CF1916E Happy Life in University 题解
题目: CF1916E Happy Life in University
链接: 洛谷 或者 CF
前置知识点: 线段树与HH的项链
先简单回顾下HH的项链这题怎么做的吧。先去掉莫队算法,因为这个不是最优的解法。来说说利用树状数组或者线段树怎么处理查询 \([l,r]\) 上的不同数的数目值。首先值域\(1 \sim n\),那么哈希表就不需要了,可以开数组维护一些和权值有关的信息。
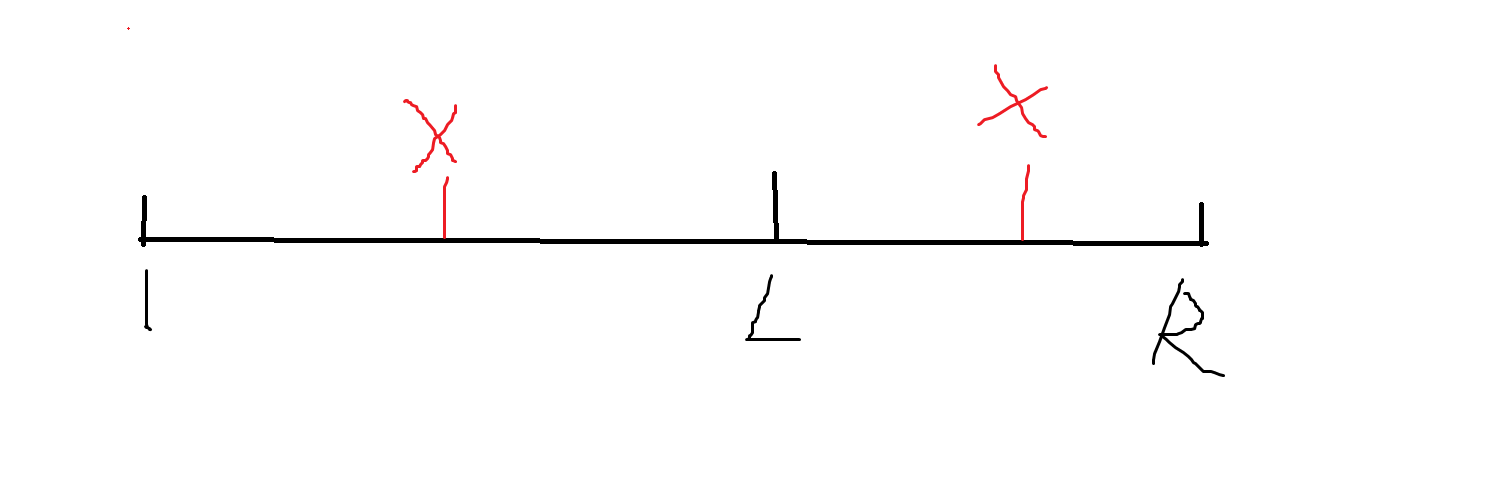
先来看一张图。对于 \(x\) 而言,假如上述标的第一个 \(x\) 为它在进入 \(L\) 前最后出现的位置,而第二个 \(x\) 为在进入待查询区间 \([L,R]\) 的第一个 \(x\)。那么很显然的是,第一个 \(x\) 并不会对这个 \([L,R]\) 造成 \(1\) 的贡献。其次再来考虑在 \([L,R]\) 中如果重复出现了 \(x\) 该如何去掉重复的贡献。很显然的一种思想是在这个查询区间 \([L,R]\) 上,后出现的 \(x\) 会代替掉前出现的 \(x\) 的贡献 \(1\)。那么很自然的一种思想就是“离线”。把查询离线下来,从 \(1 \sim n\) 跑扫描线更新查询。在更新时我们可以维护“每个值出现的最后一次的位置”。这样一来在更新 \(last\) 的时候可以清楚地去掉“前面的贡献”而增加进“当前的贡献”。
算法核心思路:
用一个 \(last\) 数组记录下每个值出现的最后一次位置。并把查询离线下来从 \(1 \sim n\) 进行更新。对于每个 \([l,r]\) 而言,我们在更新时显而易见的可以拿到 \([1,r]\) 的贡献情况,进行区间查询 \([l,r]\) 就行了。具体的每一个 \(last[val[curr]]\) 更新时去掉它原有的贡献,用新的一个位置 \(last\) 的贡献代替它的贡献就行了。
HH的项链关于上述经典算法的参考代码
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
#define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 1e6 + 10;
int bit[N];
int n;
inline void add(int x, const int v)
{
for (; x <= n; x += lowBit(x))bit[x] += v;
}
inline int query(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowBit(x))ans += bit[x];
return ans;
}
int val[N], last[N];
vector<pii> qu[N];
int ans[N];
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 1, n)cin >> val[i];
int q;
cin >> q;
forn(i, 1, q)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
qu[r].emplace_back(l, i);
}
forn(r, 1, n)
{
if (int preLast = last[val[r]])add(preLast, -1);
add(last[val[r]] = r, 1);
for (const auto [l,id] : qu[r])ans[id] = query(r) - query(l - 1);
}
forn(i, 1, q)cout << ans[i] << endl;
}
signed int main()
{
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
}
序列上的这种更新与查询当然树状数组和线段树都行啦。
正文
本文约定俗称:我们将一条路径上不同数的数目叫做“HH的项链”。
其实CF这题就是一个典型的树上HH项链问题,需要稍微转化下。
首先一个显而易见的贪心就是,对于一个 \(LCA\) 它的两个 \(dff\) 值的 \(u \text{与} v\) 的选取,应该取叶子节点。因为很显而易见的是,HH的项链与长度的关系是单调不降的。长度越长才越有可能越大。而题目给的 \(dff\) 函数不就是HH的项链吗?
树上问题怎么变序列问题?dfs序,树剖,很多很多。这里选择dfs序,并且涉及到了区间修改,我们这题采用线段树书写。考虑一下,处理dfs序以后,根据上述贪心和HH项链的基本离线思路,我们应该从叶子节点开始往上算到每个节点的HH项链值,然后嘛就很简单了。只需要记录更新到 \(LCA\) 的最大值,因为HH的项链是单调不降的,所以一定有以下结论:
\]
即 \(LCA\) 所在子树的其他点到同一个叶子节点的HH的项链并不会优于从 \(LCA\) 到叶子节点的HH的项链。
那么次大值只有可能在更新最大值之前取到。所以只需要在更新当前 \(LCA\) 全局最大值时将当前用于即将更新最大值的数进行更新答案,再更新下最大值即可。
最后考虑下上述的删除时机和添加时机如何搬到树上,很简单。这里需要类比几个点。
- 对于一个 \(LCA\) 而言,它的贡献范围显然是“以它为根的子树”。这点 dfs序+线段树可以轻松做到+1
- 从哪开始更新,或者说像上述一样该从哪开始扫描进入。显然根据上述应该从叶子节点开始往上去更新HH的项链值。
- 什么时候是删除时机?很显然的是当子树的 \(last\) 被父树的 \(last\) 更新时,就该去掉了,其实这个可以预处理出来。只需要为每个点维护一个 \(del\) 数组,表示的是当更新到这个节点时需要去掉哪几个子树节点的“贡献”。dfs从上往下,每需要更新一个 \(last\) 我们需要反过来写,父节点当中待删除的 \(del\) 数组加入当前节点。
- 注意到对于一个节点而言,它的子树之间互不影响,所以在退出这棵子树的dfs时需要恢复它的 \(last\)
del数组预处理核心逻辑代码
int preLast = last[val[curr]];
if (preLast)del[preLast].push_back(curr); //HH项链扫描线的删除
last[val[curr]] = curr;
至此算法框架完成,细节见代码注释
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
//#define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 3e5 + 10;
struct Node
{
int add;
int mx;
} node[N << 2];
#define add(x) node[x].add
#define mx(x) node[x].mx
inline void push_up(const int curr)
{
mx(curr) = max(mx(ls(curr)),mx(rs(curr)));
}
inline void push_down(const int curr)
{
if (add(curr))
{
mx(ls(curr)) += add(curr);
mx(rs(curr)) += add(curr);
add(ls(curr)) += add(curr);
add(rs(curr)) += add(curr);
add(curr) = 0;
}
}
int n;
vector<int> child[N];
inline void update(const int curr, const int l, const int r, const int val, const int s = 1, const int e = n)
{
if (l <= s and e <= r)
{
mx(curr) += val;
add(curr) += val;
return;
}
const int mid = (s + e) >> 1;
push_down(curr);
if (l <= mid)update(ls(curr), l, r, val, s, mid);
if (r > mid)update(rs(curr), l, r, val, mid + 1, e);
push_up(curr);
}
inline int query(const int curr, const int l, const int r, const int s = 1, const int e = n)
{
if (l <= s and e <= r)return mx(curr);
const int mid = (s + e) >> 1;
push_down(curr);
int ans = 0;
if (l <= mid)uMax(ans, query(ls(curr), l, r, s, mid));
if (r > mid)uMax(ans, query(rs(curr), l, r, mid + 1, e));
return ans;
}
int s[N], e[N], val[N], cnt;
int last[N]; //每种元素最后出现的点
vector<int> del[N];
//处理dfs序,预处理del数组
inline void dfs(const int curr, const int fa)
{
s[curr] = ++cnt;
int preLast = last[val[curr]];
if (preLast)del[preLast].push_back(curr); //HH项链扫描线的删除,父树去掉子树贡献
last[val[curr]] = curr; //进入子树更新last
for (const int nxt : child[curr])if (nxt != fa)dfs(nxt, curr);
last[val[curr]] = preLast; //退出子树时恢复last
e[curr] = cnt;
}
ll ans;
inline void getAns(const int curr, const int fa)
{
//把curr当做LCA
for (const int nxt : child[curr])if (nxt != fa)getAns(nxt, curr); //贪心从底部开始往上算HH的项链
update(1, s[curr], e[curr], 1); //扫描线扫到当前节点加入这个点的贡献,贡献范围为整棵子树
for (auto nxt : del[curr])update(1, s[nxt], e[nxt], -1); //HH的项链的删除,删掉子树贡献
ll mx2 = 1; //次小值
for (const int nxt : child[curr])
{
if (nxt == fa)continue;
ll mx1 = query(1, s[nxt], e[nxt]); //最大值
uMax(ans, mx1 * mx2); //更新max之前计算,mx1则会是次大值
uMax(mx2, mx1); //更新次大值
}
}
//多测清空
inline void clear()
{
forn(curr, 1, n<<2)
mx(curr) = add(curr) = 0;
cnt = 0;
forn(i, 1, n)last[i] = 0, del[i].clear(), child[i].clear();
ans = 1;
}
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 2, n)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
child[x].push_back(i);
}
forn(i, 1, n)cin >> val[i];
dfs(1, 0);
getAns(1, 0);
cout << ans << endl;
clear();
}
signed int main()
{
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
int test = 1;
// read(test);
cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
}
CF1916E Happy Life in University 题解的更多相关文章
- 2016-2017 National Taiwan University World Final Team Selection Contest (Codeforces Gym) 部分题解
D 考虑每个点被删除时其他点对它的贡献,然后发现要求出距离为1~k的点对有多少个. 树分治+FFT.分治时把所有点放一起做一遍FFT,然后减去把每棵子树单独做FFT求出来的值. 复杂度$nlog^ ...
- poj 2010 Moo University - Financial Aid(优先队列(最小堆)+ 贪心 + 枚举)
Description Bessie noted that although humans have many universities they can attend, cows have none ...
- 算法(第四版)C# 习题题解——2.3
写在前面 整个项目都托管在了 Github 上:https://github.com/ikesnowy/Algorithms-4th-Edition-in-Csharp 查找更为方便的版本见:http ...
- zoj 4020 The 18th Zhejiang University Programming Contest Sponsored by TuSimple - G Traffic Light(广搜)
题目链接:The 18th Zhejiang University Programming Contest Sponsored by TuSimple - G Traffic Light 题解: 题意 ...
- HDU 4352 XHXJ's LIS HDU 题解
题目 #define xhxj (Xin Hang senior sister(学姐)) If you do not know xhxj, then carefully reading the ent ...
- POJ2482 Stars in Your Window 题解
Fleeting time does not blur my memory of you. Can it really be 4 years since I first saw you? I stil ...
- 2016 华南师大ACM校赛 SCNUCPC 非官方题解
我要举报本次校赛出题人的消极出题!!! 官方题解请戳:http://3.scnuacm2015.sinaapp.com/?p=89(其实就是一堆代码没有题解) A. 树链剖分数据结构板题 题目大意:我 ...
- noip2016十连测题解
以下代码为了阅读方便,省去以下头文件: #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #incl ...
- BZOJ-2561-最小生成树 题解(最小割)
2561: 最小生成树(题解) Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 1628 Solved: 786 传送门:http://www.lyd ...
- Codeforces Round #353 (Div. 2) ABCDE 题解 python
Problems # Name A Infinite Sequence standard input/output 1 s, 256 MB x3509 B Restoring P ...
随机推荐
- Python | 解放双手,用Python实现自动发送邮件
解放双手,用Python实现自动发送邮件 使用Python实现自动化邮件发送,可以让你摆脱繁琐的重复性业务,节省非常多的时间. Python有两个内置库:smtplib和email,能够实现邮件功能, ...
- InnoDB 事务加锁分析
本文首发于 vivo互联网技术 微信公众号 链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/S7MhlsZveBHRSQhq5aTIJA作者:何志创 一般大家对数据库事务的了解可能停留在事 ...
- vue中class样式与内联样式
(1):style使用 <div class="score" :style="{ color: colorComputed(item.status) }" ...
- SIP没有摘机消息可以通话吗
概述 SIP流程中,A路没有收到摘机的200 OK响应消息可以通话吗? 客户反馈的问题千奇百怪,公共互联网的问题同样百转千回,让你欲罢不能,头秃方休. 客户报故障,问题描述是这样的,我用号码A打给号码 ...
- wxpython窗体之间传递参数
如何界面存在frame1与frame2,通过frame1打开页面frame2,并将frame2的值传递给frame1 可以使用回调函数传值参考具体代码如下: # -*- coding: utf-8 - ...
- SpringBoot中使用LocalDateTime踩坑记录
.markdown-body { line-height: 1.75; font-weight: 400; font-size: 16px; overflow-x: hidden; color: rg ...
- WPF|黑暗模式的钱包支付仪表盘界面设计
阅读目录 效果展示 准备 简单说明 + 源码 结尾(视频及源码仓库) 1. 效果展示 欣赏效果: 2. 准备 创建一个WPF工程,比如站长使用 .NET 7 创建名为 WalletPayment 的W ...
- APB Slave Design
APB Slave Design module apb_slave #( REG1_ADDR = 8'h00, REG2_ADDR = 8'h04, REG3_ADDR = 8'h08 ) ( // ...
- Keep English Level-04
firm -- 坚定的,坚固的;公司 share -- n 股份,份额 executive -- 执行官 There is no chance,no density,no fate,that can ...
- [转帖]技术分享| MySQL 的 AWR Report?— MySQL 状态诊断报告
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000039959767 作者:秦福朗 爱可生 DBA 团队成员,负责项目日常问题处理及公司平台问题排查.热爱 IT,喜欢在互联网 ...
