《Java Spring框架》SpringXML配置详解
Spring框架作为Bean的管理容器,其最经典最基础的Bean配置方式就是纯XML配置,这样做使得结构清晰明了,适合大型项目使用。Spring的XML配置虽然很繁琐,而且存在简洁的注解方式,但读懂XML配置文件对我们来说依然很重要,尚且对于老系统维护必不可少的面对XML配置。
下面通过案例来理解XML配置。
案例:(一个基础的Bean)
public class Pet {
private String petType;
private String color ;
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String toString(){
return"petType: "+petType+" color: "+color;
}
}
public class User {
String id;
String name;
String passWord;
Pet pet;
public Pet getPet() {
return pet;
}
public void setPet(Pet pet) {
this.pet = pet;
}
public User(){
System.out.println("spring 需要一个空参构造!");
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", passWord='" + passWord + '\'' +
", pet=" + pet +
'}';
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("User初始化执行init方法!");
}
public void userDestroy(){
System.out.println("userDestroy方法被执行!");
}
}
import com.bing.tao.bean.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class HelloSpring { /**
* IOC的反转:创建对象这份工作由我们自己执行反转给spring帮我们执行;
* IOC的控制:就是由spring帮我们负责创建销毁对象,掌控对象的生命周期等,我们在需要使用对象的时候跟Spring申请即可;
* IOC是一种编程思想,也是一种新的设计模式,它需要DI(依赖注入)技术的支持;
* spring是一个容器,它将帮我们管理对象
*/
@Test
public void Test1(){
//根据spring配置文件获取容器对象
//ApplicationContext 配置的所有bean都会在容器创建的时候被创建出来
//如果配置的bean较多,那么在创建容的时候,会产生内存过大的问题;这种情况在机器硬件性能较为落后的时候体现的比较明显;
//延迟加载 true就是创建容器时不加载配置的bean对象,在获取的时候才创建;
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user= (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println("user: "+user);
//通过getBean获取配置好的user对象(程序员向spring容器要对象)
user= applicationContext.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println("user: "+user);
applicationContext.close();
}
}
重要的配置:(创建一个名字叫:applicationContext.xml的配置文件)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- spring管理bean的XML,一个bean标签表示一个bean。-->
<!-- name属性给bean取名,代码中可以通过:applicationContext.getBean("user"); 获取class-->
<!-- class:是被管理对象的全包名,spring会通过这个包名来创建对象 -->
<!-- scope 属性,控制对象的单例还是多例,prototype多例-->
<!-- 在web环境下,如果scope属性为request 那么这个对象被创建出来 他的生命周期会与request请求一致-->
<!-- session 同理 ,生命周期与session一致 -->
<!-- lazy-init 延迟加载,获取bean 的时候才加载 ,否则在创建容器是就会加载bean。-->
<!-- 初始化方法:init-method,spring创建bean的时候会执行-->
<!-- 销毁bean方法:destroy-method spring销毁bean的时候会执行-->
<bean name = "user" class="com.bing.tao.bean.User" scope="singleton" lazy-init="false" init-method="init" destroy-method="userDestroy">
<!-- property 标签,是用于bean内部属性初始化值使用的。-->
<!-- name 对应bean的变量名,value 就是初始值。-->
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
<property name="name" value="蕾蕾"></property>
<property name="passWord" value="123456"></property>
<!-- 引用类型的初始化 -->
<property name="pet" ref="pet"></property>
</bean> <!-- 将pet对象交给spring管理,并注入值类型 -->
<bean name = "pet" class="com.bing.tao.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"></property>
<property name="color" value="灰灰"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行结果:
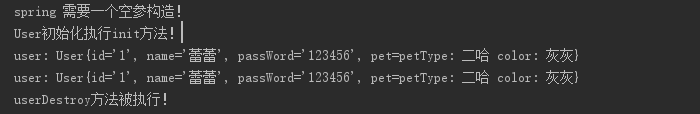
配置文件,已经将标签含义说明清楚。补充一点:如果是多例则spring不在管理bean而是交给你管理,销毁方法将不再执行。
Spring XML配置如何支持构造函数和复杂数据类型(List等):
修改User类:
public class User {
String id;
String name;
String passWord;
Pet pet;
public Pet getPet() {
return pet;
}
public void setPet(Pet pet) {
this.pet = pet;
}
public User(){
System.out.println("spring 需要一个空参构造!");
}
public User(String name, Pet pet) {
System.out.println("打印构造方法1:name :"+name +"pet:"+pet);
this.name = name;
this.pet = pet;
}
public User(Pet pet,String name) {
System.out.println("打印构造方法2:name :"+name +"pet:"+pet);
this.name = name;
this.pet = pet;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", passWord='" + passWord + '\'' +
", pet=" + pet +
'}';
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("User初始化执行init方法!");
}
public void userDestroy(){
System.out.println("userDestroy方法被执行!");
}
}
新增测试方法:
import com.bing.tao.bean.MyCollection;
import com.bing.tao.bean.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class HelloSpring2 { @Test
public void Test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_Injection.xml");
User user= (User) applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("-----------------分割线-----------------");
MyCollection myCollection= (MyCollection) applicationContext.getBean("myCollection");
System.out.println(myCollection);
}
}
新增配置文件:applicationContext_Injection.xml
配置内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 构造方法注入 -->
<bean name="user" class="com.bing.tao.bean.User">
<!-- name 调用构造方法的参数名称 value 是注入值类型 ref 注入引用类型 -->
<!-- type 是指定参数的类型 -->
<!-- index 是指定参数的 -->
<constructor-arg name="name" value="老王" type="java.lang.String" index="1"/>
<constructor-arg name="pet" ref="pet"/>
</bean> <!-- 将pet对象交给spring管理,并注入值类型 -->
<bean name = "pet" class="com.bing.tao.bean.Pet">
<property name="petType" value="二哈"></property>
<property name="color" value="灰灰"></property>
</bean> <!-- 复杂类型注入 -->
<bean name="myCollection" class="com.bing.tao.bean.MyCollection">
<!-- Array -->
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>123</value>
<value>abc</value>
<ref bean="pet"></ref>
</array>
</property> <!-- List -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>456</value>
<value>def</value>
<ref bean="user"></ref>
</list>
</property> <!-- Set -->
<!-- 当只有一个值得时候,可以简写成一下方式。 -->
<property name="set" value="789"></property> <!-- Map -->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="root" value="123"></entry>
<entry key="admin" value="456"></entry>
<entry key-ref="user" value-ref="pet"></entry>
</map>
</property> <!-- properties -->
<property name="prop">
<props>
<prop key="name">老李</prop>
<prop key="age">25</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
运行结果:

看到这边,大部分人都会觉得,每一个Bean都要这么操作一下,这么复杂,还不如直接写代码呢。
接下来,我们来简化配置。
先来简化配置:(新建一个配置文件:applicationContext_annotation.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:contest="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 将包 com.bing.tao.bean 下的Bean都交给Spring -->
<contest:component-scan base-package="com.bing.tao.bean"></contest:component-scan>
</beans>
将User修改成:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; /**
* @Component 用于标记该bean需要Spring实例化。
* @Scope 标签用于标记该bean是单例还是多例,singleton表示单例,prototype多例。
*/
@Component("user")
@Scope(scopeName = "singleton")
public class User { /**
* @Value标签可以将括号中的值注入到Spring生成的Bean中
*/
@Value("1")
String id;
@Value("蕾蕾")
String name;
@Value("123")
String passWord; public String getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
} public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
} public String toString(){
return"name: "+name+" id: "+id;
} //构造后调用
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("User初始化执行init方法!");
} //销毁前调用
@PreDestroy
public void userDestroy(){
System.out.println("userDestroy方法被执行!");
}
}
创建一个测试方法:
import com.bing.tao.bean.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class HelloSpring3 { @Test
public void Test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_annotation.xml");
//通过getBean获取配置好的user对象(程序员向spring容器要对象)
User user= (User) applicationContext.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user);
//scope="singleton" 是单例下才能出发销毁bean方法,如果是多例则spring不在关联bean而是交给你管理。
applicationContext.close();
}
}
运行结果:

这样就可以批量设置模式一样的Bean结构了。XML的配置就可以很好的简化。同时还倒逼了目录结构的整齐。
总结来源:http://www.sikiedu.com/ 网站学习。
《Java Spring框架》SpringXML配置详解的更多相关文章
- spring框架 AOP核心详解
AOP称为面向切面编程,在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题,比如日志,事务,权限等待,Struts2的拦截器设计就是基于AOP的思想,是个比较经典的例子. 一 AOP的基本概念 (1)Asp ...
- Java Spring cron表达式使用详解
Java Spring cron表达式使用详解 By:授客 QQ:1033553122 语法格式 Seconds Minutes Hours DayofMonth Month DayofWeek ...
- (网页)Java日志记录框架Logback配置详解(企业级应用解决方案)(转)
转自CSDN: 前言 Logback是现在比较流行的一个日志记录框架,它的配置比较简单学习成本相对较低,所以刚刚接触该框架的朋友不要畏惧,多花点耐心很快就能灵活应用了.本篇博文不会具体介绍Logbac ...
- spring mvc+myBatis配置详解
一.spring mvc Spring框架(框架即:编程注解+xml配置的方式)MVC是Spring框架的一大特征,Spring框架有三大特征(IOC(依赖注入),AOP(面向切面),MVC(建模M- ...
- spring sessionFactory 属性配置详解,applicationContext中各种属性详解
1.Bean的id为sessionFactory,对应的类为AnnotationSessionFactory,即采用注解的形式实现hibernate. 2.hibernateProperties,配置 ...
- JAVA spring 常用包作用详解(转)
转载地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Tmc-Blog/p/6093162.html <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org ...
- SSM三大框架整合配置详解
首先,导入框架所需要的全部jar包(此处省略...........) 第一步:先从mybatis框架开始 我们只需要在mybatis的核心配置文件sqlConfigXml里写上这么一段话,代表的是给p ...
- SSH三大框架整合配置详解
首先,三大框架整合,肯定是要导入相当多的jar包,这是不容置疑的! 这里就不一一列举了,直接截图吧: (1) 基于配置文件的整合: 第一步:我们需要在we ...
- spring+springMVC+JPA配置详解(使用缓存框架ehcache)
SpringMVC是越来越火,自己也弄一个Spring+SpringMVC+JPA的简单框架. 1.搭建环境. 1)下载Spring3.1.2的发布包:Hibernate4.1.7的发布包(没有使用h ...
随机推荐
- 隐藏input输入框的增减按钮
当input 使用了type='number'后,会出现这个增减数值的按钮,如上所示, 解决办法: 1.type='text' ,改为输入字符串,缺点是要做类型转换,而且移动端不会调出纯数字键盘 2. ...
- SpringBoot 项目脚手架
写在前面 之前也一直很少有写SpringBoot项目相关的文章,今天 准备整理一个我自己初始化SpringBoot项目时的一个脚手架,便于自己后面查阅.因为SpringBoot的约定大于配置,在整合各 ...
- 【Luogu P3379】LCA问题的倍增解法
Luogu P3379 题意:对于两个节点,寻找他们的最近公共祖先. 一个显而易见的解法是对于每一个节点我们都往上遍历一遍,记录下它每一个祖先,然后再从另一个节点出发,一步一步往上走,找到以前记录过第 ...
- vue通过控制boolean值来决定是否添加class类名
vue通过控制boolean值来决定是否添加class类名
- ##* %%* linux变量处理
链接来自他们分享,,,, 如有侵权,请联系本人删除,本人将立即删除.停止分享. https://blog.csdn.net/fengzijinliang/article/details/4252021 ...
- jsp实现增加数据功能
1. 环境的搭建 软件 数据库 sql myeclipse 8.0 tomcat 6.0 2. 安装完 myeclipse 配置下 部署tomcat 6.0 =1=> =2=> 新 ...
- List接口下的集合
集合框架 List接口下的集合特点: Set接口下的集合特点: 1.都是有序的 1.都是无序的 2.都有下标 2.没有下标 3.都可以重复 3.不可重复(覆盖) List接口下的集合 1.ArrayL ...
- 微信小程序——详细讲解页面传值(多种方法)
1.使用navigator的url带参传值 (1)在pageA页面有一个固定的值要传递到pageB页面,比如说一个固定的值user_id要传递给B <navigator url=".. ...
- Python自带又好用的代码调试工具Pdb学习笔记
返璞归真 这几天项目有一个linux下部署数据库的操作,数据库使用python进行初始化安装.然后问题来了,由于linux服务器涉及安全要求,除了代码以来的Python3.6版本外不允许安装其他插件与 ...
- 《手把手教你》系列进阶篇之1-python+ selenium自动化测试 - python基础扫盲(详细教程)
1. 简介 如果你从一开始就跟着宏哥看博客文章到这里,基础篇和练习篇的文章.如果你认真看过,并且手动去敲过每一篇的脚本代码,那边恭喜你,至少说你算真正会利用Python+Selenium编写自动化脚本 ...
