线程状态及各状态下与锁和CPU的关系
线程的状态
Thread.State枚举类型中定义了线程的六种状态:NEW,RUNNABLE,BLOCKED,WAITING,TIMED_WAITING和TERMINATED。
线程在某一时刻只能拥有一种状态,但是在线程的整个生命周期,线程的状态会发生变化。
public enum State {
NEW,
RUNNABLE,
BLOCKED,
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
}
各状态的说明
NEW
NEW状态是线程已经被创建,但还没调用start()。此时的线程是不可运行的,CPU将不会为其分配时间。
RUNNABLE
当新创建的线程调用了start(),线程便进入了RUNNABLE状态。
RUNNABLE状态是指可以获得CPU运行时间的状态,如果线程在此状态下,线程有两种子状态,一种是等待CPU时间,另一种是获得了CPU时间在执行代码。
BLOCKED
BLOCKED状态是线程无法获取对象锁时的状态。此状态下线程会阻塞,当线程成功获取到锁,线程将切换为RUNNABLE状态。
BLOCKED状态无法获得CPU运行时间。
WAITING
WAITING状态是指是指线程在执行过程中,主动出让自己CPU运行时间,让其他线程先执行,自己等待其它线程的特定操作后再恢复执行。
TIMED_WAITING
TIMED_WAITING和WAITING状态相似,TIMED_WAITING增加了时间限制,其实没有外部信号,在等待时间超时后,线程也会恢复。
TERMINATED
TERMINATED是线程的终止态,当线程执行完自己的任务,或在执行任务中发生了异常,线程都会进入TERMINATED,表示线程已经到了生命周期的末尾。
下图是关于线程间各状态切换的过程及发生状态切换的一些条件。
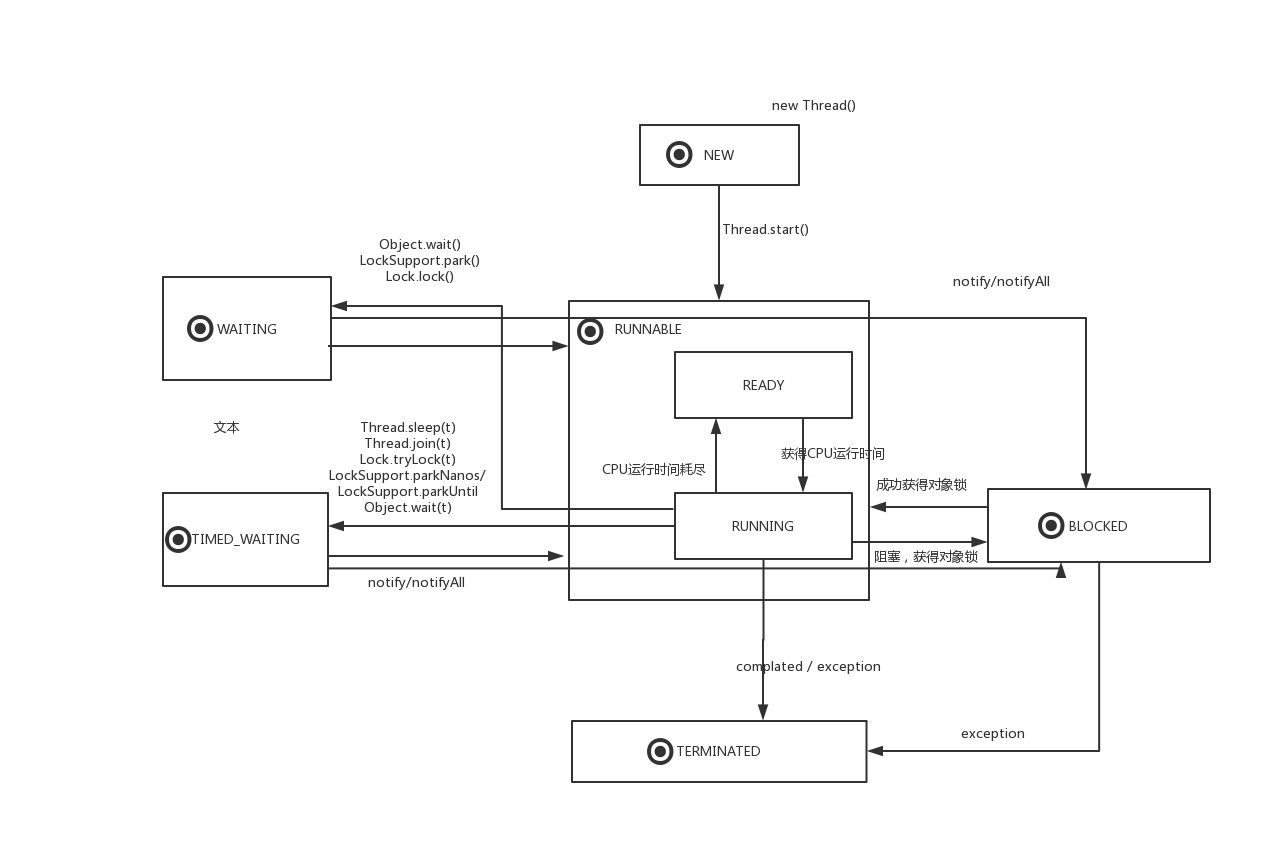
| 操作 | 操作前线程状态 | 操作后线程状态 | 是否出让CPU时间 | 是否需要先持有对象锁 | 是否释放对象锁 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| new Thread() | 无 | NEW | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| Thread.start() | NEW | RUNNABLE | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| synchronized能得到对象锁 | RUNNABLE | RUNNABLE | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| synchronized无法得到对象锁 | RUNNABLE | BLOCKED | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Thread.join() | RUNNABLE | WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Thread.join(t) | RUNNABLE | TIMED_WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Thread.sleep(t) | RUNNABLE | TIMED_WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Object.wait() | RUNNABLE | WAITING | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| Object.wait(t) | RUNNABLE | TIMED_WAITING | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| Object.notify() / Object.notifyAll() | RUNNABLE | RUNNABLE | 否 | 是 | 否 |
| Lock.lock() | RUNNABLE | WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| Lock.tryLock(t) | RUNNABLE | TIMED_WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| LockSupport.park() | RUNNABLE | WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| LockSupport.parkNanos(t)/LockSupport.parkUntil(t) | RUNNABLE | TIMED_WAITING | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 执行结束/执行异常 | RUNNABLE | TERMINATED | 是 | 否 | 否 |
以下是一些测试代码,可以运行下清晰的了解到状态。
各状态切换测试:
public class ThreadStateTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
threadStateNew();
workingThread();
threadStateTerminate();
threadBlockedByLock();
threadBlockedBySynchronized();
threadSleep();
threadWait();
threadTimedWait();
}
private static void threadStateNew(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Never Start Thread State:");
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
}, "Thread Never Start");
//print NEW
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void workingThread(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
doSomeElse();
}
});
thread.start();
doSomeElse();
//print RUNNABLE
System.out.println("Working Thread State:" + thread.getState());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void threadStateTerminate(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Finish Job Thread State:");
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
}, "Thread Finish Job");
thread.start();
try {
//Main Thread Will Wait util this thread finished job
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//print TERMINATED
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void threadBlockedByLock(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Thread State Blocked By Lock:");
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
lock.lock();
}, "Blocked Thread");
lock.lock();
thread.start();
doSomeElse();
//print WAITING
System.out.println(thread.getState());
lock.unlock();
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void threadBlockedBySynchronized(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Thread Blocked By Synchronized:");
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (ThreadStateTest.class){
}
}, "Blocked by Synchronized Thread");
synchronized (ThreadStateTest.class){
thread.start();
doSomeElse();
//print BLOCKED
System.out.println(thread.getState());
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void threadSleep(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Sleeping Thread:");
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "Thread sleep");
thread.start();
doSomeElse();
//print TIMED_WAITING
System.out.println(thread.getState());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void threadWait(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Thread Waiting:");
Object lock = new Object();
Thread threadA = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (lock){
try {
lock.wait();
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
doSomeElse();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "Thread Waiting");
Thread threadB = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (lock){
//print WAITING
System.out.println("Before Notify, Thread A State:" + threadA.getState());
lock.notify();
//print BLOCKED
System.out.println("After Notify, Thread A State:" + threadA.getState());
}
});
threadA.start();
doSomeElse();
threadB.start();
try {
threadB.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//print RUNNABLE
System.out.println("After Thread B finish job, Thread A State:" + threadA.getState());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
private static void threadTimedWait(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.print("Thread Waiting:");
Object lock = new Object();
Thread threadA = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (lock){
try {
lock.wait(1000);
for(int i=0; i<100; i++){
doSomeElse();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "Thread Waiting");
Thread threadB = new Thread(()->{
synchronized (lock){
//print TIMED_WAITING
System.out.println("Before Notify, Thread A State:" + threadA.getState());
lock.notify();
//print BLOCKED
System.out.println("After Notify, Thread A State:" + threadA.getState());
}
});
threadA.start();
doSomeElse();
threadB.start();
try {
threadB.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//print RUNNABLE
System.out.println("After Thread B finish job, Thread A State:" + threadA.getState());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
/**
* take some times, let the thread get cpu time
*/
private static void doSomeElse(){
double meanless = 0d;
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++){
meanless += Math.random();
}
}
}
CPU时间运行测试:
public class ThreadCPUTimeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testBlockedThreadCPUTime();
}
protected static void testBlockedThreadCPUTime() {
Object lock = new Object();
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
doSomethingElse();
}
}, "ThreadA: Blocked because of synchronized");
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
threadA.start();
Thread.sleep(100000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "ThreadB: With Monitor But Sleep");
threadB.start();
//Main Thread Executing Job
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
doSomethingElse();
}
}
private static void doSomethingElse() {
double meanless = 0d;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
meanless += Math.random();
}
}
}
用VISUALVM可以统计CPU时间:

详细代码可以GitHub
线程状态及各状态下与锁和CPU的关系的更多相关文章
- java 线程的几种状态
java thread的运行周期中, 有几种状态, 在 java.lang.Thread.State 中有详细定义和说明: NEW 状态是指线程刚创建, 尚未启动 RUNNABLE 状态是线程正在正常 ...
- 在java中怎样实现多线程?线程的4种状态
一.在java中怎样实现多线程? extends Thread implement Runnable 方法一:继承 Thread 类,覆盖方法 run(),我们在创建的 Thread 类的子类中重写 ...
- Java线程Thread的状态解析以及状态转换分析 多线程中篇(七)
线程与操作系统中线程(进程)的概念同根同源,尽管千差万别. 操作系统中有状态以及状态的切换,Java线程中照样也有. State 在Thread类中有内部类 枚举State,用于抽象描述Java线程的 ...
- 透彻讲解,Java线程的6种状态及切换
Java中线程的状态分为6种. 1. 初始(NEW):新创建了一个线程对象,但还没有调用start()方法.2. 运行(RUNNABLE):Java线程中将就绪(ready)和运行中(running) ...
- Java线程的5种状态及切换(透彻讲解)-京东面试
一.Thread的几个重要方法: 我们先了解一下Thread的几个重要方法. a.start()方法,开始执行该线程:b.stop()方法,强制结束该线程执行:c.join方法,等待该线程结束.d.s ...
- 【转】java 线程的几种状态
java thread的运行周期中, 有几种状态, 在 java.lang.Thread.State 中有详细定义和说明: NEW 状态是指线程刚创建, 尚未启动 RUNNABLE 状态是线程正在正常 ...
- 线程的几种状态转换<转>
线程在一定条件下,状态会发生变化.线程一共有以下几种状态: 1.新建状态(New):新创建了一个线程对象. 2.就绪状态(Runnable):线程对象创建后,其他线程调用了该对象的start()方法. ...
- Java 多线程 线程的五种状态,线程 Sleep, Wait, notify, notifyAll
一.先来看看Thread类里面都有哪几种状态,在Thread.class中可以找到这个枚举,它定义了线程的相关状态: public enum State { NEW, RUNNABLE, BLOCKE ...
- Java线程基础知识(状态、共享与协作)
1.基础概念 CPU核心数和线程数的关系 核心数:线程数=1:1 ;使用了超线程技术后---> 1:2 CPU时间片轮转机制 又称RR调度,会导致上下文切换 什么是进程和线程 进程:程序运行资源 ...
随机推荐
- pinpoint配置使用
一.下载pinpoint包 从https://github.com/naver/pinpoint/releases 下载 pinpoint-agent.tar.gz pinpoint-collecto ...
- PTA | 1009说反话(20分)
给定一句英语,要求你编写程序,将句中所有单词的顺序颠倒输出. 输入格式: 测试输入包含一个测试用例,在一行内给出总长度不超过80的字符串.字符串由若干单词和若干空格组成,其中单词是由英文字母(大小写有 ...
- 使用 python 查看谁没有交作业
话说实验报告每天都要查人数,何不用程序实现 使用 python 查看谁没有交作业 version 1.0 程序嘛,肯定是可以改进的.使用该程序的前提是实验报告文件名中包含学号信息.将以上程序放在实验报 ...
- 29 collection 集合体系结构
/*collection:采集 * ArrayList * 集合的体系结构: * 由于不同的数据结构(数据的组织,存储方式),所以Java为我们提供了不同的集合, * 但是不同的集合他们的功能都是相似 ...
- hadoop(七)集群配置同步(hadoop完全分布式四)|9
前置配置:rsync远程同步|xsync集群分发(hadoop完全分布式准备三)|9 1. 分布式集群分配原则 部署分配原则 说明Namenode和secondarynamenode占用内存较大,建议 ...
- 013-结构体-C语言笔记
013-结构体-C语言笔记 学习目录 1.[掌握]返回指针的函数 2.[掌握]指向函数的指针 3.[掌握]结构体的声明 4.[掌握]结构体与数组 5.[掌握]结构体与指针 6.[掌握]结构体的嵌套 7 ...
- ViewStub
在书上了解了ViewStub,但只是带过两笔,没能了解.在网上搜索了一些资料,虽然很多文章都讲得比较完善,但是觉得可能是表达的原因,导致某个点上我理解错误,慢慢的才算比较清楚的认识ViewStub. ...
- zathura-vim风格轻量级pdf阅读器
安装(arch/manjaro) yay -Sy zathura-pdf-poppler 0.2.9-1 使用 `快捷键` gg 行首 G 行尾 j/k/h/l 单行移动 J/K 或 Ctrl + f ...
- Product Owner交流记录1
Abstract 最终我们选择了UWP版必应词典功能开发. 项目:“单词挑战”功能 然后我们今天中午我们和Product owner聊了聊. Content Product owner是Travis ...
- niuke --abc
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/1083/A来源:牛客网 给出一个字符串s,你需要做的是统计s中子串”abc”的个数.子串的定义就是存在任意下标a< ...
