CyclicBarrier、CountDownLatch、Callable、FutureTask、thread.join() 、wait()、notify()、Condition
CyclicBarrier使用:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
/**
* 三个运动员各自准备,等到三个人都准备好后,再一起跑</br>@see 1:先创建一个公共 CyclicBarrier 对象,设置 同时等待 的线程数,CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(3);</br>
2:这些线程同时开始自己做准备,自身准备完毕后,需要等待别人准备完毕,这时调用 cyclicBarrier.await(); 即可开始等待别人;</br>
3:当指定的 同时等待 的线程数都调用了 cyclicBarrier.await();时,意味着这些线程都准备完毕好,然后这些线程才 同时继续执行。</br>
*
*/
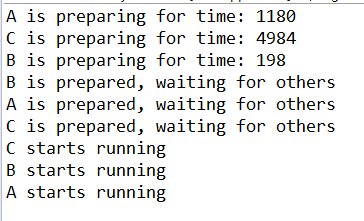
public class TestCyclicBarrier { public static void main(String[] args) {
int runner = 3;
final CyclicBarrier cycliBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(runner);
final Random random = new Random(); for (char runnerName = 'A'; runnerName <= 'C'; runnerName++) {
final String rName = String.valueOf(runnerName);
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
long prepareTime = random.nextInt(10000)+100;
System.out.println(rName + " is preparing for time: " + prepareTime);
try {
Thread.sleep(prepareTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(rName + " is prepared, waiting for others");
try {
cycliBarrier.await(); // 当前运动员准备完毕,等待别人准备好
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(rName + " starts running"); // 所有运动员都准备好了,一起开始跑
} }).start();
}
} }
输出:
CountDownLatch例子
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* 四个线程 A B C D,其中 D 要等到 A B C 全执行完毕后才执行,而且 A B C 是同步运行的@see 1:创建一个计数器,设置初始值,CountdownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(2);</br>
2:在 等待线程 里调用 countDownLatch.await() 方法,进入等待状态,直到计数值变成 0;</br>
3:在 其他线程 里,调用 countDownLatch.countDown() 方法,该方法会将计数值减小 1;</br>
4:当 其他线程 的 countDown() 方法把计数值变成 0 时,等待线程 里的 countDownLatch.await() 立即退出,继续执行下面的代码。</br>
*
*/
public class TestCountDownLatch { public static void main(String[] args) {
int workerNum = 3;
final CountDownLatch countDownlatch = new CountDownLatch(workerNum); new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("D is waiting for other three threads");
try {
countDownlatch.await();
System.out.println("D is start work");
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("D finsh Work");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start(); for (char threadName = 'A'; threadName <= 'C'; threadName++) {
final String tName = String.valueOf(threadName);
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(tName + " is working");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(tName + " finished");
countDownlatch.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
} }
输出:

FutureTask、Callable例子
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
/**
* 我们想让子线程去计算从 1 加到 100,并把算出的结果返回到主线程</br>
* @see
* 如何把子线程的结果回传回来呢?在 Java 里,有一个类是配合 Callable 使用的:FutureTask,不过注意,它获取结果的 get 方法会阻塞主线程。
*
*/
public class TestCallableAndFutureTask { public static void main(String[] args) {
Callable<Integer> callAble = new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
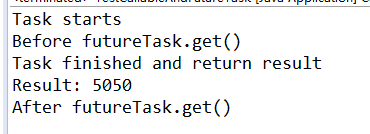
System.out.println("Task starts");
Thread.sleep(100);
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
result += i;
}
System.out.println("Task finished and return result");
return result;
}
}; FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(callAble);
new Thread(futureTask).start(); try {
System.out.println("Before futureTask.get()");
System.out.println("Result: " + futureTask.get());
System.out.println("After futureTask.get()");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} }
输出:
thread.join() 例子
/**
* 实现效果:线程B在线程A完成之后再执行
* thread.join()
*
*/
public class TestThreadJoin { public static void main(String[] args) {
demo1();
} private static void demo1() {
final Thread A = new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override
public void run() {
PrintNumber("A");
} }) ; Thread B = new Thread(new Runnable(){ @Override
public void run() {
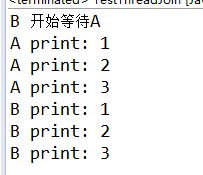
System.out.println("B 开始等待A");
try {
A.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
PrintNumber("B");
} }) ;
A.start();
B.start();
} private static void PrintNumber(String ThreadName) {
int i = 0;
while (i++ < 3) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(ThreadName + " print: " + i);
}
}
}
输出:
wait()、notify() 例子:
public class TestWaitAndnotify {
public static void main(String[] args) {
demo2();
}
public static void demo2 () {
final Object lock = new Object();
Thread A = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("INFO: A 等待锁 ");
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("INFO: A 得到了锁 lock");
System.out.println("A1");
try {
System.out.println("INFO: A 准备进入等待状态,放弃锁 lock 的控制权 ");
lock.wait();//挂起线程A 放弃锁 lock 的控制权
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("INFO: 有人唤醒了 A, A 重新获得锁 lock");
System.out.println("A2");
System.out.println("A3");
}
}
});
Thread B = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("INFO: B 等待锁 ");
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("INFO: B 得到了锁 lock");
System.out.println("B1");
System.out.println("B2");
System.out.println("B3");
System.out.println("INFO: B 打印完毕,调用 notify 方法 ");
lock.notify(); // notify()方法唤醒正在等待lock锁的线程A
System.out.println("线程 B do notify method 完毕");
}
}
});
A.start();
B.start();
}
}
输出:

Condition 例子(生产消费):
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class TestCondition { public static void main(String[] args) {
final BoundedBuffer b = new BoundedBuffer(); new Thread(new Runnable() { // 写线程
public void run() {
int i = 1;
while (true) {
try {
b.put(i++);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start(); new Thread(new Runnable() { // 读线程
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
b.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
class BoundedBuffer{
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 锁对象
final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition(); // 写线程条件
final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); // 读线程条件 final Integer[] items = new Integer[10]; // 缓存队列
int putptr; // 写索引
int takeptr; // 读索引
int count; // 队列中存在的数据个数 public void put(Integer x) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(count == items.length) { // 如果队列满了
notFull.await(); // 阻塞写线程
}
items[putptr] = x; // 赋值
System.out.println("写入:" + x);
if(++putptr == items.length) { // 如果写索引写到队列的最后一个位置了,那么置为0
putptr = 0;
}
++count; // 个数++
notEmpty.signal(); // 唤醒读线程
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} public Integer take() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while(count == 0) { // 如果队列为空
notEmpty.await(); // 阻塞读线程
}
Integer x = items[takeptr]; // 取值
System.out.println("读取:" + x);
if(++takeptr == items.length) { // 如果读索引读到队列的最后一个位置了,那么置为0
takeptr = 0;
}
--count; // 个数--
notFull.signal();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
输出:

.......
CyclicBarrier、CountDownLatch、Callable、FutureTask、thread.join() 、wait()、notify()、Condition的更多相关文章
- Java 如何实现线程间通信?(notify、join、CountdownLatch、CyclicBarrier、FutureTask、Callable )
转自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI4Njc5NjM1NQ==&mid=2247486499&idx=1&sn=d3f2d6959df ...
- Java并发编程:Semaphore、CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier
首先我们来实现一个功能:当我们启动一个系统的时候需要初始化许多数据,这时候我们可能需要启动很多线程来进行数据的初始化,只有这些系统初始化结束之后才能够启动系统.其实在Java的类库中已经提供了Sema ...
- java并发之同步辅助类(Semphore、CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Phaser)
线程同步辅助类,主要学习两点: 1.上述几种同步辅助类的作用以及常用的方法 2.适用场景,如果有适当的场景可以用到,那无疑是最好的 semaphore(seməˌfôr) 含义 信号量就是可以声明多把 ...
- Thread.join(), CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier和 Semaphore区别,联系及应用
在java 1.5中,提供了一些非常有用的辅助类来帮助我们进行并发编程,比如CountDownLatch,CyclicBarrier和Semaphore,今天我们就来学习一下这三个辅助类的用法, 由于 ...
- java线程并发工具类CyclicBarrier、CountDownLatch及Semaphore
一.CyclicBarrier (原文链接:http://www.studyshare.cn/blog-front/blog/index ) 1.定义 CyclicBarrier是线程并发工具类之 ...
- java并发系列(二)-----线程之间的协作(wait、notify、join、CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier)
在java中,线程之间的切换是由操作系统说了算的,操作系统会给每个线程分配一个时间片,在时间片到期之后,线程让出cpu资源,由其他线程一起抢夺,那么如果开发想自己去在一定程度上(因为没办法100%控制 ...
- JUC-JUC强大的辅助类讲解(Semaphore、CyclicBarrier、CountDownLatch)
一.CountDownLatch 减少计数 1.原理 * CountDownLatch主要有两个方法,当一个或多个线程调用await方法时,这些线程会阻塞. * 其它线程调用countDown方法会将 ...
- Android进阶——多线程系列之Semaphore、CyclicBarrier、CountDownLatch
今天向大家介绍的是多线程开发中的一些辅助类,他们的作用无非就是帮助我们让多个线程按照我们想要的执行顺序来执行.如果我们按照文字来理解Semaphore.CyclicBarrier.CountDownL ...
- 温故知新-多线程-forkjoin、CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore用法
Posted by 微博@Yangsc_o 原创文章,版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名 | Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 3.0 文章目录 摘要 forkjoin C ...
随机推荐
- F12谷歌开发者工具preserve log
谷歌开发者工具里面这个preserve log :保留请求日志,跳转页面的时候勾选上,可以看到跳转前的请求,也可适用于chrome开发者工具抓包的问题
- matlab中句柄@的用法
@是Matlab中的句柄函数的标志符,即间接的函数调用方法. 1 句柄函数 主要有两种语法: handle = @functionname handle = @(arglist)anonymous_f ...
- 也谈HTTP协议
HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol,超文转移协议,超文本传输协议的译法并不严谨.) 一.网络基础 TCP/IP 1.1 TCP/IP 协议族 TCP/IP 协议族是互联网 ...
- [BZOJ4237]稻草人:CDQ分治+单调栈
分析 按\(y\)排序后CDQ分治,可以发现每个点可以影响的是\(x\)坐标的一段区间,可以使用扫描线+单调栈,在单调栈上二分即可解决,时间复杂度\(O(n \log^2 n)\). 通过归并排序可以 ...
- 不使用spring-boot-starter-parent进行依赖的版本管理
spring-boot-starter-parent 提供了Dependency Management 进行项目依赖的版本管理,默认的资源过滤和插件配置. 但是,当需要将其他项目作为parent 的时 ...
- javadoc生成文档
标签(空格分隔): javadoc java生成html的文档: 要生成注释文档html格式,java里面提供一个工具:javadoc 例如: javadoc -d myhelp -author -v ...
- 第五周总结&实验报告三
第五周总结&实验报告三 实验报告 1.已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码.结果截图.) ① 统计该字符串中字母s ...
- HTTP请求方式之POST和GET的区别
GET请求方式: 如果我们的网页收集到的用户数据,他规定了,此网页用户数据用GET的请求方式去处理的话,我们会发现,比如百度,就是一个很经典的GET请求方式 当我们在百度搜索上输入一个‘java’,点 ...
- nginx回源使用localhost产生问题
最近测试ngx_http_slice模块,回源的时候填的localhost结果老是超时,还以为是slice模块有问题,后来无意间改成127.0.0.1后就没有问题了 真是见鬼了 #user root; ...
- PADS LAYOUT的一般流程
1.概述 本文档的目的在于说明使用PADS的印制板设计软件PowerPCB进行印制板设计的流程和一些注意事项,为一个工作组的设计人员提供设计规 范,方便设计人员之间进行交流和相互检查. 2.设计 ...
