Winform GDI+ 绘图一:绘制2D电池
winform桌面软件开发,在工业控制领域的使用还是很广泛的,打算好好学习一下GDI+绘图。以前都是用别人的轮子,自己也打算封装一些工业控制领域常用的控件。
今天要将的是,利用缓动函数动态绘制电池。
首先在网上搜索了一些常用的缓动函数,并用Animation类做了二次封装。(引用自:http://dsqiu.iteye.com ,感谢)
public enum AnimationType
{
Linear,
EaseIn,
EaseOut,
EaseInOut,
BounceIn,
BounceOut,
QuadEaseOut,
QuadEaseIn,
QuadEaseInOut,
QuadEaseOutIn, //新增40种动画效果
ExpoEaseOut,
ExpoEaseIn,
ExpoEaseInOut,
ExpoEaseOutIn,
CubicEaseOut,
CubicEaseIn,
CubicEaseInOut,
CubicEaseOutIn,
QuartEaseOut,
QuartEaseIn,
QuartEaseInOut,
QuartEaseOutIn,
QuintEaseOut,
QuintEaseIn,
QuintEaseInOut,
QuintEaseOutIn,
CircEaseOut,
CircEaseIn,
CircEaseInOut,
CircEaseOutIn,
SineEaseOut,
SineEaseIn,
SineEaseInOut,
SineEaseOutIn,
ElasticEaseOut,
ElasticEaseIn,
ElasticEaseInOut,
ElasticEaseOutIn,
BounceEaseOut,
BounceEaseIn,
BounceEaseInOut,
BounceEaseOutIn,
BackEaseOut,
BackEaseIn,
BackEaseInOut,
BackEaseOutIn
}
自己二次封装Animation的类,对外公开一个缓动函数值改变的事件,以及动画开始、结束的方法。
封装的逻辑是,调用AnimationStart方法后,会在线程池中加入一个定时生产缓动函数对应值的方法,通过调用对外公开的事件。
外部不停调用AnimationStart方法时,会自动扔弃上一次未完成的定时生产缓动函数值的任务。
public class Animation
{
private AnimationType animationType = AnimationType.EaseInOut;
/// <summary>
/// 设置动画类型
/// </summary>
public AnimationType AnimationType { get => animationType; set => animationType = value; }
/// <summary>
/// 设置动画持续时间
/// </summary>
public int Duration
{
get => duration;
set => duration = value;
} private int duration = 200; private int span = 10; private int version = 0; public event EventHandler<AnimationEventArgs> AnimationComing; public float GetEaseProgress(AnimationType ease_type, float linear_progress)
{
switch (ease_type)
{
case AnimationType.Linear:
return linear_progress;
case AnimationType.BackEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.BackEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BackEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.BackEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BackEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.BackEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BackEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.BackEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BounceEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.BounceEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BounceEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.BounceEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BounceEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.BounceEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.BounceEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.BounceEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CircEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.CircEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CircEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.CircEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CircEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.CircEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CircEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.CircEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CubicEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.CubicEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CubicEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.CubicEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CubicEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.CubicEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.CubicEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.CubicEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ElasticEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.ElasticEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration); case AnimationType.ElasticEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.ElasticEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ElasticEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.ElasticEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ElasticEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.ElasticEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ExpoEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.ExpoEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ExpoEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.ExpoEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ExpoEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.ExpoEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.ExpoEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.ExpoEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuadEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.QuadEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuadEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.QuadEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuadEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.QuadEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuadEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.QuadEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuartEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.QuartEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuartEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.QuartEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuartEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.QuartEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuartEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.QuartEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuintEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.QuintEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuintEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.QuintEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuintEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.QuintEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.QuintEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.QuintEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration); case AnimationType.SineEaseIn:
return AnimationMethod.SineEaseIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.SineEaseInOut:
return AnimationMethod.SineEaseInOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.SineEaseOut:
return AnimationMethod.SineEaseOut(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
case AnimationType.SineEaseOutIn:
return AnimationMethod.SineEaseOutIn(linear_progress, 0, 1, duration);
default:
return linear_progress;
}
} /// <summary>
/// 动画开始
/// </summary>
public void AnimationStart()
{
int number = Interlocked.Increment(ref version);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(Start, number);
}
/// <summary>
/// 动画结束
/// </summary>
public void AnimationStop()
{
Interlocked.Increment(ref version);
} private void Start(object state)
{
try
{
int number = Convert.ToInt32(state);
float timespan = duration / span;
float currentTime = timespan;
while (currentTime < duration)
{
if (number != version)
break;
Thread.Sleep((int)timespan);
AnimationComing.Invoke(this, new AnimationEventArgs() { NowValue = GetEaseProgress(AnimationType, currentTime) });
currentTime += timespan;
if (currentTime >= duration)
{
Thread.Sleep((int)(duration-currentTime));
AnimationComing.Invoke(this, new AnimationEventArgs() { NowValue = GetEaseProgress(AnimationType, currentTime) });
}
} Interlocked.Decrement(ref version);
}
catch
{ }
}
} public class AnimationEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public float NowValue;
}
自绘控件时,只需要注册AnimationComing事件的处理方法,进行控件重绘。如下:
animation.AnimationComing += Animation_AnimationComing; private void Animation_AnimationComing(object sender, AnimationEventArgs e)
{
easeFunctionValue = e.NowValue;
Invalidate();
}
2D电池控件自绘部分就不贴代码,代码已开源,见文章尾部。总体效果如下:
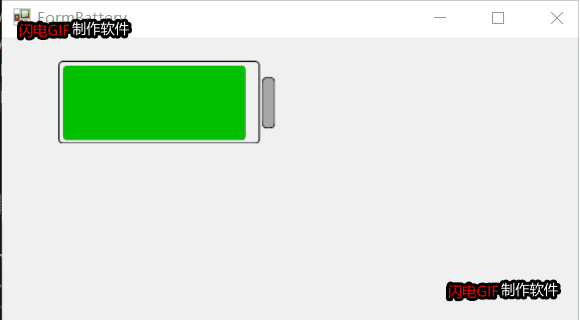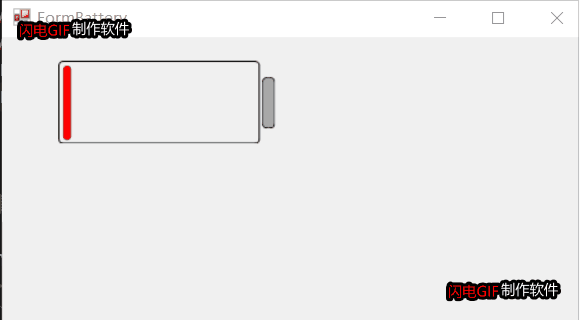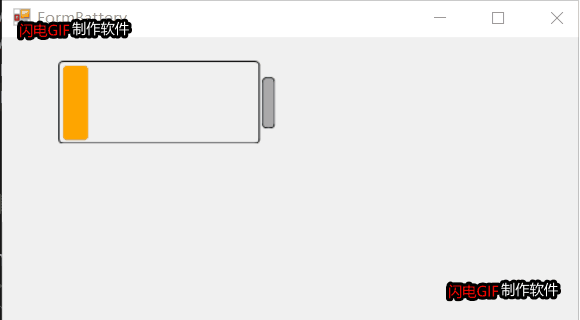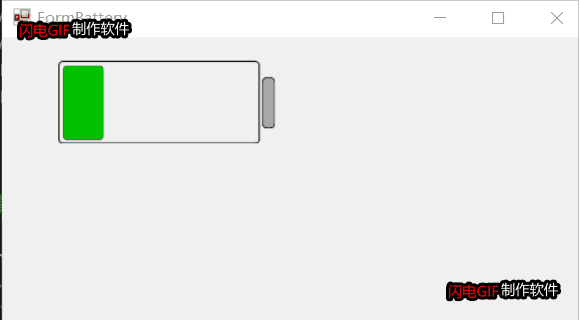
项目开源地址:https://gitee.com/james_happy/IndustryControls
Winform GDI+ 绘图一:绘制2D电池的更多相关文章
- Winform GDI+绘图二:绘制旋转太极图
大家好,今天有时间给大家带来Winform自绘控件的第二部分,也是比较有意思的一个控件:旋转太极图. 大家可以停下思考一下,如果让你来绘制旋转的太极图,大家有什么样的思路呢?我今天跟大家展示一下,我平 ...
- WinForm GDI+ 资料收集
UI(User Interface)编程在整个项目开发过程中是个颇为重要的环节,任何好的解决方案若没有良好的用户界面呈现给最终用户,那么就算包含了最先进的技术也不能算是好程序.UI编程体现在两个方面, ...
- Winform GDI+
什么是GDI+ GDI (Graphics Device Interface), 是属于绘图方面的 API (Application Programming Interface). 因为应用程序不能直 ...
- MFC GDI绘图基础
一.关于GDI的基本概念 什么是GDI? Windows绘图的实质就是利用Windows提供的图形设备接口GDI(Graphics Device Interface)将图形绘制在显示器上. 在Wind ...
- C#-gdi绘图,双缓冲绘图,Paint事件的触发
一. 画面闪烁问题与双缓冲技术 1.1 导致画面闪烁的关键原因分析: 1 绘制窗口由于大小位置状态改变进行重绘操作时 绘图窗口内容或大小每改变一次,都要调用Paint事件进行重绘操作,该操作会使画面 ...
- GDI+ 绘图闪烁解决方法
闲着没事,准备做一个类似于TeeChart的自定义控件,结果第一步的绘图就把我给难倒了,虽然早就知道GDI绘图的闪烁问题很坑,但是却没有想到如此之坑,折腾了两天,才找到解决方法. 首先在窗体加载的时候 ...
- GDI+(一):GDI+ 绘图基础
一.GDI+绘图基础 编写图形程序时需要使用GDI(Graphics Device Interface,图形设备接口),从程序设计的角度看,GDI包括两部分:一部分是GDI对象,另一部分是GDI函数. ...
- Windows GDI绘图基础知识
一.Windows可以画直线.椭圆线(椭圆圆周上的曲线)和贝塞尔曲线.////////////7 个画线函式是:(1)画直线LineTo BOOL LineTo(HDC hdc,int nXEn ...
- WinForm GDI编程:Graphics画布类
命名空间: using System.Drawing;//提供对GDI+基本图形功能的访问 using System.Drawing.Drawing2D;//提供高级的二维和矢量图像功能 using ...
随机推荐
- Java 集合框架总结--导图
java的集合导图总结:
- php 通过 yield 实现协程有什么使用场景
来源:https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000010018151 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/lynxcat/p/7954456.html 协程可 ...
- Visual Studio 添加图标和版本
在Visual Studio中,如果你创建的是纯C语言的工程,那么给可执行程序添加图标就没有便捷的入口. 但也只是入口不好找了,添加步骤还是比较简单的,以下为具体操作方法: 1. 右键点击C工 ...
- 新版gitbook导出pdf
文章目录 gitbook自带的npm模块gitbook 使用vscode的插件Markdown PDF 使用CommandBox GitBook Exporter 最近想把自己写的一个gitbook转 ...
- 常用的CSS小技巧
实际开发过程中会遇到一些需要用CSS小技巧处理的布局问题,现在分享几个个人工作中遇到的小问题和解决方案. 1.inline元素间的空白间隙 这里要介绍一个神器font-size:0. 如果你写了个列表 ...
- 解决 Retrofit 多 BaseUrl 及运行时动态改变 BaseUrl ?
原文地址: juejin.im/post/597856- 解决Retrofit多BaseUrl及运行时动态改变BaseUrl(一) 解决Retrofit多BaseUrl及运行时动态改变BaseUrl( ...
- python实现二分叉查找
*二分叉查找就是折半查找 比如12345这几个数字当中找2,他会先找到这五个数字中的中坚的那个与2进行比较,比如中间的3>2他就认为3以后的不用查找了,然后查找3左边的,即123,再把这个分半, ...
- 数学--数论--HDU 2802 F(N) 公式推导或矩阵快速幂
Giving the N, can you tell me the answer of F(N)? Input Each test case contains a single integer N(1 ...
- python(读取 excel 操作 xlrd 模块)
一.安装 xlrd 模块 到 python 官网下载 http://pypi.python.org/pypi/xlrd 模块安装,前提是已经安装了 python 环境. 或者在 cmd 窗口 pip ...
- andorid jar/库源码解析之Butterknife
目录:andorid jar/库源码解析 Butterknife: 作用: 用于初始化界面控件,控件方法,通过注释进行绑定控件和控件方法 栗子: public class MainActivity e ...
