多线程编程CompletableFuture与parallelStream
一、简介
平常在页面中我们会使用异步调用$.ajax()函数,如果是多个的话他会并行执行相互不影响,实际上Completable我理解也是和它类似,是java 8里面新出的异步实现类,CompletableFuture类实现了Future接口,CompletableFuture与Stream的设计都遵循了类似的设计模式:使用Lambda表达式以及流水线的思想,从这个角度可以说CompletableFuture与Future的关系类似于Stream与Collection的关系。
二、代码
直接上代码,运行之后可以看出CompletableFuture是调用的时候就开始执行,当后续代码调到get的取值方法时,如果内部已经返回结果则直接拿到,如果还没有返回将阻塞线程等待结果,可以设置超时时间避免长时间等待。
以下是模拟并行调用多个方法的场景,比如查询页可能会有多个条件选择,这些条件需要后台数据相互之间有没有联系的场景,就不需要串行执行,异步执行可以节省大量时间
import org.joda.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class AppTest { public void printlnConsole(String msg) {
String time = new LocalDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("[%s]%s", time, msg));
} /**
* 多任务单次异步执行
*/
@Test
public void testManyFunAsync() {
long start = System.nanoTime();//程序开始时间
try {
int id = 1;//模拟一个参数,如学校Id
printlnConsole("调用异步任务...");
//使用异步方式调用方法【调用时就会开始执行方法】
CompletableFuture futureClassCount = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getClassCount(id));
CompletableFuture futureStudentCount = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getStudentCount(id)); //do something 做了一些其他的事情超过了异步任务执行的时间
printlnConsole("做一些其他的事情...");
Thread.sleep(3000);
printlnConsole("其他事情完成"); //下面获取异步任务的结果,就会立即拿到返回值
printlnConsole("获取异步任务结果...");
Object classCount = futureClassCount.get();
//Object classCount = futureClassCount.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//可以设置超时时间,超过这个时间时将不再等待,返回异常
Object studentCount = futureStudentCount.get();
//Object studentCount = futureStudentCount.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
printlnConsole("异步任务结果获取完成"); printlnConsole("ClassCount:" + classCount);
printlnConsole("StudentCount:" + studentCount); } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();//程序结束时间
long time = (end - start) / 1000000;//总耗时
System.out.println("运行时间:" + time);
} public int getClassCount(int id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
printlnConsole("getClassCount(" + id + ")执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 20;
} public int getStudentCount(int id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
printlnConsole("getStudentCount(" + id + ")执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 100;
}
}
anyOf()为任意一个子任务线程执行完毕后返回
allOf()为等待所有子任务线程全部执行完毕后返回
getNow()表示我需要立即拿到结果,如果当前的线程并未执行完成,则使用我传入的值进行任务调用,参数为无法获取结果时使用我传入的值
get()获取子线程运算的结果,会抛出检查到的异常
join()获取子线程运算的结果,不会抛出异常
package com.ysl; import org.joda.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class AppTest { public void printlnConsole(String msg) {
String time = new LocalDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("[%s]%s", time, msg));
} /**
* 并行执行等待全部结果或等待任意结果
*/
@Test
public void testAllOfAnyOf() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
printlnConsole("调用异步任务...");
List<Integer> ids = Arrays.asList(1, 3, 5);//准备的请求参数
//创建异步方法数组
CompletableFuture[] futures = ids.stream().map(id -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getClassName(id))).toArray(size -> new CompletableFuture[size]);
//指定该异步方法数组的子任务线程等待类型
CompletableFuture.anyOf(futures).join();//anyOf()为任意一个子任务线程执行完毕后返回
//CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join();//allOf()为等待所有子任务线程全部执行完毕后返回 printlnConsole("做一些其他的事情...");
Thread.sleep(2000);
printlnConsole("其他事情完成"); printlnConsole("获取异步任务结果:");
for (CompletableFuture f : futures) {
//Object obj = f.getNow(1);//getNow()表示我需要立即拿到结果,如果当前的线程并未执行完成,则使用我传入的值进行任务调用,参数为无法获取结果时使用我传入的值
Object obj = f.get();//get()获取子线程运算的结果,会抛出检查到的异常
//Object obj = f.join();//join()获取子线程运算的结果,不会抛出异常
printlnConsole(String.valueOf(obj));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} long end = System.nanoTime();
long time = (end - start) / 1000000;
System.out.println("运行时间:" + time);
} public String getClassName(int id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(id * 1000);
printlnConsole("getClassName(" + id + ")执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "taiyonghai-" + id;
}
}
下面是并行流的演示parallelStream也是java 8新特性
ids.stream()转化为流.map()映射每个元素对应的结果.collect(Collectors.toList)把结果归纳为List;还有.filter()过滤元素.sorted()对元素进行排序.limit()获取指定数量元素;也可以toArray(size -> new Class[size])转化为数组
以下是模拟根据Id查询学生名称的场景,接收到的是一个集合又都是调用同一个方法获取,就可以使用并行流同时异步请求等待返回结果
import org.joda.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class AppTest { public void printlnConsole(String msg) {
String time = new LocalDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("[%s]%s", time, msg));
} /**
* 单任务多次并行流执行
*/
@Test
public void testParallelStream() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
printlnConsole("调用异步任务...");
List<Integer> ids = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);//准备的请求参数
//串行执行会等待每一个方法执行完毕后在继续执行下一个
//List<String> names = ids.stream().map(id -> getStudentName(id)).collect(Collectors.toList());
//并行执行会同时调用多个方法待全部执行完毕后一起返回(parallelStream是非线程安全的,配合collect达到线程安全,后续验证一下)
List<String> names = ids.parallelStream().map(id -> getStudentName(id)).collect(Collectors.toList());
//无论stream()或者parallelStream()调用时均会阻断线程执行
printlnConsole("做一些其他的事情...");
Thread.sleep(3000);
printlnConsole("其他事情完成"); printlnConsole("获取异步任务结果:");
names.forEach(item -> printlnConsole(item));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
long time = (end - start) / 1000000;
System.out.println("运行时间:" + time);
} public String getStudentName(int id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
printlnConsole("getStudentName(" + id + ")执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "taiyonghai-" + id;
}
}
上面能看到并行流虽然是并行执行但等待结果是阻塞线程的,所以可以利用异步CompletableFuture配合串行流来实现
以下是采用串行流配合异步实现的并发处理
import org.joda.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class AppTest { public void printlnConsole(String msg) {
String time = new LocalDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("[%s]%s", time, msg));
} /**
* 单任务多次异步执行
*/
@Test
public void testOneFunAsync() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
printlnConsole("调用异步任务...");
List<Integer> ids = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);//准备的请求参数
//ids.stream()转化为流.map()映射每个元素对应的结果.collect()把结果归纳为List;还有.filter()过滤元素.sorted()对元素进行排序.limit()获取指定数量元素;
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = ids.stream().map(id -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getStudentName(id))).collect(Collectors.toList()); //不用并行流parallelStream()调用时就不会阻断线程执行
printlnConsole("做一些其他的事情...");
Thread.sleep(3000);
printlnConsole("其他事情完成"); printlnConsole("获取异步任务结果:");
futures.forEach(f -> {
try {
Object obj = f.get();
printlnConsole(String.valueOf(obj));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} long end = System.nanoTime();
long time = (end - start) / 1000000;
System.out.println("运行时间:" + time);
} public String getStudentName(int id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
printlnConsole("getStudentName(" + id + ")执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "taiyonghai-" + id;
}
}
当我的并行任务数量超过了我机器的核心数就会产生等待,我电脑是8核使用并行流执行数量就可以开8个子线程,当多余这个数量时剩下的就需要等待前面线程执行完再执行
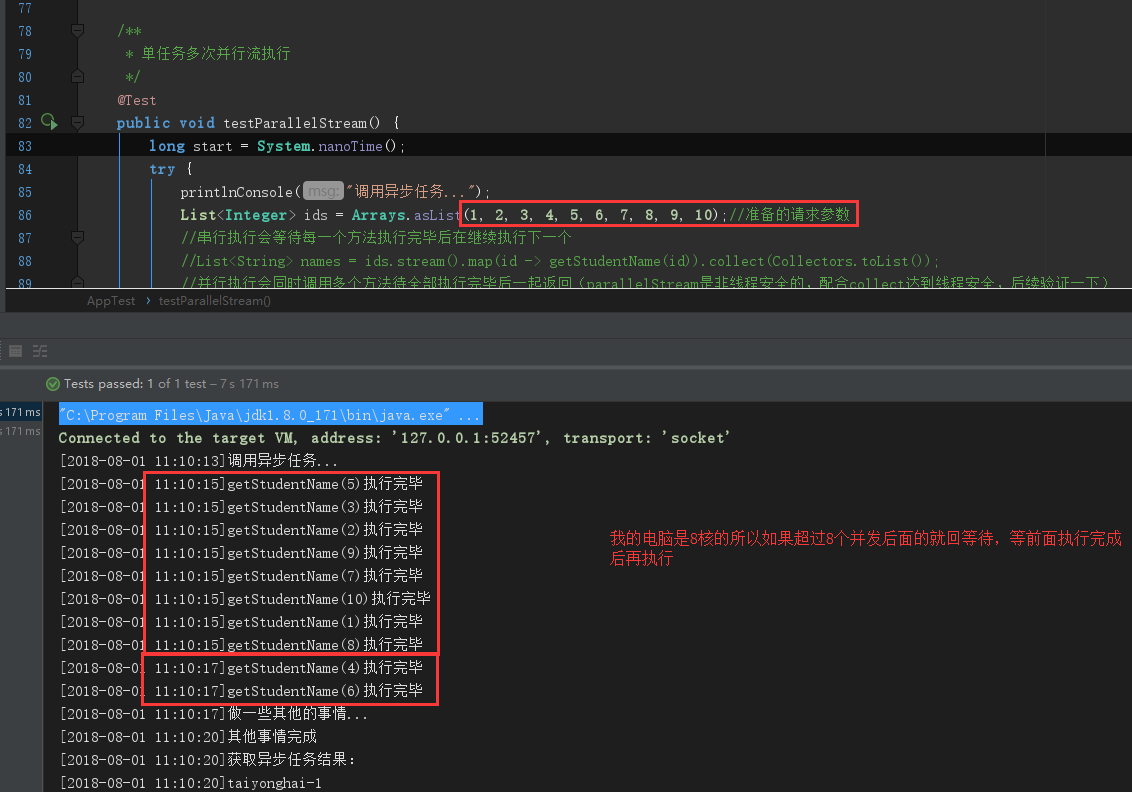
当需要并行执行的任务数量大于核心数的时候,产生的等待是我们不想看到的,这时CompletableFuture就更加适用,它可以手动这只线程池大小,避免并行任务过多时的等待
我们将代码做些修正
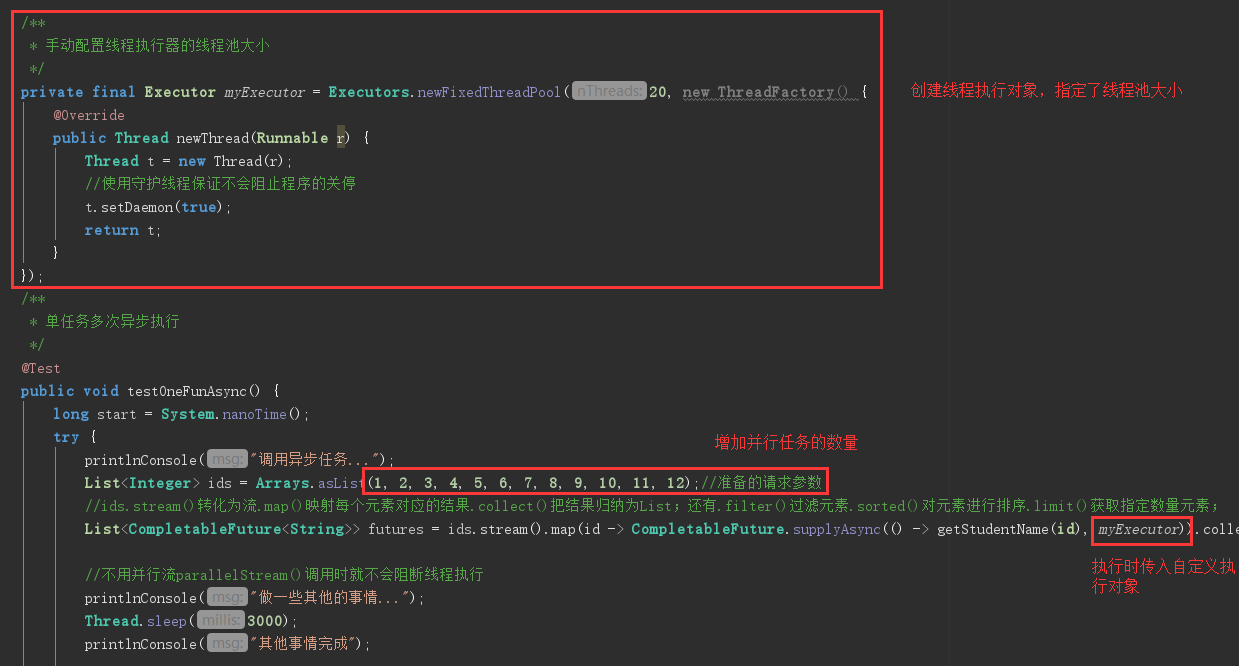
以下是源码,这样就可以提高对多任务并行处理的支持了
import org.joda.time.LocalDateTime;
import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class AppTest { public void printlnConsole(String msg) {
String time = new LocalDateTime().toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("[%s]%s", time, msg));
} /**
* 手动配置线程执行器的线程池大小
*/
private final Executor myExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20, new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(r);
//使用守护线程保证不会阻止程序的关停
t.setDaemon(true);
return t;
}
});
/**
* 单任务多次异步执行
*/
@Test
public void testOneFunAsync() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
printlnConsole("调用异步任务...");
List<Integer> ids = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12);//准备的请求参数
//ids.stream()转化为流.map()映射每个元素对应的结果.collect()把结果归纳为List;还有.filter()过滤元素.sorted()对元素进行排序.limit()获取指定数量元素;
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = ids.stream().map(id -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getStudentName(id), myExecutor)).collect(Collectors.toList()); //不用并行流parallelStream()调用时就不会阻断线程执行
printlnConsole("做一些其他的事情...");
Thread.sleep(3000);
printlnConsole("其他事情完成"); printlnConsole("获取异步任务结果:");
futures.forEach(f -> {
try {
Object obj = f.get();
printlnConsole(String.valueOf(obj));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} long end = System.nanoTime();
long time = (end - start) / 1000000;
System.out.println("运行时间:" + time);
} public String getStudentName(int id) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
printlnConsole("getStudentName(" + id + ")执行完毕");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "taiyonghai-" + id;
}
}
java 8的新特性也只做到了会用,很多深入的还不了解,还望指导谢谢,下面备份一下别人的总结我觉得挺有用的:
选择正确的线程池大小
《Java并发编程实战》中给出如下公式:
Number = NCpu * Ucpu * ( 1 + W/C)
Number : 线程数量
NCpu : 处理器核数
UCpu : 期望cpu利用率
W/C : 等待时间与计算时间比
我们这里:99%d的时间是等待商店响应 W/C = 99 ,cpu利用率期望 100% ,NCpu = 9,推断出 number = 800。但是为了避免过多的线程搞死计算机,我们选择商店数与计算值中较小的一个。
并行流与CompletableFuture
目前,我们对集合进行计算有两种方式:1.并行流 2.CompletableFuture;
1、而CompletableFuture更加的灵活,我们可以配置线程池的大小确保整体的计算不会因为等待IO而发生阻塞。
书上给出的建议如下:如果是计算密集型的操作并且没有IO推荐stream接口,因为实现简单效率也高,如果所有的线程都是计算密集型的也就没有必要创建比核数更多的线程。
2、反之,如果任务涉及到IO,网络等操作:CompletableFuture灵活性更好,因为大部分线程处于等待状态,需要让他们更加忙碌,并且再逻辑中加入异常处理可以更有效的监控是什么原因触发了等待。
参考地址:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012833183
多线程编程CompletableFuture与parallelStream的更多相关文章
- Java多线程编程基础知识汇总
多线程简介 多任务 现代操作系统(Windows.Linux.MacOS)都可以执行多任务,多任务就是同时运行多个任务.例如在我们的计算机上,一般都同时跑着多个程序,例如浏览器,视频播放器,音乐播 ...
- 异步编程CompletableFuture
多线程优化性能,串行操作并行化 串行操作 // 以下2个都是耗时操作 doBizA(); doBizB(); 修改变为并行化 new Thread(() -> doBizA()).start() ...
- Web Worker javascript多线程编程(一)
什么是Web Worker? web worker 是运行在后台的 JavaScript,不占用浏览器自身线程,独立于其他脚本,可以提高应用的总体性能,并且提升用户体验. 一般来说Javascript ...
- Web Worker javascript多线程编程(二)
Web Worker javascript多线程编程(一)中提到有两种Web Worker:专用线程dedicated web worker,以及共享线程shared web worker.不过主要讲 ...
- windows多线程编程实现 简单(1)
内容:实现win32下的最基本多线程编程 使用函数: #CreateThread# 创建线程 HANDLE WINAPI CreateThread( LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpT ...
- Rust语言的多线程编程
我写这篇短文的时候,正值Rust1.0发布不久,严格来说这是一门兼具C语言的执行效率和Java的开发效率的强大语言,它的所有权机制竟然让你无法写出线程不安全的代码,它是一门可以用来写操作系统的系统级语 ...
- windows多线程编程星球(一)
以前在学校的时候,多线程这一部分是属于那种充满好奇但是又感觉很难掌握的部分.原因嘛我觉得是这玩意儿和编程语言无关,主要和操作系统的有关,所以这部分内容主要出现在讲原理的操作系统书的某一章,看完原理是懂 ...
- Java多线程编程核心技术---学习分享
继承Thread类实现多线程 public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); Sys ...
- python多线程编程
Python多线程编程中常用方法: 1.join()方法:如果一个线程或者在函数执行的过程中调用另一个线程,并且希望待其完成操作后才能执行,那么在调用线程的时就可以使用被调线程的join方法join( ...
随机推荐
- PLSQL使用scott登录
Oracle有3种用户: system.sys.scott,其中system和sys的区别在与能否创建数据库,sys用户登录才可以创建数据库,而scott是给初学者学习的用户,学习者可以用Scott登 ...
- python列表(list)的简单学习
列表是由一系列按特定顺序排列的元素组成, 是 Python 中使用最频繁的数据类型.列表可以完成大多数集合类的数据结构实现.列表中元素的类型可以不相同,它支持数字,字符串甚至可以包含列表.字典(即嵌套 ...
- vue-manage-system 后台管理系统开发总结
前言 vue-manage-system,一个基于 Vue.js 和 element-ui 的后台管理系统模板,从2016年年底第一个commit,到现在差不多两年了,GitHub上也有了 5k st ...
- 好用的shell可以事半功倍
程序员离不开shell,一个好用的shell可以事半功倍,推荐zsh以及一些插件 # install zsh $ brew install zsh # install a framework, we ...
- Android--UI之ProgressBar
前言 开门见山,开篇明意.这篇博客主要讲解一下Android中ProgressBar控件以及间接继承它的两个子控件SeekBar.RatingBar的基本用法,因为其有继承关系,存在一些共有特性,所以 ...
- less用法小结
1,采用koala进行编译,可以实时地在vscode这样的工具中看到less到css的转换: 2,均支持/**/以及//两种形式的注释,由于后期维护是维护less,因此推荐使用后者,因为后者不会被编译 ...
- vue-06-过度和动画
1, css过度与动画 需要使用 v-if, v-show 来进行 1), 过度类名 v-enter: 进入时触发 v-enter-active: 执行过程中 v-enter-to: 停止时进行 v- ...
- C# 获取 sha256
C# 获取 sha256, 输入可以是 字符串,也可以是 字节流流: 自定义的输入类型的枚举: public enum Sha26ParseType { StringType, StreamType ...
- 项目实战2—实现基于LVS负载均衡集群的电商网站架构
负载均衡集群企业级应用实战-LVS 实现基于LVS负载均衡集群的电商网站架构 背景:随着业务的发展,网站的访问量越来越大,网站访问量已经从原来的1000QPS,变为3000QPS,网站已经不堪重负,响 ...
- NiftyNet开源平台的使用 -- 配置文件
NiftyNet开源平台的使用 NiftyNet基础架构是使研究人员能够快速开发和分发用于分割.回归.图像生成和表示学习应用程序,或将平台扩展到新的应用程序的深度学习解决方案. 详细介绍请见: ...
