661. Image Smoother【easy】
661. Image Smoother【easy】
Given a 2D integer matrix M representing the gray scale of an image, you need to design a smoother to make the gray scale of each cell becomes the average gray scale (rounding down) of all the 8 surrounding cells and itself. If a cell has less than 8 surrounding cells, then use as many as you can.
Example 1:
Input:
[[1,1,1],
[1,0,1],
[1,1,1]]
Output:
[[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]]
Explanation:
For the point (0,0), (0,2), (2,0), (2,2): floor(3/4) = floor(0.75) = 0
For the point (0,1), (1,0), (1,2), (2,1): floor(5/6) = floor(0.83333333) = 0
For the point (1,1): floor(8/9) = floor(0.88888889) = 0
Note:
- The value in the given matrix is in the range of [0, 255].
- The length and width of the given matrix are in the range of [1, 150].
错误解法:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> imageSmoother(vector<vector<int>>& M) {
int row = M.size();
int col = M[].size();
vector<vector<int>> temp(row + , vector<int>(col + ));
for (int j = ; j < col + ; ++j) {
temp[][j] = ;
}
for (int i = ; i < row + ; ++i) {
temp[i][] = ;
}
for (int j = ; j < col + ; ++j) {
temp[row][j] = ;
}
for (int i = ; i < row + ; ++i) {
temp[i][col] = ;
}
for (int i = ; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = ; j < col; ++j) {
temp[i][j] = M[i - ][j - ];
}
}
for (int i = ; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = ; j < col; ++j) {
int sum = ;
for (int x = -; x <= ; ++x) {
for (int y = -; y <= ; ++y) {
sum += temp[i + x][j + y];
}
}
temp[i][j] = floor(sum / );
}
}
vector<vector<int>> result(row, vector<int>(col));
for (int i = ; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = ; j < col; ++j) {
result[i][j] = temp[i + ][j + ];
}
}
return result;
}
};
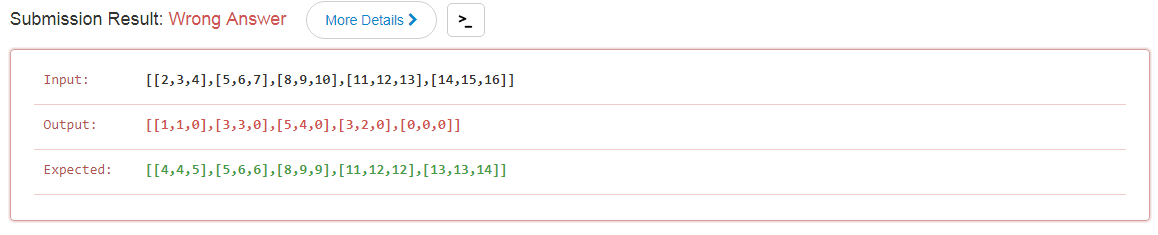
一开始我还想取巧,把边界扩充,想着可以一致处理,但是发现没有审清题意,坑了啊!
解法一:
class Solution {
private:
bool valid(int i,int j,vector<vector<int>>& M)
{
if (i >= && i<M.size() && j>= && j<M[].size())
return true;
return false;
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> imageSmoother(vector<vector<int>>& M) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (M.size()== || M[].size()==)
return res;
for (int i = ; i< M.size(); i++)
{
vector<int> cur;
for(int j = ; j< M[].size(); j++)
{
int total = ;
int count = ;
for (int x = -; x<;x++)
{
for (int y = -; y<; y++)
{
if(valid(i+x,j+y,M))
{
count++;
total +=M[i+x][j+y];
}
}
}
cur.push_back(total/count);
}
res.push_back(cur);
}
return res;
}
};
中规中矩的解法,完全按照题目意思搞
解法三:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> imageSmoother(vector<vector<int>>& M) {
int m = M.size(), n = M[].size();
if (m == || n == ) return {{}};
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{,},{,-},{,},{-,},{-,-},{,},{-,},{,-}};
for (int i = ; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = ; j < n; j++) {
int sum = M[i][j], cnt = ;
for (int k = ; k < dirs.size(); k++) {
int x = i + dirs[k][], y = j + dirs[k][];
if (x < || x > m - || y < || y > n - ) continue;
sum += (M[x][y] & 0xFF);
cnt++;
}
M[i][j] |= ((sum / cnt) << );
}
}
for (int i = ; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = ; j < n; j++) {
M[i][j] >>= ;
}
}
return M;
}
};
真正的大神解法!大神解释如下:Derived from StefanPochmann's idea in "game of life": the board has ints in [0, 255], hence only 8-bit is used, we can use the middle 8-bit to store the new state (average value), replace the old state with the new state by shifting all values 8 bits to the right.
661. Image Smoother【easy】的更多相关文章
- 170. Two Sum III - Data structure design【easy】
170. Two Sum III - Data structure design[easy] Design and implement a TwoSum class. It should suppor ...
- 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【easy】
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists[easy] Write a program to find the node at which the intersecti ...
- 206. Reverse Linked List【easy】
206. Reverse Linked List[easy] Reverse a singly linked list. Hint: A linked list can be reversed eit ...
- 203. Remove Linked List Elements【easy】
203. Remove Linked List Elements[easy] Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have ...
- 83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List【easy】
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List[easy] Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such ...
- 21. Merge Two Sorted Lists【easy】
21. Merge Two Sorted Lists[easy] Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new ...
- 142. Linked List Cycle II【easy】
142. Linked List Cycle II[easy] Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If ther ...
- 141. Linked List Cycle【easy】
141. Linked List Cycle[easy] Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up:Can y ...
- 237. Delete Node in a Linked List【easy】
237. Delete Node in a Linked List[easy] Write a function to delete a node (except the tail) in a sin ...
随机推荐
- iOS 10 资料整理笔记
1.Notification(通知) 自从Notification被引入之后,苹果就不断的更新优化,但这些更新优化只是小打小闹,直至现在iOS 10开始真正的进行大改重构,这让开发者也体会到UserN ...
- 关于GIT的一些注意点
往空仓库提交代码之前先将文档区的_gitignore放到项目根目录然后改名成.gitignore然后git add .gitignore以上的目的是忽略一些不应该提交GIT的文件,多人编辑工程的时候不 ...
- 我们知道写入过程比ZooKeeper集合中的读取过程要贵,因为所有节点都需要在数据库中写入相同的数据。因此,对于平衡的环境拥有较少数量(例如3,5,7)的节点比拥有大量的节点要好。
我们知道写入过程比ZooKeeper集合中的读取过程要贵,因为所有节点都需要在数据库中写入相同的数据.因此,对于平衡的环境拥有较少数量(例如3,5,7)的节点比拥有大量的节点要好. 组件 描述 写入( ...
- android多线程-AsyncTask之工作原理深入解析(下)
关联文章: Android 多线程之HandlerThread 完全详解 Android 多线程之IntentService 完全详解 android多线程-AsyncTask之工作原理深入解析(上) ...
- Android 多线程之HandlerThread 完全详解
关联文章: Android 多线程之HandlerThread 完全详解 Android 多线程之IntentService 完全详解 android多线程-AsyncTask之工作原理深入解析(上) ...
- 表格中的IE BUG
在表格应用了跨列单元格后,在IE6/7下当跨列单元格中的元素长度超过其跨列单元格中第一个单元格的宽度时会产生换行,如下所示: 解决方法: 1. 设置 table 的 'table-layout' 特性 ...
- [Python爬虫] 之二十七:Selenium +phantomjs 利用 pyquery抓取今日头条视频
一.介绍 本例子用Selenium +phantomjs爬取今天头条视频(http://www.tvhome.com/news/)的信息,输入给定关键字抓取图片信息. 给定关键字:视频:融合:电视 二 ...
- MySQL5.6 怎样优化慢查询的SQL语句 -- SQL优化
上篇:MySQL5.6 怎样优化慢查询的SQL语句 -- 慢日志介绍 在实际的日志分析中,通常慢日志的log数量不少,同一时候同样的查询被记录的条数也会非常多.这里就须要怎样从慢日志查询中找到最有问题 ...
- Java 字符串计算频率出现最高的字符
public class HighFrequencyWord { public static void findFrequencyWord(String str) { Collect ...
- 配置git账号和密码
最开始启动的时候 配置用户名和用户邮箱,安装完git第一件要做的事情! git config --global uesr.name "Sunnshino" git config - ...
