论文解读(APCA)《Adaptive prototype and consistency alignment for semi-supervised domain adaptation》
[ Wechat:Y466551 | 付费咨询,非诚勿扰 ]
论文信息
论文标题:Adaptive prototype and consistency alignment for semi-supervised domain adaptation
论文作者:Jihong Ouyang、Zhengjie Zhang、Qingyi Meng
论文来源:2023 aRxiv
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
视屏讲解:click
1 介绍
2 问题定义
Formally, the semi-supervised domain adaptation scenario constitutes a labeled source domain $\mathcal{D}_{s}=\left\{\left(x_{i}^{s}, y_{i}^{s}\right)\right\}_{i=1}^{n_{s}}$ drawn from the distribution $P$ . For the target domain, a labeled set $\mathcal{D}_{t}=\left\{\left(x_{i}^{t}, y_{i}^{t}\right)\right\}_{i=1}^{n_{t}}$ and an unlabeled set $\mathcal{D}_{u}=\left\{x_{i}^{u}\right\}_{i=1}^{n_{u}}$ drawn from distribution $Q$ are given. The source and target domain are drawn from the same label space $y=\{1,2, \ldots, K\}$ . Usually, the number of labeled samples in $\mathcal{D}_{t}$ is minimal, e.g., one or three samples per class. SSDA aims to train the model on $\mathcal{D}_{s}$, $\mathcal{D}_{t}$ and $\mathcal{D}_{u}$ to correctly predict labels for samples in $\mathcal{D}_{u} $.
3 方法
3.1 模型框架
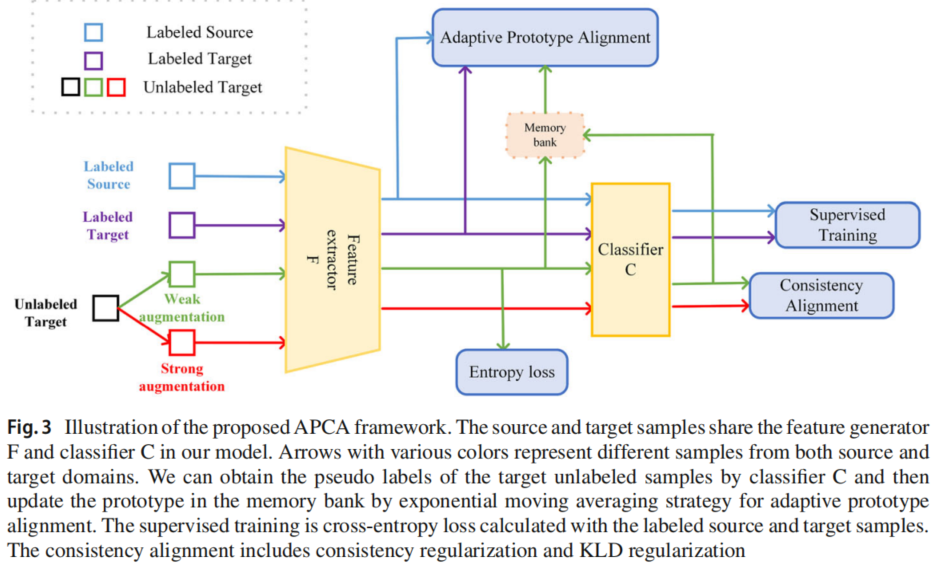
3.2 Supervised training
3.3 Adaptive prototype alignment
利用目标域代标记数据计算原型:
$\mathbf{c}_{k}^{\mathcal{T}}=\frac{1}{\left|\mathcal{D}_{k}\right|} \sum_{\left(x_{i}^{t}, y_{i}^{t}\right) \in \mathcal{D}_{k}} F\left(x_{i}^{t}\right)\quad\quad(3)$
利用目标域未带标记的数据计算原型(mini-batch级别):
$c_{k}^{u}=\frac{\sum_{i \in B_{t}} \mathbb{1}_{\left[k=\hat{y}_{i}\right]} F\left(x_{i}^{u}\right)}{\sum_{i \in B_{t}} \mathbb{1}_{\left[k=\hat{y}_{i}\right]}}\quad\quad(4)$
Note:目标域未带标记样本使用分类器给出伪标签;
$c_{k(m)}^{\mathcal{U}}=\eta c_{k}^{u}+(1-\eta) c_{k(m-1)}^{\mathcal{U}}\quad\quad(5)$
利用 EMA 修改用目标域未带标记样本计算的原型:
$c_{k(m)}^{\mathcal{U}}=\eta c_{k}^{u}+(1-\eta) c_{k(m-1)}^{\mathcal{U}}\quad\quad(6)$
目标域总的原型:
$c_{k}=\frac{\mathbf{c}_{k}^{\mathcal{T}}+c_{k(m)}^{\mathcal{U}}}{2}\quad\quad(7)$
对于源域带标记数据,可以通过目标类原型距离函数得到概率分布如下:
$p(y \mid x)=\frac{e^{-d\left(F(x), c_{y}\right)}}{\sum_{k} e^{-d\left(F(x), c_{k}\right)}}\quad\quad(8)$
然后,计算总体源样本的原型损失如下:
$\mathcal{L}_{A P A}=-\mathbb{E}_{\left(x_{i}^{s}, y_{i}^{s}\right) \in \mathcal{D}_{s}} \log p\left(y_{i}^{s} \mid x_{i}^{s}\right)\quad\quad(9)$
小结阐述:使用目标域数据(带、不带标记)计算目标域原型,然后预测源域样本的类别,并使用源域标签做监督;
3.4 Consistency alignment
如模型框架图所示,目标域未带标记数据被分为弱、强数据增强样本,对于弱数据增强样本,使用分类器得到硬标签,并计算交叉熵(基于阈值$\gamma$):
$\left.\ell_{c r}=-\mathbb{1}\left(\max \left(\mathbf{p}_{w}\right)>\tau\right) \log \mathbf{p}\left(y=\hat{p} \mid \mathcal{S}\left(x_{i}^{u}\right)\right)\right)\quad\quad(10)$
为了避免过拟合,使用多样性损失:
$\ell_{k l d}=-\mathbb{1}\left(\max \left(\mathbf{p}_{w}\right)>\tau\right) \sum_{k=1}^{C} \frac{1}{C} \log \mathbf{p}\left(y=k \mid \mathcal{S}\left(x_{i}^{u}\right)\right)\quad\quad(11)$
Note:KLD正则化鼓励预测结果接近均匀分布,从而使预测结果不会过拟合伪标签。
因此,一致性对齐模块的整体损失函数可以表示如下:
$\mathcal{L}_{C O N}=\mathbb{E}_{x_{i}^{u} \in \mathcal{D}_{u}}\left(\ell_{c r}+\lambda_{k l d} \ell_{k l d}\right)\quad\quad(12)$
3.5 Overall framework and training objective
本文方法是基于MME [45]的,它采用对抗性学习来改进域间自适应的样本特征对齐。将MME[45]中提到的熵损失纳入到本文的损失函数中。总体损失函数是上述损失函数的和,如下:
$\theta_{\mathcal{F}}=\underset{\theta_{\mathcal{F}}}{\arg \min } \mathcal{L}_{C E}+\mathcal{L}_{H}+\lambda_{1} \mathcal{L}_{A P A}+\lambda_{2} \mathcal{L}_{C O N}\quad\quad(13)$
$\theta_{\mathcal{C}}=\underset{\theta_{\mathcal{A}}}{\arg \min } \mathcal{L}_{C E}-\mathcal{L}_{H}+\lambda_{1} \mathcal{L}_{A P A}+\lambda_{2} \mathcal{L}_{C O N}$
其中:
$\mathcal{L}_{H}=-\mathbb{E}_{x_{i}^{u} \in \mathcal{D}_{u}} \sum_{i=1}^{K} p\left(y=i \mid x_{i}^{u}\right) \log p\left(y=i \mid x_{i}^{u}\right)$
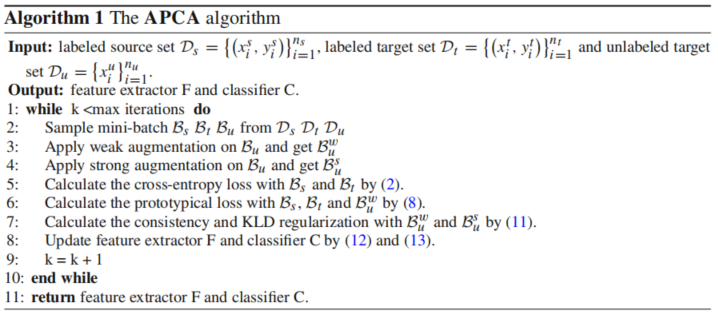
3.6 算法框架
4 实验
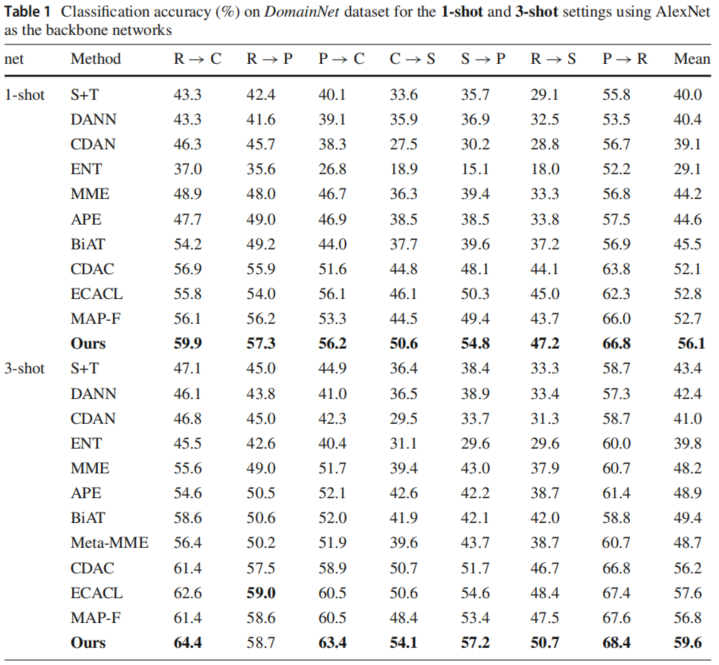
分类准确度
参数敏感性
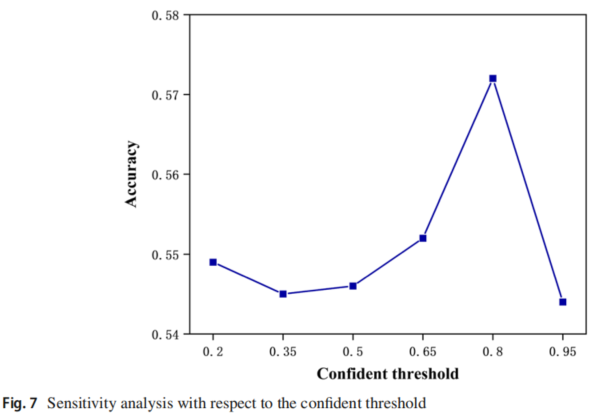
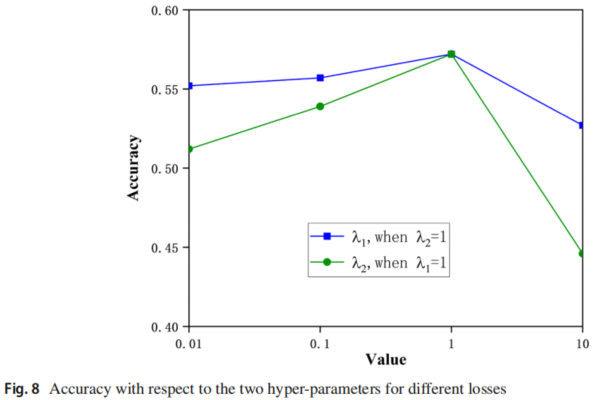
消融实验

论文解读(APCA)《Adaptive prototype and consistency alignment for semi-supervised domain adaptation》的更多相关文章
- 论文解读(CDCL)《Cross-domain Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:Cross-domain Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation论文作者:Rui Wang, Zuxuan ...
- 论文解读(CDTrans)《CDTrans: Cross-domain Transformer for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:CDTrans: Cross-domain Transformer for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation论文作者:Tongkun Xu, Weihu ...
- 迁移学习()《Attract, Perturb, and Explore: Learning a Feature Alignment Network for Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:Attract, Perturb, and Explore: Learning a Feature Alignment Network for Semi-supervised Do ...
- 论文解读(AGC)《Attributed Graph Clustering via Adaptive Graph Convolution》
论文信息 论文标题:Attributed Graph Clustering via Adaptive Graph Convolution论文作者:Xiaotong Zhang, Han Liu, Qi ...
- 论文解读(AGE)《Adaptive Graph Encoder for Attributed Graph Embedding》
论文信息 论文标题:Adaptive Graph Encoder for Attributed Graph Embedding论文作者:Gayan K. Kulatilleke, Marius Por ...
- 论文解读(ToAlign)《ToAlign: Task-oriented Alignment for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:ToAlign: Task-oriented Alignment for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation论文作者:Guoqiang Wei, Cuil ...
- 《Stereo R-CNN based 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Driving》论文解读
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09738v2.pdf 这两个月忙着做实验 博客都有些荒废了,写篇用于3D检测的论文解读吧,有理解错误的地方,烦请有心人指正). 博客原 ...
- CVPR2020论文解读:OCR场景文本识别
CVPR2020论文解读:OCR场景文本识别 ABCNet: Real-time Scene Text Spotting with Adaptive Bezier-Curve Network∗ 论文 ...
- 自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning)多篇论文解读(上)
自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning)多篇论文解读(上) 前言 Supervised deep learning由于需要大量标注信息,同时之前大量的研究已经解决了许多问题.所以 ...
- 人工智能论文解读精选 | PRGC:一种新的联合关系抽取模型
NLP论文解读 原创•作者 | 小欣 论文标题:PRGC: Potential Relation and Global Correspondence Based Joint Relational ...
随机推荐
- 面试题:react、vue中的key
1.虚拟DOM中key的作用 key是虚拟DOM对象的标识,当数据发生变化时,React/Vue会根据[新数据]生成新的[虚拟DOM],随后React/Vue进行[新虚拟DOM]与[旧虚拟DO ...
- nuxt下运行项目时内存溢出(out of memory)的一种情况
话不多说直接上代码: 如图,点红点的三行引入了一个组件,内容是同意注册协议的弹窗.但是在run dev的时候提示说内存溢出了(out of memory)...经过多方排查,定位到这个组件,警察叔叔就 ...
- Python定时任务框架apscheduler的简单使用
apscheduler的简单使用 APScheduler有四大组件: 1.触发器 triggers : 触发器包含调度逻辑.每个作业都有自己的触发器,用于确定下一个任务何时运行.除了初始配置之外,触发 ...
- 文心一言 VS chatgpt (3)-- 算法导论2.1
一.以图 2-2 为模型,说明INSERTION-SORT 在数组 A=(31,41,59,26,41,58)上的执行过程. 文心一言: 以图 2-2 为模型,说明INSERTION-SORT 在数组 ...
- 2022-12-16:给你一个长度为n的数组,并询问q次 每次询问区间[l,r]之间是否存在小于等于k个数的和大于等于x 每条查询返回true或者false。 1 <= n, q <= 10^5 k
2022-12-16:给你一个长度为n的数组,并询问q次 每次询问区间[l,r]之间是否存在小于等于k个数的和大于等于x 每条查询返回true或者false. 1 <= n, q <= 1 ...
- 2021-10-22:颠倒二进制位。颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。提示:请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型。在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不
2021-10-22:颠倒二进制位.颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位.提示:请注意,在某些语言(如 Java)中,没有无符号整数类型.在这种情况下,输入和输出都将被指定为有符号整数类型,并且不 ...
- Python从零到壹丨详解图像锐化Roberts、Prewitt算子实现边缘检测
摘要:图像锐化和边缘提取技术可以消除图像中的噪声,提取图像信息中用来表征图像的一些变量,为图像识别提供基础.本章主要介绍Robert算子.Prewitt算子.Sobel算子.Laplacian算子.S ...
- Vue cli3 整合SuperMap巧遇js异步加载的坑
最近使用到superMap做三维地图,而项目又分为可视化大屏与后台管理系统两部分,所以项目配置了多入口,然引入cesium依赖就成了问题,在vue cli3 整合Cesium,处理build 时内存溢 ...
- Hugging News #0526: Hugging Cast 发布第一期、邀请来认领自己的论文啦!
每一周,我们的同事都会向社区的成员们发布一些关于 Hugging Face 相关的更新,包括我们的产品和平台更新.社区活动.学习资源和内容更新.开源库和模型更新等,我们将其称之为「Hugging Ne ...
- 代码随想录算法训练营Day50 动态规划
代码随想录算法训练营 代码随想录算法训练营Day50 动态规划| 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III 188.买卖股票的最佳时机IV 123.买卖股票的最佳时机III 题目链接:123.买卖股票的最佳时 ...
