ht-2 arrayList特性
一、arrayList对象创建
当调用无参构造方法来构造一个ArrayList对象时,它会在内部分配一个初始大小为10的一个Object类型数组, 当添加的数据容量超过数组大小的时候,会产生一个新的数组,新的数组大小为原来数组大小的1.5倍+1, 接着把原数组中的数据拷贝到新的素组中,并让原来的引用变量指向这个新数组,参见ArrayList源代码 ;
二、arrayList相关方法:
添加元素:add(E e)
指定位置添加:add(int index, E element)
获取指定位置的元素:public E get(int index)
设置指定位置的元素: public E set(int index, E element) 返回该位置原来存储的元素
删除指定位置的元素 public E remove(int index) 返回被删除的元素
删除指定元素: public boolean remove(Object o) 如果指定元素在集合中存在,返回true 否则返回false
是否包指定元素:public boolean contains(Object o) @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
数组大小: public int size()
list转数组: public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); }
查找元素在list中的索引值: int indexOf(Object o); 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含该指定元素,则返回-1
三、arraylist遍历:
1. for循环
2.foreach
3.迭代器遍历 list实现了 Collection接口,collection接口实现了 Iterable 接口,因此list 可以使用Iterable接口的iterator()方法获得一个迭代器对象
package com.iotek.list; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List; public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> nlist = new ArrayList<String>(); // 接口的引用变量指向子类对象
nlist.add("null"); // 向容器中添加元素
nlist.add("lucy");
nlist.add("jack");
nlist.add("tom");
nlist.add("john");
nlist.add("jack");
// foreach遍历
for (String s : nlist) {
System.out.print(s + " ");
} nlist.add(1, "jay"); // 将元素“jay”插入到下标1的位置处
nlist.set(0, "chengang"); // 将下标0位置处的元素替换成“chengang” // 使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println();
Iterator<String> it = nlist.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) { // it.hashNext()判断下一个元素是否为空
String name = it.next();
System.out.print(name + " ");
} System.out.println();
System.out.println("获取下标:" + nlist.indexOf("lucy")); // 输出元素“lucy”的索引值(在容器数组中的下标值)
System.out.println("删除元素:" + nlist.remove("jack"));// 删除,如果列表中有这个元素,返回true
System.out.println("删除指定位置元素:" + nlist.remove(0)); // 返回被删除位置的元素
System.out.println("是否包含某个元素:" + nlist.contains("chengang")); // 已删除该元素,故返回false
nlist.clear(); // 清空容器
System.out.println("判断容器是否为空:" + nlist.isEmpty()); } }

四 、indexof(Object o) 以及Contains(Object o)原理:
indexof(Object o) 方法本质上是调用对象o的equals()方法去list里查找,找到了就返回这个元素的下标,没有找到则返回-1;
而equals 本质比较的是两个对象的引用地址,而非对象的内容:
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
contains方法源码如下,本质上是调用indexof来判断是否包含指定对象的,如果用contains方法判断list里面是否包含自定义的对象,那么也需要重写该对象的类的equals方法
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains
* at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) >= 0;
}
测试示例,不重写对象的equals方法时:
package com.iotek.list; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class ArrayListDemo2_1 { /**
* 用ArrayList容器存放对象数据
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> stuList = new ArrayList<Student>(); // 通过泛型限定数组元素的数据类型为Student
Student stu1 = new Student("zhangsan", 10);
Student stu2 = new Student("lisi", 20);
Student stu3 = new Student("jack", 30);
Student stu4 = new Student("mandy", 10);
Student stu5 = new Student("mary", 20); // 创建5个Student对象
stuList.add(stu1);
stuList.add(stu2);
stuList.add(stu3);
stuList.add(stu4);
stuList.add(stu5); // 将5个Student对象添加到容器中
Student stu6 = new Student("mary", 20); // 如果使用默认的equals方法,由于indexOf(Object
// o)方法的实现原理,stu6还未添加到容器中,因此找不到stu6的地址,返回-1
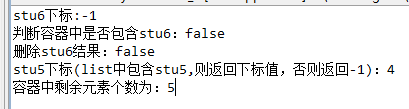
System.out.println("stu6下标:" + stuList.indexOf(stu6));
System.out.println("判断容器中是否包含stu6:" + stuList.contains(stu6));
System.out.println("删除stu6结果:"+stuList.remove(stu6)); // 删除stu6,不含stu6,返回false
System.out.println("stu5下标(list中包含stu5,则返回下标值,否则返回-1):"+stuList.indexOf(stu5));
System.out.println("容器中剩余元素个数为:" + stuList.size());
} } class Student {
private String name;
private int age; public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} }
结果如下:
重写对象的equals方法后:
package com.iotek.list; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class ArrayListDemo2_2 { /**
* 用ArrayList容器存放对象数据
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student1> stuList = new ArrayList<Student1>(); // 通过泛型限定数组元素的数据类型为Student
Student1 stu1 = new Student1("zhangsan", 10);
Student1 stu2 = new Student1("lisi", 20);
Student1 stu3 = new Student1("jack", 30);
Student1 stu4 = new Student1("mandy", 10);
Student1 stu5 = new Student1("mary", 20);
stuList.add(stu1);
stuList.add(stu2);
stuList.add(stu3);
stuList.add(stu4);
stuList.add(stu5);
Student1 stu6 = new Student1("mary", 20);//重复元素
System.out.println("stu6下标:" + stuList.indexOf(stu6));
System.out.println("判断容器中是否包含stu6:" + stuList.contains(stu6));
System.out.println("删除stu6结果:" + stuList.remove(stu6)); // 删除stu6,不含stu6,返回false,如果包含,返回该元素
System.out.println("stu5下标:" + stuList.indexOf(stu5)); // 删除stu6后再查看,返回-1
System.out.println("容器中剩余元素个数为:" + stuList.size()); } } class Student1 {
private String name;
private int age; public Student1(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} @Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true; // 如果2个指针指向同一对象,返回true
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) // 如果2个类型不一样,返回false
return false;
Student1 other = (Student1) obj; // 接下来将obj转换成Student对象
if (age != other.age) // 如果年龄或者姓名有一个不相等,返回false,都相等,返回true
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} }
结果如下:

对自定义的类,需要比较该类的两个对象是否相等时,需要比较这两个对象的属性是否相等,(而不是通过比较这两个对象的引用变量,因为2个对象的引用变量的地址永远不相同,除非这两个引用变量指向了同一个对象), 那么此时,需要重写equals方法,默认的Object类中的equals方法比较的是2个对象的地址
ht-2 arrayList特性的更多相关文章
- 利用ArrayList对Hashtable其进行排序
前言: 最近在使用Hashtable的时候发现一个问题:就是当你对Hashtable进行遍历的时候整个输出结果是毫无顺序的, 上网查了一下说是Hashtable有自己内部的排序机制,如果要自定义排序的 ...
- 重识 ArrayList
前言 ArrayList 作为 Java 集合框架中最常用的类,在一般情况下,用它存储集合数据最适合不过.知其然知其所以然,为了能更好地认识和使用 ArrayList,本文将从下面几方面深入理解 Ar ...
- 常用数据结构之ArrayList
前言 ArrayList想必是广大Java程序员开发时最常用的数据结构了,但不一定对其原理都有了解,今天我将结合ArrayList的源码对其进行讲解.本文将围绕ArrayList主要特性(包括适用场景 ...
- 使用NPOI导入导出标准的Excel
关于NPOI NPOI是POI项目的.NET版本,是由@Tony Qu(http://tonyqus.cnblogs.com/)等大侠基于POI开发的,可以从http://npoi.codeplex. ...
- 《java JDK7 学习笔记》之Collection
一.使用Collection 收集对象 1.认识Collection架构 Java SE提供了满足各种需求的API,在使用这些API前,建议先了解其继承与接口操作架构,才能了解何时使用哪个类,以及类之 ...
- 20145235 《Java程序设计》第5周学习总结
教材学习内容总结 8.1语法与继承架构 try和catch语法,如果被try{}的语句出现了catch()的问题就执行catch{}的语句. 错误的对象都继承于java.long.Throwable, ...
- 20145218 《Java程序设计》第五周学习总结
20145218 <Java程序设计>第五周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 异常 程序中总有些意想不到的状况所引发的错误,如果不对异常进行正确的处理,则可能导致程序的中断执行,造成不必要的损失 ...
- # 20145210 《Java程序设计》第05周学习总结
教材学习内容总结 第八章 异常处理 8.1语法与继承架构 •使用 try.catch •Java中所有信息都会被打包为对象,如果愿意,可以尝试(try)捕捉(catch)代表错误的对象后做一些处理 • ...
- 学号20145220 《Java程序设计》第5周学习总结
学号20145220 <Java程序设计>第5周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 语法与继承结构 8.1.1使用try.catch java中所有的错误都会被打包为对象,并提供了特有的语句进行处 ...
随机推荐
- 015-elasticsearch5.4.3【五】-搜索API【四】Joining 多文档查询、GEO查询、moreLikeThisQuery、script脚本查询、span跨度查询
一.Joining 多文档查询 joining query 像Elasticsearch这样的分布式系统中执行完整的SQL样式连接非常昂贵.相反,Elasticsearch提供两种形式的连接,旨在水平 ...
- Linux_文件系统&磁盘分区
目录 目录 前言 文件系统 目录结构 File文件标识符 文件系统修复指令 两种磁盘格式 MBR格式 GPT格式 磁盘分区 查看分区 分区的类型 分区最小存储单元 查看当前分区的block的大小 GP ...
- 阶段1 语言基础+高级_1-3-Java语言高级_1-常用API_1_第5节 String类_1_字符串概述和特点
在api中查找 java.lang包里面的不用引用
- 类HashMap
/* * Map集合的特点 * 将键映射值的对象,一个映射不能包含重复的值:每个键最多只能映射到一个值 * * Map集合和Collection集合的区别? * Map集合存储元素是成对出现的,Map ...
- 使用autofac的一些问题
None of the constructors found with 'Autofac.Core.Activators.Reflection.DefaultConstructorFinder' on ...
- 排序算法七:基数排序(Radix sort)
上一篇提到了计数排序,它在输入序列元素的取值范围较小时,表现不俗.但是,现实生活中不总是满足这个条件,比如最大整形数据可以达到231-1,这样就存在2个问题: 1)因为m的值很大,不再满足m=O(n) ...
- Redis功能迅速回忆
- SpringBoot 使用JPA+MySQL+Thymeleaf 总结 一
SpringBoot 使用JPA+MySQL+Thymeleaf 总结 一 SpringBoot 使用JPA+MySQL+Thymeleaf 总结 二 pom引用 <?xml version=& ...
- 不用找了,300 分钟帮你搞定 Spring Cloud!
最近几年,微服务架构一跃成为 IT 领域炙手可热的话题,大量一线互联网公司因为庞大的业务体量和业务需求,纷纷投入了微服务架构的建设中,像阿里巴巴.百度.美团等大厂,很早就已经开始了微服务的实践和应用. ...
- POJ-1502 MPI Maelstrom 迪杰斯特拉+题解
POJ-1502 MPI Maelstrom 迪杰斯特拉+题解 题意 题意:信息传输,总共有n个传输机,先要从1号传输机向其余n-1个传输机传输数据,传输需要时间,给出一个严格的下三角(其实就是对角线 ...
