JavaSE学习总结第17天_集合框架3
17.01 ArrayList集合的toString()方法源码解析
代码:
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
System.out.println(c);
输出c时默认调用的是c的toString()方法
A:Collection c = new ArrayList();
这是多态,所以输出c的 toString()方法,其实是输出ArrayList的toString()方法
B:看 ArrayList 的 toString()方法
在ArrayList里面却没有发现toString()。应该去父类查找→ AbstractList → AbstractCollection
C:toString()的方法源码
public String toString()
{
Iterator<E> it = iterator(); //集合本身调用迭代器方法,得到集合迭代器
if (! it.hasNext())
return "[]"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;)
{
E e = it.next(); //e=hello,world,java
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (! it.hasNext())
//[hello, world, java]
return sb.append(']').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
17.02 Set集合概述及特点
Set接口概述:一个不包含重复元素的 collection
特点:
无序(存入与取出的顺序不一致)
唯一(存入集合的元素唯一)
17.03 HashSet存储字符串并遍历
HashSet类概述:不保证 set 的迭代顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。此类允许使用 null 元素。
例:
public class Practice
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
hs.add("hello");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("java"); for (String s : hs)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
运行结果:
hello
java
world
17.04 HashSet保证元素唯一性的源码解析
interface Collection
{...} interface Set extends Collection
{...} class HashSet implements Set
{
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; public HashSet()
{
map = new HashMap<>();
} public boolean add(E e)
{ //e=hello,world
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
} class HashMap implements Map
{
public V put(K key, V value)
{ //key=e=hello,world //看哈希表是否为空,如果空,就开辟空间
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE)
{
inflateTable(threshold);
} //判断对象是否为null
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); //和对象的hashCode()方法相关 //在哈希表中查找hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
{
//这次的e其实是第一次的world
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
{
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
//走这里其实是没有添加元素
}
} modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i); //把元素添加
return null;
} transient int hashSeed = 0; final int hash(Object k)
{ //k=key=e=hello,
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String)
{
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
} h ^= k.hashCode(); //这里调用的是对象的hashCode()方法 // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
}
通过查看add方法的源码,知道这个方法底层依赖两个方法:hashCode()和equals()。
判断元素唯一性的方式:通过对象的hashCode和equals方法来完成元素唯一性
如果对象的hashCode值不同,那么不用判断equals方法,就直接存储到哈希表中。
如果对象的hashCode值相同,那么要再次判断对象的equals方法是否为true。
如果为true,视为相同元素,不存。如果为false,那么视为不同元素,就进行存储。
如果类没有重写这两个方法,默认使用的Object()。一般来说不会相同。
17.05 HashSet存储自定义对象并遍历
public class Practice
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>(); hs.add(new Student("小明",23));
hs.add(new Student("旺财",12));
hs.add(new Student("旺财",12));
hs.add(new Student("小强",24));
hs.add(new Student("小明",22));
hs.add(new Student("小红",22)); for(Student s : hs)
{
System.out.println(s.getName()+":"+s.getAge());
}
}
}
17.06 HashSet保证元素唯一性的代码体现
上例中重复元素被存入到了集合中,因为Student没有重写hashCode和equals方法,默认使用的Object()的hashCode和equals方法,一般来说结果不会相同,所以存入到了集合中,Student类应重写hashCode和equals方法(自动生成)。
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Student other = (Student) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null)
{
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
17.07 LinkedHashSet的概述和使用
LinkedHashSet类概述:
元素有序唯一:由链表保证元素有序、由哈希表保证元素唯一
例:
public class Practice
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashSet<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
hs.add("hello");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("world");
hs.add("java"); for(String s : hs)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
运行结果:
hello
world
java
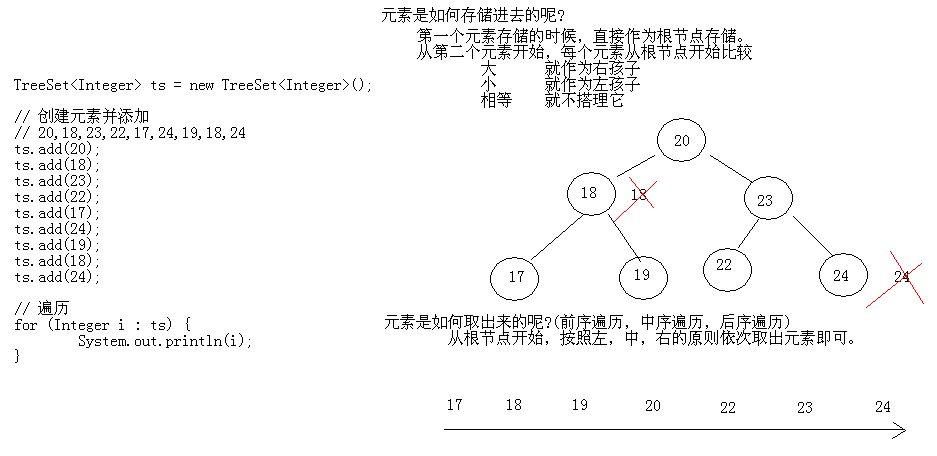
17.08 TreeSet存储Integer类型的元素并遍历
TreeSet类概述:使用元素的自然顺序对元素进行排序,或者根据创建 set 时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
例:
public class Practice
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>();
ts.add(20);
ts.add(18);
ts.add(23);
ts.add(22);
ts.add(17);
ts.add(24);
ts.add(19);
ts.add(18); for(Integer i : ts)
{
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
运行结果:
17 18 19 20 22 23 24
17.09 TreeSet保证元素排序的源码解析
interface Collection {...}
interface Set extends Collection {...}
interface NavigableMap {}
class TreeMap implements NavigableMap
{
public V put(K key, V value)
{
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null)
{
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null)
{
do
{
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else
{
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do
{
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
}
class TreeSet implements Set
{
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
public TreeSet()
{
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
public boolean add(E e)
{
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
}
真正的比较是依赖于元素的compareTo()方法,而这个方法是定义在 Comparable里面的。
所以,要想重写该方法,就必须是先实现 Comparable接口。这个接口表示的就是自然排序。
17.10 TreeSet保证元素唯一性和自然排序的原理和图解
17.11 TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习1
Student类实现自然排序接口Comparable,重写compareTo()方法
@Override
public int compareTo(Student s)
{
//主要条件,按年龄排
int num = this.age - s.age;
//次要条件,年龄相同按姓名排
int num2 = (num == 0)?this.name.compareTo(s.name):num;
return num2;
}
17.12 TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习2
Student类实现自然排序接口Comparable,重写compareTo()方法
@Override
public int compareTo(Student s)
{
// 主要条件 姓名的长度
int num = this.name.length() - s.name.length();
// 姓名的长度相同,比较姓名的内容是否相同
int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : num;
// 姓名的长度和内容相同,比较年龄是否相同,继续判断年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? this.age - s.age : num2;
return num3;
}
17.13 TreeSet保证元素唯一性和比较器排序的原理及代码实现
// 比较器排序,让集合具备比较性,匿名内部类实现
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>()
{
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
{
// 姓名长度
int num = s1.getName().length() - s2.getName().length();
// 姓名内容
int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num;
// 年龄
int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getAge() - s2.getAge() : num2;
return num3;
} });
17.14 TreeSet对元素排序的总结
唯一性:根据比较的返回的是否是0来决定
排序: 1.自然排序,一个类的元素想要进行自然排序就必须实现自然排序接口Comparable(元素具备比较性)
2.比较器排序,让集合的构造方法接收一个比较器接口的子类对象Comparator(集合具备比较性)
17.15 产生10个1-20之间的随机数要求随机数不能重复案例简洁版
编写一个程序,获取10个1至20的随机数,要求随机数不能重复。
public class Practice
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// 创建随机数对象
Random r = new Random(); // 创建一个Set集合
HashSet<Integer> ts = new HashSet<Integer>(); // 判断集合的长度是不是小于10
while (ts.size() < 10)
{
int num = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
ts.add(num);
} // 遍历Set集合
for (Integer i : ts)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
17.16 键盘录入学生信息按照总分排序后输出在控制台案例
Student类
public class Student
{
private String name;
private int chinese;
private int math;
private int english;
public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english)
{
super();
this.name = name;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public int getChinese()
{
return chinese;
}
public void setChinese(int chinese)
{
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public int getMath()
{
return math;
}
public void setMath(int math)
{
this.math = math;
}
public int getEnglish()
{
return english;
}
public void setEnglish(int english)
{
this.english = english;
} public int getSum()
{
return this.chinese+this.english+this.math;
}
}
测试类
public class Practice
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>()
{
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
{
//按总分比较
int num1 = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum();
//总分相同按语文成绩比较
int num2 = num1==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num1;
//语文成绩相同按数学成绩比较
int num3 = num2==0?s1.getMath() - s2.getMath():num2;
//数学成绩相同按英语成绩比较
int num4 = num3==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num3;
//英语成绩相同按姓名比较
int num5 = num4==0?s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()):num4;
return num5;
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的姓名");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的语文成绩");
String chinese = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的数学成绩");
String math = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的英语成绩");
String english = sc.nextLine(); Student s = new Student(name, Integer.parseInt(chinese), Integer.parseInt(math), Integer.parseInt(english));
ts.add(s);
}
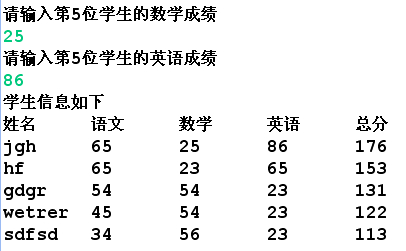
System.out.println("学生信息如下");
System.out.println("姓名\t语文\t数学\t英语\t总分");
for(Student s:ts)
{
System.out.println(s.getName()+"\t"+s.getChinese()+"\t"+s.getMath()+"\t"+s.getEnglish()+"\t"+s.getSum());
}
}
}
运行结果:
JavaSE学习总结第17天_集合框架3的更多相关文章
- JavaSE学习总结第15天_集合框架1
15.01 对象数组的概述和使用 public class Student { // 成员变量 private String name; private int age; // 构造方法 publ ...
- JavaSE学习总结第16天_集合框架2
16.01 ArrayList存储字符串并遍历 ArrayList类概述:底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢,线程不安全,效率高 ArrayList类是List 接口的大小可变数组的实现.实现了所 ...
- JavaSE学习总结第18天_集合框架4
18.01 Map集合概述和特点 Map接口概述:将键映射到值的对象,一个映射不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值 Map接口和Collection接口的不同 1.Map是双列的,Coll ...
- javaSE学习笔记(17)---锁
javaSE学习笔记(17)---锁 Java提供了种类丰富的锁,每种锁因其特性的不同,在适当的场景下能够展现出非常高的效率.本文旨在对锁相关源码(本文中的源码来自JDK 8).使用场景进行举例,为读 ...
- Java基础学习(四)-- 接口、集合框架、Collection、泛型详解
接口 一.接口的基本概念 关键字为:Interface,在JAVA编程语言中是一个抽象类型,是抽象方法的集合.也是使用.java文件编写. 二.接口声明 命名规范:与类名的命名规范相同,通常情况下 ...
- Java之旅_高级教_集合框架
摘自:http://www.runoob.com/java/java-collections.html Java 集合框架 早在Java2之前,java 就提供了特设类.比如:Dictionary,V ...
- Java学习日记基础篇(九) —— 集合框架,泛型,异常
集合框架 有事我们会需要一个能够动态的调整大小的数组,比如说要添加新员工但是数组已经满了,并且数组的大小是在定义的时候定死的,所以我们就需要一个能够动态调整大小的数组或者用链表解决,而java中提供了 ...
- java oop第07章_集合框架
一. 什么是集合: 在Java中提供了一些可以保存同一数据类型的数据集称为集合,就是规定了一些集合的规范(接口.抽象类.实现类)及方法, 方便我们程序在保存数据时进行增.删.改.查操作,编程更加高效. ...
- JavaSE学习总结第27天_反射 & 设计模式 & JDK5、7、8新特性
27.01 反射_类的加载概述和加载时机 类的加载:当程序要使用某个类时,如果该类还未被加载到内存中,则系统会通过加载,连接,初始化三步来实现对这个类进行初始化. 加载:就是指将class文件读 ...
随机推荐
- RHEL6.4 NFS文件共享服务搭建
NFS文件共享服务 1 实验方案 使用2台RHEL6.4虚拟机,其中一台作为NFS共享服务器(192.168.100.1).另外一台作为测试用的NFS客户机(192.168.100.2) 2.实现 2 ...
- Android studio之更改快捷键及自动导包
更改AS中的代码提示快捷键,AS做的也挺智能的,在Keymap中可以选择使用eclipse的快捷键设置,但是虽然设置了,对有些快捷键还是不能使用,那么就需要我们手动去修改了. 在代码提示AS默认的快捷 ...
- 让Java的反射跑快点
由于反射涉及动态解析的类型,某些Java虚拟机的优化不能被执行,所以导致了一定的性能的问题,特别是在JDK6以前特别严重,有时甚至达到数百倍,但是在JDK6以后,据说性能差别就不是哪么大了,JDK对此 ...
- javascript集合求交集
两集合求交集 思路: 1. 每一次从B数组中取一值,然后在A数组里逐个比较,如果有相等的,则保存.该算法复杂度为 O(MN). M, N 分别为数组 A B 的长度. 2. 因为A B 都排过序,所以 ...
- 用Java实现 ,冒泡排序与普通排序的区别
冒泡排序与普通排序的区别 /** *个人网址: http://www.lipengfei2013.tk * 功能:冒泡排序与普通排序的区别 */ package www.csdn ...
- 黑马程序员_<<StringBuffer,包装类>>
--------------------ASP.Net+Android+IOS开发..Net培训.期待与您交流! -------------------- 1. StringBuffer 1.概述 S ...
- CodeForces 154B- Colliders
预处理...由于10^5<2^20..所以每个数的质因子个数最多20个..为了避免重复运算..将素有数的质因子打表出来... 两个数如果互质..那么他们的最大公约数为1..反过来说..两个数如果 ...
- java之Set源代码浅析
Set的接口和实现类是最简单的,说它简单原因是由于它的实现都是基于实际的map实现的. 如 hashSet 基于hashMap,TreeSet 基于TreeMap,CopyOnWriteArraySe ...
- Android Fragment 嵌套使用报错
在新的SDK每次创建activity时,会自己主动生成 <pre name="code" class="java">public static c ...
- 火狐浏览器开始支持3D游戏和视屏通话
最近,Mozilla发布了第22版本的火狐浏览器,这个版本增加了对3D游戏.视频通话和文件分享功能的支持.现在使用者不必下载额外的插件或者第三方软件就可以使用上面的所有特性.为了鼓励更多的开发者为火狐 ...
