dataset的reparation和coalesce
/**
* Returns a new Dataset that has exactly `numPartitions` partitions, when the fewer partitions
* are requested. If a larger number of partitions is requested, it will stay at the current
* number of partitions. Similar to coalesce defined on an `RDD`, this operation results in
* a narrow dependency, e.g. if you go from 1000 partitions to 100 partitions, there will not
* be a shuffle, instead each of the 100 new partitions will claim 10 of the current partitions.
*
* However, if you're doing a drastic coalesce, e.g. to numPartitions = 1,
* this may result in your computation taking place on fewer nodes than
* you like (e.g. one node in the case of numPartitions = 1). To avoid this,
* you can call repartition. This will add a shuffle step, but means the
* current upstream partitions will be executed in parallel (per whatever
* the current partitioning is).
*
* @group typedrel
* @since 1.6.0
*/
def coalesce(numPartitions: Int): Dataset[T] = withTypedPlan {
Repartition(numPartitions, shuffle = false, planWithBarrier)
}
关于coalsece:
1、用于减少分区数量,如果设置的numPartitions超过目前实际有的分区数,则分区数保持不变。
2、窄依赖,不会发生shuffle
3、极端的coalsece可能会影响性能,比如coalsece(1),则只会在一个节点上运行单个任务。这种情况下建议使用repartition,
虽然repartition会发生shuffle,但是repartition对上游的计算,还是多分区并行执行的。
4、应用场景:多用于对一个大数据集filter以后,执行coalsece
/**
* Returns a new Dataset that has exactly `numPartitions` partitions.
*
* @group typedrel
* @since 1.6.0
*/
def repartition(numPartitions: Int): Dataset[T] = withTypedPlan {
Repartition(numPartitions, shuffle = true, planWithBarrier)
}
关于repartition:
跟coalsece一样,都是用于明确设置多少个分区,但是repartition是个宽依赖,会发生shuffle。主要注意的地方就是repartition不影响上游计算的分区
如果想极端的控制生成的文件数量来避免太多的小文件,建议repartition
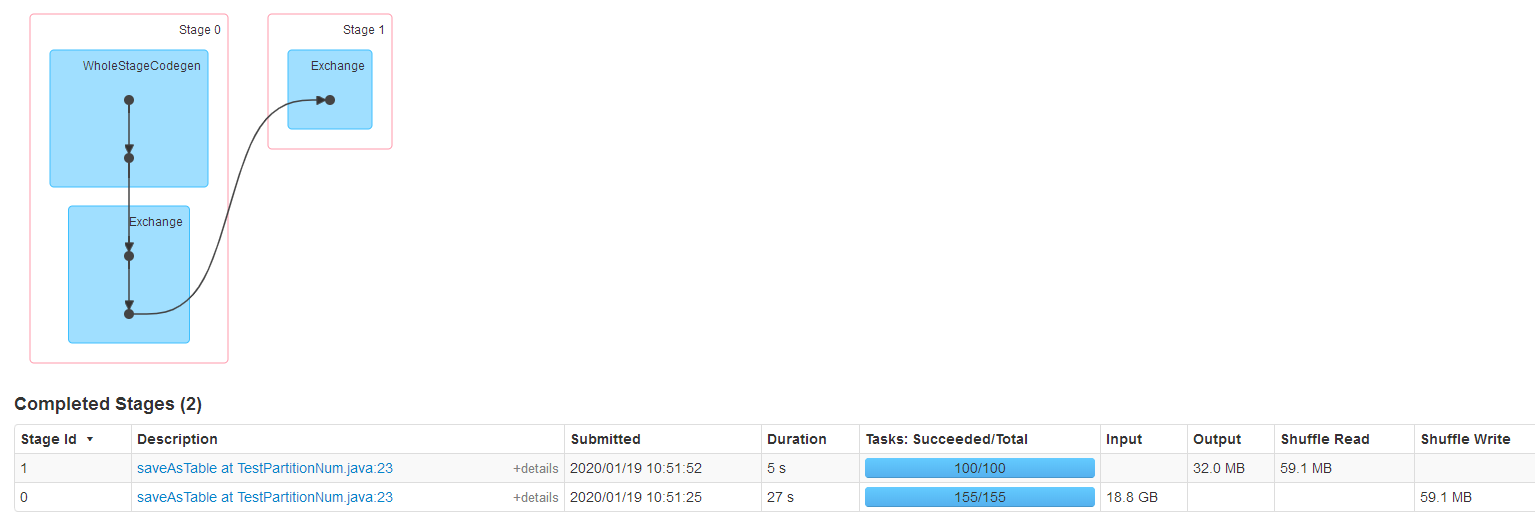
测试:对一个大表查询,将查询的结果写到一张表
coalsece测试,coalsece(100),可以看到只有一个stage,并且并行度是100

repartition测试,repartition(100),发生了shuffle。两个stage,stage0对大表指定条件查询,对应的并行度默认是大表的数据量/128M,在repartition将结果输出到表的时候并行度为我们设置的repartition(100),然后shuffle数据,最后输出
/**
* Return a new RDD that has exactly numPartitions partitions.
*
* Can increase or decrease the level of parallelism in this RDD. Internally, this uses
* a shuffle to redistribute data.
*
* If you are decreasing the number of partitions in this RDD, consider using `coalesce`,
* which can avoid performing a shuffle.
*
* TODO Fix the Shuffle+Repartition data loss issue described in SPARK-23207.
*/
def repartition(numPartitions: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null): RDD[T] = withScope {
coalesce(numPartitions, shuffle = true)
} /**
* Return a new RDD that is reduced into `numPartitions` partitions.
*
* This results in a narrow dependency, e.g. if you go from 1000 partitions
* to 100 partitions, there will not be a shuffle, instead each of the 100
* new partitions will claim 10 of the current partitions. If a larger number
* of partitions is requested, it will stay at the current number of partitions.
*
* However, if you're doing a drastic coalesce, e.g. to numPartitions = 1,
* this may result in your computation taking place on fewer nodes than
* you like (e.g. one node in the case of numPartitions = 1). To avoid this,
* you can pass shuffle = true. This will add a shuffle step, but means the
* current upstream partitions will be executed in parallel (per whatever
* the current partitioning is).
*
* @note With shuffle = true, you can actually coalesce to a larger number
* of partitions. This is useful if you have a small number of partitions,
* say 100, potentially with a few partitions being abnormally large. Calling
* coalesce(1000, shuffle = true) will result in 1000 partitions with the
* data distributed using a hash partitioner. The optional partition coalescer
* passed in must be serializable.
*/
def coalesce(numPartitions: Int, shuffle: Boolean = false,
partitionCoalescer: Option[PartitionCoalescer] = Option.empty)
(implicit ord: Ordering[T] = null)
: RDD[T] = withScope {
require(numPartitions > 0, s"Number of partitions ($numPartitions) must be positive.")
if (shuffle) {
/** Distributes elements evenly across output partitions, starting from a random partition. */
val distributePartition = (index: Int, items: Iterator[T]) => {
var position = new Random(hashing.byteswap32(index)).nextInt(numPartitions)
items.map { t =>
// Note that the hash code of the key will just be the key itself. The HashPartitioner
// will mod it with the number of total partitions.
position = position + 1
(position, t)
}
} : Iterator[(Int, T)] // include a shuffle step so that our upstream tasks are still distributed
new CoalescedRDD(
new ShuffledRDD[Int, T, T](mapPartitionsWithIndex(distributePartition),
new HashPartitioner(numPartitions)),
numPartitions,
partitionCoalescer).values
} else {
new CoalescedRDD(this, numPartitions, partitionCoalescer)
}
}
dataset的reparation和coalesce的更多相关文章
- Spark编程指南分享
转载自:https://www.2cto.com/kf/201604/497083.html 1.概述 在高层的角度上看,每一个Spark应用都有一个驱动程序(driver program).驱动程序 ...
- Spark学习笔记之SparkRDD
Spark学习笔记之SparkRDD 一. 基本概念 RDD(resilient distributed datasets)弹性分布式数据集. 来自于两方面 ① 内存集合和外部存储系统 ② ...
- Spark-RDD之Partition源码分析
概要 Spark RDD主要由Dependency.Partition.Partitioner组成,Partition是其中之一.一份待处理的原始数据会被按照相应的逻辑(例如jdbc和hdfs的spl ...
- spark(二)
一.spark的提交模式 --master(standalone\YRAN\mesos) standalone:-client -cluster 如果我们用client模式去提交程序,我们在哪个地方 ...
- Spark:JavaRDD 转化为 Dataset<Row>的两种方案
JavaRDD 转化为 Dataset<Row>方案一: 实体类作为schema定义规范,使用反射,实现JavaRDD转化为Dataset<Row> Student.java实 ...
- Spark入门之DataFrame/DataSet
目录 Part I. Gentle Overview of Big Data and Spark Overview 1.基本架构 2.基本概念 3.例子(可跳过) Spark工具箱 1.Dataset ...
- Update(Stage4):sparksql:第3节 Dataset (DataFrame) 的基础操作 & 第4节 SparkSQL_聚合操作_连接操作
8. Dataset (DataFrame) 的基础操作 8.1. 有类型操作 8.2. 无类型转换 8.5. Column 对象 9. 缺失值处理 10. 聚合 11. 连接 8. Dataset ...
- SQL Server-分页方式、ISNULL与COALESCE性能分析(八)
前言 上一节我们讲解了数据类型以及字符串中几个需要注意的地方,这节我们继续讲讲字符串行数同时也讲其他内容和穿插的内容,简短的内容,深入的讲解,Always to review the basics. ...
- HTML5 数据集属性dataset
有时候在HTML元素上绑定一些额外信息,特别是JS选取操作这些元素时特别有帮助.通常我们会使用getAttribute()和setAttribute()来读和写非标题属性的值.但为此付出的代价是文档将 ...
随机推荐
- iOS 上通过 802.11k、802.11r 和 802.11v 实现 Wi-Fi 网络漫游
在 iOS 上通过 802.11k.802.11r 和 802.11v 实现 Wi-Fi 网络漫游 了解 iOS 如何使用 Wi-Fi 网络标准提升客户端漫游性能. iOS 支持在企业级 Wi-Fi ...
- Nexus-配置VDC
1.配置资源模板This example shows how to configure a VDC resource template: vdc resource template TemplateA ...
- java操作nginx
一,判断程序的部署环境是nginx还是windows /** * 判断操作系统是不是windows * * @return true:是win false:是Linux */ public stati ...
- linux 管道相关命令(待学)
1.1 cut cut:以某种方式按照文件的行进行分割 参数列表: -b 按字节选取 忽略多字节字符边界,除非也指定了 -n 标志 -c 按字符选取 -d 自定义分隔符,默认为制表符. -f 与-d一 ...
- location练习!(重点)
写location最重要的就是hosts文件,添加一次域名跳转就得添加一条hosts文件 hosts文件: 192.168.200.120 www.a.com 192.168.200.119 www. ...
- 关于Java大整数是否是素数
题目描述 请编写程序,从键盘输入两个整数m,n,找出等于或大于m的前n个素数. 输入格式: 第一个整数为m,第二个整数为n:中间使用空格隔开.例如: 103 3 输出格式: 从小到大输出找到的等于或大 ...
- unity优化-内存(网上整理)
内存优化内存的开销无外乎以下三大部分:1.资源内存占用:2.引擎模块自身内存占用:3.托管堆内存占用.在一个较为复杂的大中型项目中,资源的内存占用往往占据了总体内存的70%以上.因此,资源使用是否恰当 ...
- scrapy-redis分布式
scrapy是python界出名的一个爬虫框架,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架,可以应用在包括数据挖掘,信息处理或存储历史数据等一系列的程序中. 虽然scrapy 能做的事情很多,但是要做到大规模的分 ...
- 机器学习之SVM多分类
实验要求数据说明 :数据集data4train.mat是一个2*150的矩阵,代表了150个样本,每个样本具有两维特征,其类标在truelabel.mat文件中,trainning sample 图展 ...
- twisted 模拟scrapy调度循环
"""模拟scrapy调度循环 """from ori_test import pr_typeimport loggingimport ti ...
