Go语言并发模型 G源码分析
Go 的线程实现模型,有三个核心的元素 M、P、G,它们共同支撑起了这个线程模型的框架。其中,G 是 goroutine 的缩写,通常称为 “协程”。关于协程、线程和进程三者的异同,可以参照 “进程、线程和协程的区别”。
每一个 Goroutine 在程序运行期间,都会对应分配一个 g 结构体对象。g 中存储着 Goroutine 的运行堆栈、状态以及任务函数,g 结构的定义位于 src/runtime/runtime2.go 文件中。
g 对象可以重复使用,当一个 goroutine 退出时,g 对象会被放到一个空闲的 g 对象池中以用于后续的 goroutine 的使用,以减少内存分配开销。
1. Goroutine 字段注释
g 字段非常的多,我们这里分段来理解:
type g struct {
// Stack parameters.
// stack describes the actual stack memory: [stack.lo, stack.hi).
// stackguard0 is the stack pointer compared in the Go stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard normally, but can be StackPreempt to trigger a preemption.
// stackguard1 is the stack pointer compared in the C stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard on g0 and gsignal stacks.
// It is ~0 on other goroutine stacks, to trigger a call to morestackc (and crash).
stack stack // offset known to runtime/cgo
// 检查栈空间是否足够的值, 低于这个值会扩张, stackguard0 供 Go 代码使用
stackguard0 uintptr // offset known to liblink
// 检查栈空间是否足够的值, 低于这个值会扩张, stackguard1 供 C 代码使用
stackguard1 uintptr // offset known to liblink
}
stack 描述了当前 goroutine 的栈内存范围[stack.lo, stack.hi),其中 stack 的数据结构:
// Stack describes a Go execution stack.
// The bounds of the stack are exactly [lo, hi),
// with no implicit data structures on either side.
// 描述 goroutine 执行栈
// 栈边界为[lo, hi),左包含右不包含,即 lo≤stack<hi
// 两边都没有隐含的数据结构。
type stack struct {
lo uintptr // 该协程拥有的栈低位
hi uintptr // 该协程拥有的栈高位
}
stackguard0 和 stackguard1 均是一个栈指针,用于扩容场景,前者用于 Go stack ,后者用于 C stack。
如果 stackguard0 字段被设置成 StackPreempt,意味着当前 Goroutine 发出了抢占请求。
在g结构体中的stackguard0 字段是出现爆栈前的警戒线。stackguard0 的偏移量是16个字节,与当前的真实SP(stack pointer)和爆栈警戒线(stack.lo+StackGuard)比较,如果超出警戒线则表示需要进行栈扩容。先调用runtime·morestack_noctxt()进行栈扩容,然后又跳回到函数的开始位置,此时此刻函数的栈已经调整了。然后再进行一次栈大小的检测,如果依然不足则继续扩容,直到栈足够大为止。
type g struct {
preempt bool // preemption signal, duplicates stackguard0 = stackpreempt
preemptStop bool // transition to _Gpreempted on preemption; otherwise, just deschedule
preemptShrink bool // shrink stack at synchronous safe point
}
preempt抢占标记,其值为 true 执行 stackguard0 = stackpreempt。preemptStop将抢占标记修改为 _Gpreedmpted,如果修改失败则取消。preemptShrink在同步安全点收缩栈。
type g struct {
_panic *_panic // innermost panic - offset known to liblink
_defer *_defer // innermost defer
}
_panic当前Goroutine 中的 panic。_defer当前Goroutine 中的 defer。
type g struct {
m *m // current m; offset known to arm liblink
sched gobuf
goid int64
}
m当前 Goroutine 绑定的 M。sched存储当前 Goroutine 调度相关的数据,上下方切换时会把当前信息保存到这里,用的时候再取出来。goid当前 Goroutine 的唯一标识,对开发者不可见,一般不使用此字段,Go 开发团队未向外开放访问此字段。
gobuf 结构体定义:
type gobuf struct {
// The offsets of sp, pc, and g are known to (hard-coded in) libmach.
// 寄存器 sp, pc 和 g 的偏移量,硬编码在 libmach
//
// ctxt is unusual with respect to GC: it may be a
// heap-allocated funcval, so GC needs to track it, but it
// needs to be set and cleared from assembly, where it's
// difficult to have write barriers. However, ctxt is really a
// saved, live register, and we only ever exchange it between
// the real register and the gobuf. Hence, we treat it as a
// root during stack scanning, which means assembly that saves
// and restores it doesn't need write barriers. It's still
// typed as a pointer so that any other writes from Go get
// write barriers.
sp uintptr
pc uintptr
g guintptr
ctxt unsafe.Pointer
ret sys.Uintreg
lr uintptr
bp uintptr // for GOEXPERIMENT=framepointer
}
sp栈指针位置。pc程序计数器,运行到的程序位置。
ctxt
- 不常见,可能是一个分配在heap的函数变量,因此GC 需要追踪它,不过它有可能需要设置并进行清除,在有
写屏障
- 的时候有些困难。重点了解一下
write barriers
- 。
g当前gobuf的 Goroutine。ret系统调用的结果。
调度器在将 G 由一种状态变更为另一种状态时,需要将上下文信息保存到这个gobuf结构体,当再次运行 G 的时候,再从这个结构体中读取出来,它主要用来暂存上下文信息。其中的栈指针 sp 和程序计数器 pc 会用来存储或者恢复寄存器中的值,设置即将执行的代码。
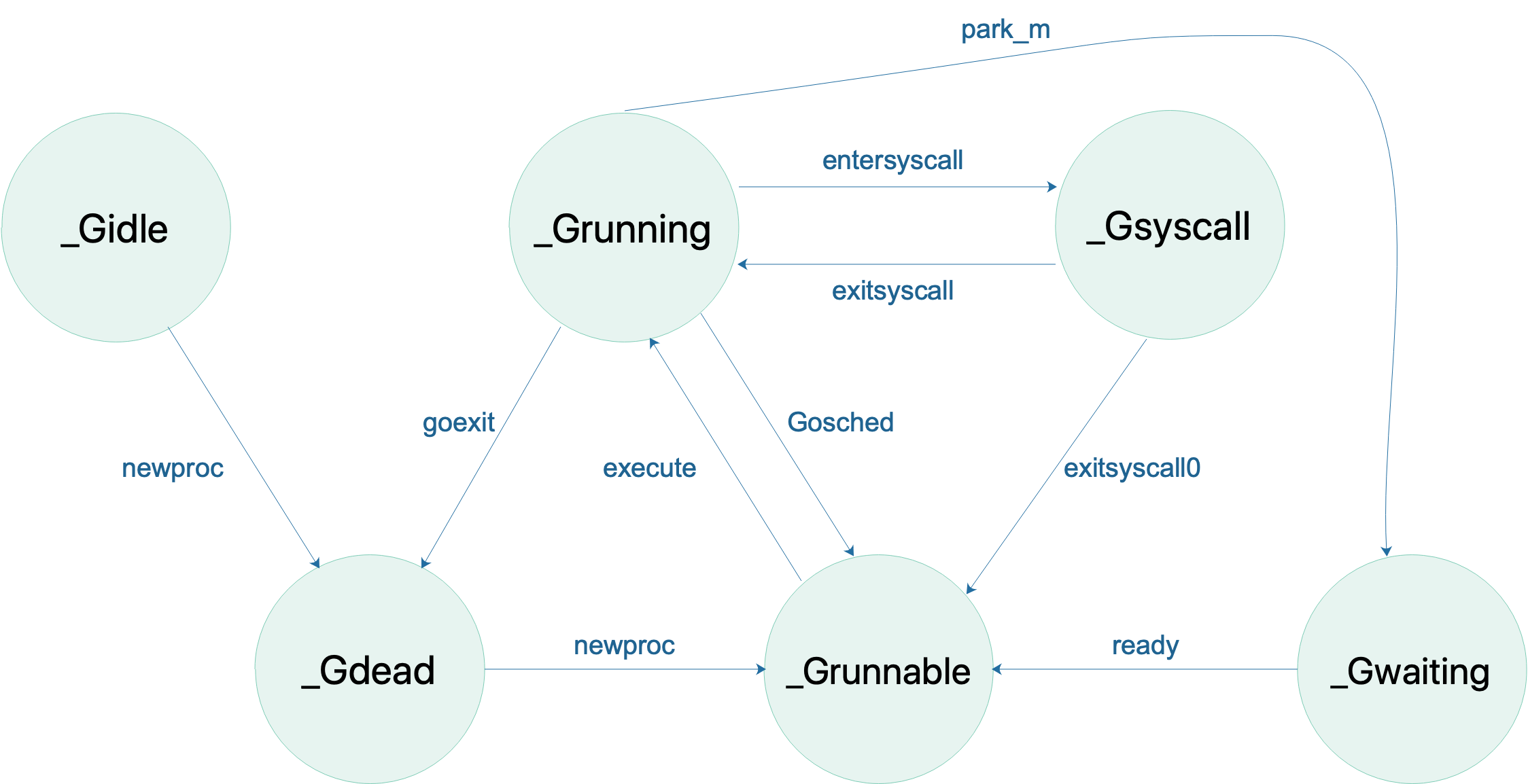
2. Goroutine 状态种类
Goroutine 的状态有以下几种:
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
_Gidle |
0 刚刚被分配并且还没有被初始化 |
_Grunnable |
1 没有执行代码,没有栈的所有权,存储在运行队列中 |
_Grunning |
2 可以执行代码,拥有栈的所有权,被赋予了内核线程 M 和处理器 P |
_Gsyscall |
3 正在执行系统调用,没有执行用户代码,拥有栈的所有权,被赋予了内核线程 M 但是不在运行队列上 |
_Gwaiting |
4 由于运行时而被阻塞,没有执行用户代码并且不在运行队列上,但是可能存在于 Channel 的等待队列上。若需要时执行ready()唤醒。 |
_Gmoribund_unused |
5 当前此状态未使用,但硬编码在了gdb 脚本里,可以不用关注 |
_Gdead |
6 没有被使用,可能刚刚退出,或在一个freelist;也或者刚刚被初始化;没有执行代码,可能有分配的栈也可能没有;G和分配的栈(如果已分配过栈)归刚刚退出G的M所有或从free list 中获取 |
_Genqueue_unused |
7 目前未使用,不用理会 |
_Gcopystack |
8 栈正在被拷贝,没有执行代码,不在运行队列上 |
_Gpreempted |
9 由于抢占而被阻塞,没有执行用户代码并且不在运行队列上,等待唤醒 |
_Gscan |
10 GC 正在扫描栈空间,没有执行代码,可以与其他状态同时存在 |
需要注意的是对于 _Gmoribund_unused 状态并未使用,但在 gdb 脚本中存在;而对于 _Genqueue_unused 状态目前也未使用,不需要关心。
_Gscan 与上面除了_Grunning 状态以外的其它状态相组合,表示 GC 正在扫描栈。Goroutine 不会执行用户代码,且栈由设置了 _Gscan 位的 Goroutine 所有。
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
_Gscanrunnable |
= _Gscan + _Grunnable // 0x1001 |
_Gscanrunning |
= _Gscan + _Grunning // 0x1002 |
_Gscansyscall |
= _Gscan + _Gsyscall // 0x1003 |
_Gscanwaiting |
= _Gscan + _Gwaiting // 0x1004 |
_Gscanpreempted |
= _Gscan + _Gpreempted // 0x1009 |
3. Goroutine 状态转换
可以看到除了上面提到的两个未使用的状态外一共有14种状态值。许多状态之间是可以进行改变的。如下图所示:
type g strcut {
syscallsp uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallsp = sched.sp to use during gc
syscallpc uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallpc = sched.pc to use during gc
stktopsp uintptr // expected sp at top of stack, to check in traceback
param unsafe.Pointer // passed parameter on wakeup
atomicstatus uint32
stackLock uint32 // sigprof/scang lock; TODO: fold in to atomicstatus
}
atomicstatus当前 G 的状态,上面介绍过 G 的几种状态值。syscallsp如果 G 的状态为Gsyscall,那么值为sched.sp主要用于GC 期间。syscallpc如果 G 的状态为GSyscall,那么值为sched.pc主要用于GC 期间。由此可见这两个字段通常一起使用。stktopsp用于回源跟踪。param唤醒 G 时传入的参数,例如调用ready()。stackLock栈锁。
type g struct {
waitsince int64 // approx time when the g become blocked
waitreason waitReason // if status==Gwaiting
}
waitsinceG 阻塞时长。waitreason阻塞原因。
type g struct {
// asyncSafePoint is set if g is stopped at an asynchronous
// safe point. This means there are frames on the stack
// without precise pointer information.
asyncSafePoint bool
paniconfault bool // panic (instead of crash) on unexpected fault address
gcscandone bool // g has scanned stack; protected by _Gscan bit in status
throwsplit bool // must not split stack
}
asyncSafePoint异步安全点;如果 g 在异步安全点停止则设置为true,表示在栈上没有精确的指针信息。paniconfault地址异常引起的 panic(代替了崩溃)。gcscandoneg 扫描完了栈,受状态_Gscan位保护。throwsplit不允许拆分 stack。
type g struct {
// activeStackChans indicates that there are unlocked channels
// pointing into this goroutine's stack. If true, stack
// copying needs to acquire channel locks to protect these
// areas of the stack.
activeStackChans bool
// parkingOnChan indicates that the goroutine is about to
// park on a chansend or chanrecv. Used to signal an unsafe point
// for stack shrinking. It's a boolean value, but is updated atomically.
parkingOnChan uint8
}
activeStackChans表示是否有未加锁定的 channel 指向到了 g 栈,如果为 true,那么对栈的复制需要 channal 锁来保护这些区域。parkingOnChan表示 g 是放在 chansend 还是 chanrecv。用于栈的收缩,是一个布尔值,但是原子性更新。
type g struct {
raceignore int8 // ignore race detection events
sysblocktraced bool // StartTrace has emitted EvGoInSyscall about this goroutine
sysexitticks int64 // cputicks when syscall has returned (for tracing)
traceseq uint64 // trace event sequencer
tracelastp puintptr // last P emitted an event for this goroutine
lockedm muintptr
sig uint32
writebuf []byte
sigcode0 uintptr
sigcode1 uintptr
sigpc uintptr
gopc uintptr // pc of go statement that created this goroutine
ancestors *[]ancestorInfo // ancestor information goroutine(s) that created this goroutine (only used if debug.tracebackancestors)
startpc uintptr // pc of goroutine function
racectx uintptr
waiting *sudog // sudog structures this g is waiting on (that have a valid elem ptr); in lock order
cgoCtxt []uintptr // cgo traceback context
labels unsafe.Pointer // profiler labels
timer *timer // cached timer for time.Sleep
selectDone uint32 // are we participating in a select and did someone win the race?
}
gopc创建当前 G 的 pc。startpcgo func 的 pc。timer通过time.Sleep 缓存 timer。
type g struct {
// Per-G GC state
// gcAssistBytes is this G's GC assist credit in terms of
// bytes allocated. If this is positive, then the G has credit
// to allocate gcAssistBytes bytes without assisting. If this
// is negative, then the G must correct this by performing
// scan work. We track this in bytes to make it fast to update
// and check for debt in the malloc hot path. The assist ratio
// determines how this corresponds to scan work debt.
gcAssistBytes int64
}
gcAssistBytes与 GC 相关。
4. Goroutin 总结
- 每个 G 都有自己的状态,状态保存在
atomicstatus字段,共有十几种状态值。 - 每个 G 在状态发生变化时,即
atomicstatus字段值被改变时,都需要保存当前G的上下文的信息,这个信息存储在sched字段,其数据类型为gobuf,想理解存储的信息可以看一下这个结构体的各个字段。 - 每个 G 都有三个与抢占有关的字段,分别为
preempt、preemptStop和premptShrink。 - 每个 G 都有自己的唯一id, 字段为
goid,但此字段官方不推荐开发使用。 - 每个 G 都可以最多绑定一个m,如果可能未绑定,则值为 nil。
- 每个 G 都有自己内部的
defer和panic。 - G 可以被阻塞,并存储有阻塞原因,字段
waitsince和waitreason。 - G 可以被进行 GC 扫描,相关字段为
gcscandone、atomicstatus(_Gscan与上面除了_Grunning状态以外的其它状态组合)
参考资料:
Go语言并发模型 G源码分析的更多相关文章
- 并发工具CyclicBarrier源码分析及应用
本文首发于微信公众号[猿灯塔],转载引用请说明出处 今天呢!灯塔君跟大家讲: 并发工具CyclicBarrier源码分析及应用 一.CyclicBarrier简介 1.简介 CyclicBarri ...
- Java并发-ConcurrentModificationException原因源码分析与解决办法
一.异常原因与异常源码分析 对集合(List.Set.Map)迭代时对其进行修改就会出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException异常.这里以ArrayList ...
- Java并发编程-ReentrantLock源码分析
一.前言 在分析了 AbstractQueuedSynchronier 源码后,接着分析ReentrantLock源码,其实在 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 的分析中,已经提到 ...
- Java并发编程 ReentrantLock 源码分析
ReentrantLock 一个可重入的互斥锁 Lock,它具有与使用 synchronized 方法和语句所访问的隐式监视器锁相同的一些基本行为和语义,但功能更强大. 这个类主要基于AQS(Abst ...
- 并发工具CountDownLatch源码分析
CountDownLatch的作用类似于Thread.join()方法,但比join()更加灵活.它可以等待多个线程(取决于实例化时声明的数量)都达到预期状态或者完成工作以后,通知其他正在等待的线程继 ...
- 并发编程—— FutureTask 源码分析
1. 前言 当我们在 Java 中使用异步编程的时候,大部分时候,我们都会使用 Future,并且使用线程池的 submit 方法提交一个 Callable 对象.然后调用 Future 的 get ...
- 并发编程 —— Timer 源码分析
前言 在平时的开发中,肯定需要使用定时任务,而 Java 1.3 版本提供了一个 java.util.Timer 定时任务类.今天一起来看看这个类. 1.API 介绍 Timer 相关的有 3 个类: ...
- Java精通并发-通过openjdk源码分析ObjectMonitor底层实现
在我们分析synchronized关键字底层信息时,其中谈到了Monitor对象,它是由C++来实现的,那,到底它长啥样呢?我们在编写同步代码时完全木有看到该对象的存在,所以这次打算真正来瞅一下它的真 ...
- Java并发编程-AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
简介 提供了一个基于FIFO队列,可以用于构建锁或者其他相关同步装置的基础框架.该同步器(以下简称同步器)利用了一个int来表示状态,期望它能够成为实现大部分同步需求的基础.使用的方法是继承,子类通过 ...
随机推荐
- javascript 享元模式 flyweight
* 适应条件 ** 一个程序中使用了大量的相似对象 造成大的内存开销 ** 对象的大多数状态都可以变为外部状态 ** 剥离出对象的外部状态之后, 可以使用相对较少的共享对象取代大量对象 * 上传文件的 ...
- 配置阿里云maven
在安装好Maven之后,默认的~/.m2目录下是没有maven仓库配置文件settings.xml的,默认使用的是官方的仓库,访问速度会非常慢,我们需要配置下国内的仓库. 创建~/.m2/settin ...
- P7726-天体探测仪(Astral Detector)【构造】
正题 题目链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P7726 题目大意 一个长度为\(n\)的排列,给出\(n\)个可重集\(S_i\)表示所有长度为\(i\)的区间的 ...
- 深入浅出WPF-11.Template(模板)03
模板 如果把WPF窗体看做一个舞台的话,窗体上的控件就是演员,他们的职责就是在用户界面上按照业务逻辑的需呀哦扮演自己的角色.为了让同一个控件担当起不同的角色,程序员就要为他们设计多种外观样式和行为动作 ...
- 数据结构与算法——迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
tip:这个算法真的很难讲解,有些地方只能意会了,多思考多看几遍还是可以弄懂的. 应用场景-最短路径问题 战争时期,胜利乡有 7 个村庄 (A, B, C, D, E, F, G) ,现在有六个邮差, ...
- Vulnhub实战-JIS-CTF_VulnUpload靶机👻
Vulnhub实战-JIS-CTF_VulnUpload靶机 下载地址:http://www.vulnhub.com/entry/jis-ctf-vulnupload,228/ 你可以从上面地址获取靶 ...
- 利用OpenCV存储一段视频中的每一帧
// vfc.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点.#include "stdafx.h"#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> ...
- 题解 「2017 山东一轮集训 Day7」逆序对
题目传送门 Description 给定 $ n, k $,请求出长度为 $ n $ 的逆序对数恰好为 $ k $ 的排列的个数.答案对 $ 10 ^ 9 + 7 $ 取模. 对于一个长度为 $ n ...
- 阿里P8面试官:如何设计一个扛住千万级并发的架构?
大家先思考一个问题,这也是在面试过程中经常遇到的问题. 如果你们公司现在的产品能够支持10W用户访问,你们老板突然和你说,融到钱了,会大量投放广告,预计在1个月后用户量会达到1000W,如果这个任务交 ...
- NX 图标
vector_on_curve crosscut_zig_zag_with_lifts vector_along_curve zlevel_zig add_new_sc zlevel_zi ...
