String类对象的比较
1.字符串比较,是按照字符串(String)中每一个字符(char)的字段表顺序进行比较
/**
* Compares two strings lexicographically(字典序,按照字典顺序).
* The comparison is based on the Unicode value of each character in
* the strings. The character sequence represented by this
* {@code String} object is compared lexicographically to the
* character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is
* a negative integer if this {@code String} object
* lexicographically precedes(先于) the argument string. The result is a
* positive integer if this {@code String} object lexicographically
* follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings
* are equal; {@code compareTo} returns {@code 0} exactly when
* the {@link #equals(Object)} method would return {@code true}.
* <p>
* This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are
* different, then either they have different characters at some index
* that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different,
* or both. If they have different characters at one or more index
* positions, let <i>k</i> be the smallest such index; then the string
* whose character at position <i>k</i> has the smaller value, as
* determined by using the < operator, lexicographically precedes the
* other string. In this case, {@code compareTo} returns the
* difference of the two character values at position {@code k} in
* the two string -- that is, the value:
* <blockquote><pre>
* this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
* </pre></blockquote>
* If there is no index position at which they differ, then the shorter
* string lexicographically precedes the longer string. In this case,
* {@code compareTo} returns the difference of the lengths of the
* strings -- that is, the value:
* <blockquote><pre>
* this.length()-anotherString.length()
* </pre></blockquote>
*
* @param anotherString the {@code String} to be compared.
* @return the value {@code 0} if the argument string is equal to
* this string; a value less than {@code 0} if this string
* is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a
* value greater than {@code 0} if this string is
* lexicographically greater than the string argument.
*/
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value; int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}
String str1 = "abd";
String str2 = "aba";
int res1 = str1.compareTo(str2);
//
System.out.println(res1);
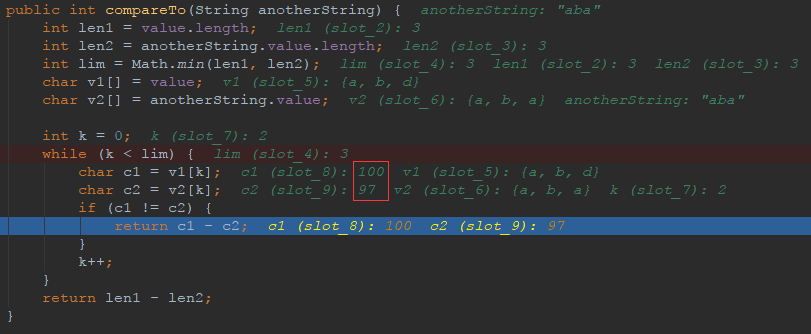
String str1 = "Abd";
String str2 = "aba";
int res1 = str1.compareTo(str2);
//-32
System.out.println(res1);
2.比较时忽略大小写
/**
* Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case
* differences. This method returns an integer whose sign is that of
* calling {@code compareTo} with normalized versions of the strings
* where case differences have been eliminated by calling
* {@code Character.toLowerCase(Character.toUpperCase(character))} on
* each character.
* <p>
* Note that this method does <em>not</em> take locale into account,
* and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
* The java.text package provides <em>collators</em> to allow
* locale-sensitive ordering.
*
* @param str the {@code String} to be compared.
* @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the
* specified String is greater than, equal to, or less
* than this String, ignoring case considerations.
* @see java.text.Collator#compare(String, String)
* @since 1.2
*/
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) {
return CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER.compare(this, str);
}
String str1 = "Abd";
String str2 = "aba";
int res = str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2);
//
System.out.println(res);
String类对象的比较的更多相关文章
- 反射消除String类对象的不可变特性
大家都知道,在JAVA中字符串一旦声明就不可改变,如果尝试修改字符串的内容,将会重新实例化一个新的字符串对象,这也是为了安全性和效率. 由于字符串在程序之中被大量使用,所以JAVA引入了一个字符串常量 ...
- java笔记--String类对象解析与运用
--如果朋友您想转载本文章请注明转载地址"http://www.cnblogs.com/XHJT/p/3877236.html "谢谢-- 1.String中的equals和==的 ...
- String类对象两种实例化方式比较
第一种:直接赋值 String str = "hello!" ; 在java中,有一个字符串常量池,对于这种直接赋值的,会直接写进常量池(常量池里面不存在其value,) 自JD ...
- JAVA笔记3__字符串String类/对象一对一关联
import java.lang.String; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(Strin ...
- c++中string类对象和字符数组之间的相互转换
string类在c++中是一个模板类,位于名字空间std中,注意这里不是string.h,string.h是C字符串头文件. 将string类型转换为字符数组char arr[10];string s ...
- String类对象相加时做了什么
我们都知道java中的加号操作符除了加法.表示正数之外,还可以用作字符串的连接.初学java时,你很可能会碰到类似下面的题目: 以下这段代码产生了几个String对象: String str1 = & ...
- Scanner类、匿名对象、Random类、ArrayList集合、String类、static静态类、math类和Arrays工具类
一.Scanner类 1.除了八种基本数据类型,其他都是引用类型: 引用类型使用三步骤: 2.Scanner类 引用jdk提供的类,Scanner在java.util包下,不在java.lang包(S ...
- String类和StringBuffer类的区别
首先,String和StringBuffer主要有2个区别: (1)String类对象为不可变对象,一旦你修改了String对象的值,隐性重新创建了一个新的对象,释放原String对象,StringB ...
- 【Java 进阶篇】【第一课】String类
引用 String类包含在java.lang包中.这个包会在Java启动的时候自动import,所以可以当做一个内置类(built-in class).我们不需要显式的使用import引入String ...
随机推荐
- ESLint处理
当有遇到下划线的问题,会提示有问题,无法通过检测 需要在代码的前面加入以下代码就可以解决,地址是:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44126983/eslint ...
- ThinkPHP导入第三方类库Vendor
详情查看ThinkPHP3.2手册 架构 > 自动加载 章节 vendor('Uploader','','.class.php')
- 解决python2.x文件读写编码问题
转自: https://xrlin.github.io/%E8%A7%A3%E5%86%B3python2.x%E6%96%87%E4%BB%B6%E8%AF%BB%E5%86%99%E7%BC%96 ...
- DataTable,List,Dictonary互转,筛选及相关写法
1.创建自定义DataTable /// 创建自定义DataTable(一) 根据列名字符串数组, /// </summary> /// <param name="sLi ...
- springboot项目打war包部署到服务器(eclipse & gradle环境)
1.右键项目run as -> run configurations,打开Run configurations弹出框 2.右键Gradle Project -> New Configur ...
- [BZOJ4570][SCOI2016]妖怪(凸包)
两种做法,前一种会TLE. 第一种是高一数学题做法,设一个妖怪的atk和dnf分别为x和y,则它在(a,b)环境下的战斗力为x+y/a*b+y+x/a*b. 设t为b/a,则战斗力即$f(x,y,t) ...
- 【推导】【单调性】Petrozavodsk Winter Training Camp 2018 Day 1: Jagiellonian U Contest, Tuesday, January 30, 2018 Problem B. Tribute
题意:有n个数,除了空集外,它们会形成2^n-1个子集,给你这些子集的和的结果,让你还原原来的n个数. 假设原数是3 5 16, 那么它们形成3 5 8 16 19 21 24, 那么第一轮取出开头的 ...
- hrbust 2176 Mac的投票 二分/水题
Mac的投票 Time Limit: 1000 MS Memory Limit: 32768 K Total Submit: 52(12 users) Total Accepted: 12(10 us ...
- POJ Anniversary party 树形DP
/* 树形dp: 给一颗树,要求一组节点,节点之间没有父子关系,并且使得所有的节点的权值和最大 对于每一个节点,我们有两种状态 dp[i][0]表示不选择节点i,以节点i为根的子树所能形成的节点集所能 ...
- jquery中的 $.fn $.fx
$.fn是指 jquery的命名空间,加上fn上的方法及属性,会对jquery实例每一个有效. 如扩展$.fn.abc() 那么你可以这样子:$("#div").abc(); 常使 ...
