CNN初步-1
Convolution:
个特征,则这时候把输入层的所有点都与隐含层节点连接,则需要学习10^6个参数,这样的话在使用BP算法时速度就明显慢了很多。
所以后面就发展到了局部连接网络,也就是说每个隐含层的节点只与一部分连续的输入点连接。这样的好处是模拟了人大脑皮层中视觉皮层不同位置只对局部区域有响应。局部连接网络在神经网络中的实现使用convolution的方法。它在神经网络中的理论基础是对于自然图像来说,因为它们具有稳定性,即图像中某个部分的统计特征和其它部位的相似,因此我们学习到的某个部位的特征也同样适用于其它部位。
下面具体看一个例子是怎样实现convolution的,假如对一张大图片Xlarge的数据集,r*c大小,则首先需要对这个数据集随机采样大小为a*b的小图片,然后用这些小图片patch进行学习(比如说sparse autoencoder),此时的隐含节点为k个。因此最终学习到的特征数为:

此时的convolution移动是有重叠的。
Formally, given some large 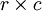 images xlarge, we first train a sparse autoencoder on small
images xlarge, we first train a sparse autoencoder on small 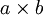 patches xsmall sampled from these images, learning k features f = σ(W(1)xsmall + b(1)) (where σ is the sigmoid function), given by the weights W(1) and biases b(1) from the visible units to the hidden units. For every
patches xsmall sampled from these images, learning k features f = σ(W(1)xsmall + b(1)) (where σ is the sigmoid function), given by the weights W(1) and biases b(1) from the visible units to the hidden units. For every 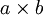 patch xs in the large image, we compute fs = σ(W(1)xs+ b(1)), giving us fconvolved, a
patch xs in the large image, we compute fs = σ(W(1)xs+ b(1)), giving us fconvolved, a 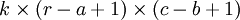 array of convolved features.
array of convolved features.
总结:
convolution解决了训练输入特征过多的问题。采用小patch 采样训练,训练后的结果filter 再作用到所有图片区域。
Pooling:
个隐含层,则其需要训练的参数个数减小到了10^3,大大的减小特征提取过程的困难。但是此时同样出现了一个问题,即它的输出向量的维数变得很大,本来完全连接的网络输出只有100维的,现在的网络输出为89*89*100=792100维,大大的变大了,这对后面的分类器的设计同样带来了困难,所以pooling方法就出现了。
为什么pooling的方法可以工作呢?首先在前面的使用convolution时是利用了图像的stationarity特征,即不同部位的图像的统计特征是相同的,那么在使用convolution对图片中的某个局部部位计算时,得到的一个向量应该是对这个图像局部的一个特征,既然图像有stationarity特征,那么对这个得到的特征向量进行统计计算的话,所有的图像局部块应该也都能得到相似的结果。对convolution得到的结果进行统计计算过程就叫做pooling,由此可见pooling也是有效的。常见的pooling方法有max pooling和average pooling等。并且学习到的特征具有旋转不变性(这个原因暂时没能理解清楚)。
从上面的介绍可以简单的知道,convolution是为了解决前面无监督特征提取学习计算复杂度的问题,而pooling方法是为了后面有监督特征分类器学习的,也是为了减小需要训练的系统参数(当然这是在普遍例子中的理解,也就是说我们采用无监督的方法提取目标的特征,而采用有监督的方法来训练分类器)。
总结:
convolution解决了输入层参数多问题,但是输出特征太多,pooling解决了这一问题。
来自 <http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/03/25/2980766.html>
http://deeplearning.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Feature_extraction_using_convolution
http://deeplearning.stanford.edu/wiki/index.php/Pooling
http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/lenet.html
先看下 convolution
import theano
from theano import tensor as T
from theano.tensor.nnet import conv
import numpy
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455)
# instantiate 4D tensor for input
input = T.tensor4(name='input')
# initialize shared variable for weights.
w_shp = (2, 3, 9, 9)
w_bound = numpy.sqrt(3 * 9 * 9)
W = theano.shared( numpy.asarray(
rng.uniform(
low=-1.0 / w_bound,
high=1.0 / w_bound,
size=w_shp),
dtype=input.dtype), name ='W')
# initialize shared variable for bias (1D tensor) with random values
# IMPORTANT: biases are usually initialized to zero. However in this
# particular application, we simply apply the convolutional layer to
# an image without learning the parameters. We therefore initialize
# them to random values to "simulate" learning.
b_shp = (2,)
b = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(
rng.uniform(low=-.5, high=.5, size=b_shp),
dtype=input.dtype), name ='b')
# build symbolic expression that computes the convolution of input with filters in w
conv_out = conv.conv2d(input, W)
# build symbolic expression to add bias and apply activation function, i.e. produce neural net layer output
# A few words on ``dimshuffle`` :
# ``dimshuffle`` is a powerful tool in reshaping a tensor;
# what it allows you to do is to shuffle dimension around
# but also to insert new ones along which the tensor will be
# broadcastable;
# dimshuffle('x', 2, 'x', 0, 1)
# This will work on 3d tensors with no broadcastable
# dimensions. The first dimension will be broadcastable,
# then we will have the third dimension of the input tensor as
# the second of the resulting tensor, etc. If the tensor has
# shape (20, 30, 40), the resulting tensor will have dimensions
# (1, 40, 1, 20, 30). (AxBxC tensor is mapped to 1xCx1xAxB tensor)
# More examples:
# dimshuffle('x') -> make a 0d (scalar) into a 1d vector
# dimshuffle(0, 1) -> identity
# dimshuffle(1, 0) -> inverts the first and second dimensions
# dimshuffle('x', 0) -> make a row out of a 1d vector (N to 1xN)
# dimshuffle(0, 'x') -> make a column out of a 1d vector (N to Nx1)
# dimshuffle(2, 0, 1) -> AxBxC to CxAxB
# dimshuffle(0, 'x', 1) -> AxB to Ax1xB
# dimshuffle(1, 'x', 0) -> AxB to Bx1xA
output = T.nnet.sigmoid(conv_out + b.dimshuffle('x', 0, 'x', 'x')) #(1,2,1,1)
# create theano function to compute filtered images
f = theano.function([input], output)
import sys
import numpy
import pylab
from PIL import Image
# open random image of dimensions 639x516
img = Image.open(open(sys.argv[1]))
# dimensions are (height, width, channel)
img = numpy.asarray(img, dtype='float64') / 256.
# put image in 4D tensor of shape (1, 3, height, width)
img_ = img.transpose(2, 0, 1).reshape(1, 3, img.shape[0], img.shape[1])
filtered_img = f(img_)
# plot original image and first and second components of output
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 1); pylab.axis('off'); pylab.imshow(img)
pylab.gray();
# recall that the convOp output (filtered image) is actually a "minibatch",
# of size 1 here, so we take index 0 in the first dimension:
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 2); pylab.axis('off'); pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0, 0, :, :])
pylab.subplot(1, 3, 3); pylab.axis('off'); pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0, 1, :, :])
#pylab.show()
from gezi import show
show()
狼的例子
img.shape
Out[57]: (639, 516, 3)
In [58]: img_.shape
Out[58]: (1, 3, 639, 516) #conv输入数据
filtered_img.shape
Out[56]: (1, 2, 631, 508)
这个刚好 因为w_shp = (2, 3, 9, 9)
In [66]: rng.uniform(low=-1.0 / w_bound, high=1.0 / w_bound, size=w_shp).shape
Out[66]: (2, 3, 9, 9)
采用的是9*9的patch
所以处理后
是 (639 - 9 + 1) * (516 - 9 + 1) 631 * 508
参考这个

结果刚好类似一个edge detector ,用一个非狼的例子

CNN初步-1的更多相关文章
- CNN初步-2
Pooling 为了解决convolved之后输出维度太大的问题 在convolved的特征基础上采用的不是相交的区域处理 http://www.wildml.com/2015/11/unde ...
- 初步认识CNN
1.机器学习 (1)监督学习:有数据和标签 (2)非监督学习:只有数据,没有标签 (3)半监督学习:监督学习+非监督学习 (4)强化学习:从经验中总结提升 (5)遗传算法:适者生存,不适者淘汰 2.神 ...
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)学习算法之----基于LeNet网络的中文验证码识别
由于公司需要进行了中文验证码的图片识别开发,最近一段时间刚忙完上线,好不容易闲下来就继上篇<基于Windows10 x64+visual Studio2013+Python2.7.12环境下的C ...
- (六)6.18 cnn 的反向传导算法
本文主要内容是 CNN 的 BP 算法,看此文章前请保证对CNN有初步认识,可参考Neurons Networks convolutional neural network(cnn). 网络表示 CN ...
- [置顶] VB6基本数据库应用(三):连接数据库与SQL语句的Select语句初步
同系列的第三篇,上一篇在:http://blog.csdn.net/jiluoxingren/article/details/9455721 连接数据库与SQL语句的Select语句初步 ”前文再续, ...
- Tensorflow的CNN教程解析
之前的博客我们已经对RNN模型有了个粗略的了解.作为一个时序性模型,RNN的强大不需要我在这里重复了.今天,让我们来看看除了RNN外另一个特殊的,同时也是广为人知的强大的神经网络模型,即CNN模型.今 ...
- 用于NLP的CNN架构搬运:from keras0.x to keras2.x
本文亮点: 将用于自然语言处理的CNN架构,从keras0.3.3搬运到了keras2.x,强行练习了Sequential+Model的混合使用,具体来说,是Model里嵌套了Sequential. ...
- 深入学习卷积神经网络(CNN)的原理知识
网上关于卷积神经网络的相关知识以及数不胜数,所以本文在学习了前人的博客和知乎,在别人博客的基础上整理的知识点,便于自己理解,以后复习也可以常看看,但是如果侵犯到哪位大神的权利,请联系小编,谢谢.好了下 ...
- CS229 6.18 CNN 的反向传导算法
本文主要内容是 CNN 的 BP 算法,看此文章前请保证对CNN有初步认识. 网络表示 CNN相对于传统的全连接DNN来说增加了卷积层与池化层,典型的卷积神经网络中(比如LeNet-5 ),开始几层都 ...
随机推荐
- [KOJ95603]全球奥运
[COJ95603]全球奥运 试题描述 一个环形的图中有N个城市,奥运会重要项目就是传递圣火,每个城市有A[i]个圣火,每个城市可以向它相邻的城市传递圣火(其中1号城市可以传递圣火到N号城市或2号城市 ...
- 160809228_符瑞艺_C语言程序设计实验3 循环结构程序设计
#include <stdio.h> int main(){ //使用for循环完成1+2+......+100 ; ;i<=;i++) sum +=i; //sum = sum ...
- .oi 小游戏
http://agar.io/ http://diep.io/ http://slither.io/ http://splix.io/ http://wilds.io/ http://kingz.io ...
- Python自动化之常用模块
1 time和datetime模块 #_*_coding:utf-8_*_ __author__ = 'Alex Li' import time # print(time.clock()) #返回处理 ...
- PHP 面向对象:抽象类继承抽象类
抽象类继承另外一个抽象类时,不用重写其中的抽象方法.抽象类中,不能重写抽象父类的抽象方法.这样的用法,可以理解为对抽象类的扩展. 下面的例子,演示了一个抽象类继承自另外一个抽象类时,不需要重写其中的抽 ...
- 大小端; union
#include<stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef union { int m; char a[4]; }Node; int main ...
- 1.把二元查找树转变成排序的双向链表[BST2DoubleLinkedList]
[题目]:输入一棵二元查找树,将该二元查找树转换成一个排序的双向链表.要求不能创建任何新的结点,只调整指针的指向. 比如将二元查找树 . 10 / \ 6 14 / \ / \ 4 8 12 16 转 ...
- php调用c/c++的一种方式
php调用c/c++有很多方式,最常用的是通过tcp或者http去调用,通过发送请求去调用c/c++编写的cgi/fastcgi来实现,另外php还有一种直接执行外部应用程序的方式,这种方式会影响到系 ...
- Windows下给鼠标右键菜单添加获得完全控制权限的菜单项
这段时间计算机C分区里多了很多无用的文件,而且不在同一个目录下,搜索出来删除的时候提示没有管理员权限,需要在右键属性里面修改,非常麻烦,于是查询了一下发现可以在文件右键菜单添加一个获取权限的菜单项,这 ...
- Androd核心基础01
Androd核心基础01包含的主要内容如下 Android版本简介 Android体系结构 JVM和DVM的区别 常见adb命令操作 Android工程目录结构 点击事件的四种形式 电话拨号器Demo ...
