使用mxnet实现卷积神经网络LeNet
1.LeNet模型
LeNet是一个早期用来识别手写数字的卷积神经网络,这个名字来源于LeNet论文的第一作者Yann LeCun。LeNet展示了通过梯度下降训练卷积神经网络可以达到手写数字识别在当时最先进的成果,这个尊基性的工作第一次将卷积神经网络推上舞台
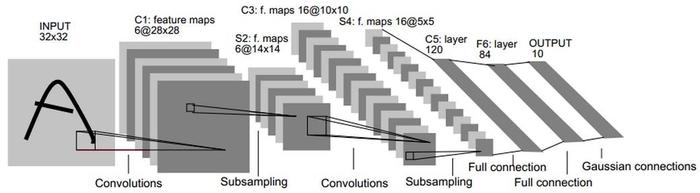
上图就是LeNet模型,下面将对每层参数进行说明
1.1 input输入层
假设输入层数据shape=(32,32)
1.2 C1卷积层
- 卷积核大小: kernel_size=(5,5)
- 步幅:stride = 1
- 输出通道为6
- 可训练参数为: (5 * 5 + 1) * 6
- 激活函数:采用relu
输入层数据经过C1卷积层后将得到feature maps形状(6 * 28 * 28),注:28 = 32 -5 + 1
1.3 S2池化层
池化层(Max Pooling)窗口形状均为2*2,步幅度为2,输出feature maps为(6 *14 * 14),6为feature map的数量
1.4 C3卷积层
- 卷积核大小: kernel_size=(5,5)
- 步幅:stride = 1
- 输出通道为16
- 激活函数:采用relu得到feature maps为(16 * 10 * 10),(10*10)为每个feature map形状,16为feature map数量
1.5 S4池化层
池化层(Max Pooling)窗口形状依然均为2*2,步幅度为2,输出feature maps为(16 *5 * 5),16为feature map的数量
1.6 C5全链接层
- 输出120个神经元
- 激活函数:relu
1.7 F6全连接层
- 输出84个神经元
- 激活函数:relu
1.8 output
- 输出10个神经元
- 激活函数:无
2.用Mxnet实现LeNet模型
import mxnet as mx
from mxnet import autograd,init,nd
from mxnet.gluon import nn,Trainer
from mxnet.gluon import data as gdata
from mxnet.gluon import loss as gloss
import time
class LeNet_mxnet:
def __init__(self):
self.net = nn.Sequential()
self.net.add(nn.Conv2D(channels=6,kernel_size=5,activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size =(2,2),strides=(2,2)),
nn.Conv2D(channels=16,kernel_size=(5,5),strides=(1,1),padding=(0,0),activation='relu'),
nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size =(2,2),strides=(2,2)),
nn.Dense(units=120,activation='relu'),
nn.Dense(units=84,activation='relu'),
nn.Dense(units=10) #最后一个全连接层激活函数取决于损失函数
)
def train(self,train_iter,test_iter,n_epochs,ctx):
print('training on',ctx)
self.net.initialize(force_reinit=True,ctx=ctx,init=init.Xavier())
trainer_op = Trainer(self.net.collect_params(),'adam',{'learning_rate':0.01})
loss = gloss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()
accuracy_val = 0
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
train_loss_sum,train_acc_sum,n,start = 0.0,0.0,0,time.time()
for x_batch,y_batch in train_iter:
x_batch,y_batch = x_batch.as_in_context(ctx),y_batch.as_in_context(ctx)
with autograd.record():
y_hat = self.net(x_batch)
loss_val = loss(y_hat,y_batch).sum()
loss_val.backward()
trainer_op.step(n_batches)
y_batch = y_batch.astype('float32')
train_loss_sum += loss_val.asscalar()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(axis=1) == y_batch).sum().asscalar()
n += y_batch.size
test_acc = self.accuracy_score(test_iter,ctx)
accuracy_val += self.accuracy_score(test_iter,ctx)
print('epoch:%d,train_loss:%.4f,train_acc:%.3f,test_acc:%.3f,time:%.1f sec'
%(epoch+1, train_loss_sum / n, train_acc_sum/ n,test_acc,time.time() - start))
def accuracy_score(self,data_iter,ctx):
acc_sum,n = nd.array([0],ctx=ctx),0
for x,y in data_iter:
x,y = x.as_in_context(ctx),y.as_in_context(ctx)
y = y.astype('float32')
acc_sum += (self.net(x).argmax(axis=1) == y).sum()
n += y.size
return acc_sum.asscalar() / n
def __call__(self,x):
return self.net(x)
def predict(self,x,ctx):
x = x.as_in_context(ctx)
return self.net(x).argmax(axis=1)
def print_info(self):
print(self.net[4].params)
3.使用mnist手写数字数据集进行测试
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
(x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test) = mnist.load_data()
print(x_train.shape,y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape,y_test.shape)
x_train = x_train.reshape(60000,1,28,28).astype('float32')
x_test = x_test.reshape(10000,1,28,28).astype('float32')
(60000, 28, 28) (60000,)
(10000, 28, 28) (10000,)
lenet_mxnet = LeNet_mxnet()
epochs = 10
n_batches = 500
train_iter = gdata.DataLoader(gdata.ArrayDataset(x_train,y_train),batch_size=n_batches)
test_iter = gdata.DataLoader(gdata.ArrayDataset(x_test,y_test),batch_size=n_batches)
lenet_mxnet.train(train_iter,test_iter,epochs,ctx=mx.gpu())
training on gpu(0)
epoch:1,train_loss:1.8267,train_acc:0.571,test_acc:0.896,time:3.0 sec
epoch:2,train_loss:0.2449,train_acc:0.924,test_acc:0.948,time:2.6 sec
epoch:3,train_loss:0.1563,train_acc:0.952,test_acc:0.954,time:2.6 sec
epoch:4,train_loss:0.1302,train_acc:0.961,test_acc:0.962,time:2.5 sec
epoch:5,train_loss:0.1169,train_acc:0.964,test_acc:0.958,time:2.5 sec
epoch:6,train_loss:0.1017,train_acc:0.969,test_acc:0.967,time:2.5 sec
epoch:7,train_loss:0.0855,train_acc:0.973,test_acc:0.964,time:3.3 sec
epoch:8,train_loss:0.0848,train_acc:0.973,test_acc:0.964,time:3.6 sec
epoch:9,train_loss:0.0767,train_acc:0.976,test_acc:0.963,time:3.5 sec
epoch:10,train_loss:0.0771,train_acc:0.977,test_acc:0.970,time:3.5 sec
# 将预测结果可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plt_image(image):
n = 20
plt.figure(figsize=(20,4))
for i in range(n):
ax = plt.subplot(2,10,i+1)
plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28,28))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
plt_image(x_test)
print('predict result:',lenet_mxnet.predict(nd.array(x_test[0:20]),ctx=mx.gpu()))
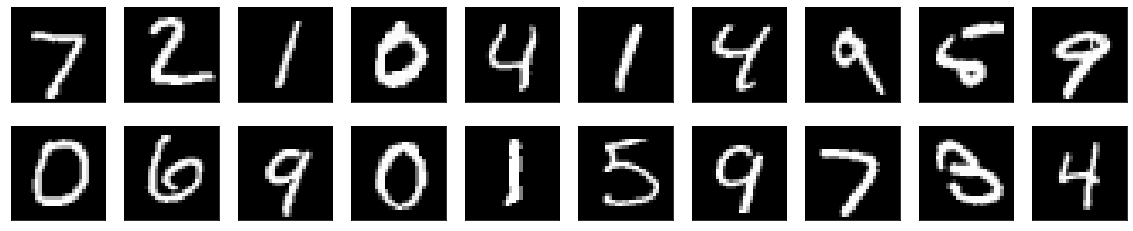
predict result:
[7. 2. 1. 0. 4. 1. 4. 9. 5. 9. 0. 6. 9. 0. 1. 5. 9. 7. 3. 4.]
<NDArray 20 @gpu(0)>
4. 附:需要注意的知识点
(1) 注意SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss的使用,hybrid_forward源码说明,若from_logits为False时(默认为Flase),会先通过log_softmax计算各分类的概率,再计算loss,同样SigmoidBinaryCrossEntropyLoss也提供了from_sigmoid参数决定是否在hybrid_forward函数中要计算sigmoid函数,所以在创建模型最后一层的时候要特别注意是否要给激活函数
(2) 注意权重初始化选择
(3) 注意(y_hat.argmax(axis=1) == y_batch)操作时y_batch数据类型转换
(4) 上面的模型没有对数据集进行归一化处理,可以添加该步骤
使用mxnet实现卷积神经网络LeNet的更多相关文章
- MXNET:卷积神经网络
介绍过去几年中数个在 ImageNet 竞赛(一个著名的计算机视觉竞赛)取得优异成绩的深度卷积神经网络. LeNet LeNet 证明了通过梯度下降训练卷积神经网络可以达到手写数字识别的最先进的结果. ...
- TensorFlow+实战Google深度学习框架学习笔记(12)------Mnist识别和卷积神经网络LeNet
一.卷积神经网络的简述 卷积神经网络将一个图像变窄变长.原本[长和宽较大,高较小]变成[长和宽较小,高增加] 卷积过程需要用到卷积核[二维的滑动窗口][过滤器],每个卷积核由n*m(长*宽)个小格组成 ...
- MXNET:卷积神经网络基础
卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network).它是近年来深度学习能在计算机视觉中取得巨大成果的基石,它也逐渐在被其他诸如自然语言处理.推荐系统和语音识别等领域广泛使用. 目 ...
- 卷积神经网络LeNet Convolutional Neural Networks (LeNet)
Note This section assumes the reader has already read through Classifying MNIST digits using Logisti ...
- 卷积神经网络之LeNet
开局一张图,内容全靠编. 上图引用自 [卷积神经网络-进化史]从LeNet到AlexNet. 目前常用的卷积神经网络 深度学习现在是百花齐放,各种网络结构层出不穷,计划梳理下各个常用的卷积神经网络结构 ...
- 卷积神经网络详细讲解 及 Tensorflow实现
[附上个人git完整代码地址:https://github.com/Liuyubao/Tensorflow-CNN] [如有疑问,更进一步交流请留言或联系微信:523331232] Reference ...
- 经典卷积神经网络(LeNet、AlexNet、VGG、GoogleNet、ResNet)的实现(MXNet版本)
卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)是一种前馈神经网络,它的人工神经元可以响应一部分覆盖范围内的周围单元,对于大型图像处理有出色表现. 其中 文章 详解卷 ...
- 卷积神经网络的一些经典网络(Lenet,AlexNet,VGG16,ResNet)
LeNet – 5网络 网络结构为: 输入图像是:32x32x1的灰度图像 卷积核:5x5,stride=1 得到Conv1:28x28x6 池化层:2x2,stride=2 (池化之后再经过激活函数 ...
- 从LeNet到SENet——卷积神经网络回顾
从LeNet到SENet——卷积神经网络回顾 从 1998 年经典的 LeNet,到 2012 年历史性的 AlexNet,之后深度学习进入了蓬勃发展阶段,百花齐放,大放异彩,出现了各式各样的不同网络 ...
随机推荐
- laravel中如何执行请求
laravel中如何执行request请求?本篇文章给大家介绍关于laravel中执行请求的方法,需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助. 我们先来看一下request是什么? 客户端(例如Web浏 ...
- 洛谷疯狂coding~
1.关于数学建模思想在coding之中的应用. 将马路作为一条数轴,每棵树的位置作为数轴上的坐标点,再将坐标点与数组的下标联系到一起,完成建模. 2.本题坑点在于对“其中有多少个数,恰好等于集合中另外 ...
- 【leetcode】字母异位词分组
给定一个字符串数组,将字母异位词组合在一起.字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串. 示例: 输入: ["eat", "tea", "tan&quo ...
- office常用技巧汇总
1.excel篇 (1)一次选择多行 可以利用SHIFT+鼠标实现,点第一行,按下鼠标,点200行,就能实现1~200行选择了. 总结:就是一直按住shift键,鼠标点击要选择的首行,再点击尾行.
- linux下c++如何输入不回显
#include <stdio.h> #include <termios.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <iostream& ...
- bean的shutdown
使用@Bean注解,在不配置destroyMethod时,其默认值为: String destroyMethod() default AbstractBeanDefinition.INFER_METH ...
- Java 8创建Stream流的5种方法
不知不觉间,Java已经发展到13了,来不及感慨时间过得真的太快了,来不及学习日新月异的技术更新,目前大多数公司还是使用的JDK8版本,一方面是版本的稳定,另一方面是熟悉,所以很多公司都觉得不升级也挺 ...
- 「vue基础」一篇浅显易懂的 Vue 路由使用指南( Vue Router 上)
大家好,今天的内容,我将和大家一起聊聊 Vue 路由相关的知识,如果你以前做过服务端相关的开发,那你一定会对程序的URL结构有所了解,我没记错的话也是路由映射的概念,需要进行配置. 其实前端这些框架的 ...
- Queue接口分析:add和offer区别,remove和poll方法到底啥区别
Queue接口: public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> { /* * add方法,在不违背队列的容量限制的情况,往队列 ...
- asp.net webapi 随笔
第一次写博客,文笔有限,记录下学习的过程 话不多说,直接开干 首先用vs2017建立一个空网站项目,然后只勾选api 项目建立后,如下结构 其中WebApiConfig类配置了路由相关信息 publi ...
