jackson json序列化 首字母大写 第二个字母需小写
有这样一个类:
@Setter
@Getter
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategy.UpperCamelCaseStrategy.class)
public class Student { private String bName; }
序列化后,希望首字母大写,如下面的测试代码:
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws IOException { Student test = new Student();
test.setBName("234234"); String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(test); Assert.assertEquals("{\"BName\":\"234234\"}", s); }
可实际运行后,结果与希望不一样:
org.junit.ComparisonFailure:
Expected :{"BName":"234234"}
Actual :{"Bname":"234234"}
jackson在序列化时把第二个大写字母n转成了小写,这是为什么呢?
以下是跟踪源码的过程:
直接找到:com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.introspect.POJOPropertiesCollector#collectAll这个方法:
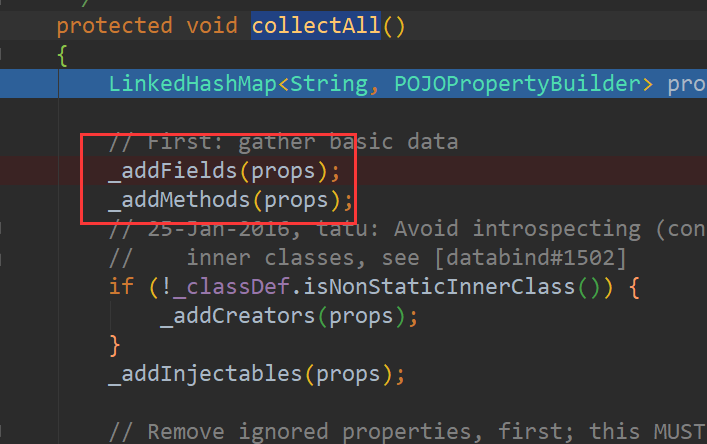
执行完_addFields(props)方法后:
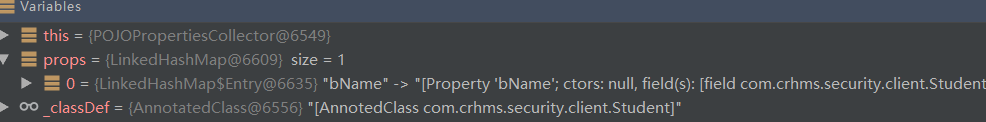
执行完_addMethods(props)方法后:

一个是bName,一个是bname;
第一个bName取的是字段的名称,
第二个bname是取的它的set方法:
public static String okNameForIsGetter(AnnotatedMethod am, String name,
boolean stdNaming)
{
if (name.startsWith("is")) { // plus, must return a boolean
Class<?> rt = am.getRawType();
if (rt == Boolean.class || rt == Boolean.TYPE) {
return stdNaming
? stdManglePropertyName(name, 2)
: legacyManglePropertyName(name, 2);
}
}
return null;
}
根据stdNaming来决定这个name是以什么标准输出,默认的是false;
stdManglePropertyName 就是原始输出。
legacyManglePropertyName 就是规范输出。
下面的代码就是规范输出:
protected static String legacyManglePropertyName(final String basename, final int offset)
{
final int end = basename.length();
if (end == offset) { // empty name, nope
return null;
}
// next check: is the first character upper case? If not, return as is
char c = basename.charAt(offset);
char d = Character.toLowerCase(c); if (c == d) {
return basename.substring(offset);
}
// otherwise, lower case initial chars. Common case first, just one char
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(end - offset);
sb.append(d);
int i = offset+1;
for (; i < end; ++i) {
c = basename.charAt(i);
d = Character.toLowerCase(c);
if (c == d) {
sb.append(basename, i, end);
break;
}
sb.append(d);
}
return sb.toString();
}
主要逻辑在for循环中,去除set后,第一个字母小写,
第二字母小写后,与第二个字母比较,如果都是小写,则直接接上,返回,
如果第二字母大写,就如我们的这种情况,就以小写的情况,接上,再去找下一个字母,直到找到小写字母为止。
意思就是为了满足驼峰命名规则,要规范输出。
如果我们的字段命名正如它的规范的话,props是只有一条记录的,因为:名称相同,就不插入了,由于咱们的名称不同,所以就有两条记录。
protected POJOPropertyBuilder _property(Map<String, POJOPropertyBuilder> props,
String implName)
{
POJOPropertyBuilder prop = props.get(implName);
if (prop == null) {
prop = new POJOPropertyBuilder(_config, _annotationIntrospector, _forSerialization,
PropertyName.construct(implName));
props.put(implName, prop);
}
return prop;
}
可是我们输出中只有一条,没有bName这条,
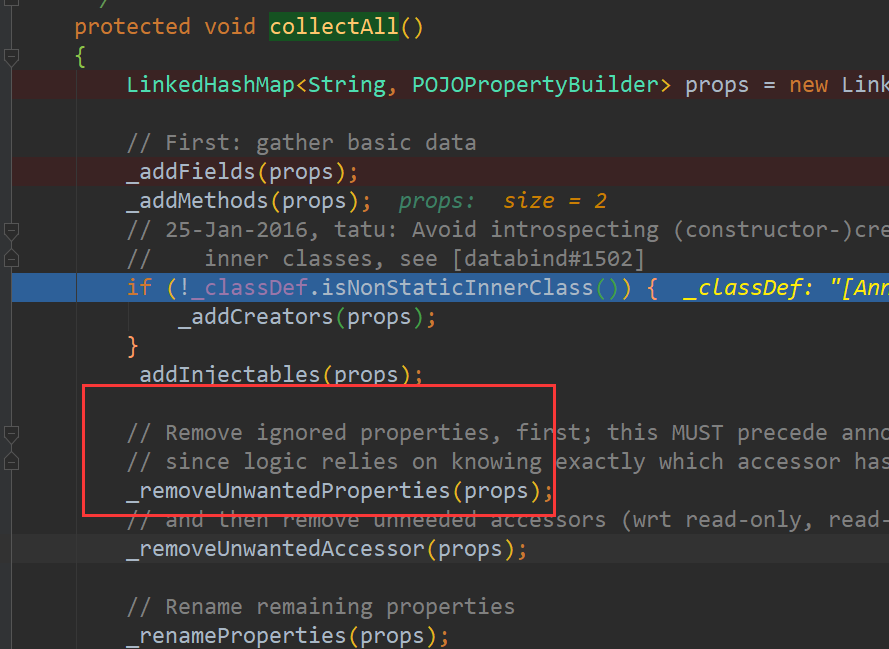
其实在是这里把第一条删除了。因为:
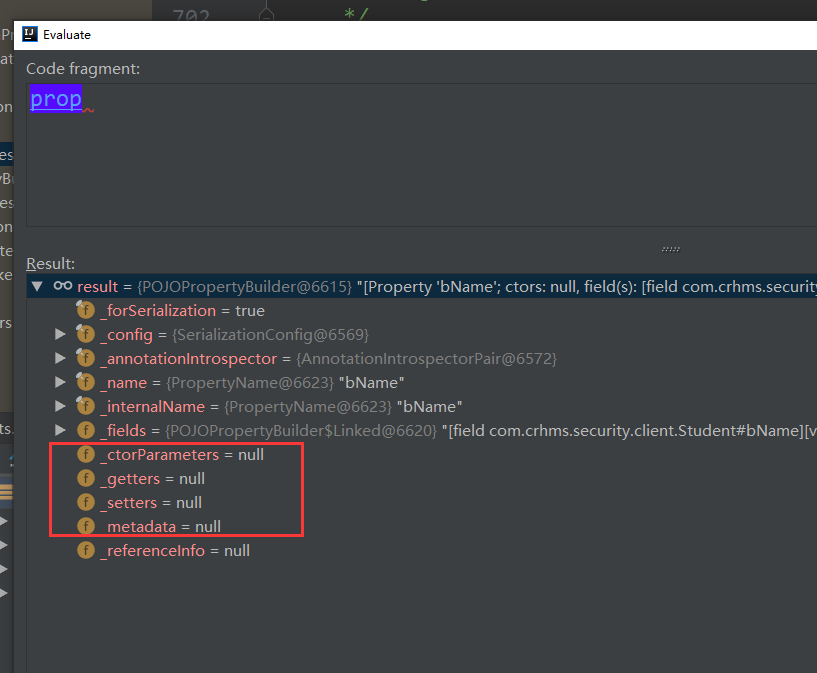
这些属性为空,导致这个字段不可见:
protected void _removeUnwantedProperties(Map<String, POJOPropertyBuilder> props)
{
Iterator<POJOPropertyBuilder> it = props.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
POJOPropertyBuilder prop = it.next(); // First: if nothing visible, just remove altogether
if (!prop.anyVisible()) {
it.remove();
continue;
}
// Otherwise, check ignorals
if (prop.anyIgnorals()) {
// first: if one or more ignorals, and no explicit markers, remove the whole thing
if (!prop.isExplicitlyIncluded()) {
it.remove();
_collectIgnorals(prop.getName());
continue;
}
// otherwise just remove ones marked to be ignored
prop.removeIgnored();
if (!prop.couldDeserialize()) {
_collectIgnorals(prop.getName());
}
}
}
}
只剩第二记录bname,再首字母大写,所以就是Bname了。
解决方案:
第一个就是JsonProperty
@Setter
@Getter
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategy.UpperCamelCaseStrategy.class)
public class Student { @JsonProperty("BName")
private String bName; }
测试结果如下:
org.junit.ComparisonFailure:
Expected :{"BName":"234234"}
Actual :{"Bname":"234234","BName":"234234"}
虽然生成了BName,但是Bname仍在(加了JsonProperty就visable了)。
第二个就是配置objectMapper的MapperFeature.USE_STD_BEAN_NAMIN 如上文提到了,非规范化输出。
如下代码:
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws IOException { Student test = new Student();
test.setBName("234234");
objectMapper.configure(MapperFeature.USE_STD_BEAN_NAMING, true);
String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(test); Assert.assertEquals("{\"BName\":\"234234\"}", s); }
第三个方案:重写PropertyNamingStrategy:
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws IOException { Student test = new Student();
test.setBName("234234");
//objectMapper.configure(MapperFeature.USE_STD_BEAN_NAMING, true); objectMapper.setPropertyNamingStrategy(new PropertyNamingStrategy() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// 反序列化时调用
@Override
public String nameForSetterMethod(MapperConfig<?> config,
AnnotatedMethod method, String defaultName) {
return method.getName().substring(3);
}
// 序列化时调用
@Override
public String nameForGetterMethod(MapperConfig<?> config,
AnnotatedMethod method, String defaultName) {
return method.getName().substring(3);
}
}); String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(test); Assert.assertEquals("{\"BName\":\"2342344\"}", s); }
修改objectMapper的配置,要注意对其他功能的影响。
jackson json序列化 首字母大写 第二个字母需小写的更多相关文章
- python字符串的操作(去掉空格strip(),切片,查找,连接join(),分割split(),转换首字母大写, 转换字母大小写...)
#可变变量:list, 字典#不可变变量:元祖,字符串字符串的操作(去掉空格, 切片, 查找, 连接, 分割, 转换首字母大写, 转换字母大小写, 判断是否是数字字母, 成员运算符(in / not ...
- .net core json序列化首字符小写和日期格式处理
打开Startup.cs文件,在ConfigureServices方法中添加如下代码 public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services ...
- Python3基础 str title 单词首字母大写,其余均为小写
Python : 3.7.0 OS : Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS IDE : PyCharm 2018.2.4 Conda ...
- java中pojo对象首字母大写导致无法赋值问题
命名规范(文末附有java命名规范)中指出,属性变量命名应采用驼峰命名的方式,即首字母小写,其他单词首字母大写: 但有时候我们对接三方的接口时,想要封装实体类来接受,但是发现接收到的参数的变量首字母是 ...
- CSS通过text-transform实现大写、小写和首字母大写转换
再日常项目中可能会用到一些特殊的样式,比如大写字母转小写.小写字母转大写.首字母大写等. 可以通过 CSS 的 text-transform 属性来实现: text-transform 转换不同的文本 ...
- 使用Jackson解析首字母大写的json字符串
Jackson在解析返回的json字符串时始终报错,纠结很久之后才找到原因,原来是是由于json字符串中的字母都是首字母大写,导致jackson找不到相应的KEY. 在项目中经常使用从服务器获取的数据 ...
- javabean转成json字符首字母大写
今天写接口的时候有个需求将接口返回的json字符串首字母大写:{"SN":"","Result":""}格式, 只需要在 ...
- 如果json中的key需要首字母大写怎么解决?
一般我们命名都是驼峰式的,可是有时候和第三方接口打交道,也会遇到一些奇葩,比如首字母大写........额 这是个什么鬼,对方这么要求,那我们也得这么写呀. 于是乎,第一种方式:把类中的字段首字母大写 ...
- fastjson JSON.toJavaObject() 实体类首字母大写属性无法解析问题
fastjson JSON.toJavaObject() 实体类首字母大写属性无法解析问题
随机推荐
- CF1213E Two Small Strings
题目链接 问题分析 由于三个字母是等价的,所以大致可以分为如下几种情况: aa, ab ab, ac ab, ba ab, bc 不难发现,第\(3\)中情况可能造成无解(\(n>1\)时),而 ...
- [The Annotated Transformer] Iterators
Iterators 对torchtext的batch实现的修改算法原理 Batching matters a ton for speed. We want to have very evenly di ...
- Android_(游戏)打飞机03:控制玩家飞机
(游戏)打飞机01:前言 传送门 (游戏)打飞机02:游戏背景滚动 传送门 (游戏)打飞机03:控制玩家飞机 传送门 (游戏)打飞机04:绘画敌机.添加子弹 传送门 (游戏)打飞机05:处理子弹, ...
- 前后端分离,get请求导出
[HttpGet] public HttpResponseMessage Export(string obj) { string eventType = string.Empty; string ex ...
- 基于dubbo的分布式系统(一)安装docker
1.安装过程参考: #uname -r 查看内核是否高于3.10 #sudo yum update root权限登陆确保yum包最新 #sudo yum remove docker docker-c ...
- TreeMap元素必须实现Comparable接口
纠正一下,TreeMap实现一定顺序是通过Comparable接口的,而他实现元素不重复也是完全通过compareTo,而不是hashCode和equals,因为debug不会走到hashCode和e ...
- Spark学习(一)——Spark运行架构
基本概念 在具体讲解Spark运行架构之前,需要先了解几个重要的概念: RDD:是弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Dataset)的简称,是分布式内存的一个抽象概念,提供 ...
- Web(八) commons-fileupload上传下载
在网上看见一篇不错的文章,写的详细. 以下内容引用那篇博文.转载于<http://www.cnblogs.com/whgk/p/6479405.html>,在此仅供学习参考之用. 一.上传 ...
- Selenium 2自动化测试实战5(模块调用)
一.模块调用 1.创建一个目录project,并且在目录下面创建两个文件 project/ 一 pub.py L一 count.py 在pub.py文件中创建add函数. #pub.py def ad ...
- Centos 6.5 磁盘修复 破解删除root密码
起因:由于存储设备故障.导致虚拟机断开.恢复后虚拟机无法启动,发现报磁盘损坏,需要运行fsck运行 问题解决思路: 1.虚拟机无法启动,所以需要进入系统进行修复 2.root密码是自动修改的.由于虚拟 ...
