LeetCode 460. LFU Cache LFU缓存 (C++/Java)
题目:
Design and implement a data structure for Least Frequently Used (LFU)cache. It should support the following operations: get and put.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.put(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least frequently used item before inserting a new item. For the purpose of this problem, when there is a tie (i.e., two or more keys that have the same frequency), the least recently used key would be evicted.
Note that the number of times an item is used is the number of calls to the get and put functions for that item since it was inserted. This number is set to zero when the item is removed.
Follow up:
Could you do both operations in O(1) time complexity?
Example:
LFUCache cache = new LFUCache( 2 /* capacity */ ); cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // returns 1
cache.put(3, 3); // evicts key 2
cache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.get(3); // returns 3.
cache.put(4, 4); // evicts key 1.
cache.get(1); // returns -1 (not found)
cache.get(3); // returns 3
cache.get(4); // returns 4
分析:
设计并实现最不经常使用(LFU)缓存的数据结构。相比LRU,LFU增加了频率这一概念,在cache满了的时候,将会把最不经常使用的缓存清除掉,在本题则是以访问频率体现的。
利用hashmap来记录当前数据{key, value}和其出现次数之间的映射,我们可以把出现频率相同的key都放到一个list集合中,再使用一个hashmap建立频率和list之间的映射。为了能够在O(1)的时间内完成操作了,要快速的定位list中key的位置,我们再用一个hashmap来建立key和freq中key的位置之间的映射。最后当然我们还需要两个变量cap和minFreq,分别来保存cache的大小,和当前最小的频率。
我们假设容量为2,先put(1, 1)和put(2, 2),此时容器的存储情况如下:
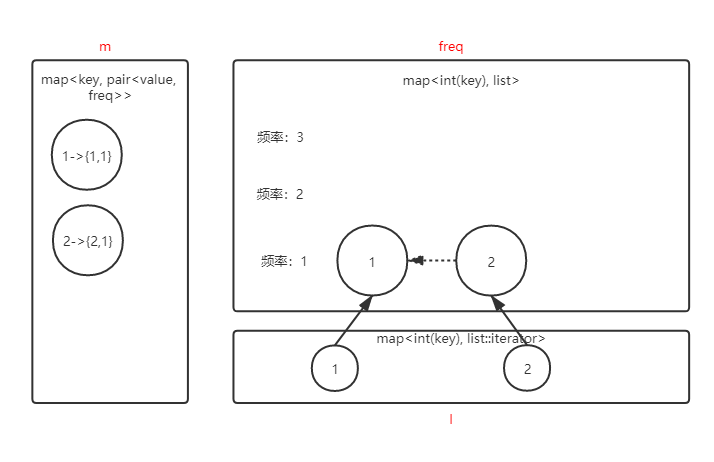
此时调用get(1,1),我们需要做的操作如下:
1.如果m中不存在key1,那么返回-1
2. 从freq中频率为1(从m中获取到的key对应的频率值)的list中将1删除
3. 将m中1对应的频率值自增1
4. 将1保存到freq中频率为2(当前频率加+1)的list的末尾
5. 在l中保存1在freq中频率为2的list中的位置
6. 如果freq中频率为minFreq的list为空,minFreq自增1
7. 返回m中1对应的value值
经过这些步骤后,我们再来看下此时内部容器情况:
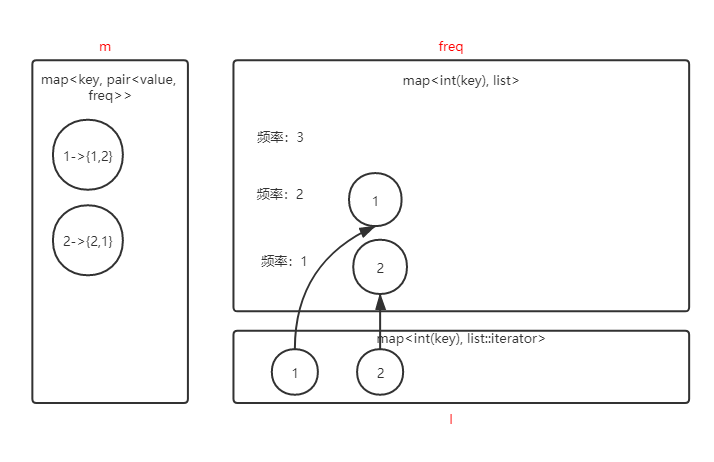
此时再put(3, 3),我们需要做的操作如下:
1. 先调用get(3)返回的结果不是-1,也就是说此时cache中已经存在3这块缓存了,我们可以直接将m中3对应的value更新为当前value,并返回。
2. 如果此时m的大小大于了cap,即超过了cache的容量,则:
a)在m中移除minFreq对应的list的首元素的key。
b)在l中清除3对应的纪录
c)在freq中移除minFreq对应的list的首元素。
3. 在m中建立3的映射,即 3 -> {value 3, frequent1}
4. 在freq中频率为1的list末尾加上3
5. 在l中保存3在freq中频率为1的list中的位置
6. minFreq重置为1
此时内部容器情况:

虚线表示此步骤删去的元素。
程序:
C++
class LFUCache {
public:
LFUCache(int capacity) {
cap = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
if(m.count(key) == 0)
return -1;
freq[m[key].second].erase(l[key]);
m[key].second++;
freq[m[key].second].push_back(key);
l[key] = --freq[m[key].second].end();
if(freq[minFreq].size() == 0)
minFreq++;
return m[key].first;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(cap <= 0)
return;
if(get(key) != -1){
m[key].first = value;
return;
}
if(m.size() >= cap){
m.erase(freq[minFreq].front());
l.erase(freq[minFreq].front());
freq[minFreq].pop_front();
}
m[key] = make_pair(value, 1);
freq[1].push_back(key);
l[key] = --freq[1].end();
minFreq = 1;
}
private:
int cap, minFreq;
unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> m;
unordered_map<int, list<int>> freq;
unordered_map<int, list<int>::iterator> l;
};
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LFUCache* obj = new LFUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/
Java
public class LFUCache {
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
cap = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
freq = new HashMap<>();
list = new HashMap<>();
minFreq = 1;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!map.containsKey(key))
return -1;
int count = freq.get(key);
list.get(count).remove(key);
freq.put(key, count + 1);
if(list.get(minFreq).size() == 0)
minFreq++;
if(!list.containsKey(count + 1)){
LinkedHashSet<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
set.add(key);
list.put(count+1, set);
}else{
list.get(count+1).add(key);
}
return map.get(key);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(cap <= 0)
return;
if(get(key) != -1){
map.put(key, value);
return;
}
if(map.size() >= cap){
Integer removeKey = list.get(minFreq).iterator().next();
map.remove(removeKey);
list.get(minFreq).remove(removeKey);
freq.remove(removeKey);
}
//System.out.println(map.toString());
map.put(key, value);
freq.put(key, 1);
if(!list.containsKey(1)){
LinkedHashSet<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<Integer>();
set.add(key);
list.put(1, set);
}else{
list.get(1).add(key);
}
minFreq = 1;
}
private int cap;
private int minFreq;
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> map;
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> freq;
private HashMap<Integer, LinkedHashSet<Integer>> list;
}
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LFUCache obj = new LFUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
LeetCode 460. LFU Cache LFU缓存 (C++/Java)的更多相关文章
- LeetCode:146_LRU cache | LRU缓存设计 | Hard
题目:LRU cache Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should su ...
- [LeetCode] 460. LFU Cache 最近最不常用页面置换缓存器
Design and implement a data structure for Least Frequently Used (LFU) cache. It should support the f ...
- [LeetCode] LFU Cache 最近最不常用页面置换缓存器
Design and implement a data structure for Least Frequently Used (LFU) cache. It should support the f ...
- leetcode 146. LRU Cache 、460. LFU Cache
LRU算法是首先淘汰最长时间未被使用的页面,而LFU是先淘汰一定时间内被访问次数最少的页面,如果存在使用频度相同的多个项目,则移除最近最少使用(Least Recently Used)的项目. LFU ...
- Leetcode: LFU Cache && Summary of various Sets: HashSet, TreeSet, LinkedHashSet
Design and implement a data structure for Least Frequently Used (LFU) cache. It should support the f ...
- LeetCode LFU Cache
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/lfu-cache/?tab=Description 题目: Design and implement a data str ...
- LeetCode之LRU Cache 最近最少使用算法 缓存设计
设计并实现最近最久未使用(Least Recently Used)缓存. 题目描述: Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently ...
- [LeetCode] 146. LRU Cache 最近最少使用页面置换缓存器
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the fol ...
- LFU Cache
2018-11-06 20:06:04 LFU(Least Frequently Used)算法根据数据的历史访问频率来淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据过去被访问多次,那么将来被访问的频率也更高”. ...
- LRU缓存实现(Java)
LRU Cache的LinkedHashMap实现 LRU Cache的链表+HashMap实现 LinkedHashMap的FIFO实现 调用示例 LRU是Least Recently Used 的 ...
随机推荐
- 力扣627(MySQL)-变更性别(简单)
题目: Salary 表: 请你编写一个 SQL 查询来交换所有的 'f' 和 'm' (即,将所有 'f' 变为 'm' ,反之亦然),仅使用 单个 update 语句 ,且不产生中间临时表. 注意 ...
- 力扣665(java)-非递减数列(中等)
题目: 给你一个长度为 n 的整数数组 nums ,请你判断在 最多 改变 1 个元素的情况下,该数组能否变成一个非递减数列. 我们是这样定义一个非递减数列的: 对于数组中任意的 i (0 <= ...
- 巧用API网关构建大型应用体系架构
简介: 近期阿里云重磅发布了BizWorks一体化的云原生应用的开发和运营平台,内置阿里巴巴业务中台构建的最佳技术实践.它已经将API网关作为关键组件融入其中,并且基于API网关为用户提供能力开放平台 ...
- iLogtail使用入门-K8S环境日志采集到SLS
简介:iLogtail是阿里云中简单日志服务又名"SLS"的采集部分. 它用于收集遥测数据,例如日志.跟踪和指标,目前已经正式开源(https://github.com/alib ...
- 【开通指南】 实时计算 Flink 全托管版本
简介: [开通指南]实时计算 Flink 全托管版本 1.试用的实时计算 Flink 版产品是后付费还是预付费?是否有额外费用产生?预付费,有额外的SLB费用,一天2元封顶.(开通 Flink 全托管 ...
- PHP vs Golang ? 想什么呢 ! What Are You Thinking !
在使用 PHP 多年之后,我对 PHP 的优势和劣势已经非常清楚,与后起之秀 Golang 相比,两者已经不在一个重量级. PHP 更像是 70 kg 级别的选手,脚本语言,极速开发,部署方便,性能可 ...
- WPF 框架开发 调试和开发 XAML 构建过程的 PresentationBuildTasks 方法
阅读本文,你可以了解如何编写开发和调试 XAML 构建为 Baml 和 g.cs 文件的过程和工具.本文也适合想要了解 WPF 的 XAML 构建过程的开发者阅读,本文提供了可以断点调试 WPF 的 ...
- 案例-java贪吃蛇(附源码)
创建屏幕 开始游戏的窗口,首先引入窗口,然后在窗口画布上进行添加各类动画. JFrame frame=new JFrame("My SnakeGame"); Jframe 是个类, ...
- C#.Net筑基-运算符🔣Family
C#运算符 内置了丰富的运算符操作类型,使用方便,极大的简化了编码,同时还支持多种运算符重载机制,让自定义的类型也能支持运算符行为. 01.运算符概览 运算符分类 描述 数学运算 基础的加减乘除,及+ ...
- 利用pearcmd实现裸文件包含
利用pearcmd实现裸文件包含 在 ctf 中,常常有这样一类题: 题目很简单,一般围绕一个 include 函数展开. 例: ctfshow 元旦水友赛 easy_include 这类题目没有提供 ...
