PAT/简单模拟习题集(二)
B1018. 锤子剪刀布 (20)
Discription:
大家应该都会玩“锤子剪刀布”的游戏:两人同时给出手势,胜负规则如图所示:
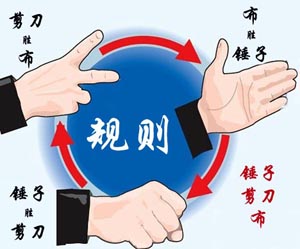
现给出两人的交锋记录,请统计双方的胜、平、负次数,并且给出双方分别出什么手势的胜算最大。
Input:
输入第1行给出正整数N(<=105),即双方交锋的次数。随后N行,每行给出一次交锋的信息,即甲、乙双方同时给出的的手势。C代表“锤子”、J代表“剪刀”、B代表“布”,第1个字母代表甲方,第2个代表乙方,中间有1个空格。
Output:
输出第1、2行分别给出甲、乙的胜、平、负次数,数字间以1个空格分隔。第3行给出两个字母,分别代表甲、乙获胜次数最多的手势,中间有1个空格。如果解不唯一,则输出按字母序最小的解。
Sample Input:
10
C J
J B
C B
B B
B C
C C
C B
J B
B C
J J
Sample Output:
5 3 2
2 3 5
B B
#include <cstdio> #define MaxSize 3 int ListA[MaxSize], ListB[MaxSize], Time[MaxSize]; int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int N;
char c1, c2;
scanf("%d", &N);
for(int i=; i<N; i++) {
getchar();
scanf("%c %c", &c1, &c2);
if(c1 == 'B') {
if(c2 == 'B') {
Time[]++;
} else if(c2 == 'C') {
Time[]++;
ListA[]++;
} else {
Time[]++;
ListB[]++;
}
} else if(c1 == 'C') {
if(c2 == 'B') {
Time[]++;
ListB[]++;
} else if(c2 == 'C') {
Time[]++;
} else {
Time[]++;
ListA[]++;
}
} else {
if(c2 == 'B') {
Time[]++;
ListA[]++;
} else if(c2 == 'C') {
Time[]++;
ListB[]++;
} else {
Time[]++;
}
}
} printf("%d %d %d\n%d %d %d\n", Time[], Time[], Time[], Time[], Time[], Time[]);
if(ListA[] >= ListA[]) {
if(ListA[] >= ListA[])
printf("B ");
else
printf("J ");
} else {
if(ListA[] >= ListA[])
printf("C ");
else
printf("J ");
}
if(ListB[] >= ListB[]) {
if(ListB[] >= ListB[])
printf("B\n");
else
printf("J\n");
} else {
if(ListB[] >= ListB[])
printf("C\n");
else
printf("J\n");
} return ;
}
#include <cstdio> int change(char c)
{
if(c == 'B')
return ;
else if(c == 'C')
return ;
else
return ;
} int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); char mp[] = {'B', 'C', 'J'};
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int times_A[] = {}, times_B[] = {};
int hand_A[] = {}, hand_B[] = {};
char c1, c2;
int k1, k2;
for(int i=; i<n; i++) {
getchar();
scanf("%c %c", &c1, &c2);
k1 = change(c1);
k2 = change(c2);
if((k1+)% == k2) {
times_A[]++;
times_B[]++;
hand_A[k1]++;
} else if(k1 == k2) {
times_A[]++;
times_B[]++;
} else {
times_A[]++;
times_B[]++;
hand_B[k2]++;
}
} printf("%d %d %d\n", times_A[], times_A[], times_A[]);
printf("%d %d %d\n", times_B[], times_B[], times_B[]);
int id1 = , id2 = ;
for(int i=; i<; i++) {
if(hand_A[i] > hand_A[id1])
id1 = i;
if(hand_B[i] > hand_B[id2])
id2 = i;
}
printf("%c %c\n", mp[id1], mp[id2]); return ;
}
A1042. Shuffling Machine (20)
Description:
Shuffling is a procedure used to randomize a deck of playing cards. Because standard shuffling techniques are seen as weak, and in order to avoid "inside jobs" where employees collaborate with gamblers by performing inadequate shuffles, many casinos employ automatic shuffling machines. Your task is to simulate a shuffling machine.
The machine shuffles a deck of 54 cards according to a given random order and repeats for a given number of times. It is assumed that the initial status of a card deck is in the following order:
S1, S2, ..., S13, H1, H2, ..., H13, C1, C2, ..., C13, D1, D2, ..., D13, J1, J2
where "S" stands for "Spade", "H" for "Heart", "C" for "Club", "D" for "Diamond", and "J" for "Joker". A given order is a permutation of distinct integers in [1, 54]. If the number at the i-th position is j, it means to move the card from position i to position j. For example, suppose we only have 5 cards: S3, H5, C1, D13 and J2. Given a shuffling order {4, 2, 5, 3, 1}, the result will be: J2, H5, D13, S3, C1. If we are to repeat the shuffling again, the result will be: C1, H5, S3, J2, D13.
Input:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer K (<= 20) which is the number of repeat times. Then the next line contains the given order. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output:
For each test case, print the shuffling results in one line. All the cards are separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
2
36 52 37 38 3 39 40 53 54 41 11 12 13 42 43 44 2 4 23 24 25 26 27 6 7 8 48 49 50 51 9 10 14 15 16 5 17 18 19 1 20 21 22 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 45 46 47
Sample Output:
S7 C11 C10 C12 S1 H7 H8 H9 D8 D9 S11 S12 S13 D10 D11 D12 S3 S4 S6 S10 H1 H2 C13 D2 D3 D4 H6 H3 D13 J1 J2 C1 C2 C3 C4 D1 S5 H5 H11 H12 C6 C7 C8 C9 S2 S8 S9 H10 D5 D6 D7 H4 H13 C5
#include <cstdio> #define MaxSize 55 int List1[MaxSize], List2[MaxSize], List3[MaxSize]; int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int N, temp;
scanf("%d", &N);
for(int i=; i<MaxSize; i++) {
List1[i] = i;
scanf("%d", &List2[i]);
}
for(int i=; i<N; i++) {
for(int j=; j<MaxSize; j++) {
List3[List2[j]] = List1[j];
}
for(int k=; k<MaxSize; k++) {
List1[k] = List3[k];
}
} for(int i=; i<MaxSize-; i++) {
if(List1[i] > ) {
printf("J%d ", List1[i]-);
} else if(List1[i] > ) {
printf("D%d ", List1[i]-);
} else if(List1[i] > ) {
printf("C%d ", List1[i]-);
} else if(List1[i] > ) {
printf("H%d ", List1[i]-);
} else {
printf("S%d ", List1[i]);
}
}
if(List1[MaxSize-] > ) {
printf("J%d\n", List1[MaxSize-]-);
} else if(List1[MaxSize-] > ) {
printf("D%d\n", List1[MaxSize-]-);
} else if(List1[MaxSize-] > ) {
printf("C%d\n", List1[MaxSize-]-);
} else if(List1[MaxSize-] > ) {
printf("H%d\n", List1[MaxSize-]-);
} else {
printf("S%d\n", List1[MaxSize-]);
} return ;
}
#include <cstdio> const int N = ;
char mp[] = {'S', 'H', 'C', 'D', 'J'};
int start[N], end[N], next[N]; int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int K;
scanf("%d", &K);
for(int i=; i<=N; i++)
start[i] = i;
for(int i=; i<=N; i++)
scanf("%d", &next[i]); for(int step = ; step < K; step++) {
for(int i=; i<=N; i++)
end[next[i]] = start[i];
for(int i=; i<=N; i++)
start[i] = end[i];
} for(int i=; i<=N; i++) {
if(i != )
printf(" ");
start[i]--;
printf("%c%d", mp[start[i]/], start[i]%+);
} return ;
}
A1046.Shortest Distance (20)
Description:
The task is really simple: given N exits on a highway which forms a simple cycle, you are supposed to tell the shortest distance between any pair of exits.
Input:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains an integer N (in [3, 105]), followed by N integer distances D1 D2 ... DN, where Di is the distance between the i-th and the (i+1)-st exits, and DN is between the N-th and the 1st exits. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The second line gives a positive integer M (<=104), with M lines follow, each contains a pair of exit numbers, provided that the exits are numbered from 1 to N. It is guaranteed that the total round trip distance is no more than 107.
Output:
For each test case, print your results in M lines, each contains the shortest distance between the corresponding given pair of exits.
Sample Input:
5 1 2 4 14 9
3
1 3
2 5
4 1
Sample Output:
3
10
7
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; const int MAXN = ;
int dis[MAXN], A[MAXN]; int main()
{
int sum = , query, n, left, right;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &A[i]);
sum += A[i];
dis[i] = sum;
}
scanf("%d", &query);
for(int i=; i<query; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &left, &right);
if(left > right)
swap(left, right);
int temp = dis[right-]-dis[left-];
printf("%d\n", min(temp, sum-temp));
} return ;
}
A1065. A+B and C (64bit) (20)
Description:
Given three integers A, B and C in [-263, 263], you are supposed to tell whether A+B > C.
Input:
The first line of the input gives the positive number of test cases, T (<=10). Then T test cases follow, each consists of a single line containing three integers A, B and C, separated by single spaces.
Ouput:
For each test case, output in one line "Case #X: true" if A+B>C, or "Case #X: false" otherwise, where X is the case number (starting from 1).
Sample Input:
3
1 2 3
2 3 4
9223372036854775807 -9223372036854775808 0
Output:
Case #1: false
Case #2: true
Case #3: false
#include <cstdio> int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int T, tcase = ;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
long long a, b, c;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &a, &b, &c);
long long res = a+b;
bool flag;
if(a> && b> && res<)
flag = true;
else if(a< && b< && res>=)
flag = false;
else if(res > c)
flag = true;
else
flag = false;
if(flag == true)
printf("Case #%d: true\n", tcase++);
else
printf("Case #%d: false\n", tcase++);
} return ;
}
B1010. 一元多项式求导 (25)
Description:
设计函数求一元多项式的导数。(注:xn(n为整数)的一阶导数为n*xn-1。)
Input:
以指数递降方式输入多项式非零项系数和指数(绝对值均为不超过1000的整数)。数字间以空格分隔。
Output:
以与输入相同的格式输出导数多项式非零项的系数和指数。数字间以空格分隔,但结尾不能有多余空格。注意“零多项式”的指数和系数都是0,但是表示为“0 0”。
Sample Input:
3 4 -5 2 6 1 -2 0
Sample Output:
12 3 -10 1 6 0
#include <cstdio> int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int a[] = {};
int k, e, counter = ;
while(scanf("%d%d", &k, &e) != EOF) {
a[e] = k;
}
a[] = ; for(int i=; i<=; ++i) {
a[i-] = a[i]*i;
a[i] = ;
if(a[i-] != )
counter++;
}
if(counter == )
printf("0 0\n");
else {
for(int i=; i>=; --i) {
if(a[i] != ) {
printf("%d %d", a[i], i);
counter--;
if(counter != )
printf(" ");
}
}
} return ;
}
A1002. A+B for Polynomials (25)
Description:
This time, you are supposed to find A+B where A and B are two polynomials.
Input:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies 2 lines, and each line contains the information of a polynomial: K N1 aN1 N2 aN2 ... NK aNK, where K is the number of nonzero terms in the polynomial, Ni and aNi (i=1, 2, ..., K) are the exponents and coefficients, respectively. It is given that 1 <= K <= 10,0 <= NK < ... < N2 < N1 <=1000.
Output:
For each test case you should output the sum of A and B in one line, with the same format as the input. Notice that there must be NO extra space at the end of each line. Please be accurate to 1 decimal place.
Sample Input:
2 1 2.4 0 3.2
2 2 1.5 1 0.5
Sample Output:
3 2 1.5 1 2.9 0 3.2
#include <cstdio> #define MaxSize 1010
double List[MaxSize]; int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int K, expon, counter = ;
double coef;
scanf("%d", &K);
for(int i=; i<K; ++i) {
scanf("%d %lf", &expon, &coef);
List[expon] += coef;
}
scanf("%d", &K);
for(int i=; i<K; ++i) {
scanf("%d %lf", &expon, &coef);
List[expon] += coef;
} for(int i=; i<MaxSize; ++i) {
if(List[i] != )
++counter;
}
printf("%d", counter);
for(int i=MaxSize-; i>=; --i) {
if(List[i] != ) {
printf(" %d %.1f", i, List[i]);
}
} return ;
}
A1009. Product of Polynomials (25)
Description:
This time, you are supposed to find A*B where A and B are two polynomials.
Input:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies 2 lines, and each line contains the information of a polynomial: K N1 aN1 N2 aN2 ... NK aNK, where K is the number of nonzero terms in the polynomial, Ni and aNi (i=1, 2, ..., K) are the exponents and coefficients, respectively. It is given that 1 <= K <= 10, 0 <= NK < ... < N2 < N1 <=1000.
Output:
For each test case you should output the product of A and B in one line, with the same format as the input. Notice that there must be NO extra space at the end of each line. Please be accurate up to 1 decimal place.
Sample Input:
2 1 2.4 0 3.2
2 2 1.5 1 0.5
Sample Output:
3 3 3.6 2 6.0 1 1.6
#include <cstdio> #define MaxSize 2010
double List1[MaxSize], List2[MaxSize]; int main()
{
//freopen("E:\\Temp\\input.txt", "r", stdin); int K, expon, counter = ;
double coef;
scanf("%d", &K);
for(int i=; i<K; ++i) {
scanf("%d %lf", &expon, &coef);
List1[expon] += coef;
}
scanf("%d", &K);
for(int i=; i<K; ++i) {
scanf("%d %lf", &expon, &coef);
for(int j=; j<MaxSize; j++)
List2[expon+j] += List1[j]*coef;
} for(int i=; i<MaxSize; ++i) {
if(List2[i] != )
++counter;
}
printf("%d", counter);
for(int i=MaxSize-; i>=; --i) {
if(List2[i] != )
printf(" %d %.1f", i, List2[i]);
} return ;
}
#include <cstdio>
struct Poly {
int exp;
double cof;
}poly[];
double ans[];
int main()
{
int n, m, number = ;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=; i<n; ++i)
scanf("%d %lf", &poly[i].exp, &poly[i].cof);
scanf("%d", &m);
for(int i=; i<m; ++i) {
int exp;
double cof;
scanf("%d %lf", &exp, &cof);
for(int j=; j<n; j++)
ans[exp+poly[j].exp] += (cof*poly[j].cof);
}
for(int i=; i<=; ++i) {
if(ans[i] != )
++number;
}
printf("%d", number);
for(int i=; i>=; --i) {
if(ans[i] != )
printf(" %d %.1f", i, ans[i]);
}
return ;
}
PAT/简单模拟习题集(二)的更多相关文章
- PAT/简单模拟习题集(一)
B1001.害死人不偿命的(3n+1)猜想 (15) Description: 卡拉兹(Callatz)猜想: 对任何一个自然数n,如果它是偶数,那么把它砍掉一半:如果它是奇数,那么把(3n+1)砍掉 ...
- java web学习总结(二十二) -------------------简单模拟SpringMVC
在Spring MVC中,将一个普通的java类标注上Controller注解之后,再将类中的方法使用RequestMapping注解标注,那么这个普通的java类就够处理Web请求,示例代码如下: ...
- JavaWeb学习总结(四十九)——简单模拟Sping MVC
在Spring MVC中,将一个普通的java类标注上Controller注解之后,再将类中的方法使用RequestMapping注解标注,那么这个普通的java类就够处理Web请求,示例代码如下: ...
- (hdu step 8.1.6)士兵队列训练问题(数据结构,简单模拟——第一次每2个去掉1个,第二次每3个去掉1个.知道队伍中的人数<=3,输出剩下的人 )
题目: 士兵队列训练问题 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total ...
- spring之mvc原理分析及简单模拟实现
在之前的一篇博客中已经简单的实现了spring的IOC和DI功能,本文将在之前的基础上实现mvc功能. 一 什么是MVC MVC简单的说就是一种软件实现的设计模式,将整个系统进行分层,M(model ...
- C++笔记(7)——一些模拟题:简单模拟、查找元素、图形输出、日期处理、进制转换、字符串处理
以下内容基本来自<算法笔记>,作者为胡凡,建议直接买书看,我这里只是摘抄部分当笔记,不完整的. 简单模拟 就是一类"题目怎么说你就怎么做"的题目.这类题目不涉及算法,只 ...
- sort回调的简单模拟
本来是准备讲CPP中的std::sort,但因为最近Java用得多,不知怎么的便习惯性走Java角度看问题了,所以这篇文章看起来估计会有点奇怪... 一.简单模拟sort回调 std::sort函数本 ...
- WPF简单模拟QQ登录背景动画
介绍 之所以说是简单模拟,是因为我不知道QQ登录背景动画是怎么实现的.这里是通过一些办法把它简化了,做成了类似的效果 效果图 大体思路 首先把背景看成是一个4行8列的点的阵距,X轴Y轴都是距离70.把 ...
- Linux 内核 链表 的简单模拟(2)
接上一篇Linux 内核 链表 的简单模拟(1) 第五章:Linux内核链表的遍历 /** * list_for_each - iterate over a list * @pos: the & ...
随机推荐
- Android Studio线下版和线上版都使用正式签名脚本(保证keysore签名文件和项目在同级目录),不用再因为繁琐的发正式版而烦恼
场景:调用微信等第三方应用时如果生成的版本不是正式签名的可能会调用失败,使用如下脚本不用再为繁琐的发正式签名版而烦恼 app项目中的build.gradle追加如下代码: //使用正式签名脚本(保证k ...
- 关于在gridview中有dorpdownlist的情况下使用自带编辑模板的方法
今天记录一下在gridview中,如果有dropdownlist的情况下使用gridview自带编辑模式的方法. 好吧,今天的这个问题有点绕,详细解释一下目的. 因为gridview中的某些列的数据是 ...
- 强连通分量的一二三 | | JZOJ【P1232】 | | 我也不知道我写的什么
贴题: 在幻想乡,上白泽慧音是以知识渊博闻名的老师.春雪异变导致人间之里的很多道路都被大雪堵塞,使有的学生不能顺利地到达慧音所在的村庄.因此慧音决定换一个能够聚集最多人数的村庄作为新的教学地点.人间之 ...
- URAL 1992 CVS 可持久化链栈
http://www.cnblogs.com/tedzhao/archive/2008/11/12/1332112.html 看这篇的链表部分的介绍应该就能理解“可持久化”了 动态分配内存的会T,只能 ...
- .net加密解密
.net加密概述 .net加密编程模型 .net加密解密类
- cocoapods specs 镜像
在使用cocoapods 进行update 或者 install的时候 每次回去更新获取的pod specs,每次速度都不是很理想,博主最近对github上的specs仓库进行了镜像,分别在gitca ...
- ASP.NET ashx实现无刷新页面生成验证码
现在大部分网站登陆时都会要求输入验证码,在网上也看了一些范例,现在总结一下如何实现无刷新页面生成验证码. 效果图: 实现方式: 前台: <div> <span>Identify ...
- 设计模型MVC和JavaBean
六.设计模型1和设计模型2(MVC)1.模型1:JSP+JavaBean2.模型2:MVC M:Model模型 JavaBean V:视图 JSP C:控制器 Servlet 七.模型1开发一个简单的 ...
- STL 跨模块 调用 异常 解决
本文为转载别人的,以作收藏之用 百度了一天,现在把结论放上边: 1.不要用STL(std::string属于STL)来跨模块传输数据,例如:dll(so)之间,dll(so)和exe(elf)之间. ...
- oracle 11gr2 官方文档下载
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-edition/documentation/index.html
