线程池 execute 和 submit 的区别
代码示例:
public class ThreadPool_Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
pool.execute(new MyRunner());
Future<String> future = pool.submit(new MyCaller());
String ret = future.get();
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
class MyCaller implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("calling");
return "return_from_call";
}
}
class MyRunner implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("running");
}
}
execute 方法执行 runnable 任务,submit 方法执行 callable 任务,callable 任务有返回值,而 runnable 任务是 void 的,无返回值。
// void java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask;
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // allow interrupts
boolean completedAbruptly = true;
try {
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock();
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt();
try {
beforeExecute(wt, task);
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run();
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
afterExecute(task, thrown);
}
} finally {
task = null;
w.completedTasks++;
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
对于 Runnable,task 是 MyRunner,对于 Callable,task 是 FutureTask。
submit 方法的调用栈:
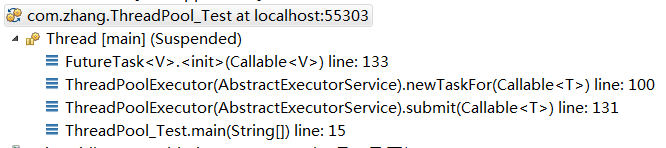
创建 FutureTask 对象,把 Callable 对象包裹起来,在 run 方法中调用 Callable 对象的方法,并设置返回值。
// java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.FutureTask
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
} public void run() {
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
线程池 execute 和 submit 的区别的更多相关文章
- 详解线程池execute和submit用法
在使用线程池时,我们都知道线程池有两种提交任务的方式,那么他们有什么区别呢? 1.execute提交的是Runnable类型的任务,而submit提交的是Callable或者Runnable类型的任务 ...
- 线程池提交任务的两种方式:execute与submit的区别
Java中的线程池在进行任务提交时,有两种方式:execute和submit方法. 一.execute和submit的区别 execute只能提交Runnable类型的任务,无返回值.submit既可 ...
- execute和submit的区别与联系
execute和submit都属于线程池的方法,execute只能提交Runnable类型的任务,而submit既能提交Runnable类型任务也能提交Callable类型任务. execute会直接 ...
- JAVA线程池shutdown和shutdownNow的区别
一.区别介绍 shutDown() 当线程池调用该方法时,线程池的状态则立刻变成SHUTDOWN状态.此时,则不能再往线程池中添加任何任务,否则将会抛出RejectedExecutionExcept ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor中execute和submit的区别
1:入参不同 excute() 传入的是 Runable, submit 传入的是 Callable 或 Runable 1):execute 方法源码 public void execute(Run ...
- ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor线程池scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay的区别
ScheduledFuture<?> result = executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(task,2, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 在延迟2秒之后 ...
- Java 并发编程——Executor框架和线程池原理
Eexecutor作为灵活且强大的异步执行框架,其支持多种不同类型的任务执行策略,提供了一种标准的方法将任务的提交过程和执行过程解耦开发,基于生产者-消费者模式,其提交任务的线程相当于生产者,执行任务 ...
- Java提高班(二)深入理解线程池ThreadPool
本文你将获得以下信息: 线程池源码解读 线程池执行流程分析 带返回值的线程池实现 延迟线程池实现 为了方便读者理解,本文会由浅入深,先从线程池的使用开始再延伸到源码解读和源码分析等高级内容,读者可根据 ...
- 线程池-Executors
合理使用线程池能够带来三个好处 减少创建和销毁线程上所花的时间以及系统资源的开销 提高响应速度.当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行 提高线程的客观理性.线程是稀缺资源,如果无限制的创 ...
随机推荐
- C++中substr函数的用法
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main(){ string str("12 ...
- 清华镜像方法更新python包
来自:Jinlong_Xu cmd环境下执行: conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pk ...
- JDBC的通用查询的方法
PreparedStatement 1.Why 1):使用Statement需要进行拼写SQL语句,很辛苦,而且容易出错. 2):使用Statement可以发生SQL注入. SQl注入: SQL注入是 ...
- java类加载器和双亲委派模型
一. 类加载器 ClassLoader即常说的类加载器,其功能是用于从Class文件加载所需的类,主要场景用于热部署.代码热替换等场景. 系统提供3种的类加载器:Bootstrap ClassLoad ...
- MySQL学习(六)
1 注意 select cout(*) from 表名: 查询的就是绝对的行数,哪怕某一列所有字段全部为NULL,也计算在内.而select cout(列名) form 表名:查询的是该列不为null ...
- 简单实现Java的RMI——远程方法调用
一.RMI简介: 说到RMI就不得不说RPC了. RPC:(Remote Procedure Call),远程过程调用. RMI(Remote Method Invocation),远程方法调用. R ...
- JAVA基础知识总结:二十一
一.URL和URLConnection 1.HTTP 超文本传输协议 是一个应用层的协议 是一个被动的协议 只有客户端主动给服务端发送消息,服务端才会给客户端一个响应 2.URL 统一的资源定位符(网 ...
- (转)C#反射使用时注意BindingFlags的用法
c#反射查找方法时,默认只能查到public方法.如果想要查找private方法,需要设定BindingFlags. 即: BindingFlags.Public|BindingFlags.Insta ...
- 单细胞数据初步处理 | drop-seq | QC | 质控 | 正则化 normalization
比对 The raw Drop-seq data was processed with the standard pipeline (Drop-seq tools version 1.12 from ...
- springboot---->java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
springboot aop编程时,在方法上加入通知的注解,添加织入路径测试,发生报错: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Pointcut is not wel ...
