HDFS Lease Recovey 和 Block Recovery
这篇分析一下Lease Recovery 和 Block Recovery
hdfs支持hflush后,需要保证hflush的数据被读到,datanode重启不能简单的丢弃文件的最后一个block,而是需要保留下hflush的数据。同时为了支持append,需要将已经finalized的block重新打开追加数据。这就为宕机的恢复处理带来了更大的困难,支持hflush/append之前,hdfs只需要将未关闭文件的最后一个block的多个副本删除即可.
在hdfs的设计中,Lease是为了实现一个文件在一个时刻只能被一个客户端写。客户端写文件或者append之前都需要向namenode申请这个文件的Lease,在客户端写数据的过程中,后台线程会不断的renew lease,不断的延长独占写的时间.实际上,Lease有两个limit,一个是soft limit,默认60s,一个是hard limit,默认1小时。这两个limit的区别如下:
lease soft limit过期之前,该客户端拥有对这个文件的独立访问权,其他客户端不能剥夺该客户端独占写这个文件的权利。
lease soft limit过期后,任何一个客户端都可以回收lease,继而得到这个文件的lease,获得对这个文件的独占访问权。
lease hard limit过期后,namenode强制关闭文件,撤销lease.
考虑客户端写文件的过程中宕机,那么在lease soft limit过期之前,其他的客户端不能写这个文件,等到lease soft limit过期后,其他客户端可以写这个文件,在写文件之前,会首先检查文件是不是没有关闭,如果没有,那么就会进入lease recovery和block recovery阶段,这个阶段的目的是使文件的最后一个block的所有副本数据达到一致,因为客户端写block的多个副本是pipeline写,pipeline中的副本数据不一致很正常。
本文考虑客户端写的过程中客户端宕机,随后其他客户端对这个文件进行append操作的场景。
客户端通过如下代码对一个文件进行append:
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(configuration);
FSDataOutputStream out = fs.append(path);
out.write(byte[]);
append操作在namenode这端主要逻辑在FSNameSystem的appendFileInternal函数中处理,内部会调用
// Opening an existing file for write - may need to recover lease.
recoverLeaseInternal(myFile, src, holder, clientMachine, false);
来检查是否需要首先对文件进行lease recovery.重点看看这个函数.
private void recoverLeaseInternal(INodeFile fileInode,
String src, String holder, String clientMachine, boolean force)
throws IOException {
// holder是对这个文件进行append的clientname
assert hasWriteLock();
if (fileInode != null && fileInode.isUnderConstruction()) {
//
// If the file is under construction , then it must be in our
// leases. Find the appropriate lease record.
//
Lease lease = leaseManager.getLease(holder);
//
// We found the lease for this file. And surprisingly the original
// holder is trying to recreate this file. This should never occur.
//
if (!force && lease != null) {
Lease leaseFile = leaseManager.getLeaseByPath(src);
if ((leaseFile != null && leaseFile.equals(lease)) ||
lease.getHolder().equals(holder)) {
throw new AlreadyBeingCreatedException(
"failed to create file " + src + " for " + holder +
" for client " + clientMachine +
" because current leaseholder is trying to recreate file.");
}
}
//
// Find the original holder.
//
FileUnderConstructionFeature uc = fileInode.getFileUnderConstructionFeature();
String clientName = uc.getClientName();
lease = leaseManager.getLease(clientName);
if (lease == null) {
throw new AlreadyBeingCreatedException(
"failed to create file " + src + " for " + holder +
" for client " + clientMachine +
" because pendingCreates is non-null but no leases found.");
}
if (force) {
// close now: no need to wait for soft lease expiration and
// close only the file src
LOG.info("recoverLease: " + lease + ", src=" + src +
" from client " + clientName);
internalReleaseLease(lease, src, holder);
} else {
assert lease.getHolder().equals(clientName) :
"Current lease holder " + lease.getHolder() +
" does not match file creator " + clientName;
//
// If the original holder has not renewed in the last SOFTLIMIT
// period, then start lease recovery.
//
if (lease.expiredSoftLimit()) {
LOG.info("startFile: recover " + lease + ", src=" + src + " client "
+ clientName);
boolean isClosed = internalReleaseLease(lease, src, null);
if(!isClosed)
throw new RecoveryInProgressException(
"Failed to close file " + src +
". Lease recovery is in progress. Try again later.");
} else {
final BlockInfo lastBlock = fileInode.getLastBlock();
if (lastBlock != null
&& lastBlock.getBlockUCState() == BlockUCState.UNDER_RECOVERY) {
throw new RecoveryInProgressException("Recovery in progress, file ["
+ src + "], " + "lease owner [" + lease.getHolder() + "]");
} else {
throw new AlreadyBeingCreatedException("Failed to create file ["
+ src + "] for [" + holder + "] for client [" + clientMachine
+ "], because this file is already being created by ["
+ clientName + "] on ["
+ uc.getClientMachine() + "]");
}
}
}
}
}
通过检查文件的INode看文件的状态,如果处于under construction状态,说明,该文件不处于关闭状态,那么很可能这个文件需要经过lease recovery和block recovery阶段来对文件的最后一个block的多个副本达到一致.
从lease manager中根据clientname拿到clientname持有的Lease(holder是调用此次append操作的clientname),如果不为空,说明该客户端依然持有lease,那么接着看这个lease中是否包含append的这个文件名,如果确实有,那么说明当前客户端仍然持有这个文件的lease,append失败,因为append的前提条件是文件处于closed状态.如果lease中不包含这个文件,说明客户端当前不持有这个文件的Lease,那么继续往下走
从INode中找出这个之前拥有这个文件的leaseholder,也就是在我们设定的场景中的宕机的客户端,然后从lease manager中找到宕机的客户端对应的Lease,然后检查是否这个lease已经soft limit过期,如果过期,则调用
boolean isClosed = internalReleaseLease(lease, src, null);
这个函数检查是否需要真正的进入block recovery阶段,这个阶段需要datanode的参与。下面函数的主要逻辑如下.
3.1. 如果文件的所有block都是completed状态,则不需要进行block recovery,关闭文件.
则从lease manager将这个文件的lease删除,将INode的状态置为complete,最后记一条close file的edit log
3.2. 如果最后一个block是committed状态,那么看该文件的最后两个block的状态,如果倒数第二个block和最后一个block都满足最小副本数要求(默认是1),关闭文件.否则,客户端抛异常。
3.3. 如果最后一个block是under construction或者under recovery状态,并且最后一个block没有任何datanode汇报上来,很有可能是pipeline还没建立起来,客户端就宕机了,这种情况下,只需要把最后一个block从INode中溢出,并且关闭文件.
3.4. 进入block recovery阶段.
为这次block recovery过程申请一个block recovery id,标示这次block recovery过程.block recovery id实际是一个新分配的generation stamp
将block状态设置为under recovery,从block的多个副本中选择一个副本所在的datanode作为primary data node,然后将这个block放入这个datanode的recoverBlocks列表中,随后,namenode在处理datanode的定期心跳中,会将这个datanode的所有的recoverBlocks都在心跳回复中发送给datanode,以BlockRecoveryCommand的形式.代码:
DatanodeManager::handleHeartbeat
//check lease recovery
BlockInfoUnderConstruction[] blocks = nodeinfo
.getLeaseRecoveryCommand(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
if (blocks != null) {
BlockRecoveryCommand brCommand = new BlockRecoveryCommand(
blocks.length);
for (BlockInfoUnderConstruction b : blocks) {
final DatanodeStorageInfo[] storages = b.getExpectedStorageLocations();
// Skip stale nodes during recovery - not heart beated for some time (30s by default).
final List<DatanodeStorageInfo> recoveryLocations =
new ArrayList<DatanodeStorageInfo>(storages.length);
for (int i = 0; i < storages.length; i++) {
if (!storages[i].getDatanodeDescriptor().isStale(staleInterval)) {
recoveryLocations.add(storages[i]);
}
}
// If we only get 1 replica after eliminating stale nodes, then choose all
// replicas for recovery and let the primary data node handle failures.
if (recoveryLocations.size() > 1) {
if (recoveryLocations.size() != storages.length) {
LOG.info("Skipped stale nodes for recovery : " +
(storages.length - recoveryLocations.size()));
}
brCommand.add(new RecoveringBlock(
new ExtendedBlock(blockPoolId, b),
DatanodeStorageInfo.toDatanodeInfos(recoveryLocations),
b.getBlockRecoveryId()));
} else {
// If too many replicas are stale, then choose all replicas to participate
// in block recovery.
brCommand.add(new RecoveringBlock(
new ExtendedBlock(blockPoolId, b),
DatanodeStorageInfo.toDatanodeInfos(storages),
b.getBlockRecoveryId()));
}
}
return new DatanodeCommand[] { brCommand };
}
现在看DataNode端.
DataNode端的BPServiceActor处理心跳回复,在offerService()函数中,从心跳回复中拿出所有的DataNodeCommand处理。在processCommandFromActive函数中检查,command类型是DNA_RECOVERBLOCK,说明是block recovery命令,调用DataNode的recoverBlocks处理.
case DatanodeProtocol.DNA_RECOVERBLOCK:
String who = "NameNode at " + actor.getNNSocketAddress();
dn.recoverBlocks(who, ((BlockRecoveryCommand)cmd).getRecoveringBlocks());
break;
dn.recoverBlocks会起一个后台线程专门来处理这件事,对于每个需要recover的block:
从block拿出副本所在的datanode,给其他两个副本所在的datanode建立连接,datanode之间的接口定义在InterDatanodeProtocol接口中,调用DataNode(包括自己)的initReplicaRecovery(rBlock)函数,DataNode最终会调用FsDatasetImpl的initReplicaRecovery方法来初始化datanode上需要恢复的replica。看看这个函数:
static ReplicaRecoveryInfo initReplicaRecovery(String bpid, ReplicaMap map,
Block block, long recoveryId, long xceiverStopTimeout) throws IOException {
final ReplicaInfo replica = map.get(bpid, block.getBlockId());
LOG.info("initReplicaRecovery: " + block + ", recoveryId=" + recoveryId
+ ", replica=" + replica);
//check replica
if (replica == null) {
return null;
}
//stop writer if there is any
if (replica instanceof ReplicaInPipeline) {
final ReplicaInPipeline rip = (ReplicaInPipeline)replica;
rip.stopWriter(xceiverStopTimeout);
//check replica bytes on disk.
if (rip.getBytesOnDisk() < rip.getVisibleLength()) {
throw new IOException("THIS IS NOT SUPPOSED TO HAPPEN:"
+ " getBytesOnDisk() < getVisibleLength(), rip=" + rip);
}
//check the replica's files
checkReplicaFiles(rip);
}
//check generation stamp
if (replica.getGenerationStamp() < block.getGenerationStamp()) {
throw new IOException(
"replica.getGenerationStamp() < block.getGenerationStamp(), block="
+ block + ", replica=" + replica);
}
//check recovery id
if (replica.getGenerationStamp() >= recoveryId) {
throw new IOException("THIS IS NOT SUPPOSED TO HAPPEN:"
+ " replica.getGenerationStamp() >= recoveryId = " + recoveryId
+ ", block=" + block + ", replica=" + replica);
}
//check RUR
final ReplicaUnderRecovery rur;
if (replica.getState() == ReplicaState.RUR) {
rur = (ReplicaUnderRecovery)replica;
if (rur.getRecoveryID() >= recoveryId) {
throw new RecoveryInProgressException(
"rur.getRecoveryID() >= recoveryId = " + recoveryId
+ ", block=" + block + ", rur=" + rur);
}
final long oldRecoveryID = rur.getRecoveryID();
rur.setRecoveryID(recoveryId);
LOG.info("initReplicaRecovery: update recovery id for " + block
+ " from " + oldRecoveryID + " to " + recoveryId);
}
else {
rur = new ReplicaUnderRecovery(replica, recoveryId);
map.add(bpid, rur);
LOG.info("initReplicaRecovery: changing replica state for "
+ block + " from " + replica.getState()
+ " to " + rur.getState());
}
return rur.createInfo();
}
```
首先,检查副本的状态,如果当前副本的状态是正在写的过程中,那么调用replica的stopWriter停止这个写线程,停止的方法就是interupt这个写线程(写pipeline时,datanode创建replica时会将当前写线程的handle存到replica中),从这可以看出blcok recovery优先级很高。然后做一些check,比如副本在磁盘上的文件是否存在,meta文件是否存在等,然后,检查generation stamp,namenode记录的generation stamp不能比实际的大,recovery id不能比副本的generation stamp小,最后,创建一个ReplicaUnderRecovery,放入replica map中,这里还会检查,如果replica已经处于under recovery状态,则看当前的block recovery过程的recovery id和它谁大,如果更大,则强占它。
接着,将三个副本的信息(包括recovery前的副本的信息)都加入一个列表,然后开始sync,sync就是根据三个副本的原来的状态,做一些选择,规则如下,这是两个副本的情况:
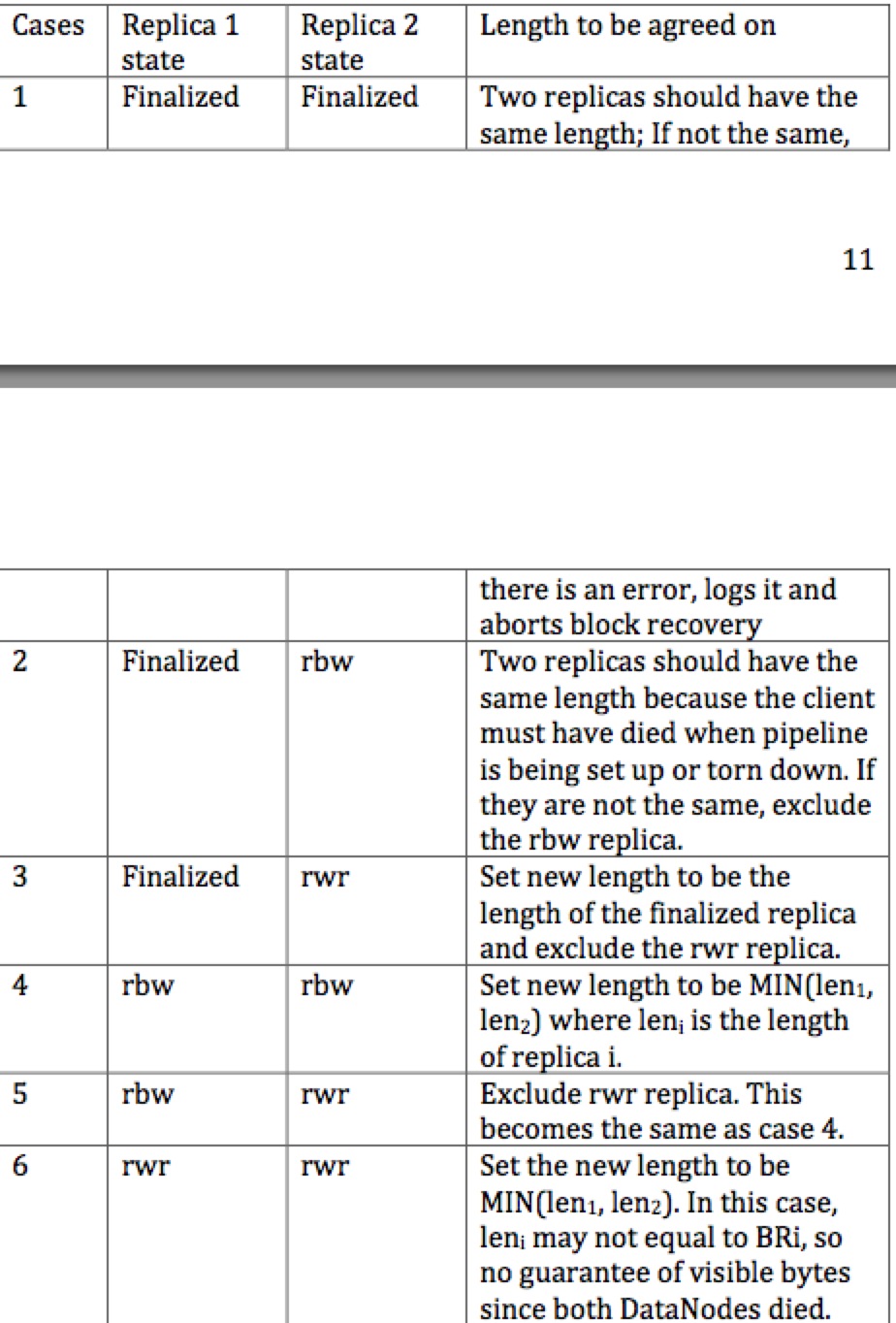
参考资料
hadoop-hdfs-2.4.1.jar
HDFS Lease Recovey 和 Block Recovery的更多相关文章
- Hadoop架构: 关于Recovery (Lease Recovery , Block Recovery, PipeLine Recovery)
该系列总览: Hadoop3.1.1架构体系——设计原理阐述与Client源码图文详解 : 总览 在HDFS中,有三种Recovery 1.Lease Recovery 2.Block Recover ...
- hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode: Block pool ID needed, but service not yet registered with NN
启动hadoop 发现 50070 的 livenode 数量是 0 查看日志, hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode: Block pool ID needed, but se ...
- Datanode启动问题 FATAL org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode: Initialization failed for Block pool <registering>
-- ::, INFO org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode: supergroup = supergroup -- ::, INFO org ...
- HDFS 异常处理与恢复
在前面的文章 <HDFS DataNode 设计实现解析>中我们对文件操作进行了描述,但并未展开讲述其中涉及的异常错误处理与恢复机制.本文将深入探讨 HDFS 文件操作涉及的错误处理与恢复 ...
- HDFS租约实践
一.租约详解 Why租约 HDFS的读写模式为 "write-once-read-many",为了实现write-once,需要设计一种互斥机制,租约应运而生租约本质上是一个有时间 ...
- 后端分布式系列:分布式存储-HDFS 异常处理与恢复
在前面的文章 <HDFS DataNode 设计实现解析>中我们对文件操作进行了描述,但并未展开讲述其中涉及的异常错误处理与恢复机制.本文将深入探讨 HDFS 文件操作涉及的错误处理与恢复 ...
- 【转载 Hadoop&Spark 动手实践 2】Hadoop2.7.3 HDFS理论与动手实践
简介 HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System )Hadoop分布式文件系统.是根据google发表的论文翻版的.论文为GFS(Google File System)Go ...
- Hadoop学习笔记之六:HDFS功能逻辑(2)
Lease(租约) HDFS(及大多数分布式文件系统)不支持文件并发写,Lease是HDFS用于保证唯一写的手段. Lease可以看做是一把带时间限制的写锁,仅持有写锁的客户端可以写文件. 租约的有效 ...
- HDFS分布式文件系统(The Hadoop Distributed File System)
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is designed to store very large data sets reliably, and to ...
随机推荐
- Twitter Bootstrap3小结
今天有空,小结一下Twitter Bootstrap 3的使用.首先不得不说,Bootstrap是迄今(2014)比较好的WEB设计框架(当然,其它的优秀WEB Framework还有:Foundat ...
- StreamSets学习系列之StreamSets的Core Tarball方式安装(图文详解)
不多说,直接上干货! 前期博客 StreamSets学习系列之StreamSets支持多种安装方式[Core Tarball.Cloudera Parcel .Full Tarball .Full R ...
- 拥抱了IDEA却发现再也回不去Eclipse...
一.背景 还记得去年入职的时候,发现很多同事都在用Intellij IDEA,其实在那之前都已经接触过,只不过没有在开发中实际应用而已. 这时候我下定决心要拥抱IDEA了,尤其被它酷酷的黑色主题所吸引 ...
- java的classLoader分析与jettty的WebAppClassLoader
classLoader,从名字就可以知道,用于加载class的东西. 我们知道在Java中,源文件是会被编译成class文件的,我们的程序的运行也是需要依赖这些编译成字节码的class文件,而这些字节 ...
- spring scope 作用域
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/qq78292959/p/3716827.html 今天研究了一下scope的作用域.默认是单例模式,即scope="singleton& ...
- postgreSql 常用查询总结
1. 日期格式转化(参考) select beg_time, end_time, extract(epoch from to_timestamp(end_time,'yyyy-mm-dd-HH24-M ...
- vue路由管理-保留滚动位置功能、按需加载模块名自定义
路由管理:保留滚动位置 其实现与组件的keep-alive相关,仅设置了keep-aive的页面,实施保留回退位置能力. keep-alive介绍 作用 把切换出去的组件保留在内存中,可以保留它的状态 ...
- unity 中Canvas MatchHeight
设置了 UI Scale Mode = Scale With Screen Size, Reference Resolution = X 1334, Y 750, Screen Match Mode ...
- 转载 HashSet用法
NET 3.5在System.Collections.Generic命名空间中包含一个新的集合类:HashSet<T>.这个集合类包含不重复项的无序列表.这种集合称为“集(set)”.集是 ...
- 导航栏pop拦截
一.新建一个分类 二.导入分类头文件 三.需要拦截的地方实现方法 - (BOOL)navigationShouldPopTwo 即可 .h #import <UIKit/UIKit.h&g ...
