Linux系统常用知识(centos7)
一、查看系统版本
1、查看linux内核版本
#cat /etc/redhat-release
二、主机名
2.1定义:
静态的(Static hostname):“静态”主机名也称为内核主机名,是系统在启动时从/etc/hostname自动初始化的主机名
瞬态的(Tansient hostname):“瞬态”主机名是在系统运行时临时分配的主机名,例如,通过DHCP或mDNS服务器分配。
灵活的(Pretty hostname):
“灵活”主机名也有人叫做“别名”主机名。
“灵活”主机名则允许使用自由形式(包括特殊/空白字符)的主机名,以展示给终端用户(如xh01@f5)。
“静态”主机名和“瞬态”主机名都遵从作为互联网域名同样的字符限制规则。
2.2查看主机名
2.2.1查看到的是瞬态的(Tansient hostname)
#hostname
2.2.2查看主机名配置文件,查看到的是静态的(Static hostname)
#cat /etc/hostname
2.2.3只查看静态、瞬态或灵活主机名,分别使用--static,--transient或--pretty选项
.hostnamectl --static //静态
.hostnamectl --transient //瞬态
.hostnamectl --pretty //灵活主机名
2.3.4修改主机名
(1)临时修改
#hostname xxx //lzw为新的主机名
(2)永久修改
- 方法一:
#hostnamectl set-hostname xxx
- 方法二:
#vim /etc/hostname
#编辑模式,输入新的主机名即可
- 方法三:
通过nmtui修改,之后重启hostnamed
#nmcli general hostname servername #systemctl restart systemd-hostnamed
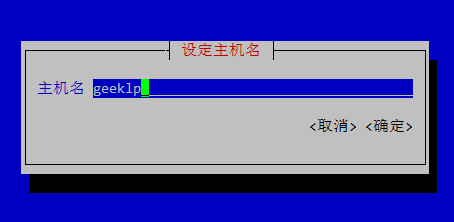
还可以通过nmtui进入图形界面来修改主机名。将光标通过键盘的上下键移动到“设定系统主机名”菜单处,按下回车键。

此时,屏幕出现“设定主机名”选项卡,输入需要设定的主机名,通过键盘方向键将光标移动到“确定”处,回车键确定即可完成主机名的修改。
三、设置网络信息
1、进入网卡
#cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
#ls
#vim eth0

2、设置网络
四、设置dns解析
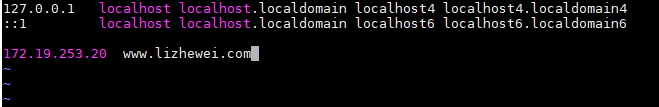
1、本地解析
#vim /etc/hosts
2、设置DNS服务器
#vim /etc/resolv.conf

五、Centos7中systemctl的使用
CentOS 7.x开始,CentOS开始使用systemd服务来代替daemon,原来管理系统启动和管理系统服务的相关命令全部由systemctl命令来代替。
1、原来的 service 命令与 systemctl 命令对比
| daemon命令 | systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| service [服务] start | systemctl start [unit type] | 启动服务 |
| service [服务] stop | systemctl stop [unit type] | 停止服务 |
| service [服务] restart | systemctl restart [unit type] | 重启服务 |
此外还是二个systemctl参数没有与service命令参数对应
- status:参数来查看服务运行情况
- reload:重新加载服务,加载更新后的配置文件(并不是所有服务都支持这个参数,比如network.service)
应用举例:
#启动网络服务
systemctl start network.service
#停止网络服务
systemctl stop network.service
#重启网络服务
systemctl restart network.service
#查看网络服务状态
systemctl status network.serivce
2、原来的chkconfig 命令与 systemctl 命令对比
2.1、设置开机启动/不启动
| daemon命令 | systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| chkconfig [服务] on | systemctl enable [unit type] | 设置服务开机启动 |
| chkconfig [服务] off | systemctl disable [unit type] | 设备服务禁止开机启动 |
应用举例:
#停止cup电源管理服务
systemctl stop cups.service
#禁止cups服务开机启动
systemctl disable cups.service
#查看cups服务状态
systemctl status cups.service
#重新设置cups服务开机启动
systemctl enable cups.service2.2、查看系统上上所有的服务
命令格式:
systemctl [command] [–type=TYPE] [–all]
参数详解:
command - list-units:依据unit列出所有启动的unit。加上 –all 才会列出没启动的unit; - list-unit-files:依据/usr/lib/systemd/system/ 内的启动文件,列出启动文件列表
–type=TYPE - 为unit type, 主要有service, socket, target
应用举例:
| systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| systemctl | 列出所有的系统服务 |
| systemctl list-units | 列出所有启动unit |
| systemctl list-unit-files | 列出所有启动文件 |
| systemctl list-units –type=service –all | 列出所有service类型的unit |
| systemctl list-units –type=service –all grep cpu | 列出 cpu电源管理机制的服务 |
| systemctl list-units –type=target –all | 列出所有target |
3、systemctl特殊的用法
| systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| systemctl is-active [unit type] | 查看服务是否运行 |
| systemctl is-enable [unit type] | 查看服务是否设置为开机启动 |
| systemctl mask [unit type] | 注销指定服务 |
| systemctl unmask [unit type] | 取消注销指定服务 |
应用举例:
#查看网络服务是否启动
systemctl is-active network.service
#检查网络服务是否设置为开机启动
systemctl is-enable network.service
#停止cups服务
systemctl stop cups.service
#注销cups服务
systemctl mask cups.service
#查看cups服务状态
systemctl status cups.service
#取消注销cups服务
systemctl unmask cups.service4、init 命令与systemctl命令对比
| init命令 | systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| init 0 | systemctl poweroff | 系统关机 |
| init 6 | systemctl reboot | 重新启动 |
与开关机相关的其他命令:
| systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| systemctl suspend | 进入睡眠模式 |
| systemctl hibernate | 进入休眠模式 |
| systemctl rescue | 强制进入救援模式 |
| systemctl emergency | 强制进入紧急救援模式 |
5、设置系统运行级别
5.1、运行级别对应表
| init级别 | systemctl target |
|---|---|
| 0 | shutdown.target |
| 1 | emergency.target |
| 2 | rescure.target |
| 3 | multi-user.target |
| 4 | 无 |
| 5 | graphical.target |
| 6 | 无 |
此外还是一个getty.target用来设置tty的数量。
5.2、设置运行级别
命令格式:
systemctl [command] [unit.target]
参数详解:
command:
- get-default :取得当前的target
- set-default :设置指定的target为默认的运行级别
- isolate :切换到指定的运行级别
- unit.target :为5.1表中列出的运行级别
| systemctl命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| systemctl get-default | 获得当前的运行级别 |
| systemctl set-default multi-user.target | 设置默认的运行级别为mulit-user |
| systemctl isolate multi-user.target | 在不重启的情况下,切换到运行级别mulit-user下 |
| systemctl isolate graphical.target | 在不重启的情况下,切换到图形界面下 |
6、使用systemctl分析各服务之前的依赖关系
命令格式:
systemctl list-dependencies [unit] [–reverse]
–reverse是用来检查寻哪个unit使用了这个unit
应用举例:
#获得当前运行级别的target
[root@www ~]# systemctl get-default
multi-user.target
#查看当前运行级别target(mult-user)启动了哪些服务
[root@www ~]# systemctl list-dependencies
default.target
├─abrt-ccpp.service
├─abrt-oops.service
├─vsftpd.service
├─basic.target
│ ├─alsa-restore.service
│ ├─alsa-state.service
.....(中间省略).....
│ ├─sockets.target
│ │ ├─avahi-daemon.socket
│ │ ├─dbus.socket
.....(中间省略).....
│ ├─sysinit.target
│ │ ├─dev-hugepages.mount
│ │ ├─dev-mqueue.mount
.....(中间省略).....
│ └─timers.target
│ └─systemd-tmpfiles-clean.timer
├─getty.target
│ └─getty@tty1.service
└─remote-fs.target
#查看哪些target引用了当前运行级别的target
[root@www ~]# systemctl list-dependencies --reverse
default.target
└─graphical.target7、关闭网络服务
在使用systemctl关闭网络服务时有一些特殊 需要同时关闭unit.servce和unit.socket
使用systemctl查看开启的sshd服务
[root@www system]# systemctl list-units --all | grep sshd
sshd-keygen.service loaded inactive dead OpenSSH Server Key Generation
sshd.service loaded active running OpenSSH server daemon
sshd.socket loaded inactive dead OpenSSH Server Socket
可以看到系统同时开启了 sshd.service 和 sshd.socket , 如果只闭关了 sshd.service 那么 sshd.socket还在监听网络,在网络上有要求连接 sshd 时就会启动 sshd.service 。因此如果想完全关闭sshd服务的话,需要同时停用 sshd.service 和 sshd.socket 。
systemctl stop sshd.service
systemctl stop sshd.socket
systemctl disable sshd.service sshd.socket
由于centos 7.x默认没有安装net-tools,因此无法使用netstat 来查看主机开发的商品。需要通过yum安装来获得该工具包:
yum -y install net-tools
查看是否关闭22端口
netstat -lnp |grep sshd
8、关闭防火墙firewall
Centos 7.x 中取消了iptables, 用firewall取而代之。要关闭防火墙并禁止开机启动服务使用下面的命令:
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl disable firewalld.serviceLinux系统常用知识(centos7)的更多相关文章
- Linux 学习手记(4):Linux系统常用Shell命令
日期时间 date命令:显示当前时间日期 date -u # 显示格林威治(UTC)事件 date +%Y-%m-%d # 格式显示日期 date -s '20:25:25' # 修改系统时间,需要使 ...
- Linux系统常用升级的基础包
Linux系统常用升级的基础包 yum -y install lrzsz gcc gcc-c++ make flex autoconf automake vixie-cron libjpeg libj ...
- linux系统常用的基本命令分类
linux系统常用的基本命令分类: 文件命令:vim vimdiff diff mkdir touch rm mv cp ln cd ls more less head tail cat grep e ...
- 9个Linux系统常用监控命令
我们的系统一旦上线跑起来我们自然希望它一直相安无事,不要宕机,不要无响应,不要慢腾腾的.但是这不是打开机器电源然后放任不管就可以得到的.所以我们要监视系统的运行状况,发现问题及时处理. 对于系统和网络 ...
- linux linux系统常用设置
linux linux系统常用设置 一.设置开机时开启数字键 修改rc.local文件 命令:vi /etc/rc.local rc.local文件中增加如下代码: INITTY=/dev/tty ...
- 一文详解 Linux 系统常用监控工一文详解 Linux 系统常用监控工具(top,htop,iotop,iftop)具(top,htop,iotop,iftop)
一文详解 Linux 系统常用监控工具(top,htop,iotop,iftop) 概 述 本文主要记录一下 Linux 系统上一些常用的系统监控工具,非常好用.正所谓磨刀不误砍柴工,花点时间 ...
- Linux系统基础知识整理
一.说明 本篇文章,我将结合自己的实践以及简介,来对linux系统做一个直观清晰的介绍,使得哪些刚接触Linux的小伙伴可以快速入门,也方便自己以后进行复习查阅. 二.基本知识整理 1.Linux文件 ...
- Linux系统基础知识整理(一)
本文来自于: https://www.cnblogs.com/hafiz/p/6686187.html#4196989 一.说明 本篇文章,我将结合自己的实践以及简介,来对linux系统做一个直观清晰 ...
- Linux 系统常用管理命令(精简笔记)
Linux是一套免费使用和自由传播的类Unix操作系统,下面的笔记是我从鸟菜中摘抄出来的重要命令,并进行了一定的排版,摒弃了一些用不到的乱七八糟的命令,目的是在生产环境中能够快速的定位并查询需要命令的 ...
随机推荐
- laravel后台账户登录验证(5.5.48版本)
首先我是菜鸟,对laravel框架也不是很熟悉,突然有一天心血来潮就想研究一下laravel的后台登录用户登录的流程, 虽然公司项目中有这样的一套流程,也看了好几遍,越看越简单,越看我就越会了,当自己 ...
- python-Exception异常使用
Exception #自定义异常类 ,MyInputExcp继承Exception异常 class MyInputExcp(Exception): def __init__(self, lenght, ...
- Dubbo学习-4-dubbo简单案例-2-服务提供者和消费者配置
在上一篇帖子的基础上,开始使用dubbo来实现RPC调用: 根据dubbo的架构图可知,需要做以下几件事情: 1.将服务提供者注册到注册中心(暴露服务) (1)引入dubbo依赖, 这里依赖2.6.2 ...
- 11:如何解决Maven的Jar版本冲突问题
右键 Exclude,排除冲突包
- [NOIP2016][luogu]换教室[DP]
[NOIP2016] Day1 T3 换教室 ——!x^n+y^n=z^n 题目描述 对于刚上大学的牛牛来说,他面临的第一个问题是如何根据实际情况申请合适的课程. 在可以选择的课程中,有 2n 节课程 ...
- [JSOI2004]平衡点 / 吊打XXX 题解
预备概念: 金属退火:将金属缓慢加热到一定温度,保持足够时间,然后以适宜速度冷却 温度:一个逐渐减小的参数,表示接受次优解的概率 模拟退火是一种解决复杂问题的算法,相当于贪心,但以一个逐渐减小的该率接 ...
- PHP-利用二叉堆实现TopK-算法
介绍 在以往工作或者面试的时候常会碰到一个问题,如何实现海量TopN,就是在一个非常大的结果集里面快速找到最大的前10或前100个数,同时要保证内存和速度的效率,我们可能第一个想法就是利用排序,然后截 ...
- data_model_action
w PowerDesigner
- Delphi Canvas的FillRect(const Rect: TRect) 函数的作用
http://blog.163.com/zhangzhifeng688@126/blog/static/165262758201131211341460/ Delphi Canvas的FillRect ...
- 20190814 On Java8 第三章 万物皆对象
第三章 万物皆对象 对象创建 数据存储 有5个不同的地方可以存储数据: 寄存器 (Registers) 最快的存储区域,位于CPU内部 .无法直接控制. 栈内存(Stack) 存在于常规内存 RAM ...
