SVM算法简单应用
第一部分:线性可分
通俗解释:可以用一条直线将两类分隔开来
一个简单的例子,直角坐标系中有三个点,A,B点为0类,C点为1类:
from sklearn import svm # 三个点
x = [[1, 1], [2, 0], [2, 3]]
# 三个点所属类
y = [0, 0, 1] clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(x, y) # 所有信息
print(clf)
# 支持向量
print(clf.support_vectors_)
# 支持向量在x中的索引
print(clf.support_)
# 支持向量在所属类中分别有几个
print(clf.n_support_)
# 预测(1,4)这个点所属分类,结果是1类
print(clf.predict([[1, 4]]))
接下来多一些数据并画图观察下:
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from sklearn import svm # 按正态分布随机取40个样本
# 前20个取[-2,-2]点附近样本,后20个取[2,2]点附近样本,再用np.r_拼接
X = np.r_[np.random.randn(20, 2) - [2, 2], np.random.randn(20, 2) + [2, 2]]
# 20个0类20个1类
Y = [0] * 20 + [1] * 20 # 调用sklearn的SVM
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
clf.fit(X, Y) # 参数
w = clf.coef_[0] '''
w_0x + w_1y +w_3=0方程转化为:
y = -(w_0/w_1) x + (w_3/w_1)
其中w_3=clf.intercept_[0]
''' # 直线斜率
a = -w[0] / w[1]
# 取-5到5之间的一些浮点数
xx = np.linspace(-5, 5)
# 直线方程
yy = a * xx - (clf.intercept_[0]) / w[1]
# 取第一个支持向量
b = clf.support_vectors_[0]
# 下方直线方程(利用点斜式方程)
yy_down = a * xx + (b[1] - a * b[0])
# 取最后一个支持向量
b = clf.support_vectors_[-1]
# 上方直线方程(同理)
yy_up = a * xx + (b[1] - a * b[0]) # 画出三条直线
pl.plot(xx, yy, 'k-')
pl.plot(xx, yy_down, 'k--')
pl.plot(xx, yy_up, 'k--') # 画出这些点
pl.scatter(clf.support_vectors_[:, 0], clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],
s=80, facecolors='none')
pl.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, cmap=pl.cm.Paired) # 使坐标系的最大值和最小值与数据范围一致
pl.axis('tight') # 展示
pl.show()
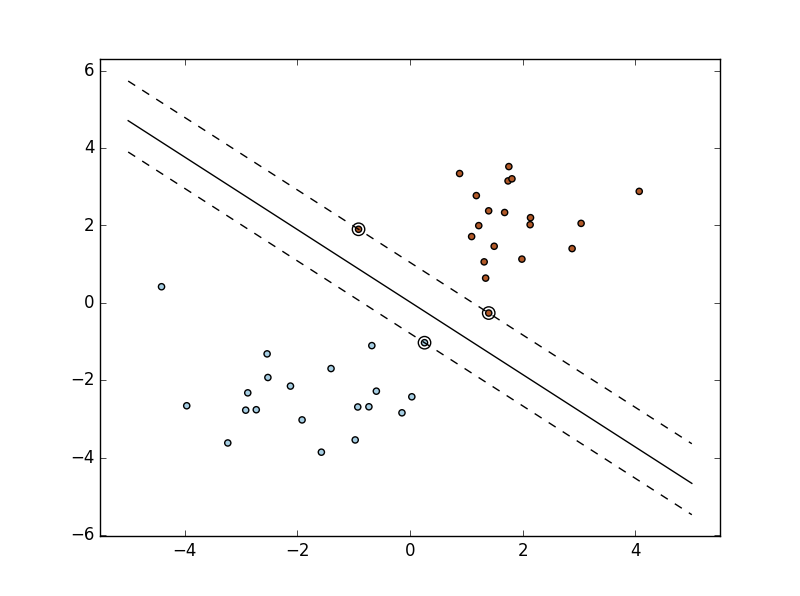
第二部分:线性不可分
不可以用一条直线分割开来的数据
方法:转换成高维度
人脸识别案例:
from __future__ import print_function
from time import time
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_people
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCA
from sklearn.svm import SVC # 打印日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')
# 装载数据集
lfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)
# 处理图片相关信息
n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape
X = lfw_people.data
n_features = X.shape[1]
y = lfw_people.target
target_names = lfw_people.target_names
n_classes = target_names.shape[0]
print("Total dataset size:")
print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)
print("n_features: %d" % n_features)
print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes) # 设置训练集和测试集
# 随机选取75%的数据作为训练样本
# 其余25%的数据作为测试样本
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25) # 降低维度(PCA算法)
n_components = 150 print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"
% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))
t0 = time()
pca = RandomizedPCA(n_components=n_components, whiten=True).fit(X_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components, h, w)) print("Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis")
t0 = time()
X_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train)
X_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) # SVM算法
print("Fitting the classifier to the training set")
t0 = time()
param_grid = {'C': [1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5],
'gamma': [0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.1], }
clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='balanced'), param_grid)
clf = clf.fit(X_train_pca, y_train)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print("Best estimator found by grid search:")
print(clf.best_estimator_) # 预测 print("Predicting people's names on the test set")
t0 = time()
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test_pca)
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=target_names))
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=range(n_classes))) # 画图展示
def plot_gallery(images, titles, h, w, n_row=3, n_col=4):
plt.figure(figsize=(1.8 * n_col, 2.4 * n_row))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=.01, right=.99, top=.90, hspace=.35)
for i in range(n_row * n_col):
plt.subplot(n_row, n_col, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h, w)), cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(titles[i], size=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(()) # 展示的每一张图标题(判断正误)
def title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i):
pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
return 'predicted: %s\ntrue: %s' % (pred_name, true_name) prediction_titles = [title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i)
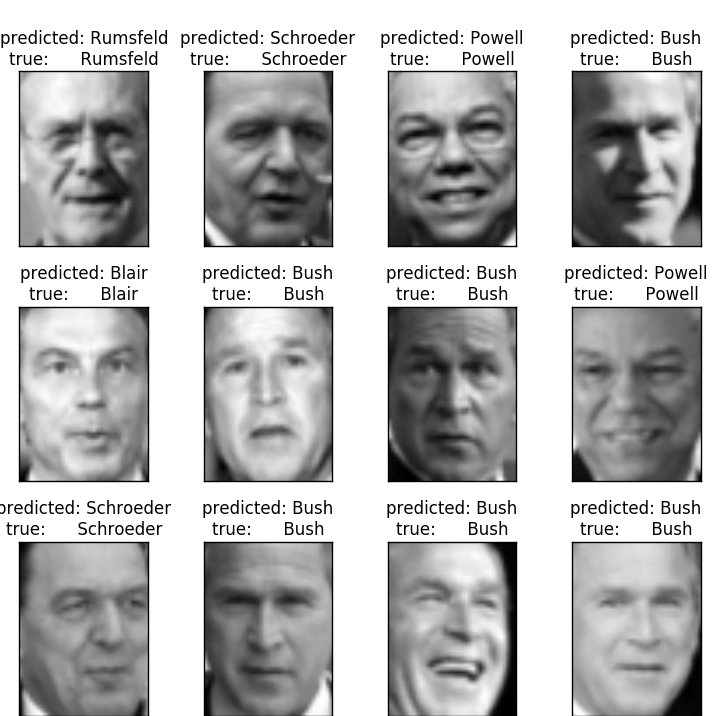
for i in range(y_pred.shape[0])] # 原来的图片
plot_gallery(X_test, prediction_titles, h, w) eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d" % i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])]
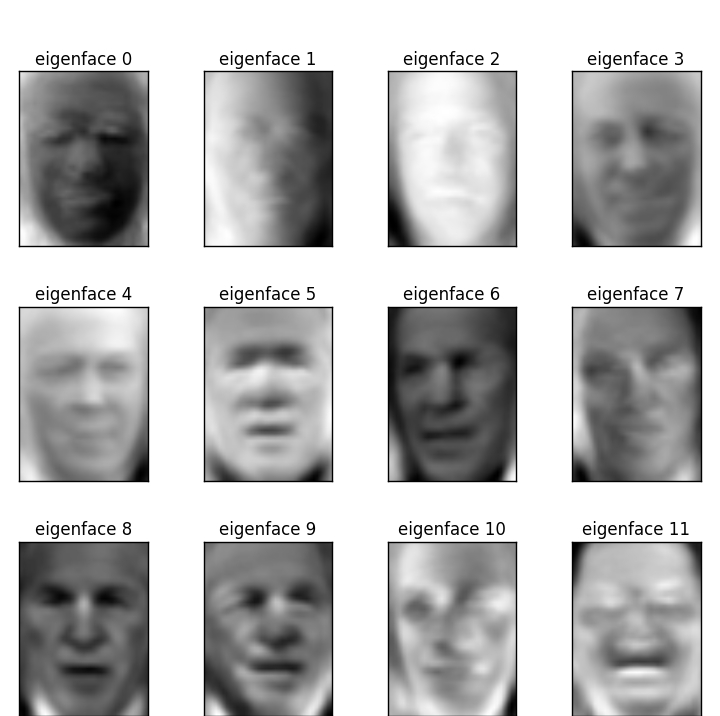
# 提取人脸特征的图片
plot_gallery(eigenfaces, eigenface_titles, h, w) plt.show()
数据相关信息:
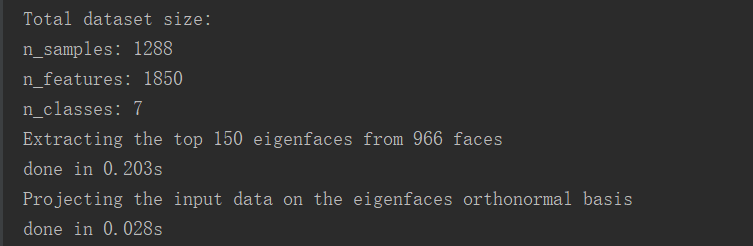
PCA和SVM算法:

预测:
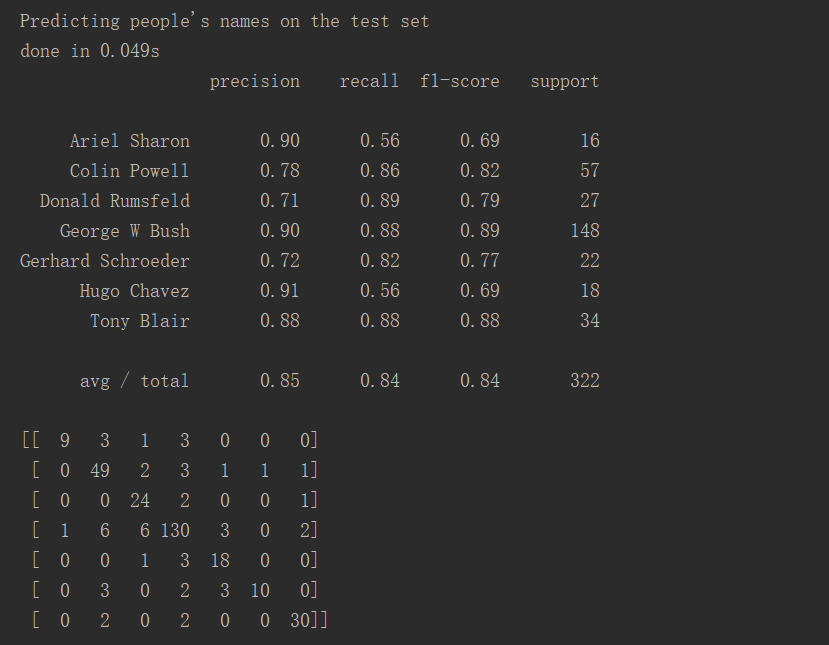
发现精确度达到85%,比较成功
观察矩阵:对角线代表预测与真实一致的个数
最后形象地看下:预测结果和真实基本一致

特征图:

SVM算法简单应用的更多相关文章
- 【转】 SVM算法入门
课程文本分类project SVM算法入门 转自:http://www.blogjava.net/zhenandaci/category/31868.html (一)SVM的简介 支持向量机(Supp ...
- SVM算法入门
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/yangliuy/article/details/7316496SVM入门(一)至(三)Refresh 按:之前的文章重新汇编一下,修改了一些错误和不当 ...
- 转载:scikit-learn学习之SVM算法
转载,http://blog.csdn.net/gamer_gyt 目录(?)[+] ========================================================= ...
- 一步步教你轻松学支持向量机SVM算法之案例篇2
一步步教你轻松学支持向量机SVM算法之案例篇2 (白宁超 2018年10月22日10:09:07) 摘要:支持向量机即SVM(Support Vector Machine) ,是一种监督学习算法,属于 ...
- 一步步教你轻松学支持向量机SVM算法之理论篇1
一步步教你轻松学支持向量机SVM算法之理论篇1 (白宁超 2018年10月22日10:03:35) 摘要:支持向量机即SVM(Support Vector Machine) ,是一种监督学习算法,属于 ...
- 程序员训练机器学习 SVM算法分享
http://www.csdn.net/article/2012-12-28/2813275-Support-Vector-Machine 摘要:支持向量机(SVM)已经成为一种非常受欢迎的算法.本文 ...
- svm算法 最通俗易懂讲解
最近在学习svm算法,借此文章记录自己的学习过程,在学习很多处借鉴了z老师的讲义和李航的统计,若有不足的地方,请海涵:svm算法通俗的理解在二维上,就是找一分割线把两类分开,问题是如下图三条颜色都可以 ...
- Machine Learning in Action(5) SVM算法
做机器学习的一定对支持向量机(support vector machine-SVM)颇为熟悉,因为在深度学习出现之前,SVM一直霸占着机器学习老大哥的位子.他的理论很优美,各种变种改进版本也很多,比如 ...
- (转载)python应用svm算法过程
除了在Matlab中使用PRTools工具箱中的svm算法,Python中一样可以使用支持向量机做分类.因为Python中的sklearn库也集成了SVM算法,本文的运行环境是Pycharm. 一.导 ...
随机推荐
- 网址导航19A
[导航] KIM主页 265导航 好866 [名站] 百度 网易 腾讯 新华 中新 凤凰 [新闻] 联合早报 南方周末 澎湃新闻 [系统] 宋永志 蒲公英 技术员 装机网 系统之家 [软件] 星愿 ...
- hid.dll
hid.dll是USB的HID相关动态链接库文件,缺少它可能会造成usb设备无法正常使用.当你的电脑弹出提示“计算机缺少hid.dll”或“无法找到hid.dll Hkapi.dll HKComman ...
- Read-only file system
mount -o remount rw /
- skyline开发——读取Shapefile要素属性
double len; IFeatures66 features = featureLayer.FeatureGroups.Polyline.GetCurrentFeatures(); foreach ...
- WinForm DotNetBar 动态添加DataGridView
DataGridView dgv = new DataGridView(); dgv.Dock = DockStyle.Fill; dgv.Location = new System.Drawing. ...
- Solved: RDP Disconnected – Error Code 2825 mremote
- Idea增加Idiff merger工具
File -- setting --- tolls -- diff & merge 选择使用外部diff工具和外部merge工具,选择winmerge工具目录. 就可以再version con ...
- 二、PyQt5基本功能和操作入门
在这里,我将根据自己的学习历程从初级到高级介绍pyqt5.因为是学到哪里就写道哪里,所以内容排版比较随意.有两点问题需要先说明: 1.虽然界面的设计可以借助qt designer进行拖拽创建,并且可以 ...
- 文件扩展关联命令(assoc)
assoc 命令: // 描述: (association) --> 联想.关联 显示或修改文件扩展名关联. 如果在没有参数的情况下使用,assoc将显示所有当前文件扩展名关联的列表. // 语 ...
- SRILM的使用及平滑方法说明
1.简介 SRILM是通过统计方法构建语言模型,主要应用于语音识别,文本标注和切分,以及机器翻译等. SRILM支持语言模型的训练和评测,通过训练数据得到语言模型,其中包括最大似然估计及相应的平滑算法 ...
