SpringBoot启动过程原理(转)
1.1 Springboot启动:
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServerApplication.class,args);
}
}
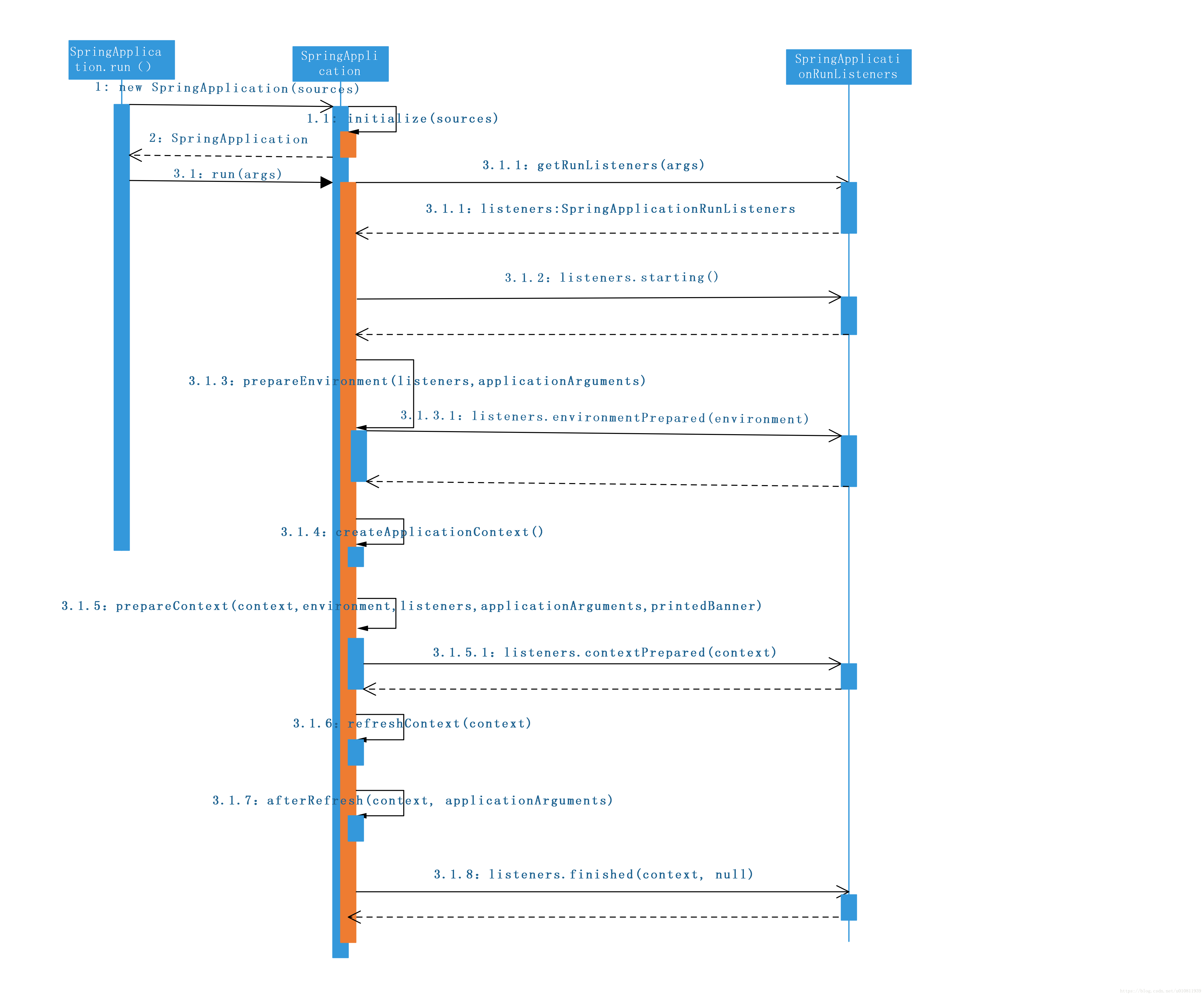
从上面代码看,调用了SpringApplication的静态方法run。这个run方法会构造一个SpringApplication的实例,然后再调用这里实例的run方法就表示启动SpringBoot。具体对象处理流程看下边时序图:
概述:
构造SpringApplication的实例(时序图步骤1-2)
调用SpringApplication.run()方法(时序图步骤3)
构造SpringApplicationRunListeners 实例(时序图步骤3.1.1)
发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件(时序图步骤3.1.2)
SpringApplicationRunListeners 实例准备环境信息(时序图步骤3.1.3)
创建ApplicationContext对象(时序图步骤3.1.4)
ApplicationContext实例准备环境信息(时序图步骤3.1.5)
刷新的上下文(时序图步骤3.1.6)
注:文章按照该顺序讲解【1.2 启动加载过程分析】
时序图:
1.2 启动加载过程分析
1.2.1 构造SpringApplication的实例(时序图步骤1-2)
代码
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
// 步骤1
return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);
}
public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
// 步骤1.1
initialize(sources);
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
//加载META-INF/spring.factories路径ApplicationContextInitializer.class
getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection)
//加载META-INF/spring.factories路径ApplicationListener.class
getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
1.2.2 步骤3.1.1:
代码
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
// (1)
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
分析
(1). 通过ClassLoader.getResources加载META-INF/spring.factories路径下的
文件信息,从中找key为SpringApplicationRunListener对应类,并实例化。
1.2.3 步骤3.1.2:
代码
public void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
分析
发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件。
1.2.4 步骤3.1.3:
代码
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
// ⑴. 得到环境对象ConfigurableEnvironment,没有则创建一个StandardServletEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// ⑵. 配置环境信息(激活环境,通过从系统环境变量里取)
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// ⑶. 发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,加载配置文件,具体请看(ConfigFileApplicationListener)。
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
if (isWebEnvironment(environment) && !this.webEnvironment) {
environment = convertToStandardEnvironment(environment);
}
return environment;
} protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,String[] args) {
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 配置ConfigurableEnvironment中的激活属性
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
environment.getActiveProfiles(); // ensure they are initialized
// additionalProfiles是项目启动时在main中SpringApplication.setAdditionalProfiles("")配置的
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
// 获取环境变量中设置的spring.profiles.active属性
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
// 赋值 activeProfiles
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
分析
⑴. 得到环境对象ConfigurableEnvironment,没有则创建一个StandardServletEnvironment
⑵. 配置激活环境信息,通过从系统环境变量里取或启动时通过SpringApplication.setAdditionalProfiles("")添加进来的
⑶. 发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,加载Spring配置文件信息,例如application.properties等。具体请看Spring Boot 属性文件(三)
步骤3.1.4:
分析
创建ApplicationContext对象 ,本文启动的是SERVLET所以会创建AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext对象
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
会创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader对象检测是否需要将一下对象放到Spring上下文中
// 用户配置Configuration注解,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,在容器刷新时,处理后置工厂处理器用来扫描Spring,注册Bean
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
// 用于配置Autowired注解,实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// 用于配置Required注解,实现了MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口
RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// 用于配置JSR-250注解,实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// 用于配置JPA注解
PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// 用于配置EventListener注解,实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口
EventListenerMethodProcessor
// EventListener工厂
DefaultEventListenerFactory
步骤3.1.5:
代码
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// ⑴.对ApplicationContext设置环境变量;
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// ⑵.配置属性ResourceLoader和ClassLoader属性;
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// ⑶.循环初始化继承ApplicationContextInitializer接口的类
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
} // Add boot specific singleton beans
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
} // Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[sources.size()]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
} @Override
public void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
super.setEnvironment(environment);
this.reader.setEnvironment(environment);
this.scanner.setEnvironment(environment);
}
分析:
⑴.对ApplicationContext设置环境变量;
⑵.配置属性ResourceLoader和ClassLoader属性;
⑶.调用步骤1查询出来ApplicationContextInitializer子类,循环调用initialize()方法。
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(
initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
⑷.发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件。
步骤3.1.6
代码:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// ⑴.准备刷新的上下文环境
prepareRefresh(); // ⑵.初始化BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // ⑶.对BeanFactory进行各种功能填充
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// ⑷.子类覆盖方法做额外的处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // ⑸.激活各种BeanFactory处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // ⑹.注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理,这里只是注册,真正调用是再拿去Bean的时候
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // ⑺.为上下文初始化Message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
initMessageSource(); // ⑻.初始化应用消息广播器,并放到applicationEventMulticaster bean中
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // ⑼.留给子类来初始化其他bean
onRefresh(); // ⑽.在所有注册的bean中查找Listener bean,注册到消息广播中
registerListeners(); // ⑾.初始化剩下的单实例(非惰性)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // ⑿.完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
} // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
分析:
⑴.准备刷新的上下文环境
⑵.初始化BeanFactory
⑶.对BeanFactory进行各种功能填充
⑷.子类覆盖方法做额外的处理,这里会调用子类AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext注入
⑸.激活各种BeanFactory处理器
⑹.注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理,这里只是注册,真正调用是再拿去Bean的时候
⑺.为上下文初始化Message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
⑻.初始化事件派发器,并放到applicationEventMulticaster bean中
⑼.留给子类来初始化其他bean
⑽.在所有注册的bean中查找Listener bean,注册到事件派发器中
⑾.初始化剩下的单实例(非惰性)
⑿.完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人
⑷.子类覆盖方法做额外的处理
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
super.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
if (this.basePackages != null && this.basePackages.length > 0) {
this.scanner.scan(this.basePackages);
}
if (!this.annotatedClasses.isEmpty()) {
this.reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.annotatedClasses));
}
} @Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 添加后置处理器,在创建Tomcat时会利用这个后置处理器来初始化Tomcat Server类
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(
new WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
registerWebApplicationScopes();
}
添加后置处理器,在创建Tomcat时会利用这个后置处理器来初始化Tomcat Server类
⑸.激活各种BeanFactory处理器
主要利用**步骤3.1.4:**创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader对象往Spring容器中注入的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor来处理组件的注入
具体请看容器刷新,
⑺.为上下文初始化Message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
protected void initMessageSource() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.messageSource = beanFactory.getBean(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, MessageSource.class);
// Make MessageSource aware of parent MessageSource.
if (this.parent != null && this.messageSource instanceof HierarchicalMessageSource) {
HierarchicalMessageSource hms = (HierarchicalMessageSource) this.messageSource;
if (hms.getParentMessageSource() == null) {
// Only set parent context as parent MessageSource if no parent MessageSource
// registered already.
hms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using MessageSource [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
else {
//
// Use empty MessageSource to be able to accept getMessage calls.
DelegatingMessageSource dms = new DelegatingMessageSource();
dms.setParentMessageSource(getInternalParentMessageSource());
this.messageSource = dms;
beanFactory.registerSingleton(MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, this.messageSource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate MessageSource with name '" + MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.messageSource + "]");
}
}
}
如果容器中没有则创建一个DelegatingMessageSource国际化,并将它注册到Spring容器中
⑻.初始化事件派发器,并放到applicationEventMulticaster bean中
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Unable to locate ApplicationEventMulticaster with name '" +
APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME +
"': using default [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
}
如果容器中没有则创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster事件派发器,并将它注册到Spring容器中
⑼.留给子类来初始化其他bean
主要目的是初始化Tomcat等内置服务器
SpingBoot启动过程二
⑽.在所有注册的bean中查找Listener bean,注册到事件派发器中
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
// 从容器中获取所有的事件监听器,添加到事件派发器
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
// 如果早期有些事件,则在此将其派发出去
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
⑾.初始化剩下的单实例(非惰性)
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 实例化单实例bean
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// 获取容器中所有的Bean,实例化
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 如果不是抽象,是单实例,并且不是懒加载
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 没有实现FactoryBean接口的Bean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
首先判断Bean不是抽象,是单实例,不是懒加载,再判断Bean没有实现FactoryBean,则调用getBean()方法创建Bean
1 getBean方法创建Bean
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
} @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else {
........省略
// 如果实现了dependsOn则现将dependsOn创建出来
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// 单实例Bean创建
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}
}
1.1 createBean
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
....省略 try {
// 处理InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor类型的后置处理器
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
} try {
// 创建Bean
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
return beanInstance;
}
catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
}
}
会先调用resolveBeforeInstantiation,判断当前后置处理器是否是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,如果是,则提前执行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation,如果applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation方法返回的结果不是null,则执行applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,如果最终结果不是null则直接返回不是则进行doCreateBean方法
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
1.1.1 doCreateBean方法
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
....省略
// 创建bean实例
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
....省略
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// 触发后置处理器MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
....省略
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 为bean属性赋值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
创建Bean,触发后置处理器MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor,执行postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法
1.1.1.1populateBean方法
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 执行后置处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInstantiation方法
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
....省略
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
// 执行后置处理器InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的postProcessPropertyValues方法
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
....省略
// 为属性赋值
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
1.1.1.2 initializeBean方法
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 处理Aware接口
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 后置处理器触发postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 执行初始化方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 后置处理器触发postProcessAfterInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
其它:
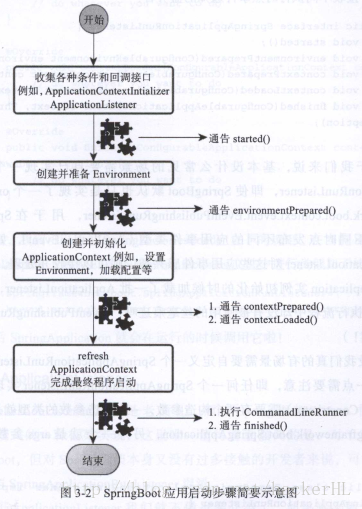
SpringBoot_run()启动流程
SpringApplication实例初始化:
a)、根据classpath里面是否存在特征类(org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationCobtext)来决定创建为web应用使用ApplicationContext类型,还是标准Standalone应用使用的ApplicationContext类型。
b)、使用SpringFactoriesLoader在classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationContextInitiazier
c)、使用SpringFactoriesLoader在classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationListener
d)、推断并main方法的定义类
SpringApplication实例初始化完成,遍历SpringFactoriesLoader可以找到并加载的SpringApplicationRunListnner,调用他们的start()方法。
创建并配置当前SpringBoot应用将要使用的Envrioment(包括配置要使用的PropertySource以及Profile)
遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared()的方法——即通知【run监听器SpringBoot应用的使用环境已经搭建完成】
创建对应类型的ApplicationContext,根据条件决定是否添加ShutdownHook,决定是否使用自定义的BeanNameGenerator、ResourceLoader。将之前准备好的Enviroment设置给创建好的ApplicationContext使用
完成创建ApplicationContext,通过SpringFactoriesLoader查找并加载classpath中所有可用的ApplicationContextInitializer的Initialize()方法来对ApplicationContext进行进一步的处理
遍历所有的SpringApplicationRunListenner的contextPrepared()方法,通知【run监听器】ApplicationContext已经准备好了。
将之前通过@EnableAutoConfiguration获取的所有配置以及其他形式的IOC容器配置加载到已经准备完毕的ApplicationContext
遍历所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()方法,通知【run监听器和ApplicationContext装填完毕】
调用ApplicationContext的refresh()——完成填充IOC容器
查找当前ApplicationContext中是否注册有CommandLineRunner,如果有,则遍历执行它们。
遍历执行SpringApplicationRunListener的finished()。
——启动完毕
————————————————
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hackerHL/article/details/78270780
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u010811939/article/details/80592461
SpringBoot启动过程原理(转)的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot启动过程原理
最近这两年springboot突然火起来了,那么我们就来看看springboot的运行原理. 一.springboot的三种启动方式: 1.运行带有main方法的2.通过命令 Java -jar命令3 ...
- Spring Boot 学习笔记一(SpringBoot启动过程)
SpringBoot启动 Spring Boot通常有一个名为*Application的入口类,在入口类里有一个main方法,这个main方法其实就是一个标准的java应用的入口方法. 在main方法 ...
- Tomcat启动过程原理详解 -- 非常的报错:涉及了2个web.xml等文件的加载流程
Tomcat启动过程原理详解 发表于: Tomcat, Web Server, 旧文存档 | 作者: 谋万世全局者 标签: Tomcat,原理,启动过程,详解 基于Java的Web 应用程序是 ser ...
- SpringBoot启动流程原理解析(二)
在上一章我们分析了SpingBoot启动流程中实例化SpingApplication的过程. return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args ...
- (四)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-预处理ApplicationContext
-- 以下内容均基于2.1.8.RELEASE版本 紧接着上一篇(三)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-创建应用程序上下文,本文将分析上下文创建完毕之后的下一步操作:预处理上下文容器. 预处理上下文 ...
- (三)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-创建应用程序上下文
-- 以下内容均基于2.1.8.RELEASE版本 紧接着上一篇(二)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-环境信息准备,本文将分析环境准备完毕之后的下一步操作:ApplicationContext的创 ...
- (一)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-启动流程概览
-- 以下内容均基于2.1.8.RELEASE版本 通过粗粒度的分析SpringBoot启动过程中执行的主要操作,可以很容易划分它的大流程,每个流程只关注重要操作为后续深入学习建立一个大纲. 官方示例 ...
- (五)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-刷新ApplicationContext
-- 以下内容均基于2.1.8.RELEASE版本 紧接着上一篇[(四)SpringBoot启动过程的分析-预处理ApplicationContext] (https://www.cnblogs.co ...
- springboot启动过程(1)-初始化
1 springboot启动时,只需要调用一个类前面加了@SpringBootApplication的main函数,执行SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication. ...
随机推荐
- 【51nod】1407 与与与与
[51nod]1407 与与与与 设\(f(x)\) 为\(A_{i} \& x == x\)的\(A_{i}\)的个数 设\(g(x)\)为\(x\)里1的个数 \(\sum_{i = 0} ...
- JMeter断言介绍
(1)作用:用于检查测试中得到的响应数据等是否符合预期,用以保证性能测试过程中的数据交互与预期一致 (2)目的:在request的返回层面增加一层判断机制:因为request成功了,并不代表结果一定正 ...
- malloc/free和new/delete详解与应用
C++面试经常会问到关于malloc/free和new/delete的区别,网上有不同版本的解释,这里总结下并加上个人理解和使用. 两者相同点 1.都可以申请动态堆内存. 两者不同点 1.new/de ...
- Idea 使用 Junit4 进行单元测试
目录 Idea 使用 Junit4 进行单元测试 1. Junit4 依赖安装 2. 编写测试代码 3. 生成测试类 4. 运行 Idea 使用 Junit4 进行单元测试 1. Junit4 依赖安 ...
- C# Enum操作
枚举定义 /// <summary> /// 节点类型 /// </summary> public enum NodeTypeEnum { 企业 = , 人员 = , 人员地址 ...
- hdu 5212 反向容斥或者莫比
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5212 题意:忽略.. 题解:把题目转化为求每个gcd的贡献.(http://www.cnblogs.com/z1 ...
- WebSocket协议探究(一)
一 复习和目标 1 复习 上一节使用wireshark抓包分析了WebSocket流量 包含连接的建立:HTTP协议升级WebSocket协议 使用建立完成的WebSocket协议发送数据 2 目标 ...
- reference website
reference website cplusplus http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/ cppreference https://en.cppreference ...
- [转载]Java中继承、装饰者模式和代理模式的区别
[转载]Java中继承.装饰者模式和代理模式的区别 这是我在学Java Web时穿插学习Java设计模式的笔记 我就不转载原文了,直接指路好了: 装饰者模式和继承的区别: https://blog.c ...
- Missing Push Notification Entitlement解决方法
原委 最近提交APP到Apple Store审核,结果很快就收到Apple很"贴心"的邮件.原文如下: Dear developer, We have discovered one ...
