python 链表
在C/C++中,通常采用“指针+结构体”来实现链表;而在Python中,则可以采用“引用+类”来实现链表。
节点类:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
链表类:
class Linkedlist:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.tail = None
link_list = LinkedList()
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None
def append(self, data):
node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = node
self.tail = node
else:
self.tail.next = node
self.tail =node
def iter(self):
if not iter.head:
return
cur = self.head
yield cur.data
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
yield cur.data
#先判断是不是空链表,yield head.data 再用while循环遍历
链表的头结点head 和 尾节点tail 都属于node.
insert:先将要插入的节点的next指向之后链表的head,然后将之前链表的next指向 将要插入的节点。
def insert(self, idx, value):
cur = self.head
cur_idx = 0
if cur is None:
raise Exception('That list is and empty list!')
while cur_idx < idx-1:
cur = cur.next
if cur is None:
raise Exception('List length less than index!')
cur_idx += 1
node = Node(value)
node.next = cur.next
cur.next = node
if node.next is None:
self.tail = node
def remove(self, idx):
cur = self.head
cur_idx = 0
#空指针
if self.head = None:
raise Exception('This is an empty list')
while cur_idx < idx-1:
cur = cur.next
#给出的索引大于链表的长度
if cur is None:
raise Exception('list length less than index')
cur_idx +=1
if idx == 0: #当删除第一个节点时
self.head = cur.next
cur = cur.next
return
if self.head is self.tail: #当只有一个节点时
self.head = None
self.tail = None
return
cur.next = cur.next.next
if cur.next is None: #当删除最后一个节点时
self.tail = cur
def size(self):
i = 0
cur = self.head
if current is None:
return 'The list is an empty list'
while cur.next is not None:
i +=1
cur = cur.next
return i
def search(self, item):
current = self.head
found = False
while current is not None and not found:
if current.data == item:
found = True
else:
current = current.next
return found
1,迭代
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#!/bin/env python
# Python2.7 class Node(object):
def __init__(self):
self.value = None
self.next = None
def __str__(self):
return str(self.value) def reverse_list(head):
if not head or not head.next:
return head
pre = None
while head:
next = head.next # 缓存当前节点的向后指针,待下次迭代用
head.next = pre # 关键:把当前节点向前指针(pre)作为当前节点的向后指针
pre = head # 把当前指针赋值给 下次迭代 节点的 向前指针
head = next # 作为下次迭代时的(当前)节点
return pre # 返回头指针,头指针就是迭代最后一次的head(赋值给类pre) if __name__ == '__main__': three = Node()
three.value = 3 two = Node()
two.value = 2
two.next = three one = Node()
one.value = 1
one.next = two head = Node()
head.value = 0
head.next = one newhead = reverse_list(head)
while newhead:
print newhead.value
newhead = newhead.next
比较形象的图
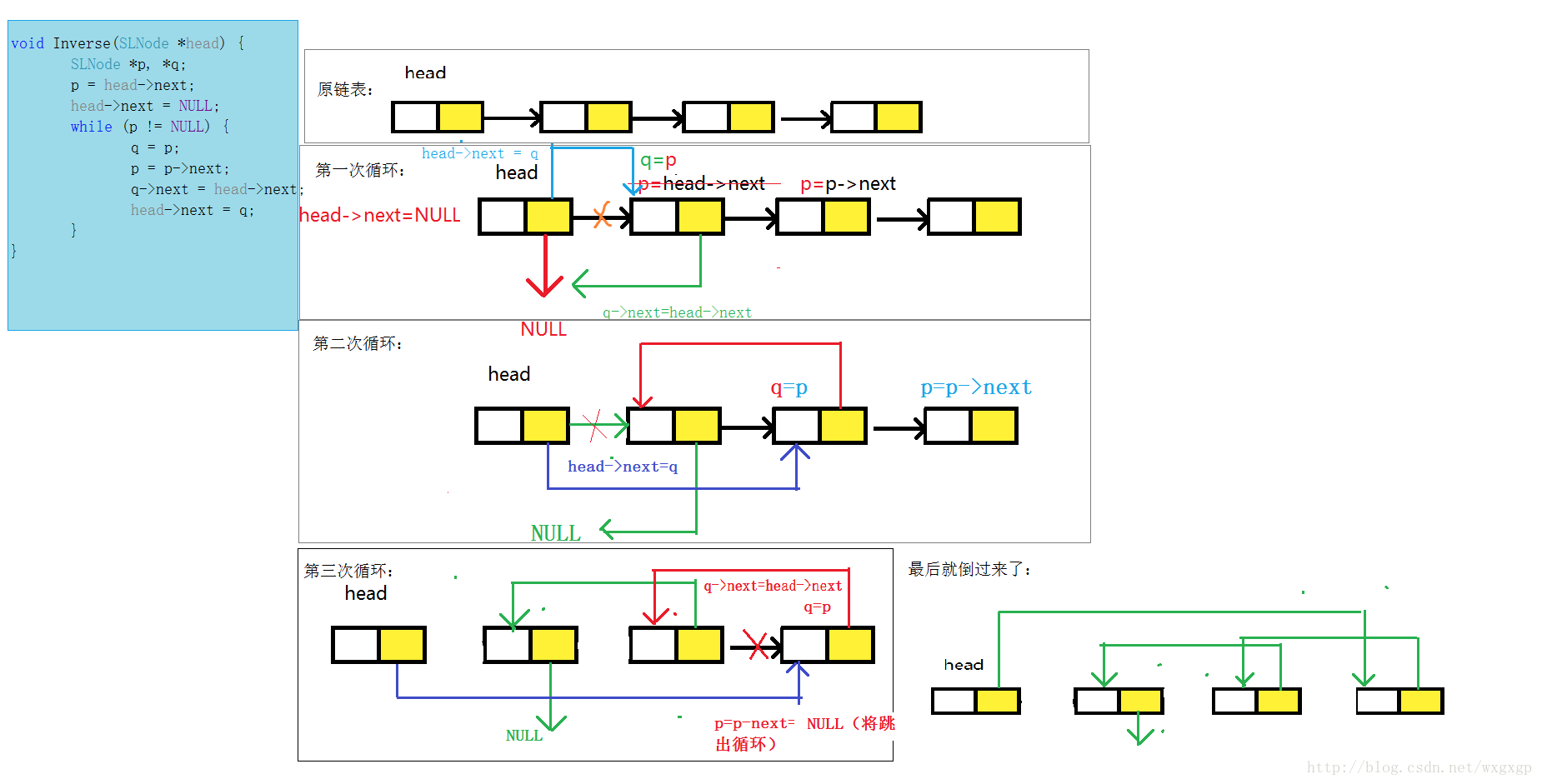
2,递归
# 临界点:head.next为None
# 先递归到 把最后一个节点指向 newhead
# 然后一步步从后往前逆置 def reverse_recursion(head):
if not head or not head.next:
return head new_head = reverse_recursion(head.next) head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return new_head
python 链表的更多相关文章
- Python链表的实现与使用(单向链表与双向链表)
参考[易百教程]用Python实现链表及其功能 """ python链表的基本操作:节点.链表.增删改查 """ import sys cl ...
- Python链表操作(实现)
Python链表操作 在Python开发的面试中,我们经常会遇到关于链表操作的问题.链表作为一个非常经典的无序列表结构,也是一个开发工程师必须掌握的数据结构之一.在本文中,我将针对链表本身的数据结构特 ...
- python 链表表达式 map、filter易读版
链表推导式 [x for x in x] 链表推导式提供了一个创建链表的简单途径,无需使用 map(), filter() 以及 lambda.返回链表的定义通常要比创建这些链表更清晰.每一个链表推导 ...
- Python链表与反链表
# -*- coding:utf8 -*- #/usr/bin/env python class Node(object): def __init__(self, data, pnext = None ...
- python链表的实现
根据Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Structures using Python 一书用python实现链表 书籍在线网址http://intera ...
- python链表的实现,有注释
class Node(): #node实现,每个node分为两部分:一部分含有链表元素,成数据域;另一部分为指针,指向下一个 __slots__=['_item' ...
- python 链表的反转
code #!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf- -*- class ListNode: def __init__(self,x): self.val=x self. ...
- python 链表、堆、栈
简介 很多开发在开发中并没有过多的关注数据结构,当然我也是,因此,我写这篇文章就是想要带大家了解一下这些分别是什么东西. 链表 概念:数据随机存储,并且通过指针表示数据之间的逻辑关系的存储结构. 链表 ...
- Add Two Numbers(from leetcode python 链表)
给定两个非空链表来表示两个非负整数.位数按照逆序方式存储,它们的每个节点只存储单个数字.将两数相加返回一个新的链表. 你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头. 示例: 输入:(2 -& ...
随机推荐
- JVM类加载流程
1.加载 a.装载类的第一个阶段 b.取得类的二进制流 c.转为方法区数据结构 d.在Java堆中生成对应的java.lang.Class对象 2.链接 a.验证(保证Class流的格式是正确的) 文 ...
- java 死锁产生原因及解锁(转)
原文地址 进程死锁及解决办法 一.要点提示 (1) 掌握死锁的概念和产生死锁的根本原因. (2) 理解产生死锁的必要条件--以下四个条件同时具备:互斥条件.不可抢占条件.占有且申请条件.循环等待条件. ...
- 为什么下了android 4.1 的SDK后在本地用浏览器看api说明文档时,浏览器打开api的html文件很慢?试了好几款浏览器都一样。为什么?
http://www.oschina.net/question/436724_61401 http://www.google.com/jsapi 他惹的祸 注释掉就可以了- <!-- < ...
- Yii2 高级查询
首先我们要自己写一个ActiveQuery 类并且继承 Yii2 的 ActiveQuery: namespace api\models; class ActiveQuery extends \yii ...
- 【leetcode】Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. For this problem, a height-balanced binary ...
- PHP操作MySQL事务处理
PHP操作MySQL事务处理 /*************** 用begin,rollback,commit来实现 ***************/ /*方法二*/ $conn = mysqli_co ...
- grep egrep
grep: Global search REgular expression and Print out the line. 作用: 文本搜索工具,根据用户指定的“模式”对目标文本逐行进行匹配检查:打 ...
- Hive报错 Failed with exception java.io.IOException:java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: java.net.URISyntaxException: Relative path in absolute URI: ${system:user.name%7D
报错信息如下 Failed with exception java.io.IOException:java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: java.net.URISyn ...
- Oracle数据库定义语言(DDL)
--使用Create遇见创建表 Create Table table_name ( column_name datatype [null|not null], column_name datatype ...
- jQuery绑定事件的四种方式区别
jQuery中提供了四种事件监听方式,分别是bind.live.delegate.on,对应的解除监听的函数分别是unbind.die.undelegate.off.在开始看他们之前 一:bind(t ...
