,因此偷懒通过MATLAB转换一下数据. 用到的Matlab子程序可通过一下链接找到. Matlab处理数据导出 ...
- 利用PHPExcel将数据导出到xls格式的excel文件
在开发某地的经营许可证管理系统的时候需要将数据导出打excel文件,虽然一年前做某集团的ERP的时候用到过一次导入和导出,但是那时候太忙没时间写博客,一年过去了我也忘的差不多了,所以趁着今天将此次的使 ...
- 彻底理解使用JavaScript 将Json数据导出CSV文件
前言 将数据报表导出,是web数据报告展示常用的附带功能.通常这种功能都是用后端开发人员编写的.今天我们主要讲的是直接通过前端js将数据导出Excel的CSV格式的文件. 原理 首先在本地用Excel ...
- MATLAB 的数据导入与导出
1 数据导入: %% 高层次读取数据. importdata 函数是一个高层次的函数 filename = 'weeklydata.txt'; delimiterIn =' '; %delimiter ...
- dataview将excel表格的数据导出成txt文件
有时候需要处理大量的数据,且这些数据又存在于excel表格内,在平时的时候,我是非常喜欢这样的数据的,因为只要是excel表格内的数据,处理起来的方法就很方便.也可能我平时遇见的数据总是以一种杂乱无章 ...
- 【matlab】将matlab中数据输出保存为txt或dat格式
将matlab中数据输出保存为txt或dat格式 总结网上各大论坛,主要有三种方法. 第一种方法:save(最简单基本的) 具体的命令是:用save *.txt -ascii x x为变量 *.txt ...
- .net解决数据导出excel时的格式问题
在项目中一般都需要将报表数据导出到EXCEL中,但经常出现导出长串数据(如身份证)到EXCEL中后显示为科学计数法的格式,或者报表中显示为001的数据导出到Excel后成了1的格式. 下面简单介绍一下 ...
- Winform数据导出Execl小工具
前台界面.cs文件 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System. ...
- 数据导出至Excel文件--好库编程网http://code1.okbase.net/codefile/SerializeHelper.cs_2012122018724_118.htm
using System; using System.IO; using System.Data; using System.Collections; using System.Data.OleDb; ...
随机推荐
- 【题解】回文串 APIO 2014 BZOJ 3676 COGS 1985 Manacher+后缀数组+二分
这题可以用回文自动机来做,但是我并没有学,于是用Manacher+SA的做法O(nlogn)水过 首先,看到回文串就能想到用Manacher 同样还是要利用Manacher能不重复不遗漏地枚举每个回文 ...
- HRBUST 1819
石子合并问题--圆形版 Time Limit: 1000 MS Memory Limit: 32768 K Total Submit: 61(27 users) Total Accepted: 26( ...
- 使用kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.12
使用kubeadm安装Kubernetes 1.12 https://blog.frognew.com/2018/10/kubeadm-install-kubernetes-1.12.html 测试环 ...
- UVA 1638 Pole Arrangement
https://vjudge.net/problem/UVA-1638 题意: n根长度分别为1,2,3,4……n的木棍 将这些木棍竖着排成一列 问从左边看能看到L根,从右边看能看到R根的方案数 将木 ...
- mysql数据库cmd直接登录
找到mysql的安装路径: 将该路径配置到环境变量中: win+R代开dos窗口:输入mysql -uroot -p回车,输入密码.
- jQuery简单日历插件版
先来看demo:http://codepen.io/jonechen/pen/xOgZMz 插件代码: ; (function($) { var Calendar = function(ele, op ...
- 判定对象是否存活的算法----GC_ROOT算法
要应用GC_ROOT算法,判定某个对象是否会被回收,关键是要确定root.确定root之后,你就可以根据代码绘制可达链,从而就可以进行分析了,分析哪些对象会被泄漏,哪些对象会被回收,如果GC执行的时候 ...
- PHP 练习1:新闻发布
1.新闻发布主页面 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://w ...
- Linux中关机,重启,注销命令
关机: shutdown -h now #立刻关机重启,工作中常用 shutdown -h +1 #1分钟后关机 init 0 halt #立即停 ...
- 【洛谷 P2761】 软件补丁问题(状态压缩,最短路)
题目链接 第四题. 初看题目很懵,网络流这么厉害的吗,毫无头绪去看题解.. 所以这和网络流有什么关系呢? 把规则用二进制保存下来,然后跑最短路救星了. 在线跑,离线连边太慢了. (以后干脆不管什么题直 ...
