NIO 组件Buffer
重要属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Capacity | 容量, 即可以容纳的最大数据量; 在缓冲区创建时被设定并且不能改变 |
| Limit | 表示缓冲区的当前终点, 不能对缓冲区超过极限的位置进行读写操作, 且极限是可以修改的。 |
| Position | 位置, 下一个要被读或写的元素的索引, 每次读写缓冲区数据时都会改变数值, 为下次读写做准备 |
| Mark | 标记 |
简单demo
- 代码:
package com.ronnie.nio;
import java.nio.IntBuffer;
public class BasicBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 举例说明Buffer 的使用
// 创建一个Buffer, 大小为n, 即可存放n个int
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(10);
// 向buffer 存放数据
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++){
intBuffer.put( i * 2);
}
// 将buffer转换, 读写切换(很重要)
intBuffer.flip();
intBuffer.position(1);
// 设置limit为3, 到不了3
intBuffer.limit(3);
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
}
- 输出结果: 2 4
- 感觉这个思想和golang里面的channel好像差不多, 不过go的channel好像并不需要flip, 若不指定方向就是双向的。
源码解读
属性
/**
* The characteristics of Spliterators that traverse and split elements
* maintained in Buffers.
* Spliterators 是一个可分割迭代器, 此处用于遍历并分割Buffer中的元素, 此类有三种
* 特征的Spliterators: 尺寸固定的, 小尺寸的, 有序的三种, 进去看一下都是16进制数
*/
static final int SPLITERATOR_CHARACTERISTICS =
Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED | Spliterator.ORDERED; // Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity 不变性排序
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity; // Used only by direct buffers 只能直接被buffers使用
// NOTE: hoisted here for speed in JNI GetDirectBufferAddress
// 挂在这用于提升 JNI(Java Native Interface) 中直接获取buffer地址方法的执行速度
long address;
常用方法
public final int capacity(){}: 返回此缓冲区的容量
/**
* Returns this buffer's capacity.
*
* @return The capacity of this buffer
*/
public final int capacity() {
return capacity;
}
public final int position(){}: 返回此缓冲区的位置
/**
* Returns this buffer's position.
*
* @return The position of this buffer
*/
public final int position() {
return position;
}public final Buffer position(int newPosition){}: 设置此缓冲区的位置
/**
* Sets this buffer's position. If the mark is defined and larger than
* the new position then it is discarded.
* 设置该buffer的位置, 如果此标记已经被定义, 且大于新定义的位置, 那么它就会被
* 抛弃。
*
* @param newPosition
* The new position value; must be non-negative
* and no larger than the current limit
*
* @return This buffer
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* If the preconditions on <tt>newPosition</tt> do not hold
*/
public final Buffer position(int newPosition) {
if ((newPosition > limit) || (newPosition < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
position = newPosition;
if (mark > position) mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final int limit(){}: 返回此缓冲区的限制
/**
* Returns this buffer's limit.
*
* @return The limit of this buffer
*/
public final int limit() {
return limit;
}
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit){}: 设置此缓冲区的限制
/**
* Sets this buffer's limit.
* If the position is larger than the new limit then it is set to the new
* limit.
* 如果位置大于新的limit, 那么就将位置设为新的limit
* If the mark is defined and larger than the new limit then it is
* discarded.
* 如果此标记已经被定义, 且大于新定义的位置, 那么它就会被抛弃。
*
* @param newLimit
* The new limit value; must be non-negative
* and no larger than this buffer's capacity
*
* @return This buffer
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* If the preconditions on <tt>newLimit</tt> do not hold
*/
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit) {
if ((newLimit > capacity) || (newLimit < 0))
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
limit = newLimit;
if (position > limit) position = limit;
if (mark > limit) mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final Buffer clear(){}: 清除此缓冲区, 即将各个标记恢复到初始状态, 但是数据并没有真正擦除。
/**
* Clears this buffer.
* The position is set to zero, the limit is set to the capacity, and the
* mark is discarded.
* 位置被设为0, limit被设置为容量, 并且标记被丢弃。
*
* <p> Invoke this method before using a sequence of channel-read or
* <i>put</i> operations to fill this buffer. For example:
*
* <blockquote><pre>
* buf.clear(); // Prepare buffer for reading
* in.read(buf); // Read data</pre></blockquote>
*
* <p> This method does not actually erase the data in the buffer, but it
* is named as if it did because it will most often be used in situations
* in which that might as well be the case. </p>
*
* @return This buffer
*/
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public abstract boolean hasArray(){}: 告知此缓冲区是否具有可访问的底层实现数组
/**
* Tells whether or not this buffer is backed by an accessible
* array.
*
* <p> If this method returns <tt>true</tt> then the {@link #array() array}
* and {@link #arrayOffset() arrayOffset} methods may safely be invoked.
* </p>
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if, and only if, this buffer
* is backed by an array and is not read-only
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public abstract boolean hasArray();
public abstract Object array(){}: 返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组
/**
* Returns the array that backs this
* buffer <i>(optional operation)</i>.
*
* <p> This method is intended to allow array-backed buffers to be
* passed to native code more efficiently.
* 该方法的目的是允许 底层的 实现数组缓冲区 更有效地被传送到本地编码中。
* Concrete subclasses provide more strongly-typed return values for this
* method.
* 实体的子类为该方法提供了更多强类型的返回值
*
* <p> Modifications to this buffer's content will cause the returned
* array's content to be modified, and vice versa.
* 修改该buffer的内容会导致返回的数组的内容也被改变, 反之亦然。
*
* <p> Invoke the {@link #hasArray hasArray} method before invoking this
* method in order to ensure that this buffer has an accessible backing
* array. </p>
* 在调用此方法前请调用hasArray方法来保证该buffer有一个可获取的底层实现数组
*
* @return The array that backs this buffer
*
* @throws ReadOnlyBufferException
* If this buffer is backed by an array but is read-only
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException
* If this buffer is not backed by an accessible array
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public abstract Object array();
其他方法
public final Buffer mark(){}: 在此缓冲区的位置设置标记
/**
* Sets this buffer's mark at its position.
*
* @return This buffer
*/
public final Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}
public final Buffer reset(){}: 将此缓冲区的位置重置为以前标记的位置(后悔药?)
/**
* Resets this buffer's position to the previously-marked position.
*
* <p> Invoking this method neither changes nor discards the mark's
* value. </p>
*
* @return This buffer
*
* @throws InvalidMarkException
* If the mark has not been set
*/
public final Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
// 将位置设为之前的标记
position = m;
return this;
}
public final Buffer rewind(){}: 重绕此缓冲区
/**
* Rewinds this buffer.
* The position is set to zero and the mark is discarded.
* 位置被设为0并且标记被丢弃
*
* <p> Invoke this method before a sequence of channel-write or <i>get</i>
* operations, assuming that the limit has already been set
* appropriately. For example:
*
* <blockquote><pre>
* out.write(buf); // Write remaining data
* buf.rewind(); // Rewind buffer
* buf.get(array); // Copy data into array</pre></blockquote>
*
* @return This buffer
*/
public final Buffer rewind() {
position = 0;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
public final int remaining(){}: 返回当前位置与限制之间的元素数量
/**
* Returns the number of elements between the current position and the
* limit.
*
* @return The number of elements remaining in this buffer
*/
public final int remaining() {
return limit - position;
}
public abstract int arrayOffset(){}: 返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组中第一个缓冲区元素的偏移量
/**
* Returns the offset within this buffer's backing array of the first
* element of the buffer <i>(optional operation)</i>.
* 返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组中第一个缓冲区元素的偏移量
*
* <p> If this buffer is backed by an array then buffer position <i>p</i>
* corresponds to array index <i>p</i> + <tt>arrayOffset()</tt>.
*
* <p> Invoke the {@link #hasArray hasArray} method before invoking this
* method in order to ensure that this buffer has an accessible backing
* array. </p>
* 在调用此方法前请调用hasArray方法来保证该buffer有一个可获取的底层实现数组
*
* @return The offset within this buffer's array
* of the first element of the buffer
*
* @throws ReadOnlyBufferException
* If this buffer is backed by an array but is read-only
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException
* If this buffer is not backed by an accessible array
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public abstract int arrayOffset();
public abstract boolean isDirect(){}: 告知此缓冲区是否为直接缓冲区
/**
* Tells whether or not this buffer is
* <a href="ByteBuffer.html#direct"><i>direct</i></a>.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if, and only if, this buffer is direct
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public abstract boolean isDirect();
ByteBuffer
是最常用的ByteBuffer类(二进制数组)
常用方法:
缓冲区创建相关:
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity){}: 创建直接缓冲区
/**
* Allocates a new direct byte buffer.
*
* <p> The new buffer's position will be zero, its limit will be its
* capacity, its mark will be undefined, and each of its elements
* will be initialized to zero.
* 新缓冲区的位置将会为0, 它的limit会是它的容量, 它的标签未被定义, 每个它
* 元素都会被定义为0.
* Whether or not it has a {@link #hasArray backing array} is
* unspecified.
* 是否有底层数组未知
*
* @param capacity
* The new buffer's capacity, in bytes
*
* @return The new byte buffer
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* If the <tt>capacity</tt> is a negative integer
*/
public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity) {
return new DirectByteBuffer(capacity);
}
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity){}: 设置缓冲区的初始容量
/**
* Allocates a new byte buffer.
*
* <p> The new buffer's position will be zero, its limit will be its
* capacity, its mark will be undefined, and each of its elements
* will be initialized to zero.
* 新缓冲区的位置将会为0, 它的limit会是它的容量, 它的标签未被定义, 每个它
* 元素都会被定义为0.
* It will have a {@link #array backing array},and its {@link
* #arrayOffset array offset} will be zero.
* 它会有一个底层数组, 并且它的数组偏移量为0
*
* @param capacity
* The new buffer's capacity, in bytes
*
* @return The new byte buffer
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* If the <tt>capacity</tt> is a negative integer
*/
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}
缓存区存取相关:
public abstract byte get(){}: 从当前位置position上get, get之后, position会自动+1
// -- Singleton get/put methods -- get/put 都是操作单例对象的 /**
* Relative <i>get</i> method.
* Reads the byte at this buffer's current position, and then
* increments the position.
* 读该字节数组在此buffer的当前位置, 并提升位置
*
* @return The byte at the buffer's current position
*
* @throws BufferUnderflowException
* If the buffer's current position is not smaller than its limit
*/
public abstract byte get();
public abstract byte get(int index){}: 从绝对位置get, position不会自动+1
/**
* Absolute <i>get</i> method. Reads the byte at the given
* index.
*
* @param index
* The index from which the byte will be read
*
* @return The byte at the given index
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* If <tt>index</tt> is negative
* or not smaller than the buffer's limit
*/
public abstract byte get(int index);
public abstract ByteBuffer put(byte b){}: 从当前位置上添加, put之后, position会自动 +1
/**
* Relative <i>put</i> method <i>(optional operation)</i>.
*
* <p> Writes the given byte into this buffer at the current
* position, and then increments the position. </p>
* 将获取的字节数组写入到该buffer中的当前位置, 并将位置上升
*
* @param b
* The byte to be written
*
* @return This buffer
*
* @throws BufferOverflowException
* If this buffer's current position is not smaller than its limit
*
* @throws ReadOnlyBufferException
* If this buffer is read-only
*/
public abstract ByteBuffer put(byte b);public abstract ByteBuffer put(int index, byte b){}: 从绝对位置上put, position不会自动+1
/**
* Absolute <i>put</i> method <i>(optional operation)</i>.
*
* <p> Writes the given byte into this buffer at the given
* index. </p>
*
* @param index
* The index at which the byte will be written
*
* @param b
* The byte value to be written
*
* @return This buffer
*
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* If <tt>index</tt> is negative
* or not smaller than the buffer's limit
*
* @throws ReadOnlyBufferException
* If this buffer is read-only
*/
public abstract ByteBuffer put(int index, byte b);
咦, 咋么都是抽象方法呐, 自习看一下层级结构:
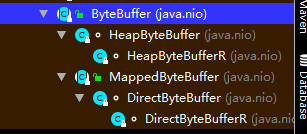
稍微看了一下, 它们的实现类在HeapByteBuffer和DirectByteBuffer中, 后者还调用了sun.misc.unsafe魔术类的方法, 在此就不做衍生了, 有兴趣的自己去撸源码。
NIO 组件Buffer的更多相关文章
- Java NIO 之 Buffer
Java NIO 之 Buffer Java NIO (Non Blocking IO 或者 New IO)是一种非阻塞IO的实现.NIO通过Channel.Buffer.Selector几个组件的协 ...
- Java NIO之Buffer(缓冲区)
Java NIO中的缓存区(Buffer)用于和通道(Channel)进行交互.数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入到通道中的. 缓冲区本质上是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存.这 ...
- NIO组件之buffer
Java NIO指的是new IO ,相对OIO,也称non-blocking IO,对应四种基本IO类型中的IO多路复用,主要有有三大核心组件,Channel(管道),Buffer(缓冲区),sel ...
- NIO组件Selector详解
Selector(选择器)是Java NIO中能够检测一到多个NIO通道,并能够知晓通道是否为诸如读写事件做好准备的组件.这样,一个单独的线程可以管理多个channel,从而管理多个网络连接. 下面是 ...
- JAVA NIO简介-- Buffer、Channel、Charset 、直接缓冲区、分散和聚集、文件锁
IO 是主存和外部设备 ( 硬盘.终端和网络等 ) 拷贝数据的过程. IO 是操作系统的底层功能实现,底层通过 I/O 指令进行完成. Java标准io回顾 在Java1.4之前的I/O系统中,提供 ...
- Java NIO教程 Buffer
缓冲区本质上是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存,这块内存中有很多可以存储byte(或int.char等)的小单元.这块内存被包装成NIO Buffer对象,并提供了一组方法,用来方便的访问 ...
- Java基础知识强化之IO流笔记74:NIO之 Buffer
Java NIO中的Buffer用于和NIO通道进行交互.如你所知,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入到通道中的. 缓冲区本质上是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存.这块内存被包装成NIO ...
- NIO组件Selector调用实例
*对于nio的非阻塞I/O操作,使用Selector获取哪些I/O准备就绪,注册的SelectionKey集合记录关联的Channel这些信息.SelectionKey记录Channel对buffer ...
- java nio之Buffer(一)
Buffer是一个包装了基本数据元素数组的对象,它以及它的子类定义了一系列API用于处理数据缓存. 一.属性 Buffer有四个基本属性: 1.capacity 容量,buffer能够容纳的最大元素 ...
随机推荐
- day3-1函数
函数: 如果写在对象内,是一个方法 函数声明 function 函数名(形参列表){ //函数体 } 函数表达式 var 函数名 = function (形参列表){ //函数体 } 匿名函数 f ...
- 2 Struts2的执行流程&配置文件的加载顺序
执行流程: 访问前段页面,通过url访问action 访问xml中Struts2核心过滤器,并执行一组拦截器(这组拦截器在struts-default.xml中,实现了部分功能) 通过action配置 ...
- java记录3--抽象
1.由来 利用抽象类是i为了更好的对类加以分类,例如各种植物有具体名字,也有“植物”这个抽象的词对所有具体植物进行归类. 2.抽象类通常用来作为一个类族的最顶层的父类(表示该类族所有事物的共性), 用 ...
- 113、Java中String类之字符串文本分割IP地址
01.代码如下: package TIANPAN; /** * 此处为文档注释 * * @author 田攀 微信382477247 */ public class TestDemo { public ...
- Scrapy采集某小说网站的全部小说
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1hrgYDzhgQIDrf4KmZxhW1w 密码: h1m6 源码以及运行图
- Html转图片 -- wkhtmltox
关于wkhtmltox,是一个可以把HTML转换为图片和pdf的工具. 不多介绍了,详见官网 https://wkhtmltopdf.org/ PHP 扩展 https://github.com/kr ...
- Vuex踩坑--数据刷新时丢失
近期做项目的过程中,使用vuex保存页面公共数据,测试无网情况后又接通网络的情况下,页面进行重新加载.遇到一个小bug——发现在苹果手机IOS系统下,页面刷新重新加载后页面中通过vuex存储并显示的数 ...
- C语言书籍入门---第三章
=======变量和数据类型========= 说 明:字符型 短整型 整型 长整型 单精度浮点型 双精度浮点型 无类型 数据类型:char short int long float d ...
- C++ 定位错误行
] = {}; SYSTEMTIME st; GetLocalTime(&st); sprintf_s(buf, , "%02d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d | ...
- Android 用ViewFlipper实现跑马灯效果的公告提示
1.代码部分private void initViewFlipper(final HomepageListModel.Notice notice) { for (int i = 0; i < n ...
