sql-3-DML_DQL
DML-操作数据
1、insert语句
--增加一行数据
insert into 表名([字段1,字段2,字段3,...])values('值1','值2','值3',...);
insert into student values('108','曾华','男','1977-09-01','95033');
-- 不加字段,数据会顺序对应table中的字段
-- 增加多行数据
insert into 表名([字段1,字段2,字段3...])
values('xx','xx','xx',...),
('xx','xx','xx',...),
('xx','xx','xx',...);
insert into student
values('108','曾华','男','1977-09-01','95033'),
('105','匡明','男','1975-10-02','95031'),
('107','王丽','女','1976-01-23','95033'),
('101','李军','男','1976-02-20','95033'),
('109','王芳','女','1975-02-10','95031'),
('103','陆君','男','1974-06-03','95031');
2、delete语句
delete from 表名
where 条件;
truncate和delete清空表单区别:
-- truncate 表名;清空这个表,可以理解为删除这个库再创一个,而且自增会归零
-- delete清零:
1、innodb:重启数据库会导致自增重新开始,记录存在内存中
2、myisam:重启数据库仍按原来的自增进行,记录在文件中
3、update语句
--注意where语句,不加这个字段的数据都会更新
update 表名s
set 字段='值1',[字段2='值2',,,]
where id='要修改的那一行的id';
-- where条件:
1、=,<>,!=,>,<,<=,>=,
2、between ... and ... ---注意这里是闭区间
3、and,or
DQL-查询数据
- 新关键词
- select
- distinct
- where
- like
- in
1、select总概语法
- 注意:select之后接上的是一个表达式(可以包含函数,加减乘除法)
select [ALL | DISTINCT]
{*| table.* | [table.flied1[as alisa1][,table.flies2[as alias2]][.....]]}
from table_name [as table_alias]
[left | right | inner join table_name2] -- 联表查询
[where ...] -- 指定结果需满足的条件
[group bg] -- 指定结果按照那几个字段来分组
[having] -- 过滤分组必须满足的次要条件
[order by ...] -- 指定查询记录按一个或多个条件排序
[limit {[offset,]row_count | row_countoffset offset}]; -- 查询的结果分页
2、准备好要演示用的数据表
create database if not exists `school`;
-- 创建一个school数据库
use `school`;-- 创建学生表
drop table if exists `student`;
create table `student`(
`studentno` int(4) not null comment '学号',
`loginpwd` varchar(20) default null,
`studentname` varchar(20) default null comment '学生姓名',
`sex` tinyint(1) default null comment '性别,0或1',
`gradeid` int(11) default null comment '年级编号',
`phone` varchar(50) not null comment '联系电话,允许为空',
`address` varchar(255) not null comment '地址,允许为空',
`borndate` datetime default null comment '出生时间',
`email` varchar (50) not null comment '邮箱账号允许为空',
`identitycard` varchar(18) default null comment '身份证号',
primary key (`studentno`),
unique key `identitycard`(`identitycard`),
key `email` (`email`)
)engine=myisam default charset=utf8;
-- 创建年级表
drop table if exists `grade`;
create table `grade`(
`gradeid` int(11) not null auto_increment comment '年级编号',
`gradename` varchar(50) not null comment '年级名称',
primary key (`gradeid`)
) engine=innodb auto_increment = 6 default charset = utf8;
-- 创建科目表
drop table if exists `subject`;
create table `subject`(
`subjectno`int(11) not null auto_increment comment '课程编号',
`subjectname` varchar(50) default null comment '课程名称',
`classhour` int(4) default null comment '学时',
`gradeid` int(4) default null comment '年级编号',
primary key (`subjectno`)
)engine = innodb auto_increment = 19 default charset = utf8;
-- 创建成绩表
drop table if exists `result`;
create table `result`(
`studentno` int(4) not null comment '学号',
`subjectno` int(4) not null comment '课程编号',
`examdate` datetime not null comment '考试日期',
`studentresult` int (4) not null comment '考试成绩',
key `subjectno` (`subjectno`)
)engine = innodb default charset = utf8;
-- 插入学生数据 其余自行添加 这里只添加了2行
insert into `student` (`studentno`,`loginpwd`,`studentname`,`sex`,`gradeid`,`phone`,`address`,`borndate`,`email`,`identitycard`)
values
(1000,'123456','张伟',0,2,'13800001234','北京朝阳','1980-1-1','text123@qq.com','123456198001011234'),
(1001,'123456','赵强',1,3,'13800002222','广东深圳','1990-1-1','text111@qq.com','123456199001011233');
-- 插入成绩数据 这里仅插入了一组,其余自行添加
insert into `result`(`studentno`,`subjectno`,`examdate`,`studentresult`)
values
(1000,1,'2013-11-11 16:00:00',85),
(1000,2,'2013-11-12 16:00:00',70),
(1000,3,'2013-11-11 09:00:00',68),
(1000,4,'2013-11-13 16:00:00',98),
(1000,5,'2013-11-14 16:00:00',58);
-- 插入年级数据
insert into `grade` (`gradeid`,`gradename`) values(1,'大一'),(2,'大二'),(3,'大三'),(4,'大四'),(5,'预科班');
-- 插入科目数据
insert into `subject`(`subjectno`,`subjectname`,`classhour`,`gradeid`)
values
(1,'高等数学-1',110,1),
(2,'高等数学-2',110,2),
(3,'高等数学-3',100,3),
(4,'高等数学-4',130,4),
(5,'C语言-1',110,1),
(6,'C语言-2',110,2),
(7,'C语言-3',100,3),
(8,'C语言-4',130,4),
(9,'Java程序设计-1',110,1),
(10,'Java程序设计-2',110,2),
(11,'Java程序设计-3',100,3),
(12,'Java程序设计-4',130,4),
(13,'数据库结构-1',110,1),
(14,'数据库结构-2',110,2),
(15,'数据库结构-3',100,3),
(16,'数据库结构-4',130,4),
(17,'C#基础',130,1);
INSERT INTO `subject`(`subjectno`,`subjectname`,`classhour`,`gradeid`)
values
(1,'高等数学-1',110,1),
(2,'高等数学-2',110,2),
(3,'高等数学-3',100,3),
(4,'高等数学-4',130,4),
(5,'C语言-1',110,1),
(6,'C语言-2',110,2),
(7,'C语言-3',100,3),
(8,'C语言-4',130,4),
(9,'Java程序设计-1',110,1),
(10,'Java程序设计-2',110,2),
(11,'Java程序设计-3',100,3),
(12,'Java程序设计-4',130,4),
(13,'数据库结构-1',110,1),
(14,'数据库结构-2',110,2),
(15,'数据库结构-3',100,3),
(16,'数据库结构-4',130,4),
(17,'C#基础',130,1);
3、查询字段下的数据
--展示student表的全部字段下的数据
select * from student;
--查询特定字段,注意这里的别名可以直接使用中文。
select `studentno` [as 别名],`studentname` [as 别名] from `student`;
--配合函数使用
select concat('姓名:',studentname) [as 别名] from `student`;
SELECT CONCAT('姓名:',sname)AS 学员 FROM student;效果如下
4、去重(distinct)
-- 去除select查出来的重复数据
select ditinct `studentno` from `student`;
5、select 其他查询作用
select varsion() --查询系统版本
select 100*3-1 as 计算结果 --用来计算
select @@auto_increment_increment --查询自增的步长
select `studentno`,`studentresult`+1 as 提分后 from result;
6、where
- 逻辑运算符
| 与 | and ,&& |
|---|---|
| 或 | ||,or |
| 非 | !,not |
- 模糊查询-like用法
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentname` like '刘'; --匹配名字里有刘的人
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `student` like '刘__'; --匹配叫刘某某的人
select `studentno` , `studentname` from `student`
where `studdent` like '刘%'; --匹配性刘的人
- in用法
select `studentno`,`studentname` from `student`
where `studentno` in (1001,1002,1003); --只匹配学号是1001,1002,1003的同学
7、联表查询(join)
- 联表查询是经常用到的一种语法,非常重要。
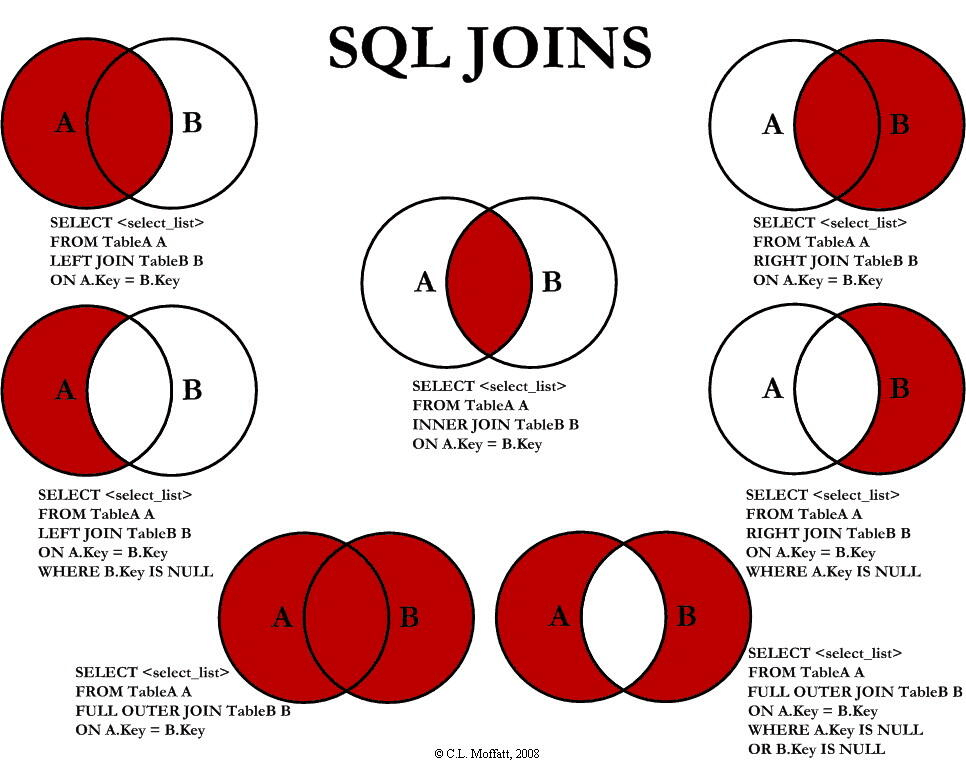
-- join语法
SELECT a.runoob_id, a.runoob_author, b.runoob_count
FROM runoob_tbl a
INNER JOIN tcount_tbl b
ON a.runoob_author = b.runoob_author;
了解:
inner join 表示必须要两个表都满足才能输出
right join 表示以右表为基准,而左表中的数据必须要满足后面的条件才能输出
left join 表示以左表为基准,而右表中的数据必须要满足后面的条件才能输出
- 自联接
select a.name as '父栏' ,b.name as '子栏'
from `biao` as a,`biao` as b
where a.id = b.parentid;
-- 实质:将一个表看成两个表进行操作
-- 条件是前一个表的id会等于后面表的parent_id;
8、分页和排序
--在前面加上我们的select语句
排序:
order by `字段` asc;
-- asc(cending)升序,desc(cending)降序
分页:
limit 5,5
-- 两个数据的意思:
-- 跳过多少个数据,显示几个数据
-- 第一页:limit 0,5;
-- 第二页:limit 5,5;
-- 第三页:limit 10,5;
9、子查询和嵌套查询
sql-3-DML_DQL的更多相关文章
- 最近帮客户实施的基于SQL Server AlwaysOn跨机房切换项目
最近帮客户实施的基于SQL Server AlwaysOn跨机房切换项目 最近一个来自重庆的客户找到走起君,客户的业务是做移动互联网支付,是微信支付收单渠道合作伙伴,数据库里存储的是支付流水和交易流水 ...
- SQL Server 大数据搬迁之文件组备份还原实战
一.本文所涉及的内容(Contents) 本文所涉及的内容(Contents) 背景(Contexts) 解决方案(Solution) 搬迁步骤(Procedure) 搬迁脚本(SQL Codes) ...
- Sql Server系列:分区表操作
1. 分区表简介 分区表在逻辑上是一个表,而物理上是多个表.从用户角度来看,分区表和普通表是一样的.使用分区表的主要目的是为改善大型表以及具有多个访问模式的表的可伸缩性和可管理性. 分区表是把数据按设 ...
- SQL Server中的高可用性(2)----文件与文件组
在谈到SQL Server的高可用性之前,我们首先要谈一谈单实例的高可用性.在单实例的高可用性中,不可忽略的就是文件和文件组的高可用性.SQL Server允许在某些文件损坏或离线的情况下,允 ...
- EntityFramework Core Raw SQL
前言 本节我们来讲讲EF Core中的原始查询,目前在项目中对于简单的查询直接通过EF就可以解决,但是涉及到多表查询时为了一步到位就采用了原始查询的方式进行.下面我们一起来看看. EntityFram ...
- 从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第一篇(配置域控)
从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第一篇(配置域控) 第一篇http://www.cnblogs.com/lyhabc/p/4678330.html第二篇http://www.cnb ...
- 从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第二篇(配置故障转移集群)
从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第二篇(配置故障转移集群) 第一篇http://www.cnblogs.com/lyhabc/p/4678330.html第二篇http://www ...
- 从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第三篇(配置AlwaysOn)
从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第三篇(配置AlwaysOn) 第一篇http://www.cnblogs.com/lyhabc/p/4678330.html第二篇http://w ...
- 从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第四篇(配置异地机房节点)
从0开始搭建SQL Server AlwaysOn 第四篇(配置异地机房节点) 第一篇http://www.cnblogs.com/lyhabc/p/4678330.html第二篇http://www ...
- SQL Server on Linux 理由浅析
SQL Server on Linux 理由浅析 今天的爆炸性新闻<SQL Server on Linux>基本上在各大科技媒体上刷屏了 大家看到这个新闻都觉得非常震精,而美股,今天微软开 ...
随机推荐
- Lidar激光雷达与Radar雷达
Lidar激光雷达与Radar雷达 自动驾驶技术正迅速成为汽车工业的驱动力.来自全球的汽车制造商正在与Google等顶级高科技巨头以及其他知名初创公司合作,共同开发下一代自动驾驶汽车.中国也开辟了自动 ...
- 【工具解析】瑞士军刀bettercap2.X_解析_第二期_内网钓鱼(嗅探)工具编写
/文章作者:Kali_MG1937 CNBLOG博客:ALDYS4 QQ:3496925334/ 第一期: https://www.cnblogs.com/aldys4/p/14877783.html ...
- java并发编程JUC第十二篇:AtomicInteger原子整型
AtomicInteger 类底层存储一个int值,并提供方法对该int值进行原子操作.AtomicInteger 作为java.util.concurrent.atomic包的一部分,从Java 1 ...
- 【题解】T749 localmaxima
# T749 localmaxima 权限限制没有超链接 题目描述 Description 给出一个排列,若其中一个数比它前面的数都大,则称为localmaxima数,求一个随机排列中localmax ...
- 树莓派FRP内网穿透及自启动
内网穿透的步骤和文件存档 实验室在远方部署了电脑主机来采集数据和图片,每次去调试会很麻烦,因而使用FRP内网穿透使得我们可以在实验室访问主机. 主要功能 实现远程可访问和开机自启FRP程序服务 安装和 ...
- .NET网页后台调用前台js方法时相同Key,调用不成功
ClientScript.RegisterStartupScript(GetType(), "key", "<script>Save()</script ...
- ceph-csi源码分析(3)-rbd driver-服务入口分析
更多ceph-csi其他源码分析,请查看下面这篇博文:kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 ceph-csi源码分析(3)-rbd driver-服务入口分析 当ceph-csi组件启动 ...
- Python分析【公众号】历史评论,看看大家的留言情况!
大家好,我是辰哥~~~ 辰哥玩公众号有一段时间了,这期文章分析一波读者的留言情况,不仅可以对公众号的各位铁粉一目了然,还可以通过分析的结果对公众号的经营进行更好的规划.如读者留言的内容通常是内容是什么 ...
- Java:java获取Linux下的路径
指定Linux的路径 //Linux系统路径 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(File.separator); String Url = sb.append( ...
- Spring缓存的注解关键词解释
Spring缓存的注解关键词解释 @Cacheable支持缓存 @Cacheable可以标记在一个方法上,也可以标记在一个类上. 1.当标记在一个方法上时表示该方法是支持缓存的,当标记在一个类上时则表 ...
