CodeForces 51F Caterpillar
An undirected graph is called a caterpillar if it is a connected graph without cycles and it has such a path p that any vertex is located at a distance of at most 1 from the path p. The caterpillar can contain loops (edges from a vertex to itself) but cannot contain multiple (parallel) edges.
The picture contains an example of a caterpillar:
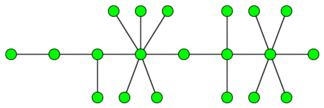
You are given an undirected graph G. You are allowed to do a merging operations, each such operation merges two vertices into one vertex. For that two any vertices a and b (a ≠ b) are chosen. These verteces are deleted together with their edges (which are incident to at least one of the vertices a or b) but a new vertex w is added together with edges (x, w) for each edge (a, w) and/or (b, w). If there was the edge (a, b) it transforms to the loop (w, w). The resulting graph (after the merging operation) may contain multiple (parallel) edges between pairs of vertices and loops. Let us note that this operation decreases the number of vertices of graph by 1 but leaves the number of edges in the graph unchanged.
The merging operation can be informally described as a unity of two vertices of the graph into one with the natural transformation of the graph edges.
You may apply this operation consecutively and make the given graph to be a caterpillar. Write a program that will print the minimal number of merging operations required to make the given graph a caterpillar.
The first line contains a pair of integers n, m (1 ≤ n ≤ 2000;0 ≤ m ≤ 105), where n represents the number of vertices in the graph andm is the number of edges in it. Then the following m lines contain edge descriptions, one edge description per line. Every line contains a pair of integers ai, bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n;ai ≠ bi), ai, bi which represent the indices of the vertices connected by the edge. The vertices are numbered from 1 to n. In the given graph it will be no more than one edge between any pair of vertices. The given graph is not necessarily connected.
Print the minimal required number of operations.
4 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 2
2
6 3
1 2
3 4
5 6
2
7 6
1 2
2 3
1 4
4 5
1 6
6 7
1
缩点
目标状态是一棵树,可以有自环,不能有重边。tarjan缩点后,原图形成一片森林,对于每一棵树,它最多可以保留点数res=直径上的点数+其他叶子结点树。处理森林中的每一棵树,ans=total-res
_____
刚开始没察觉到有森林,按照树处理,WA飞
之后因为缩点后重边加多了,T飞
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int mx[]={,,,-,};
const int my[]={,,,,-};
const int mxn=;
int read(){
int x=,f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'' || ch>''){if(ch=='-')f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='' && ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
struct edge{
int v,nxt;
}e[];
int hd[mxn],mct=;
void add_edge(int u,int v){
e[++mct].v=v;e[mct].nxt=hd[u];hd[u]=mct;return;
}
int mp[mxn][mxn];
int n,m;
int dtime=;
int low[mxn],dfn[mxn];
int belone[mxn],cnt;
int st[mxn],top=;
void tarjan(int u,int fa){
dfn[u]=low[u]=++dtime;
st[++top]=u;
for(int i=hd[u];i;i=e[i].nxt){
int v=e[i].v;
if(v==fa)continue;
if(!dfn[v]){
tarjan(v,u);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}
else low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
if(dfn[u]==low[u]){
cnt++;
int v=;
do{
v=st[top--];
belone[v]=cnt;
}while(v!=u);
}
return;
}
vector<int>eg[mxn];
int dis[mxn];
bool vis[mxn];int kct=;
int tg=;
void DFS(int u,int fa){
vis[u]=;
dis[u]=dis[fa]+;
if(dis[u]>dis[tg])tg=u;
for(int i=;i<eg[u].size();i++){
int v=eg[u][i];
if(v==fa)continue;
DFS(v,u);
}
return;
}
int pos1,pos2;
int outd[mxn];
int solve(){
if(cnt==)return n-;
int i,j;
for(i=;i<=n;i++){
for(j=hd[i];j;j=e[j].nxt){
int v=e[j].v;
if(mp[belone[i]][belone[v]])continue;
if(belone[i]!=belone[v]){
eg[belone[i]].push_back(belone[v]);
mp[belone[i]][belone[v]]=;//防止加重边
outd[belone[i]]++;
}
}
}
int res=;
for(i=;i<=cnt;i++)if(outd[i]==) res++;//叶子节点数
for(i=;i<=cnt;i++){
if(vis[i])continue;
kct++;//联通块计数
//
tg=;
DFS(i,);
pos1=tg;
tg=;
DFS(pos1,);
pos2=tg;
//求直径
if(dis[pos2]<)res++;
else res+=dis[pos2]-;
}
return n-res+kct-;
}
int main()
{
n=read();m=read();
int i,j,u,v;
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
u=read();v=read();
add_edge(u,v);
add_edge(v,u);
}
for(i=;i<=n;i++)
if(!dfn[i])tarjan(i,);
int ans=solve();
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
CodeForces 51F Caterpillar的更多相关文章
- Educational Codeforces Round 10 A. Gabriel and Caterpillar 模拟
A. Gabriel and Caterpillar 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/652/problem/A Description The 9-t ...
- codeforces 652A A. Gabriel and Caterpillar(水题)
题目链接: A. Gabriel and Caterpillar time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes in ...
- CodeForces 652A Gabriel and Caterpillar
简单模拟. #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> ...
- python爬虫学习(5) —— 扒一下codeforces题面
上一次我们拿学校的URP做了个小小的demo.... 其实我们还可以把每个学生的证件照爬下来做成一个证件照校花校草评比 另外也可以写一个物理实验自动选课... 但是出于多种原因,,还是绕开这些敏感话题 ...
- 【Codeforces 738D】Sea Battle(贪心)
http://codeforces.com/contest/738/problem/D Galya is playing one-dimensional Sea Battle on a 1 × n g ...
- 【Codeforces 738C】Road to Cinema
http://codeforces.com/contest/738/problem/C Vasya is currently at a car rental service, and he wants ...
- 【Codeforces 738A】Interview with Oleg
http://codeforces.com/contest/738/problem/A Polycarp has interviewed Oleg and has written the interv ...
- CodeForces - 662A Gambling Nim
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/662/A 题目大意: 给定n(n <= 500000)张卡片,每张卡片的两个面都写有数字,每个面都有0.5的概 ...
- CodeForces - 274B Zero Tree
http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/274/B 题目大意: 给定你一颗树,每个点上有权值. 现在你每次取出这颗树的一颗子树(即点集和边集均是原图的子集的连 ...
随机推荐
- 15个nosql数据库
1.MongoDB 介绍 MongoDB是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库.由C++语言编写.主要解决的是海量数据的访问效率问题,为WEB应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案.当数据量达到50GB以上 ...
- tomcat启动时报错
http://www.oschina.net/question/1162040_229925?sort=time 解决:
- ORACLE 定时执行存储过程
推荐用dbms_scheduler方式更好 (2012-11-19注) /* 查询: select job,broken,what,interval,t.* from user_jobs t; job ...
- python数字图像处理(16):霍夫圆和椭圆变换
在极坐标中,圆的表示方式为: x=x0+rcosθ y=y0+rsinθ 圆心为(x0,y0),r为半径,θ为旋转度数,值范围为0-359 如果给定圆心点和半径,则其它点是否在圆上,我们就能检测出来了 ...
- Incorrect string value异常解决
mysql数据库的一个问题 1366-Incorrect string value:'\xE5\x8D\xA1\xE5......' for column 'filename' at row 1 问题 ...
- 新时代的coder如何成为专业程序员
在移动互联网"泛滥"的今天,越来越多非专业(这里的非专业指的是非计算机专业毕业的程序员)程序员加入到了IT行业中来了,可能是因为移动互联网的火爆导致程序员容易就业而且工资很高,可能 ...
- js10秒倒计时鼠标点击次数统计
<html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"/> <script type="text/javascr ...
- [BZOJ3875][AHOI2014]骑士游戏(松弛操作)
题目:http://www.lydsy.com:808/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3875 分析: 类似于spfa求最短路,设d[i]表示完全消灭i号怪物的最小花费,我们对 ...
- java代码注释规范
java代码注释规范 代码注释是架起程序设计者与程序阅读者之间的通信桥梁,最大限度的提高团队开发合作效率.也是程序代码可维护性的重要环节之一.所以我们不是为写注释而写注释.下面说一下我们在诉求网二 ...
- android之远程启动服务
启动远程服务和隐式启动Activity一样 实现一个服务 为了演示方便,该服务是一个空服务 package xidian.dy.com.chujia; import android.app.Servi ...
