Android基于基于布局嵌套的页面导航实现
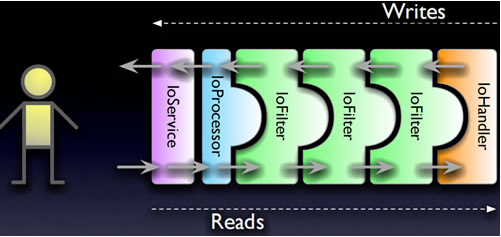
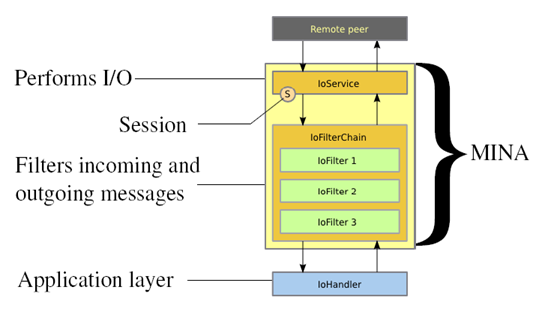
mina架构图
写数据、读数据触发点:
写数据:
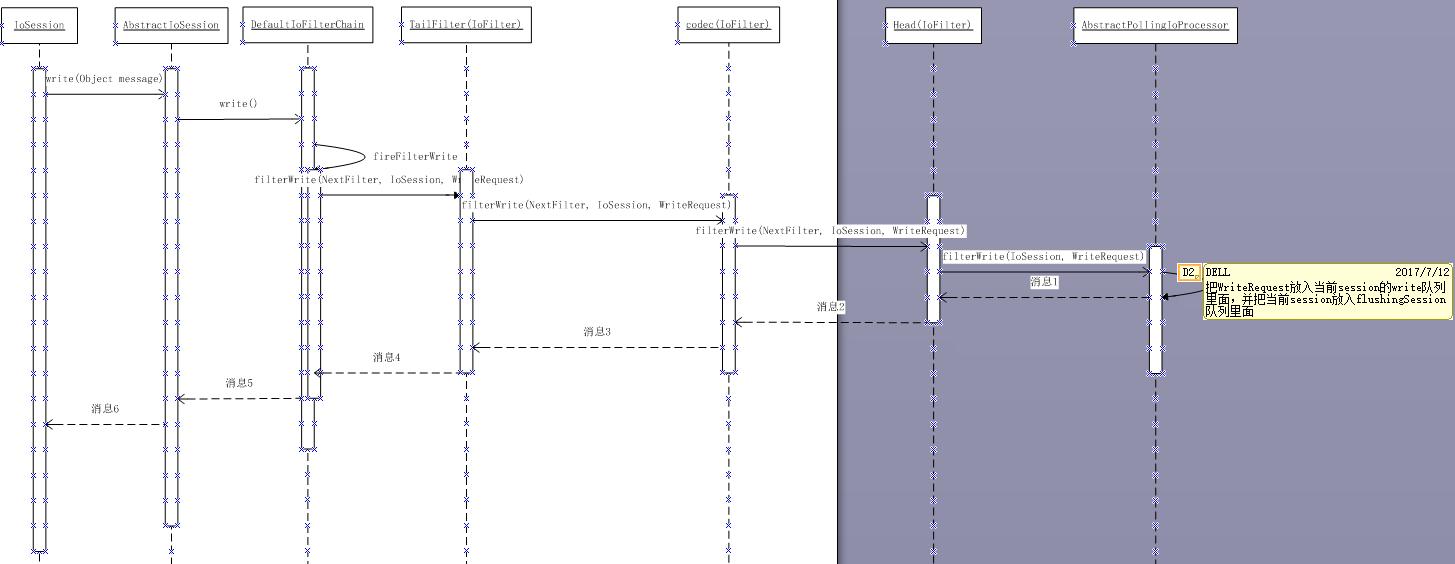
1、写操作很简单,是调用session的write方法,进行写数据的,写数据的最终结果保存在一个缓存队列里面,等待发送,并把当前session放入flushSession队列里面。
2、发数据其实和读数据是差不多的,都在Processor中的触发的,在process()完新消息后,会调用flush()方法,把flushSession队列里面的session取出来,并把缓存的消息发送到客户端。
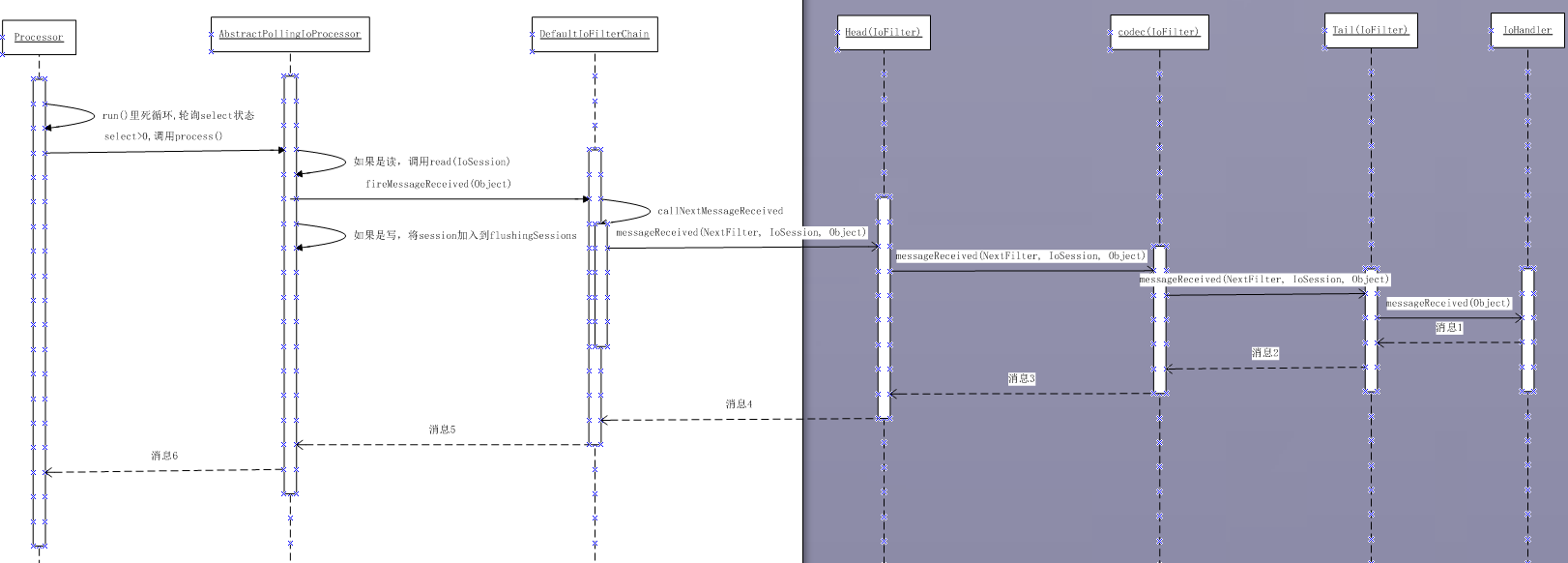
读数据:
读操作是在Processor中的触发的,Processor是AbstractPollingIoProcessor的内部私有类。
Processor中有一个死循环,循环调用Selector的select方法,若有新消息,则进行process()。
写数据过程
MINA数据类型
ByteBuffer、IoBuffer、Object。ByteBuffer是Java的NIO接口从channel读取数据的数据类型;IoBuffer是MINA自定义的数据类型,它封装了ByteBuffer;Object是用户自定义类型,通过用户自定义的codec与IoBuffer进行互相转换。
MINA数据类型转换流程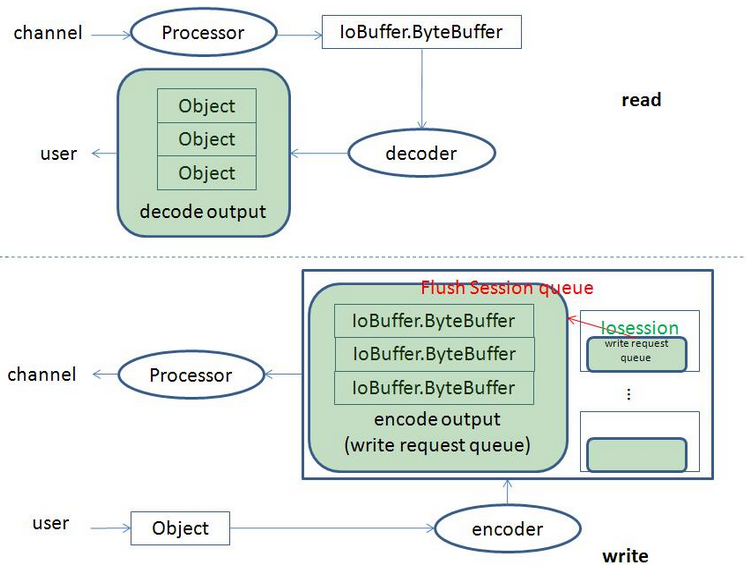
读数据过程
Processor从channel读取ByteBuffer数据,经MINA封装成IoBuffer提交给用户设置的decoder,decoder把解码结果放到一个解码输出队列(decode output queue)中,最后把队列元素按顺序提交给用户。如果设置了线程池来处理IO事件,那么Processor解码ByteBuffer数据以后的操作都由线程池执行,不然所有的操作都由Processor所在的线程执行。使用解码输出队列的原因是processor可能会收到的数据量超过decode成一个Object的所需要数据量,同时该队列是一个线程安全的,目的是防止在使用线程池运行IO事件时带来的数据竞争。
写数据过程
用户往IoSession中写入数据,通过encoder把用户类型的数据编码成IoBuffer并把它放入编码输出队列(写请求队列WriteRequestQueue),并把当前的IoSession放入Processor的刷新队列,最后Processor把每个IoSession中的写请求队列(WriteRequestQueue)中的数据写入channel。可以设置了运行IO事件的线程池执行在Processor处理之前的操作,不然这些操作都在用户写入IoSession的当前线程中执行。因为Processor所在线程跟用户往IoSession写数据的线程并不是同一个线程,所以需要一个线程安全的写请求队列(WriteRequestQueue)。
写数据:
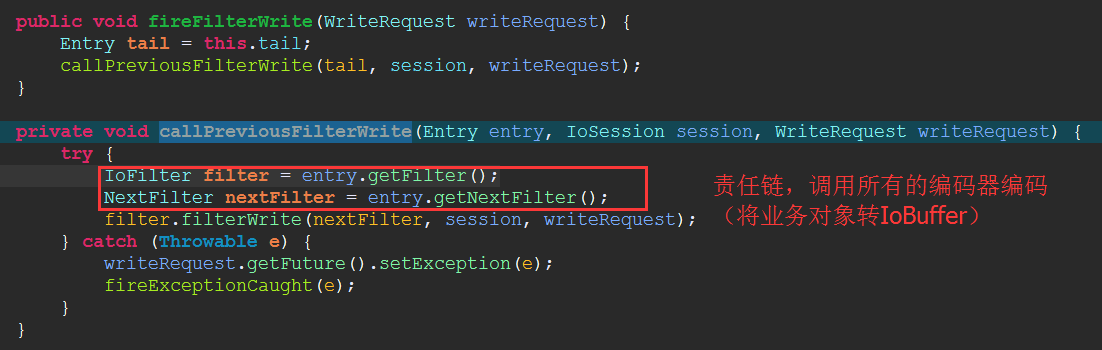
通过eclipse的单步调试:session.write()-->AbsructIoSession.write()-->DefaultIoFilterChain.fireFilterWrite()-->DefaultIoFilterChain.callPreviousFilterWrite()-->HeadFilter.filterWrite()-->SimpleIoProcessorPool-->IoProcessor(线程).write()
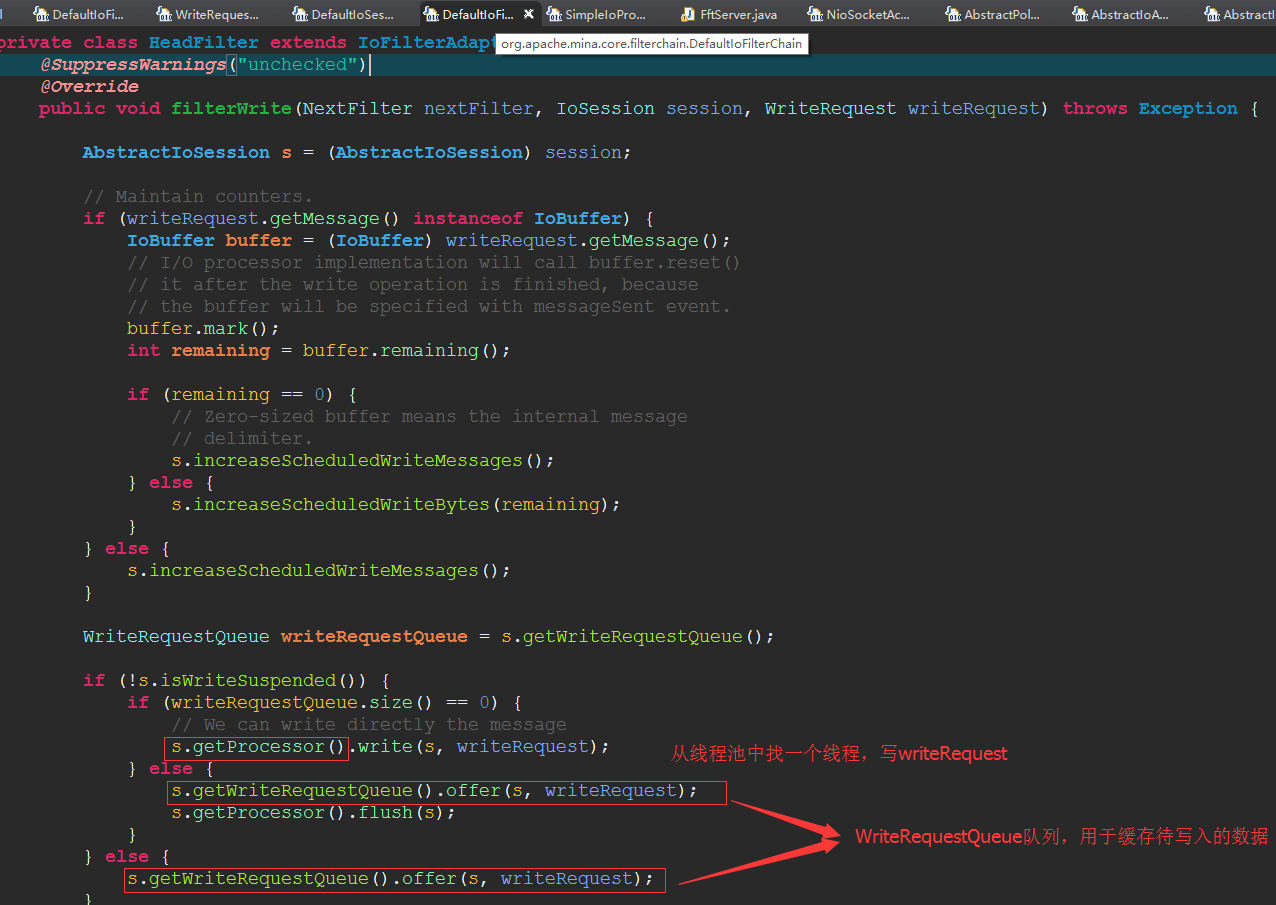
在最后一个Filter也就是HeadFilter中,会获取IoSession与之相关的 WriteRequestQueue 队列,作为应用层写出数据缓冲区。 把写出的WriteRequest放到写出缓冲区队列中。
因为apache mina 是按照SEDA架构设计,同时把要写出数据的IoSession放在 WriteRequestQueue队列中等待写出数据。
再看HeadFilter:
再来看 WriteRequestQueue中的数据是怎么处理的。
然后在Processor线程的run()方法中,来轮询flushIoSession队列。
AbstractPollingIoProcessor$Processor.run()-->AbstractPollingIoProcessor.flush(currentTime)-->AbstractPollingIoProcessor.flushNow(session, currentTime)-->
在NioProcessor(AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S>).flushNow(S, long) 方法中,依次把同一个IoSession中的writeRequest 请求写入到系统缓冲区。
private boolean flushNow(S session, long currentTime) {
if (!session.isConnected()) {
scheduleRemove(session);
return false;
}
final boolean hasFragmentation = session.getTransportMetadata().hasFragmentation();
final WriteRequestQueue writeRequestQueue = session.getWriteRequestQueue();
// Set limitation for the number of written bytes for read-write
// fairness. I used maxReadBufferSize * 3 / 2, which yields best
// performance in my experience while not breaking fairness much.
final int maxWrittenBytes = session.getConfig().getMaxReadBufferSize()
+ (session.getConfig().getMaxReadBufferSize() >>> 1);
int writtenBytes = 0;
WriteRequest req = null;
try {
// Clear OP_WRITE
setInterestedInWrite(session, false);
do {
// Check for pending writes.
req = session.getCurrentWriteRequest();
if (req == null) {
req = writeRequestQueue.poll(session);
if (req == null) {
break;
}
session.setCurrentWriteRequest(req);
}
int localWrittenBytes = 0;
Object message = req.getMessage();
if (message instanceof IoBuffer) {
localWrittenBytes = writeBuffer(session, req, hasFragmentation, maxWrittenBytes - writtenBytes,
currentTime);
if ((localWrittenBytes > 0) && ((IoBuffer) message).hasRemaining()) {
// the buffer isn't empty, we re-interest it in writing
writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
setInterestedInWrite(session, true);
return false;
}
} else if (message instanceof FileRegion) {
localWrittenBytes = writeFile(session, req, hasFragmentation, maxWrittenBytes - writtenBytes,
currentTime);
// Fix for Java bug on Linux
// http://bugs.sun.com/bugdatabase/view_bug.do?bug_id=5103988
// If there's still data to be written in the FileRegion,
// return 0 indicating that we need
// to pause until writing may resume.
if ((localWrittenBytes > 0) && (((FileRegion) message).getRemainingBytes() > 0)) {
writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
setInterestedInWrite(session, true);
return false;
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Don't know how to handle message of type '"
+ message.getClass().getName() + "'. Are you missing a protocol encoder?");
}
if (localWrittenBytes == 0) {
// Kernel buffer is full.
setInterestedInWrite(session, true);
return false;
}
writtenBytes += localWrittenBytes;
if (writtenBytes >= maxWrittenBytes) {
// Wrote too much
scheduleFlush(session);
return false;
}
} while (writtenBytes < maxWrittenBytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (req != null) {
req.getFuture().setException(e);
}
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireExceptionCaught(e);
return false;
}
return true;
}
如何在应用层缓冲区的写出数据全部写入到系统缓冲区后才关闭socket
关闭socket,从IoSession开始:IoSession(boolean immediately)-->AstractIoSession.close(boolean rightNow)
如果参数是true:-->AstractIoSession.close()
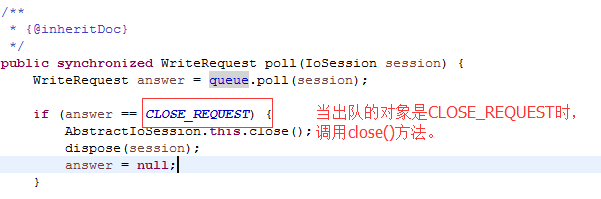
如果参数是false:-->AstractIoSession.closeOnFlush():创建了一个CLOSE_Request请求,当轮询flushIosession时,调用了close()方法。因为IoSession.close(flase) 也是一个写请求队列,所以在处理CLOSE_REQUEST请求时,之前的应用层缓冲区数据已经写入到系统缓冲区中。
CloseFuture close(boolean immediately);
IoSession的默认实现类AstractIoSession:
public final CloseFuture close(boolean rightNow) {
if (!isClosing()) {
if (rightNow) {
return close();
}
return closeOnFlush();
} else {
return closeFuture;
}
}
private final CloseFuture closeOnFlush() {
getWriteRequestQueue().offer(this, CLOSE_REQUEST);
getProcessor().flush(this);
return closeFuture;
}
CLOSE_REQUEST:(AbstractIoSession)
/**
* An internal write request object that triggers session close.
*
* @see #writeRequestQueue
*/
private static final WriteRequest CLOSE_REQUEST = new DefaultWriteRequest(new Object());
AbstractIoSession里的writeRequestQueue是CloseAwareWriteQueue
/**
* Create a new close aware write queue, based on the given write queue.
*
* @param writeRequestQueue
* The write request queue
*/
public final void setWriteRequestQueue(WriteRequestQueue writeRequestQueue) {
this.writeRequestQueue = new CloseAwareWriteQueue(writeRequestQueue);
}

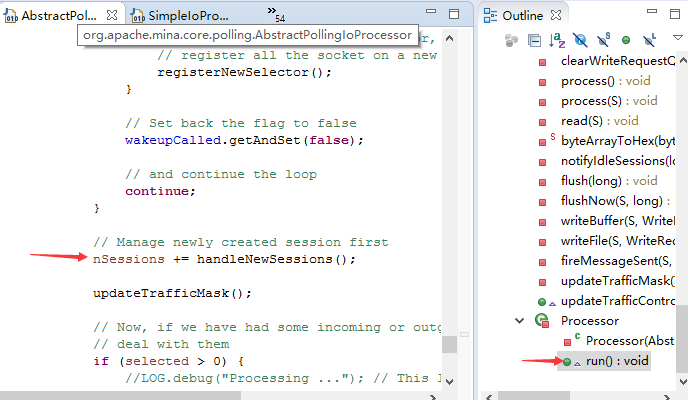
NioProcessor(AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S>)
AbstractPollingIoProcessor
/** A queue used to store the sessions to be removed */
private final Queue<S> removingSessions = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<S>();
AbstractPollingIoProcessor$Processor.run()-->NioProcessor(AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S>).removeSessions()
private class Processor implements Runnable {
public void run() {
assert (processorRef.get() == this);
int nSessions = 0;
lastIdleCheckTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (;;) {
try {
// This select has a timeout so that we can manage
// idle session when we get out of the select every
// second. (note : this is a hack to avoid creating
// a dedicated thread).
long t0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
int selected = select(SELECT_TIMEOUT);
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
long delta = (t1 - t0);
if ((selected == 0) && !wakeupCalled.get() && (delta < 100)) {
// Last chance : the select() may have been
// interrupted because we have had an closed channel.
if (isBrokenConnection()) {
LOG.warn("Broken connection");
// we can reselect immediately
// set back the flag to false
wakeupCalled.getAndSet(false);
continue;
} else {
LOG.warn("Create a new selector. Selected is 0, delta = " + (t1 - t0));
// Ok, we are hit by the nasty epoll
// spinning.
// Basically, there is a race condition
// which causes a closing file descriptor not to be
// considered as available as a selected channel, but
// it stopped the select. The next time we will
// call select(), it will exit immediately for the same
// reason, and do so forever, consuming 100%
// CPU.
// We have to destroy the selector, and
// register all the socket on a new one.
registerNewSelector();
}
// Set back the flag to false
wakeupCalled.getAndSet(false);
// and continue the loop
continue;
}
// Manage newly created session first
nSessions += handleNewSessions();
updateTrafficMask();
// Now, if we have had some incoming or outgoing events,
// deal with them
if (selected > 0) {
//LOG.debug("Processing ..."); // This log hurts one of the MDCFilter test...
process();
}
// Write the pending requests
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
flush(currentTime);
// And manage removed sessions
nSessions -= removeSessions();
// Last, not least, send Idle events to the idle sessions
notifyIdleSessions(currentTime);
// Get a chance to exit the infinite loop if there are no
// more sessions on this Processor
if (nSessions == 0) {
processorRef.set(null);
if (newSessions.isEmpty() && isSelectorEmpty()) {
// newSessions.add() precedes startupProcessor
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
if (!processorRef.compareAndSet(null, this)) {
// startupProcessor won race, so must exit processor
assert (processorRef.get() != this);
break;
}
assert (processorRef.get() == this);
}
// Disconnect all sessions immediately if disposal has been
// requested so that we exit this loop eventually.
if (isDisposing()) {
for (Iterator<S> i = allSessions(); i.hasNext();) {
scheduleRemove(i.next());
}
wakeup();
}
} catch (ClosedSelectorException cse) {
// If the selector has been closed, we can exit the loop
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(t);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(e1);
}
}
}
try {
synchronized (disposalLock) {
if (disposing) {
doDispose();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionMonitor.getInstance().exceptionCaught(t);
} finally {
disposalFuture.setValue(true);
}
}
}
可以看到这个类实现了Runnable接口, run方法中的for循环一直在处理IOSession的数据读取和写入。
int selected = select(SELECT_TIMEOUT); SELECT_TIMEOUT 的默认值为1000L 所以超时时间设置为1S 如果有数据可写或者数据可读 则返回值大于0
if ((selected == 0) && !wakeupCalled.get() && (delta < 100)) 这个地方主要是处理判断是已经断开的连接还是新建立的连接 对于delta 为什么小于100
这个暂时还不知道 哦,这个是个nio的bug 链接可以看下 http://maoyidao.iteye.com/blog/1739282
selected大于0 则开始处理IOSession的读写。
如果可读
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireMessageReceived(buf);
DefaultIoFilterChain实现fireMessageReceived的方法来处理
再由实现IoFilter接口的实现类来处理消息 基本上就结束了。
IoFilter有编解码,日志,线程池 这个有很多大家可以看下API。
private int removeSessions() {
int removedSessions = 0;
for (S session = removingSessions.poll(); session != null; session = removingSessions.poll()) {
SessionState state = getState(session);
// Now deal with the removal accordingly to the session's state
switch (state) {
case OPENED:
// Try to remove this session
if (removeNow(session)) {
removedSessions++;
}
break;
case CLOSING:
// Skip if channel is already closed
break;
case OPENING:
// Remove session from the newSessions queue and
// remove it
newSessions.remove(session);
if (removeNow(session)) {
removedSessions++;
}
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException(String.valueOf(state));
}
}
return removedSessions;
}
如果在IoSession真正关闭时,有数据尚未写入到系统缓冲区,将会有异常抛出。
AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S extends AbstractIoSession>.removeNow(S session)-->AbstractPollingIoProcessor<S extends AbstractIoSession>.clearWriteRequestQueue()
private void clearWriteRequestQueue(S session) {
WriteRequestQueue writeRequestQueue = session.getWriteRequestQueue();
WriteRequest req;
List<WriteRequest> failedRequests = new ArrayList<WriteRequest>();
if ((req = writeRequestQueue.poll(session)) != null) {
Object message = req.getMessage();
if (message instanceof IoBuffer) {
IoBuffer buf = (IoBuffer) message;
// The first unwritten empty buffer must be
// forwarded to the filter chain.
if (buf.hasRemaining()) {
buf.reset();
failedRequests.add(req);
} else {
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireMessageSent(req);
}
} else {
failedRequests.add(req);
}
// Discard others.
while ((req = writeRequestQueue.poll(session)) != null) {
failedRequests.add(req);
}
}
// Create an exception and notify.
if (!failedRequests.isEmpty()) {
WriteToClosedSessionException cause = new WriteToClosedSessionException(failedRequests);
for (WriteRequest r : failedRequests) {
session.decreaseScheduledBytesAndMessages(r);
r.getFuture().setException(cause);
}
IoFilterChain filterChain = session.getFilterChain();
filterChain.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
}
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/smart_k/article/details/6617334
http://blog.csdn.net/wzm112358/article/details/46409181
Android基于基于布局嵌套的页面导航实现的更多相关文章
- Android零基础入门第35节:Android中基于回调的事件处理
原文:Android零基础入门第35节:Android中基于回调的事件处理 通过前面两期掌握了Android中基于监听的事件处理的五种形式,那么本期一起来学习Android中基于回调的事件处理. 一. ...
- Android零基础入门第34节:Android中基于监听的事件处理
原文:Android零基础入门第34节:Android中基于监听的事件处理 上一期我们学习了Android中的事件处理,也详细学习了Android中基于监听的事件处理,同时学会了匿名内部类形式,那么本 ...
- 基于JQuery实现滚动到页面底端时自动加载更多信息
基于JQuery实现滚动到页面底端时自动加载更多信息 关键代码: 代码如下: var stop=true; $(window).scroll(function(){ totalheight = par ...
- 强大!基于拖放布局的 Twitter Bootstrap 网站生成器
强大!基于拖放布局的 Twitter Bootstrap 网站生成器 网址如下 http://www.layoutit.com/build http://demo.sc.chinaz.com/File ...
- Android之基于HTTP协议的下载
Android之基于HTTP协议的下载 http://www.blogjava.net/zh-weir/archive/2010/05/02/319892.html http://www.qianfa ...
- 【Android】基于TCP协议的网络通信
1.使用ServerSocket 创建TCP服务器端: ServerSocket server; try { server = new ServerSocket(8000); while (true) ...
- Https系列之四:https的SSL证书在Android端基于okhttp,Retrofit的使用
Https系列会在下面几篇文章中分别作介绍: 一:https的简单介绍及SSL证书的生成二:https的SSL证书在服务器端的部署,基于tomcat,spring boot三:让服务器同时支持http ...
- Asp.Net Core 2.0 项目实战(11) 基于OnActionExecuting全局过滤器,页面操作权限过滤控制到按钮级
1.权限管理 权限管理的基本定义:百度百科. 基于<Asp.Net Core 2.0 项目实战(10) 基于cookie登录授权认证并实现前台会员.后台管理员同时登录>我们做过了登录认证, ...
- Android应用---基于NDK的samples例程hello-jni学习NDK开发
Android应用---基于NDK的samples例程hello-jni学习NDK开发 NDK下载地址:http://developer.android.com/tools/sdk/ndk/index ...
随机推荐
- poj 3101 Astronomy
2个星球周期为a,b.则相差半周的长度为a*b/(2*abs(a-b)),对于n个只需求这n个 分数的最小公倍数即可! 公式: 分数的最小公倍数 = 分子的最小公倍数/分母的最大公约数 由于涉及到大数 ...
- linux入门教程(三) Linux操作系统的安装
因为笔者一直都是使用CentOS,所以这次安装系统也是基于CentOS的安装.把光盘插入光驱,设置bios光驱启动.进入光盘的欢迎界面. 其中有两个选项,可以直接按回车,也可以在当前界面下输入 lin ...
- 【转】Dr.com 5.20破解教程
Dr.com 5.20破解教程 方法一 1.首先下载相关工具 Process Explorer(大家可以自行百度 一般绿色汉化版就可以)右键选择以管理员权限运行process的主程序 然后运行drc ...
- [topcoder] EllysNumberGuessing
http://community.topcoder.com/stat?c=problem_statement&pm=12975 简单题 #include <cstdlib> #in ...
- POJ1118 Lining Up
快弄死我了 最后的原因是abs和fabs的区别... 说点收获:1.cmp函数返回的是int,所以不要直接返回double相减的结果2.define inf 1e9和eps 1e-93.在整数相除得到 ...
- asp.net中当服务器出错时显示指定的错误页面
http://blog.csdn.net/helloxiaoyu/article/details/2943537 此篇文章描述了当异常再ASP.NET中发生时怎样使用C#.NET代码去拦截和相应异常. ...
- Android 在Intent中传递接口
总结:在Activity中不能用intent传递匿名接口,原因如下:Activity A中生成了匿名接口M, 这个接口的引用就在组Activity A中,Activity A会禁止接口M 序列化.因为 ...
- Lotus Notes中编程发送邮件(二)
在编程发送各种类似通知的邮件时,时常会需要发件人显示为某个特定的帐户,比如某个部门的名称或者管理员的名字.另一种需求是,用户收到某封邮件后,回复邮件的地址不同于发件人栏显示的地址.而正常情况下,发送邮 ...
- Android开发之获取系统版本号
获取系统版本号:获取当前系统的版本号: textView.setText("Product Model: " + android.os.Build.MODEL + ",& ...
- VS2010中如果忘记函数所在的头文件或者忘记函数的输入输出参数类型怎么办?
先随便找一个熟悉的函数,右击-转到定义,然后写出目标函数,右击-转到定义