Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) A B C 思路 枚举 数学
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
A magic island Geraldion, where Gerald lives, has its own currency system. It uses banknotes of several values. But the problem is, the system is not perfect and sometimes it happens that Geraldionians cannot express a certain sum of money with any set of banknotes. Of course, they can use any number of banknotes of each value. Such sum is called unfortunate. Gerald wondered: what is the minimum unfortunate sum?
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of values of the banknotes that used in Geraldion.
The second line contains n distinct space-separated numbers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — the values of the banknotes.
Print a single line — the minimum unfortunate sum. If there are no unfortunate sums, print - 1.
5
1 2 3 4 5
-1 题意:给你n个数 可多次取任意组合并求和 令不能组成的数为 不幸运的数 问你最小的不幸运的数 若不存在输出-1
题解:可以发现若n个数中存在1则可以表示任何的数 否则不能表示的最小的数为-1
/*/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
using namespace std;
const int N=;
const int mod=;
const int MOD1=;
const int MOD2=;
const double EPS=0.00000001;
//typedef long long ll;
typedef __int64 ll;
const ll MOD=;
const int INF=;
const ll MAX=1ll<<;
const double eps=1e-;
const double inf=~0u>>;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
typedef double db;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int n;
int flag=;
int exm;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&exm);
if(exm==)
flag=;
}
if(flag)
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
else
cout<<""<<endl; return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Gerald bought two very rare paintings at the Sotheby's auction and he now wants to hang them on the wall. For that he bought a special board to attach it to the wall and place the paintings on the board. The board has shape of an a1 × b1 rectangle, the paintings have shape of a a2 × b2 and a3 × b3 rectangles.
Since the paintings are painted in the style of abstract art, it does not matter exactly how they will be rotated, but still, one side of both the board, and each of the paintings must be parallel to the floor. The paintings can touch each other and the edges of the board, but can not overlap or go beyond the edge of the board. Gerald asks whether it is possible to place the paintings on the board, or is the board he bought not large enough?
The first line contains two space-separated numbers a1 and b1 — the sides of the board. Next two lines contain numbers a2, b2, a3 and b3 — the sides of the paintings. All numbers ai, bi in the input are integers and fit into the range from 1 to 1000.
If the paintings can be placed on the wall, print "YES" (without the quotes), and if they cannot, print "NO" (without the quotes).
3 2
1 3
2 1
YES
5 5
3 3
3 3
NO
4 2
2 3
1 2
YES
That's how we can place the pictures in the first test:

And that's how we can do it in the third one.
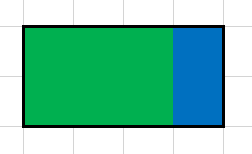
题意:给你三个矩形的边长 判断第2,3个矩形能否放入第1个矩形
题解:很恶心的列举一下 以下一种精巧的代码
/*/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
using namespace std;
#define A first
#define B second
const int N=;
const int mod=;
const int MOD1=;
const int MOD2=;
const double EPS=0.00000001;
//typedef long long ll;
typedef __int64 ll;
const ll MOD=;
const int INF=;
const ll MAX=1ll<<;
const double eps=1e-;
const double inf=~0u>>;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
typedef double db;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int main(){
pair<int,int> a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d", &a.A, &a.B, &b.A, &b.B, &c.A, &c.B);
for(int k=;k<;k++,swap(a.A,a.B))
for(int i=;i<;i++,swap(b.A,b.B))
for(int j=;j<;j++,swap(c.A,c.B))
if (a.A>=max(b.A,c.A)&&a.B>=b.B+c.B){
puts("YES");
return ;
}
puts("NO");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Gerald got a very curious hexagon for his birthday. The boy found out that all the angles of the hexagon are equal to 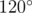 . Then he measured the length of its sides, and found that each of them is equal to an integer number of centimeters. There the properties of the hexagon ended and Gerald decided to draw on it.
. Then he measured the length of its sides, and found that each of them is equal to an integer number of centimeters. There the properties of the hexagon ended and Gerald decided to draw on it.
He painted a few lines, parallel to the sides of the hexagon. The lines split the hexagon into regular triangles with sides of 1 centimeter. Now Gerald wonders how many triangles he has got. But there were so many of them that Gerald lost the track of his counting. Help the boy count the triangles.
The first and the single line of the input contains 6 space-separated integers a1, a2, a3, a4, a5 and a6 (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1000) — the lengths of the sides of the hexagons in centimeters in the clockwise order. It is guaranteed that the hexagon with the indicated properties and the exactly such sides exists.
Print a single integer — the number of triangles with the sides of one 1 centimeter, into which the hexagon is split.
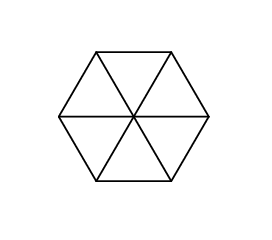
1 1 1 1 1 1
6
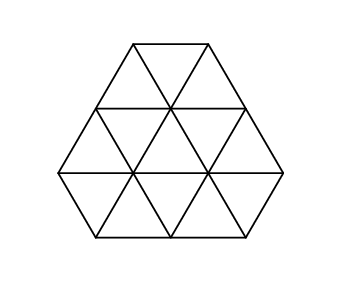
1 2 1 2 1 2
13
This is what Gerald's hexagon looks like in the first sample:
And that's what it looks like in the second sample:
题意:如图由正三角形组成的六边形 给你六条边的长度 输出三角形的个数
题解:先补全成一个大的正三角 之后剪去缺角
/*/******************************
code by drizzle
blog: www.cnblogs.com/hsd-/
^ ^ ^ ^
O O
******************************/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
using namespace std;
const int N=;
const int mod=;
const int MOD1=;
const int MOD2=;
const double EPS=0.00000001;
//typedef long long ll;
typedef __int64 ll;
const ll MOD=;
const int INF=;
const ll MAX=1ll<<;
const double eps=1e-;
const double inf=~0u>>;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
typedef double db;
typedef unsigned int uint;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6;
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d %d %d %d",&a1,&a2,&a3,&a4,&a5,&a6);
int sum=a1+a2+a3;
int ans=sum+sum*(sum-);
int ans1=a1+a1*(a1-);
int ans2=(a3+a3*(a3-));
int ans3=(a5+a5*(a5-));
printf("%d\n",ans-ans1-ans2-ans3);
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) A B C 思路 枚举 数学的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 1)
官方英文题解:http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/19237 Problem A: 题目大意: 给出内角和均为120°的六边形的六条边长(均为正整数),求最多能划分成多少 ...
- dp - Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 1) C. Gerald and Giant Chess
Gerald and Giant Chess Problem's Link: http://codeforces.com/contest/559/problem/C Mean: 一个n*m的网格,让你 ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 1) B. Equivalent Strings
Equivalent Strings Problem's Link: http://codeforces.com/contest/559/problem/B Mean: 给定两个等长串s1,s2,判断 ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 1) A. Gerald's Hexagon
Gerald's Hexagon Problem's Link: http://codeforces.com/contest/559/problem/A Mean: 按顺时针顺序给出一个六边形的各边长 ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2)B.B. Gerald is into Art
B. Gerald is into Art Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/problemset/ ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) D. Equivalent Strings
D. Equivalent Strings Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/559/ ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) C. Gerald's Hexagon 数学
C. Gerald's Hexagon Time Limit: 2 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/559/pr ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) A. Currency System in Geraldion
A. Currency System in Geraldion Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/co ...
- Codeforces Round #313 (Div. 2) E. Gerald and Giant Chess (Lucas + dp)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/560/problem/E 给你一个n*m的网格,有k个坏点,问你从(1,1)到(n,m)不经过坏点有多少条路径. 先把这些坏点排 ...
随机推荐
- 四个使用this的典型应用
(1)在html元素事件属性中使用,如 <input type=”button” onclick=”showInfo(this);” value=”点击一下”/> (2)构造函数 func ...
- POJ 2594 传递闭包的最小路径覆盖
Treasure Exploration Time Limit: 6000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 7171 Accepted: 2 ...
- 青蛙的烦恼(dp好题)
有n片荷叶正好在一凸多边形顶点上 有一只小青蛙恰好站在1号荷叶的点 小青蛙可以从一片荷叶上跳到另外任意一片荷叶上 给出N个点的坐标N<800 求小青蛙想通过最短的路程遍历所有的荷叶一次且仅一次的 ...
- WinForm 中 VScrollBar Maximum 问题
最近在做一个鼠标经过弹出 TreeView 面板功能 , 要求鼠标离开TreeView区域,隐藏面板. 功能如期开发,其中当TreeView 出现滚动条时,鼠标经过TreeView中的滚动条时,提前 ...
- xcode6 ios launchimage
1.点击Image.xcassets 进入图片管理,然后右击,弹出"New Launch Image" 2.右侧的勾选可以让你选择是否要对ipad,横屏,竖屏,以及低版本的ios系 ...
- 分布式一致性原理—CAP
背景 随着分布式事务的出现,传统的单机事务模型(ACID)已经无法胜任,尤其是对于一个高访问量.高并发的互联网分布式系统来说. 如果我们要求严格一致性,很可能就需要牺牲掉系统的可用性,反之亦然.但两者 ...
- LightOJ 1141 Program E
Description In this problem, you are given an integer number s. You can transform any integer number ...
- android shape详解
shape--> shape属性: rectangle: 矩形,默认的形状,可以画出直角矩形.圆角矩形.弧形等 solid: 设置形状填充的颜色,只有android:color一个属性 andr ...
- [windows驱动]标准驱动例程
[注]routine:例行程序. 1.标准驱动例程简介: 每一个内核态驱动程序都是由一系列系统定义的,标准的驱动例程组成.内核态驱动在这些标准例程中通过调用系统提供的驱动支持函数处理I/O请求包.为了 ...
- jsp弹出Please check the location and try again!对话框
关闭它的jsp图形模式.myeclipse10中打开jsp文件时,右键open with 选MyEclipse JSP Editor,不选MyEclipse Visual JSP Editor模式.
