Dockers启动Kafka
首先安装 Confluent Platform
Quick Start for Confluent Platform (Local install)
Use this quick start to get up and running with Confluent Platform and its main components in a development environment. This quick start uses Confluent Control Center included in Confluent Platform for topic management and event stream processing using ksqlDB.
In this quick start, you create Apache Kafka topics, use Kafka Connect to generate mock data to those topics, and create ksqlDB streaming queries on those topics. You then go to Control Center to monitor and analyze the streaming queries.
See also
You can also run an automated version of this quick start designed for Confluent Platform local installs.
Prerequisites:
Internet connectivity.Operating System currently supported by Confluent Platform.A supported version of Java downloaded and installed.Java 8 and Java 11 are supported in this version of Confluent Platform (Java 9 and 10 are not supported). For more information, see Java supported versions.
Step 1: Download and Start Confluent Platform
Go to the downloads page.
Scroll to the Download Confluent Platform section and provide the following:
- Email: Your email address
- Format:
deb,rpm,tar, orzip
Click DOWNLOAD FREE.
Tip
You have installation options for
Ansible,Docker, andKubernetes. Also, you can download a previous version from Previous Versions.
Decompress the file. You should have the directories, such as
binandetc.Set the environment variable for the Confluent Platform directory.
export CONFLUENT_HOME=<path-to-confluent>
Add the Confluent Platform
bindirectory to your PATH.export PATH=$PATH:$CONFLUENT_HOME/bin
Install the Kafka Connect Datagen source connector using the Confluent Hub client. This connector generates mock data for demonstration purposes and is not suitable for production. Confluent Hub is an online library of pre-packaged and ready-to-install extensions or add-ons for Confluent Platform and Kafka.
confluent-hub install \
--no-prompt confluentinc/kafka-connect-datagen:latest
Start Confluent Platform using the Confluent CLI confluent local services start command. This command starts all of the Confluent Platform components, including Kafka, ZooKeeper, Schema Registry, HTTP REST Proxy for Kafka, Kafka Connect, ksqlDB, and Control Center.
Important
The confluent local commands are intended for a single-node development environment and are not suitable for a production environment. The data that are produced are transient and are intended to be temporary. For production-ready workflows, see Install and Upgrade Confluent Platform.
confluent local services start
Your output should resemble:
Starting Zookeeper
Zookeeper is [UP]
Starting Kafka
Kafka is [UP]
Starting Schema Registry
Schema Registry is [UP]
Starting Kafka REST
Kafka REST is [UP]
Starting Connect
Connect is [UP]
Starting KSQL Server
KSQL Server is [UP]
Starting Control Center
Control Center is [UP]
Step 2: Create Kafka Topics
In this step, you create Kafka topics using Confluent Control Center. Confluent Control Center provides the functionality for building and monitoring production data pipelines and event streaming applications.
Navigate to the Control Center web interface at http://localhost:9021.
If you installed Confluent Platform on a different host, replace
localhostwith the host name in the address.It may take a minute or two for Control Center to come online.
Note
Control Center won’t connect to ksqlDB if Control Center isn’t open and running in a
localhostbrowser session.
Click the controlcenter.cluster tile.
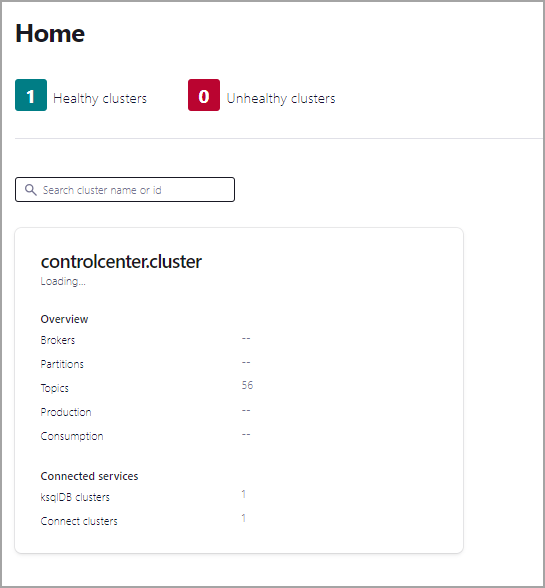
In the navigation bar, click Topics to open the topics list, and then click Add a topic.
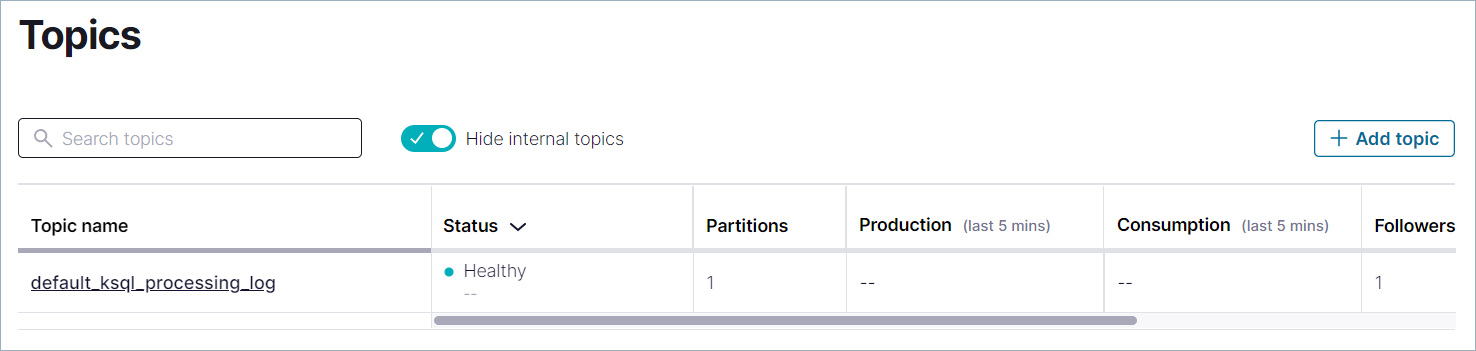
In the Topic name field, specify
pageviewsand click Create with defaults.Note that topic names are case-sensitive.
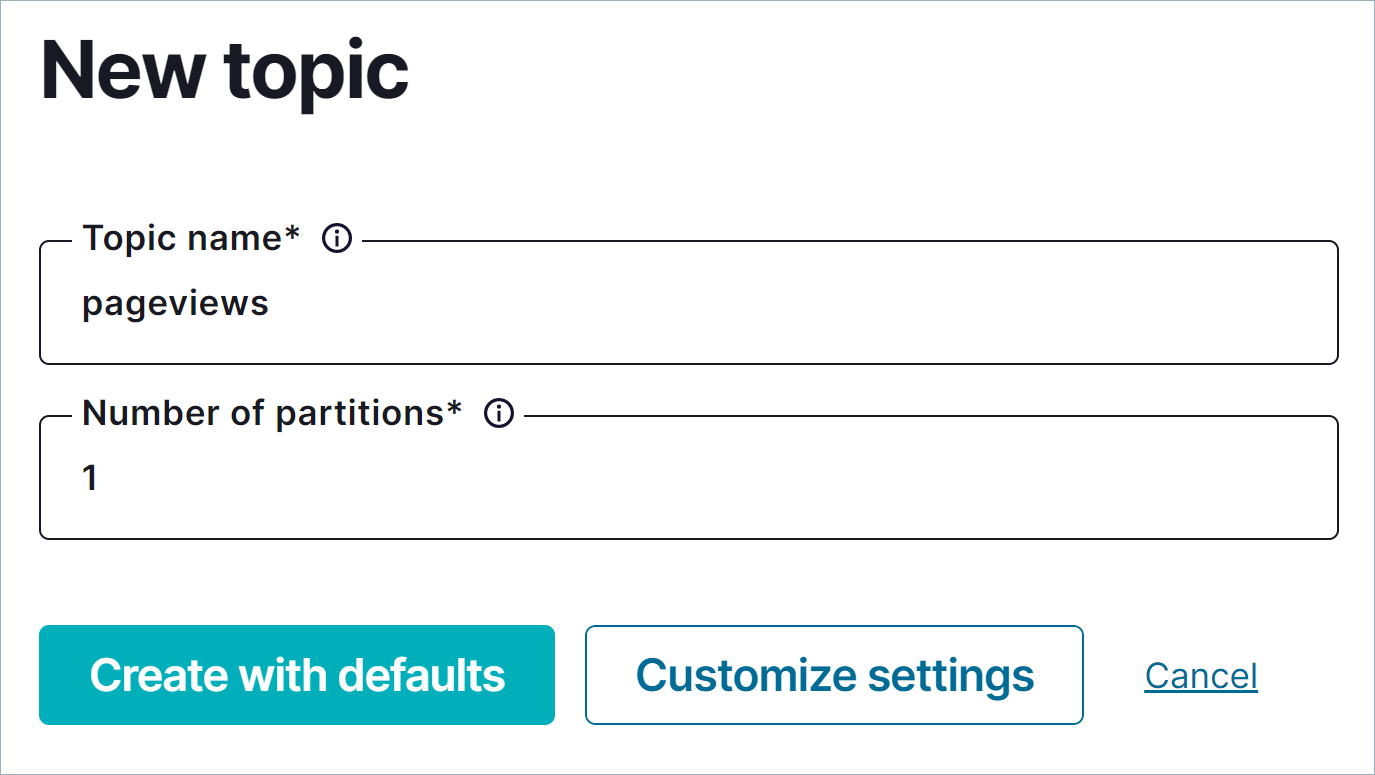
In the navigation bar, click Topics to open the topics list, and then click Add a topic.
In the Topic name field, specify
usersand click Create with defaults.
Step 3: Install a Kafka Connector and Generate Sample Data
In this step, you use Kafka Connect to run a demo source connector called kafka-connect-datagen that creates sample data for the Kafka topics pageviews and users.
Tip
The Kafka Connect Datagen connector was installed manually in Step 1: Download and Start Confluent Platform. If you encounter issues locating the Datagen Connector, refer to the Issue: Cannot locate the Datagen connector in the Troubleshooting section.
Run the first instance of the Kafka Connect Datagen connector to produce Kafka data to the
pageviewstopic in AVRO format.In the navigation bar, click Connect.
Click the
connect-defaultcluster in the Connect Clusters list.Click Add connector.
Select the
DatagenConnectortile.Tip
To narrow displayed connectors, click Filter by category and click Sources.
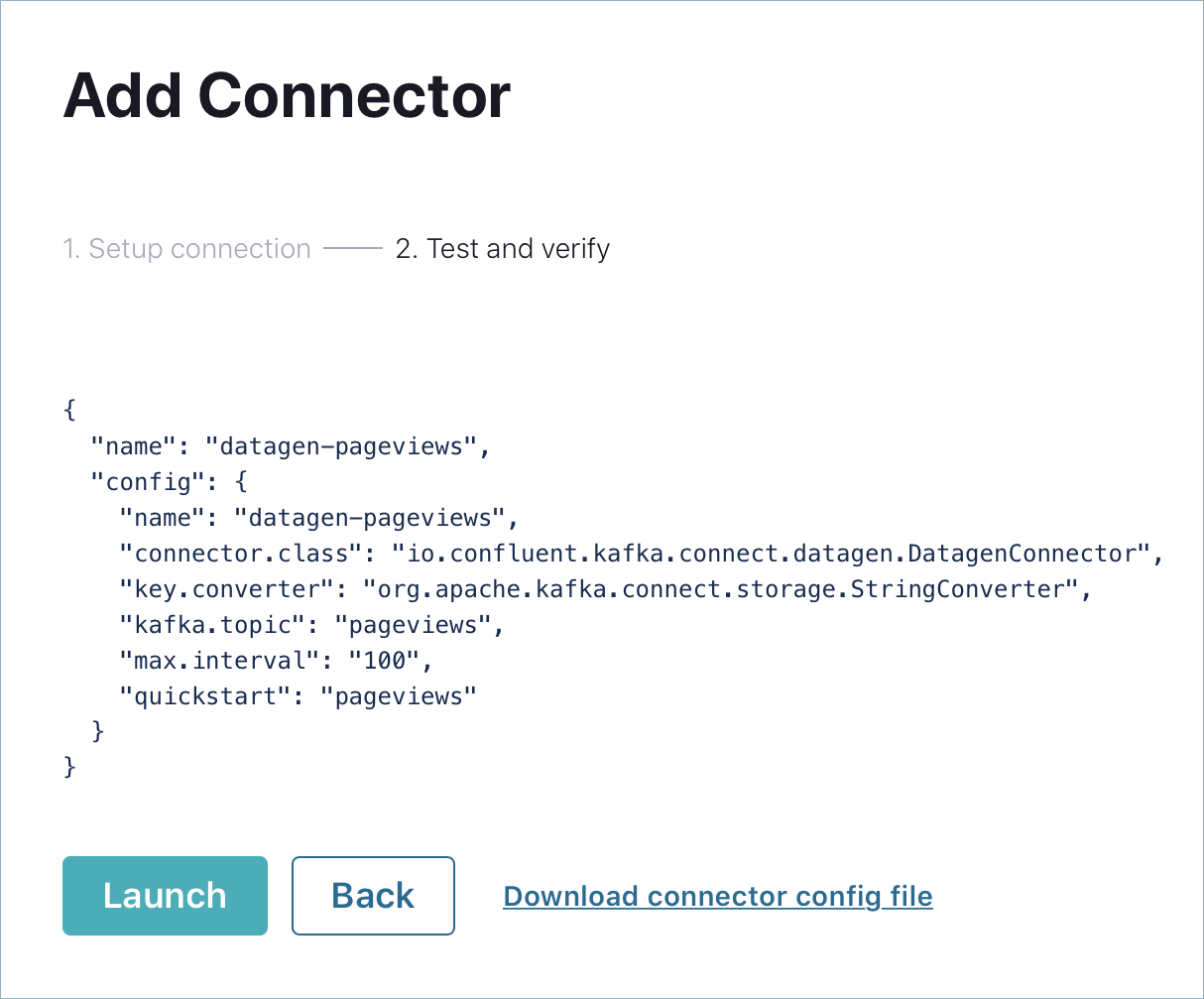
In the Name field, enter
datagen-pageviewsas the name of the connector.Enter the following configuration values:
- Key converter class:
org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter. - kafka.topic:
pageviews. - max.interval:
100. - quickstart:
pageviews.
- Key converter class:
Click Next.
Review the connector configuration and click Launch.
Run the second instance of the Kafka Connect Datagen connector to produce Kafka data to the
userstopic in AVRO format.Click Add connector.
Select the
DatagenConnectortile.Tip
To narrow displayed connectors, click Filter by category and click Sources.
In the Name field, enter
datagen-usersas the name of the connector.Enter the following configuration values:
- Key converter class:
org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter - kafka.topic:
users - max.interval:
1000 - quickstart:
users
- Key converter class:
Click Next.
Review the connector configuration and click Launch.
Step 4: Create and Write to a Stream and Table using ksqlDB
Tip
You can also run these commands using the ksqlDB CLI from your terminal with this command:
<path-to-confluent>/bin/ksql http://localhost:8088.
Create Streams and Tables
In this step, you use ksqlDB to create a stream for the pageviews topic and a table for the users topic.
In the navigation bar, click ksqlDB.
Select the
ksqlDBapplication.Copy the following code into the editor window and click Run query to create the
pageviewsstream. Stream names are not case-sensitive.CREATE STREAM pageviews WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='pageviews', VALUE_FORMAT='AVRO');
Copy the following code into the editor window and click Run query to create the
userstable. Table names are not case-sensitive.CREATE TABLE users (id VARCHAR PRIMARY KEY)
WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='users', VALUE_FORMAT='AVRO');
Write Queries
In this step, you create ksqlDB queries against the stream and the table you created above.
In the Editor tab, click Add query properties to add a custom query property.
Set the
auto.offset.resetparameter toEarliest.The setting instructs ksqlDB queries to read all available topic data from the beginning. This configuration is used for each subsequent query. For more information, see the ksqlDB Configuration Parameter Reference.
Create the following queries.
Click Stop to stop the current running query.
Create a non-persistent query that returns data from a stream with the results limited to a maximum of three rows:
Enter the following query in the editor:
SELECT pageid FROM pageviews EMIT CHANGES LIMIT 3;
Click Run query. Your output should resemble:
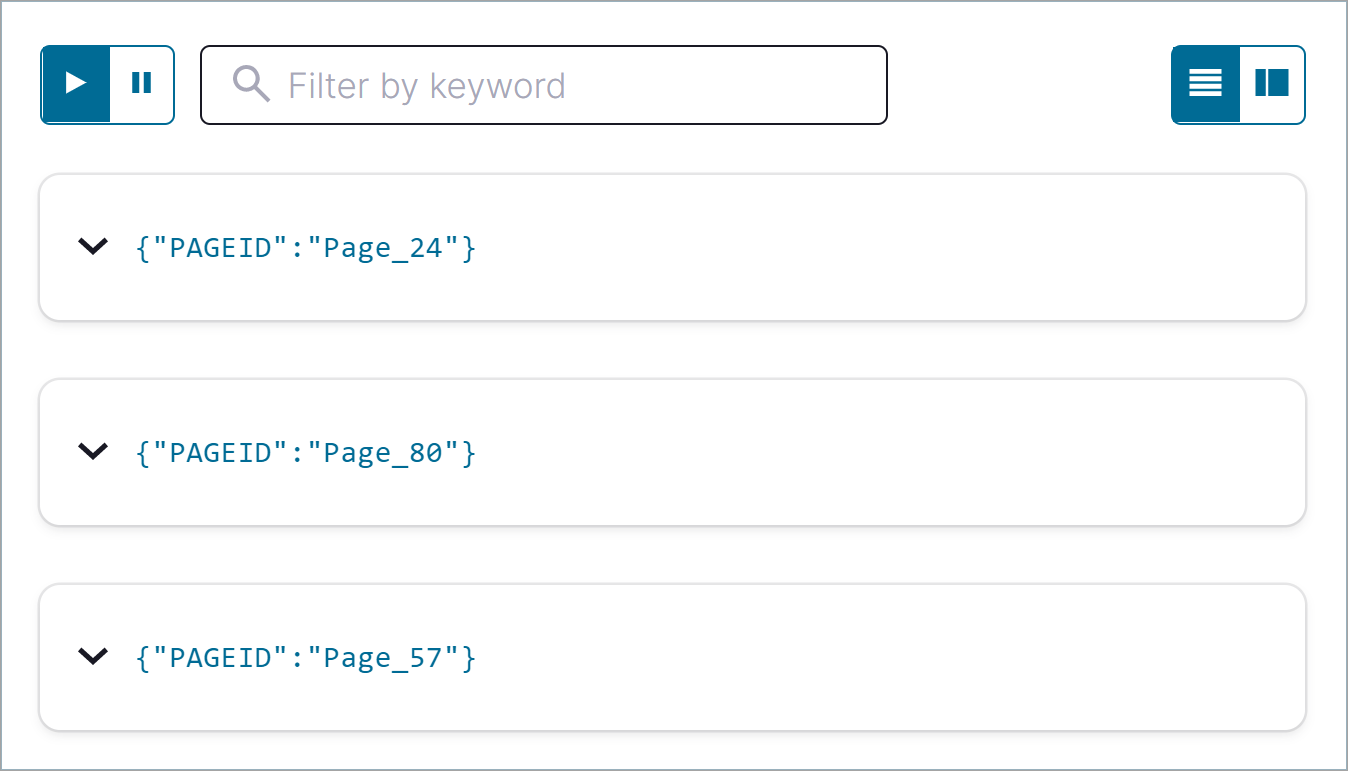
Click the Card view or Table view icon to change the output layout.
Create a persistent query (as a stream) that filters the
PAGEVIEWSstream for female users. The results from this query are written to the KafkaPAGEVIEWS_FEMALEtopic:Enter the following query in the editor:
CREATE STREAM pageviews_female
AS SELECT users.id AS userid, pageid, regionid
FROM pageviews LEFT JOIN users ON pageviews.userid = users.id
WHERE gender = 'FEMALE'
EMIT CHANGES;
Click Run query. Your output should resemble:

Create a persistent query where
REGIONIDends with8or9. Results from this query are written to the Kafka topic namedpageviews_enriched_r8_r9as explicitly specified in the query:Enter the following query in the editor:
CREATE STREAM pageviews_female_like_89
WITH (KAFKA_TOPIC='pageviews_enriched_r8_r9', VALUE_FORMAT='AVRO')
AS SELECT * FROM pageviews_female
WHERE regionid LIKE '%_8' OR regionid LIKE '%_9'
EMIT CHANGES;
Click Run query. Your output should resemble:

Create a persistent query that counts the
PAGEVIEWSfor eachREGIONandGENDERcombination in a tumbling window of 30 seconds when the count is greater than 1. Because the procedure is grouping and counting, the result is now a table, rather than a stream. Results from this query are written to a Kafka topic calledPAGEVIEWS_REGIONS:Enter the following query in the editor:
CREATE TABLE pageviews_regions WITH (KEY_FORMAT='JSON')
AS SELECT gender, regionid, COUNT(*) AS numusers
FROM pageviews LEFT JOIN users ON pageviews.userid = users.id
WINDOW TUMBLING (SIZE 30 SECOND)
GROUP BY gender, regionid
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
EMIT CHANGES;
Click Run query. Your output should resemble:

Click the Persistent queries tab. You should see the following persisted queries:
- PAGEVIEWS_FEMALE
- PAGEVIEWS_FEMALE_LIKE_89
- PAGEVIEWS_REGIONS
Click the Editor tab. The All available streams and tables pane shows all of the streams and tables that you can access.
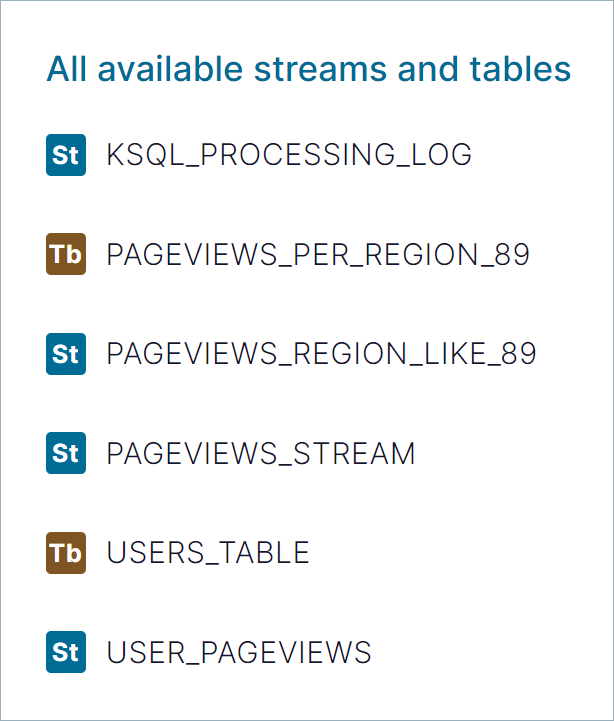
In the All available streams and tables section, click KSQL_PROCESSING_LOG to view the stream’s schema, including nested data structures.
Run Queries
In this step, you run the ksqlDB queries you save as streams and tables above in the previous section.
In the Streams tab, select the
PAGEVIEWS_FEMALEstream.Click Query stream.
The editor opens, and streaming output of the query displays.
Click Stop to stop the output generation.
In the Tables tab, select
PAGEVIEWS_REGIONStable.Click Query table.
The editor opens, and streaming output of the query displays.
Click Stop to stop the output generation.
Step 5: Monitor Consumer Lag
In the navigation bar, click Consumers to view the consumers created by ksqlDB.
Click the consumer group ID to view details for the
_confluent-ksql-default_query_CSAS_PAGEVIEWS_FEMALE_5consumer group.From the page, you can see the consumer lag and consumption values for your streaming query.
For more information, see the Control Center Consumers documentation.
Step 6: Stop Confluent Platform
When you are done working with the local install, you can stop Confluent Platform.
Stop Confluent Platform using the Confluent CLI confluent local services connect stop command.
confluent local services stop
Destroy the data in the Confluent Platform instance with the confluent local destroy command.
confluent local destroy
然后使用docker-compose运行Kafka
Kafka Commands Primer
Once you have Confluent Platform running, an intuitive next step is try out some basic Kafka commands to create topics and work with producers and consumers. This should help orient Kafka newbies and pros alike that all those familiar Kafka tools are readily available in Confluent Platform, and work the same way. These provide a means of testing and working with basic functionality, as well as configuring and monitoring deployments. The commands surface a subset of the APIs available to you.
Confluent Platform ships with Kafka commands and utilities in $CONFLUENT_HOME/etc/kafka/bin. This bin/ directory includes both Confluent proprietary and open source Kafka utilities.
A few things to note:
- With Confluent Platform installed and running on your system, you can run Kafka commands from anywhere; for example, from your
$HOME(~/) directory. You do not have to run these from within$CONFLUENT_HOME. - A full list is provided in CLI Tools for Confluent Platform. Those in the list that begin with
kafka-are the Kafka open source command utilities, also covered in various sections of the Apache Kafka documentation. - Comprehensive command line help is available by typing any of the commands with no arguments; for example,
kafka-topicsorkafka-producer-perf-test.
To help get you started, the sections below provide examples for some of the most fundamental and widely-used commands.
Create, list and describe topics
You can use kafka-topics for operations on topics (create, list, describe, alter, delete, and so forth).
In a command window, run the following commands to experiment with topics.
Create three topics,
cool-topic,warm-topic,hot-topic.kafka-topics --create --topic cool-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
kafka-topics --create --topic warm-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
kafka-topics --create --topic hot-topic --partitions 2 --replication-factor 2 --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
List all topics.
kafka-topics --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Tip
System topics are prefaced by an underscore in the output. The topics you created are listed at the end.
Describe a topic.
This shows partitions, replication factor, and in-sync replicas for the topic.
kafka-topics --describe --topic cool-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Your output should resemble the following:
Topic: cool-topic PartitionCount: 1 ReplicationFactor: 1 Configs: segment.bytes=1073741824
Topic: cool-topic Partition: 0 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0 Isr: 0 Offline:
Tip
If you run
kafka-topics --describewith no specified topic, you get a detailed description of every topic on the cluster (system and user topics).
Describe another topic, using one of the other brokers in the cluster as the bootstrap server.
kafka-topics --describe --topic hot-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9094
Here is that example output:
Topic: hot-topic PartitionCount: 2 ReplicationFactor: 2 Configs: segment.bytes=1073741824
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 0 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0 Isr: 1,0 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 1 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2 Isr: 0,2 Offline:
You can connect to any of the brokers in the cluster to run these commands because they all have the same data!
Alter a topic’s cofiguration.
For this example, change the partition count on hot-topic from
2to9.kafka-topics --alter --topic hot-topic --partitions 9 --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Tip
Dynamic topic modification is inherently limited by the current configurations. For example, you cannot decrease the number of partitions or modify the replication factor for a topic, as that would require partition reassignment.
Rerun
--describeon the same topic.kafka-topics --describe --topic hot-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Here is that example output, and verify that the partition count is updated to
9:Topic: hot-topic PartitionCount: 9 ReplicationFactor: 2 Configs: segment.bytes=1073741824
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 0 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1 Isr: 2,1 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 1 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0 Isr: 1,0 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 2 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,2 Isr: 1,2 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 3 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,1 Isr: 2,1 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 4 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,2 Isr: 0,2 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 5 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,0 Isr: 1,0 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 6 Leader: 2 Replicas: 2,0 Isr: 2,0 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 7 Leader: 0 Replicas: 0,1 Isr: 0,1 Offline:
Topic: hot-topic Partition: 8 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,2 Isr: 1,2 Offline:
Delete a topic.
kafka-topics --delete --topic warm-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
List all topics.
kafka-topics --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Run producers and consumers to send and read messages
The command utilities kafka-console-producer and kafka-console-consumer allow you to manually produce messages to and consume from a topic.
Open two new command windows, one for a producer, and the other for a consumer.
Run a producer to produce to
cool-topic.kafka-console-producer --topic cool-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Send some messages.
Type your messages at the prompt (
>), and hit Return after each one.Your command window will resemble the following:
$ kafka-console-producer --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic cool-topic
>hi cool topic
>did you get this message?
>first
>second
>third
>yes! I love you cool topic
>
Tip
You can use the
--broker-listflag in place of--bootstrap-serverfor the producer, typically used to send data to specific brokers; shown here as an example.In the other command window, run a consumer to read messages from
cool-topic. Specify that you want to start consuming from the beginning, as shown.kafka-console-consumer --topic cool-topic --from-beginning --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Your output will resemble the following:
$ kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --from-beginning --topic cool-topic
hi cool topic on origin cluster
is this getting to your replica?
first
second
third
yes! I love you cool topic
When you want to stop the producer and consumer, type Ctl-C in their respective command windows.
Tip
You may want to leave at least the producer running for now, in case you want to send more messages when we revisit topics on the Control Center.
Produce auto-generated message data to topics
You can use kafka-consumer-perf-test in its own command window to generate test data to topics.
For example, open a new command window and type the following command to send data to
hot-topic, with the specified throughput and record size.kafka-producer-perf-test \
--producer-props bootstrap.servers=localhost:9092 \
--topic hot-topic \
--record-size 1000 \
--throughput 1000 \
--num-records 3600000
The command provides status output on messages sent, as shown:
4999 records sent, 999.8 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 1.1 ms avg latency, 240.0 ms max latency.
5003 records sent, 1000.2 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 0.5 ms avg latency, 4.0 ms max latency.
5003 records sent, 1000.2 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 0.6 ms avg latency, 5.0 ms max latency.
5001 records sent, 1000.2 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 0.3 ms avg latency, 3.0 ms max latency.
5001 records sent, 1000.0 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 0.3 ms avg latency, 4.0 ms max latency.
5000 records sent, 1000.0 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 0.8 ms avg latency, 24.0 ms max latency.
5001 records sent, 1000.2 records/sec (0.95 MB/sec), 0.6 ms avg latency, 3.0 ms max latency.
...
Open a new command window to consume the messages from hot-topic as they are sent (not from the beginning).
kafka-console-consumer --topic hot-topic --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
Type Ctl-C to stop the consumer.
Tip
You may want to leave the producer running for a moment, as you are about to revisit Topics on the Control Center.
To learn more, check out Benchmark Commands, Let’s Load test, Kafka!, and How to do Performance testing of Kafka Cluster
参考文档
Confluent Community Docker Image for Apache Kafka
Dockers启动Kafka的更多相关文章
- 启动kafka时报scala相关错误:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: scala.Predef$.ArrowAssoc()
1.报错现象: 启动kafka的时候启动失败,并且会报告下面的错误: java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: scala.Predef$.ArrowAssoc(Ljava/lang/ ...
- 安装启动kafka
vim kafka/config/server.properties #确保唯一 broker.id=0 #允许删除主题 delete.topic.enable=true # 指定数据文件所在目录 l ...
- 首次启动Kafka报Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM warning: INFO: os::commit_memory(0x00000000c0000000, 1073741824, 0) failed; error='Cannot allocate memory' (errno=12)
首次启动Kafka报错如下: 原因:内存不足,查看启动配置 调小一些:
- 启动Kafka
启动zookeeper 使用命令查看zookeeper是否启动成功: 启动kafka Brokerr 使用命令查看kafka Broker是否启动更成功 在kafka中创建topic 'test' b ...
- Mac单机模式安装启动Kafka
1.下载kafka,网址: https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi?path=/kafka/2.0.0/kafka_2.12-2.0.0.tgz 2.移动tar包到 ...
- 启动kafka集群,关闭kafka集群脚本
启动kafka集群,关闭kafka集群脚本 在$KAFKA_HOME/bin下新建如下脚本文件 start-kafka.sh #!/bin/bash BROKERS="mini41 mini ...
- 启动kafka报错
启动kafka时 报错: kafka-console-consumer.sh --from-beginning --zookeeper node01:8121,node02:8121,node03:8 ...
- macOS启动Kafka
目录 kafka目录结构 先启动zookeeper 后启动kafka 创建topic 创建一个生产者 创建一个消费者 kafka目录结构 # kafka安装目录 /usr/local/Cellar/k ...
- 【kafka】一键启动kafka脚本
3.1 创建文件cd bin 跳转到bin文件夹里touch start-kafka-cluster.sh --新建一键启动文件touch stop-kafka-cluster.sh --新建一键 ...
随机推荐
- Screenshot 库和Collections 库
一.screenShot 是 robot framework的标准类库,用于截取当前窗口,需要手动加载. 示例: 运行结果: 二.Collections 库 Collections 库同样为 Robo ...
- elementUI合并表格span-method用法
官方文档 参考链接一 参考链接二
- axios 基于拦截器的取消(重复)请求
axios 基于拦截器的取消(重复)请求 // 添加请求拦截器 axios.interceptors.request.use((config) => { // 准备发请求之前, 取消未完成的请求 ...
- 编译静态库的方式使用spdlog和fmt
前言 spdlog++库,而且支持header only方式,但header only的使用方式会造成编译时长增加,所以这里简单描述一下,其编译静态库的方式. 又因为spdlog还依赖另一个开源库fm ...
- filter筛选数组
和map()类似,array的filter也接收一个函数 和map()不同的是,filter把传入的函数依次作用于每个函数,然后根据返回TRUE还是FALSE来做决定保留还是舍弃该元素 例如,删除一个 ...
- bat批处理命令及解释
相关原文链接 一.批处理概念 批处理文件:包含DOS命令的可编辑可执行文件 批处理:可以对某一对象批量操作的文件 二.批处理命令简介 命令1~10 1 echo 和 @ 回显命令 @ #关闭单行回显 ...
- 【Microsoft Azure 的1024种玩法】四. 利用Azure Virtual machines 打造个人专属云盘,速度吊打某云盘
[简介] 1.Azure Virtual machines是Azure 提供的多种可缩放按需分配计算资源之一,Nextcloud是一款开源免费的私有云存储网盘项目,可以让你快速便捷地搭建一套属于自己或 ...
- [atAGC050F]NAND Tree
当$n$为偶数,暴力$o(n)$枚举第一次操作,以下只考虑$n$为奇数的情况 此时,$n-1$即操作次数为偶数,找到最小的$i$(其中$1\le i\le \frac{n-1}{2}$),满足第$2i ...
- 保姆级神器 Maven,再也不用担心项目构建搞崩了
今天来给大家介绍一款项目构建神器--Maven,不仅能帮我们自动化构建,还能够抽象构建过程,提供构建任务实现:它跨平台,对外提供了一致的操作接口,这一切足以使它成为优秀的.流行的构建工具,从此以后,再 ...
- shiro 学习笔记
1. 权限管理 1.1 什么是权限管理? 权限管理实现对用户访问系统的控制,按照安全规则或者安全策略,可以控制用户只能访问自己被授权的资源 权限管理包括用户身份认证和授权两部分,简称认证授权 1.2 ...
