Getting Started with Blocks
本文来源为:developer.apple.com,仅仅是博主练习排版所用。
Getting Started with Blocks
The following sections help you to get started with blocks using practical examples.
Declaring and Using a Block
You use the ^ operator to declare a block variable and to indicate the beginning of a block literal. The body of the block itself is contained within {}, as shown in this example (as usual with C, ; indicates the end of the statement):
int multiplier = 7;
int (^myBlock)(int) = ^(int num) {
return num * multiplier;
};
The example is explained in the following illustration:
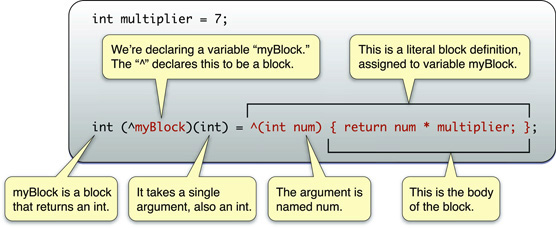
Notice that the block is able to make use of variables from the same scope in which it was defined.
If you declare a block as a variable, you can then use it just as you would a function:
int multiplier = 7;
int (^myBlock)(int) = ^(int num) {
return num * multiplier;
};
printf("%d", myBlock(3));
// prints "21"
Using a Block Directly
In many cases, you don’t need to declare block variables; instead you simply write a block literal inline where it’s required as an argument. The following example uses the qsort_b function. qsort_b is similar to the standard qsort_r function, but takes a block as its final argument.
char *myCharacters[3] = { "TomJohn", "George", "Charles Condomine" };
qsort_b(myCharacters, 3, sizeof(char *), ^(const void *l, const void *r) {
char *left = *(char **)l;
char *right = *(char **)r;
return strncmp(left, right, 1);
});
Blocks with Cocoa
Several methods in the Cocoa frameworks take a block as an argument, typically either to perform an operation on a collection of objects, or to use as a callback after an operation has finished. The following example shows how to use a block with the NSArray method sortedArrayUsingComparator:. The method takes a single argument—the block. For illustration, in this case the block is defined as an NSComparator local variable:
NSArray *stringsArray = @[ @"string 1",
@"String 21",
@"string 12",
@"String 11",
@"String 02" ];
static NSStringCompareOptions comparisonOptions = NSCaseInsensitiveSearch | NSNumericSearch |
NSWidthInsensitiveSearch | NSForcedOrderingSearch;
NSLocale *currentLocale = [NSLocale currentLocale];
NSComparator finderSortBlock = ^(id string1, id string2) {
NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(0, [string1 length]);
return [string1 compare:string2 options:comparisonOptions range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
};
NSArray *finderSortArray = [stringsArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:finderSortBlock];
NSLog(@"finderSortArray: %@", finderSortArray);
/*
Output: NSArray *stringArray = @[ @"string 1", @"string 2", @"string21", @"string 12", @"string 02"];
NSComparator finderSortBlock = ^(id string1, id string2){
NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(0, [string1 length]);
return [string1 compare:string2 options:comparisonOptions range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
};
NSArray *findSortArray = [stringArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:finderSortBlock];
NSLog(@"...:%@",findSortArray);
finderSortArray: (
"string 1",
"String 02",
"String 11",
"string 12",
"String 21"
)
*/
__block Variables
A powerful feature of blocks is that they can modify variables in the same lexical scope. You signal that a block can modify a variable using the __block storage type modifier. Adapting the example shown in Blocks with Cocoa, you could use a block variable to count how many strings are compared as equal as shown in the following example. For illustration, in this case the block is used directly and uses currentLocale as a read-only variable within the block:
NSArray *stringsArray = @[ @"string 1",
@"String 21", // <-
@"string 12",
@"String 11",
@"Strîng 21", // <-
@"Striñg 21", // <-
@"String 02" ];
NSLocale *currentLocale = [NSLocale currentLocale];
__block NSUInteger orderedSameCount = 0;
NSArray *diacriticInsensitiveSortArray = [stringsArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:^(id string1, id string2) {
NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(0, [string1 length]);
NSComparisonResult comparisonResult = [string1 compare:string2 options:NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
if (comparisonResult == NSOrderedSame) {
orderedSameCount++;
}
return comparisonResult;
}];
NSLog(@"diacriticInsensitiveSortArray: %@", diacriticInsensitiveSortArray);
NSLog(@"orderedSameCount: %d", orderedSameCount);
/*
Output:
diacriticInsensitiveSortArray: (
"String 02",
"string 1",
"String 11",
"string 12",
"String 21",
"Str\U00eeng 21",
"Stri\U00f1g 21"
)
orderedSameCount: 2
*/
This is discussed in greater detail in Blocks and Variables.
Getting Started with Blocks的更多相关文章
- 从Script到Code Blocks、Code Behind到MVC、MVP、MVVM
刚过去的周五(3-14)例行地主持了技术会议,主题正好是<UI层的设计模式——从Script.Code Behind到MVC.MVP.MVVM>,是前一天晚上才定的,中午花了半小时准备了下 ...
- 【POJ-1390】Blocks 区间DP
Blocks Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 5252 Accepted: 2165 Descriptio ...
- 开发该选择Blocks还是Delegates
前文:网络上找了很多关于delegation和block的使用场景,发现没有很满意的解释,后来无意中在stablekernel找到了这篇文章,文中作者不仅仅是给出了解决方案,更值得我们深思的是作者独特 ...
- poj 1390 Blocks
poj 1390 Blocks 题意 一排带有颜色的砖块,每一个可以消除相同颜色的砖块,,每一次可以到块数k的平方分数.问怎么消能使分数最大.. 题解 此题在徐源盛<对一类动态规划问题的研究&g ...
- Java 同步代码块 - Synchronized Blocks
java锁实现原理: http://blog.csdn.net/endlu/article/details/51249156 The synchronized keyword can be used ...
- 区块 Blocks
Structure / Blocks / Demonstrate block regions
- 使用Code::blocks在windows下写网络程序
使用Code::blocks在windows下写网络程序 作者 He YiJun – storysnail<at>gmail.com 团队 ls 版权 转载请保留本声明! 本文档包含的原创 ...
- Code::Blocks配置GTK+2和GTK+3
Code::Blocks配置GTK+2和GTK+3 作者 He YiJun – storysnail<at>gmail.com 团队 ls 版权 转载请保留本声明! 本文档包含的原创代码根 ...
- [翻译]理解Ruby中的blocks,Procs和lambda
原文出处:Understanding Ruby Blocks, Procs and Lambdas blocks,Procs和lambda(在编程领域被称为闭包)是Ruby中很强大的特性,也是最容易引 ...
- Java Synchronized Blocks
From http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-concurrency/synchronized.html By Jakob Jenkov A Java synchro ...
随机推荐
- django xadmin 模板的定制
编辑新增等页面对应的modelform为ModelFormAdminView (xadmin.views.edit.ModelFormAdminView) 通过源码分析,新增对象的template属性 ...
- phpcms评论的url替换问题
在整个项目改ip之前,评论里的url是127.0.1.113 改成localhost之后,更新了所有的url和缓存,但是v9_comment表中的url字段没有更新. 想一下后台只有一个地方是替换数据 ...
- 史上最详细的CocoaPods安装教程
虽然网上关于CocoaPods安装教程多不胜数,但是我在安装的过程中还是出现了很多错误,所以大家可以照下来步骤装一下,我相信会很好用. 前言 在iOS项目中使用第三方类库可以说是非常常见的事,但是要正 ...
- JAVA分布式事务原理及应用(转)
JTA(Java Transaction API)允许应用程序执行分布式事务处理--在两个或多个网络计算机资源上访问并且更新数据. JDBC驱动程序的JTA支持极大地增强了数据访问能力. 本文的目 ...
- mach 和 array 方法
- 将数据导入带模板EXCEL
在EXCEL模板里设置好样式和格式 点击事件 private void btnReport_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { ...
- ACM/ICPC 之 优先级队列+设置IO缓存区(TSH OJ-Schedule(任务调度))
一个裸的优先级队列(最大堆)题,但也有其他普通队列的做法.这道题我做了两天,结果发现是输入输出太过频繁,一直只能A掉55%的数据,其他都是TLE,如果将输入输出的数据放入缓存区,然后满区输出,可以将I ...
- Lake Counting_深度搜索_递归
Lake Counting Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 30414 Accepted: 15195 D ...
- 【leetcode】Binary Tree Right Side View(middle)
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nod ...
- ssh自动登陆
突然碰到有人问ssh再传输密钥时候能不手动输入密码,由于没有碰到过这种情况,所以查了一下发现可以用sshpass做到. sshpass [参数] ssh命令: 参数: -p password #将参 ...
