SQL Server 操作XML数据
1.xml.exist
输入为XQuery表达式,返回0,1或是Null。0表示不存在,1表示存在,Null表示输入为空
2.xml.value
输入为XQuery表达式,返回一个SQL Server标量值
3.xml.query
输入为XQuery表达式,返回一个SQL Server XML类型流
4.xml.nodes
输入为XQuery表达式,返回一个XML格式文档的一列行集
5.xml.modify
使用XQuery表达式对XML的节点进行insert , update 和 delete 操作。
下面通过例子对上面的五种操作进行说明:
declare @XMLVar xml = '
<catalog>
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Step By Step</title>
<author>Bill Zack</author>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
<book category="Developer">
<title>Developing ADO .NET</title>
<author>Andrew Brust</author>
<price>39.93</price>
</book>
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Cluster Server</title>
<author>Stephen Forte</author>
<price>59.99</price>
</book>
</catalog>' 1. xml.exist
select @XMLVar.exist('/catalog/book')-----返回1
select @XMLVar.exist('/catalog/book/@category')-----返回1
select @XMLVar.exist('/catalog/book1')-----返回0
set @XMLVar = null
select @XMLVar.exist('/catalog/book')-----返回null 2.xml.value
select @XMLVar.value('/catalog[1]/book[1]','varchar(MAX)')
select @XMLVar.value('/catalog[1]/book[2]/@category','varchar(MAX)')
select @XMLVar.value('/catalog[2]/book[1]','varchar(MAX)')
结果集为:
Windows Step By StepBill Zack49.99 Developer NULL 3.xml.query
select @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book')
select @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]')
select @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[2]/author')
结果集分别为:
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Step By Step</title>
<author>Bill Zack</author>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
<book category="Developer">
<title>Developing ADO .NET</title>
<author>Andrew Brust</author>
<price>39.93</price>
</book>
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Cluster Server</title>
<author>Stephen Forte</author>
<price>59.99</price>
</book>
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Step By Step</title>
<author>Bill Zack</author>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
<author>Andrew Brust</author> 4.xml.nodes
select T.c.query('.') as result from @XMLVar.nodes('/catalog/book') as T(c)
select T.c.query('title') as result from @XMLVar.nodes('/catalog/book') as T(c)
结果集分别为:
<book category="ITPro"><title>Windows Step By Step</title><author>Bill …………
<book category="Developer"><title>Developing ADO .NET</title><author>Andrew …………
<book category="ITPro"><title>Windows Cluster Server</title><author>Stephen …………
<title>Windows Step By Step</title>
<title>Developing ADO .NET</title>
<title>Windows Cluster Server</title> 5.xml.modify
SQL Server 2005/2008增加了对XML数据的支持,同时也新增了几种操作XML的方法,本文主要以SQL Server 2008为例介绍如何对XML数据进行insert、update、delete。
SQL Server中新增加了XML.Modify()方法,分别为xml.modify(insert),xml.modify(delete),xml.modify(replace)对应XML的插入,删除和修改操作。
本文以下面XML为例,对三种DML进行说明:
declare @XMLVar xml = '
<catalog>
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Step By Step</title>
<author>Bill Zack</author>
<price>49.99</price>
</book>
<book category="Developer">
<title>Developing ADO .NET</title>
<author>Andrew Brust</author>
<price>39.93</price>
</book>
<book category="ITPro">
<title>Windows Cluster Server</title>
<author>Stephen Forte</author>
<price>59.99</price>
</book>
</catalog>
' 1.XML.Modify(Insert)语句介绍
A.利用as first,at last,before,after四个参数将元素插入指定的位置
set @XMLVar.modify('insert <first name="at first" /> as first into (/catalog[1]/book[1])')
set @XMLVar.modify('insert <last name="at last"/> as last into (/catalog[1]/book[1])')
set @XMLVar.modify('insert <before name="before"/> before (/catalog[1]/book[1]/author[1])')
set @XMLVar.modify('insert <after name="after"/> after (/catalog[1]/book[1]/author[1])')
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]');
结果集为:
1: <book category="ITPro">
2: <first name="at first" />
3: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
4: <before name="before" />
5: <author>Bill Zack</author>
6: <after name="after" />
7: <price>49.99</price>
8: <last name="at last" />
9: </book> B.将多个元素插入文档中
--方法一:利用变量进行插入
DECLARE @newFeatures xml;
SET @newFeatures = N';
<first>one element</first>
<second>second element</second>'
SET @XMLVar.modify(' )
insert sql:variable("@newFeatures")
into (/catalog[1]/book[1])'
--方法二:直接插入
set @XMLVar.modify(')
insert (<first>one element</first>,<second>second element</second>)
into (/catalog[1]/book[1]/author[1])'
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]'); 结果集为: 1: <book category="ITPro">
2: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
3: <author>Bill Zack
4: <first>one element</first>
5: <second>second element</second>
6: </author>
7: <price>49.99</price>
8: <first>one element</first>
9: <second>second element</second>
10: </book> C.将属性插入文档中
--使用变量插入
declare @var nvarchar(10) = '变量插入'
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert (attribute var {sql:variable("@var")}))
into (/catalog[1]/book[1])'
--直接插入
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert (attribute name {"直接插入"}))
into (/catalog[1]/book[1]/title[1])'
--多值插入
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert (attribute Id {"多值插入1"},attribute name {"多值插入2"}) )
into (/catalog[1]/book[1]/author[1])'
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]'); 结果集为:
1: <book category="ITPro" var="变量插入">
2: <title name="直接插入">Windows Step By Step</title>
3: <author Id="多值插入1" name="多值插入2">Bill Zack</author>
4: <price>49.99</price>
5: </book> D.插入文本节点
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert text{"at first"} as first)
into (/catalog[1]/book[1])'
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]'); 结果集为:
1: <book category="ITPro">
2: at first
3: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
4: <author>Bill Zack</author>
5: <price>49.99</price>
6: </book> 注意:插入本文同样具体 as first,as last,before,after四种选项,可以参考A中的使用方法 E.插入注释节点
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert <!--插入评论-->)
before (/catalog[1]/book[1]/title[1])'
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]'); 结果集为:
1: <book category="ITPro">
2: <!--插入评论-->
3: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
4: <author>Bill Zack</author>
5: <price>49.99</price>
6: </book>
注意插入注释节点同样具体 as first,as last,before,after四种选项,可以参考A中的使用方法 F.插入处理指令
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert <?Program "Instructions.exe" ?>)
before (/catalog[1]/book[1]/title[1])'
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]');
结果集为:
1: <book category="ITPro">
2: <?Program "Instructions.exe" ?>
3: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
4: <author>Bill Zack</author>
5: <price>49.99</price>
6: </book>
注意插入处理指令同样具体 as first,as last,before,after四种选项,可以参考A中的使用方法 G.根据 if 条件语句进行插入
set @XMLVar.modify(
'insert )
if (/catalog[1]/book[1]/title[2]) then
text{"this is a 1 step"}
else ( text{"this is a 2 step"} )
into (/catalog[1]/book[1]/price[1])'
SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]/book[1]');
结果集为:
1: <book category="ITPro">
2: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
3: <author>Bill Zack</author>
4: <price>49.99this is a 2 step</price>
5: </book> 2.XML.Modify(delete)语句介绍
--删除属性
set @XMLVar.modify('delete /catalog[1]/book[1]/@category')
--删除节点
set @XMLVar.modify('delete /catalog[1]/book[1]/title[1]')
--删除内容
set @XMLVar.modify('delete /catalog[1]/book[1]/author[1]/text()')
--全部删除
set @XMLVar.modify('delete /catalog[1]/book[2]') SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]'); 结果集为:
1: <catalog>
2: <book>
3: <author />
4: <price>49.99</price>
5: </book>
6: <book category="ITPro">
7: <title>Windows Cluster Server</title>
8: <author>Stephen Forte</author>
9: <price>59.99</price>
10: </book>
11: </catalog> 3.XML.Modify(replace)语句介绍
--替换属性
set @XMLVar.modify('replace value of(/catalog[1]/book[1]/@category)) with ("替换属性")'
--替换内容
set @XMLVar.modify('replace value of(/catalog[1]/book[1]/author[1]/text()[1])) with("替换内容")'
--条件替换
set @XMLVar.modify('replace value of (/catalog[1]/book[2]/@category))
with(
if(count(/catalog[1]/book)>4) then
"条件替换1"
else
"条件替换2")' SELECT @XMLVar.query('/catalog[1]'); 结果集为:
1: <catalog>
2: <book category="替换属性">
3: <title>Windows Step By Step</title>
4: <author>替换内容</author>
5: <price>49.99</price>
6: </book>
7: <book category="条件替换2">
8: <title>Developing ADO .NET</title>
9: <author>Andrew Brust</author>
10: <price>39.93</price>
11: </book>
12: <book category="ITPro">
13: <title>Windows Cluster Server</title>
14: <author>Stephen Forte</author>
15: <price>59.99</price>
16: </book>
17: </catalog>
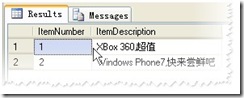
示例1:从XML中解析数据到表变量

DECLARE @ItemTable TABLE(ItemNumber INT PRIMARY KEY,ItemDescription NVARCHAR(300))
SET @ItemMessage=N'<ItemList>
<Item>
<ItemNumber>1</ItemNumber>
<ItemDescription>XBox 360,超值</ItemDescription>
</Item>
<Item>
<ItemNumber>2</ItemNumber>
<ItemDescription>Windows Phone7,快来尝鲜吧</ItemDescription>
</Item>
</ItemList>'
INSERT INTO @ItemTable
(
ItemNumber,
ItemDescription
)
SELECT T.c.value('(ItemNumber/text())[1]','INT'),
T.c.value('(ItemDescription/text())[1]','NVARCHAR(300)')
FROM @ItemMessage.nodes('/ItemList/Item') AS T(c)
SELECT ItemNumber,
ItemDescription
FROM @ItemTable

运行结果:
示例二: 解析带命名空间的XML数据
DECLARE @ItemMessage XML
DECLARE @ItemTable TABLE(ItemNumber INT PRIMARY KEY,ItemDescription NVARCHAR(300))
--包含 XML 命名空间
SET @ItemMessage=N'<ItemList xmlns="http://cd.love.com/SOA">
<Item>
<ItemNumber>1</ItemNumber>
<ItemDescription>XBox 360,超值</ItemDescription>
</Item>
<Item>
<ItemNumber>2</ItemNumber>
<ItemDescription>Windows Phone7,快来尝鲜吧</ItemDescription>
</Item>
</ItemList>'
--设置命名空间
;WITH XMLNAMESPACES(DEFAULT 'http://cd.love.com/SOA')
INSERT INTO @ItemTable
(
ItemNumber,
ItemDescription
)
SELECT T.c.value('(ItemNumber/text())[1]','INT'),
T.c.value('(ItemDescription/text())[1]','NVARCHAR(300)')
FROM @ItemMessage.nodes('/ItemList/Item') AS T(c)
SELECT ItemNumber,
ItemDescription
FROM @ItemTable
运行结果:

示例三:将 xml tag标签的中值 转为 table 格式
DECLARE @xml xml='<mssql version="10.50.4000" name="Microsoft SQL Server Developer Edition (64-bit)">
<type name="Windows 7 Main Server">
<tag KeyValue="enabled">
<boolean>true</boolean>
</tag>
<tag KeyValue="disabled">
<tag method="Read">
<type name="Windows 8 virtual pc">
<tag KeyValue="uniqueKey">
<string>SQL Server 2008</string>
</tag>
<tag KeyValue="value 8GB">
<string>SQL Server 2000</string>
</tag>
</type>
</tag>
<tag method="Read">
<type name="Windows 8 virtual pc">
<tag KeyValue="primaryKey">
<string>SQL Server 2008 R2 SP1</string>
</tag>
<tag KeyValue="value 8GB">
<string>SQL Server 2005 SP3</string>
</tag>
</type>
</tag>
<tag method="Write">
<type name="Windows Server 2008 virtual pc">
<tag KeyValue="primaryKey">
<string>SQL Server 2008 R2 SP2</string>
</tag>
<tag KeyValue="value 10GB">
<string>SQL Server 2012</string>
</tag>
</type>
</tag>
</tag>
</type>
</mssql>'; SELECT b.c.value('@version', 'varchar(100)') [version]
,b.c.value('@name', 'varchar(200)') [Name]
,f.c.value('@name', 'varchar(200)') [ServerName]
,r.c.value('@KeyValue', 'varchar(50)') [KeyValue]
,r.c.value('(boolean)[1]', 'varchar(25)') [boolean]
,k.c.value('@method', 'varchar(25)') [method]
,k.c.value('@name', 'varchar(25)') [virtual_pc]
,y.c.value('@KeyValue', 'varchar(25)') [KeyValue]
,y.c.value('(string)[1]', 'varchar(25)') [string]
FROM @xml.nodes('mssql') b(c)
CROSS APPLY b.c.nodes('type') f(c)
CROSS APPLY f.c.nodes('tag') r(c)
CROSS APPLY f.c.nodes('tag/tag') k(c)
CROSS APPLY f.c.nodes('tag/tag/type/tag') y(c);
SQL Server 操作XML数据的更多相关文章
- sql server 操作xml例子
sql server 操作xml例子 /* sql xml 入门: --by jinjazz --http://blog.csdn.net/jinjazz 1.xml: 能认识元素.属性和值 2.xp ...
- ADO.NET 快速入门(十二):从 SQL Server 生成 XML 数据
本文演示如何使用2种不同的方法从 SQL Server 生成 XML. 方法1:使用了 SqlCommand 的 ExecuteXmlReader 方法获取 XmlReader,然后使用 Data ...
- SQL Server解析XML数据的方法详解
--下面为多种方法从XML中读取EMAIL DECLARE @x XML SELECT @x = ' <People> <dongsheng> <Info Name=&q ...
- Sql Server系列:数据表操作
表是用来存储数据和操作数据的逻辑结构,用来组织和存储数据,关系数据库中的所有数据都表现为表的形式,数据表由行和列组成.SQL Server中的数据表分为临时表和永久表,临时表存储在tempdb系统数据 ...
- SQL Server对Xml字段的操作
T-Sql操作Xml数据 一.前言 SQL Server 2005 引入了一种称为 XML 的本机数据类型.用户可以创建这样的表,它在关系列之外还有一个或多个 XML 类型的列:此外,还允许带有变量和 ...
- 常见SQL Server导入导出数据的几个工具
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/chenxizhang/archive/2011/06/09/2076542.html 在我们的日常工作中,与数据库打交道的机会越来越多.这一篇文章 ...
- T-Sql操作Xml数据(转)
T-Sql操作Xml数据 一.前言 SQL Server 2005 引入了一种称为 XML 的本机数据类型.用户可以创建这样的表,它在关系列之外还有一个或多个 XML 类型的列:此外,还允许带有变量和 ...
- Expression构建DataTable to Entity 映射委托 sqlserver 数据库里面金额类型为什么不建议用float,实例告诉你为什么不能。 sql server 多行数据合并成一列 C# 字符串大写转小写,小写转大写,数字保留,其他除外 从0开始用U盘制作启动盘装Windows10系统(联想R720笔记本)并永久激活方法 纯CSS打造淘宝导航菜单栏 C# Winform
Expression构建DataTable to Entity 映射委托 1 namespace Echofool.Utility.Common { 2 using System; 3 using ...
- sql server 与oracle数据互导的一种思路--sql server链接服务器
思路:通过在sql server数据库中添加链接服务器,可以远程查询oracle数据库的表环境准备,安装sql server数据库,并安装好oracle驱动,在配置好tnsname文件中配置好orac ...
随机推荐
- Note: SE Class's Individual Project
虽然第一个Project还有点小问题需要修改,但是大体已经差不多了,先把blog记在这里,算是开博第一篇吧! 1.项目预计的用时 本来看到这个题的时候想的并不多,但是看了老师的要求才觉得如此麻烦ORZ ...
- 20135337——Linux实践二:模块
一.编译&生成&测试&删除 1.编写模块代码,查看如下 gedit 1.c(编写) cat 1.c(查看) MODULE_AUTHOR("Z") MODUL ...
- github 学习心得
https://github.com/kongxiangyu/test 通过本次实验,学会了如何使用github来管理代码.如果是开源的项目,通过网站托管方式进行统一管理,当然是非常棒的,并且有很多功 ...
- 《面向对象程序设计》c++第五次作业___calculator plus plus
c++第五次作业 Calculator plusplus 代码传送门 PS:这次作业仍然orz感谢一位同学与一位学长的windows帮助,同时再次吐槽作业对Mac系统用户的不友好.(没朋友千万别用Ma ...
- git工具使用包括上传本地代码到服务器
我是参考这个的 https://www.cnblogs.com/tonycheng93/p/4460052.html
- ECharts设置y轴显示
参考地址:https://www.w3cschool.cn/echarts_tutorial/echarts_tutorial-no3h2cul.html yAxis: { type: 'value' ...
- 递归拼装Tree结构数据
@Override public List<Map<String, Object>> queryListTree() { List<Map<String,Objec ...
- ABP框架用Dapper实现通过SQL访问数据库
ABP的框架(2) - 访问数据库 为了防止不提供原网址的转载,特在这里加上原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/skabyy/p/7517397.html 本篇我们实现数据库的 ...
- 开源的CAS实现SSO
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-cas/index.html ISC是基于CAS定制的,使用的高级的代理模式. https ...
- pandas.Series
1.系列(Series)是能够保存任何类型的数据(整数,字符串,浮点数,Python对象等)的一维标记数组.轴标签统称为索引. Pandas系列可以使用以下构造函数创建 - pandas.Series ...
