Mask rcn nanchor部分理解
Anchors
Mask 生成锚框本质与SSD一样
中心点个数等于特征层像素数
框体生成围绕中心点
Bbox的坐标是要归一化到0~1之间的,都是相对于输入图片的大小。
基本生成方式:
H乘np.sqrt(anchor_ratio)
W乘np.sqrt(anchor_ratio)
这样,H:W = ratio
Mask rcnn
self.config.BACKBONE_STRIDES = [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
# 特征层的下采样倍数,中心点计算使用
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS = [0.5, 1, 2] # 特征层锚框生成参数
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512] # 特征层锚框感
anchor生成:
锚框生成入口函数位于model.py中的get_anchor函数,需要参数image_shape,保证含有[h, w]即可,也可以包含[h, w, c],
def get_anchors(self, image_shape):
"""Returns anchor pyramid for the given image size."""
# [N, (height, width)]
backbone_shapes = compute_backbone_shapes(self.config, image_shape)
# Cache anchors and reuse if image shape is the same
if not hasattr(self, "_anchor_cache"):
self._anchor_cache = {}
if not tuple(image_shape) in self._anchor_cache:
# Generate Anchors: [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
a = utils.generate_pyramid_anchors(
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES, # (32, 64, 128, 256, 512)
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS, # [0.5, 1, 2]
backbone_shapes, # with shape [N, (height, width)]
self.config.BACKBONE_STRIDES, # [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_STRIDE) #
# Keep a copy of the latest anchors in pixel coordinates because
# it's used in inspect_model notebooks.
# TODO: Remove this after the notebook are refactored to not use it
self.anchors = a
# Normalize coordinates
self._anchor_cache[tuple(image_shape)] = utils.norm_boxes(a, image_shape[:2])
return self._anchor_cache[tuple(image_shape)]
调用函数compute_backbone_shapes计算各个特征层shape:
def compute_backbone_shapes(config, image_shape):
"""Computes the width and height of each stage of the backbone network. Returns:
[N, (height, width)]. Where N is the number of stages
"""
if callable(config.BACKBONE):
return config.COMPUTE_BACKBONE_SHAPE(image_shape) # Currently supports ResNet only
assert config.BACKBONE in ["resnet50", "resnet101"]
return np.array(
[[int(math.ceil(image_shape[0] / stride)),
int(math.ceil(image_shape[1] / stride))]
for stride in config.BACKBONE_STRIDES]) # [4, 8, 16, 32, 64]
调用函数utils.generate_pyramid_anchors生成全部锚框:
def generate_pyramid_anchors(scales, ratios, feature_shapes, feature_strides,
anchor_stride):
"""Generate anchors at different levels of a feature pyramid. Each scale
is associated with a level of the pyramid, but each ratio is used in
all levels of the pyramid. Returns:
anchors: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]. All generated anchors in one array. Sorted
with the same order of the given scales. So, anchors of scale[0] come
first, then anchors of scale[1], and so on.
"""
# Anchors
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
anchors = []
for i in range(len(scales)):
anchors.append(generate_anchors(scales[i],
ratios,
feature_shapes[i],
feature_strides[i],
anchor_stride))
# [anchor_count, (y1, x1, y2, x2)]
return np.concatenate(anchors, axis=0)
utils.generate_pyramid_anchors会调用utils.generate_anchors来生成每一层的锚框(介绍见『Numpy』np.meshgrid):
def generate_anchors(scales, ratios, shape, feature_stride, anchor_stride):
"""
scales: 1D array of anchor sizes in pixels. Example: [32, 64, 128]
ratios: 1D array of anchor ratios of width/height. Example: [0.5, 1, 2]
shape: [height, width] spatial shape of the feature map over which
to generate anchors.
feature_stride: Stride of the feature map relative to the image in pixels.
anchor_stride: Stride of anchors on the feature map. For example, if the
value is 2 then generate anchors for every other feature map pixel.
"""
# Get all combinations of scales and ratios
scales, ratios = np.meshgrid(np.array(scales), np.array(ratios))
scales = scales.flatten()
ratios = ratios.flatten() # Enumerate heights and widths from scales and ratios
heights = scales / np.sqrt(ratios)
widths = scales * np.sqrt(ratios) # Enumerate shifts in feature space
shifts_y = np.arange(0, shape[0], anchor_stride) * feature_stride
shifts_x = np.arange(0, shape[1], anchor_stride) * feature_stride
shifts_x, shifts_y = np.meshgrid(shifts_x, shifts_y) # Enumerate combinations of shifts, widths, and heights
box_widths, box_centers_x = np.meshgrid(widths, shifts_x) # (n, 3) (n, 3)
box_heights, box_centers_y = np.meshgrid(heights, shifts_y) # (n, 3) (n, 3) # Reshape to get a list of (y, x) and a list of (h, w)
# (n, 3, 2) -> (3n, 2)
box_centers = np.stack([box_centers_y, box_centers_x], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2])
#box_centers_y, box_centers_x都是坐标矩阵,要想恢复各个点的坐标,调用np.stack函数,指定axis
box_sizes = np.stack([box_heights, box_widths], axis=2).reshape([-1, 2]) # Convert to corner coordinates (y1, x1, y2, x2) boxes = np.concatenate([box_centers - 0.5 * box_sizes, box_centers + 0.5 * box_sizes], axis=1) # 框体信息是相对于原图的, [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] return boxes
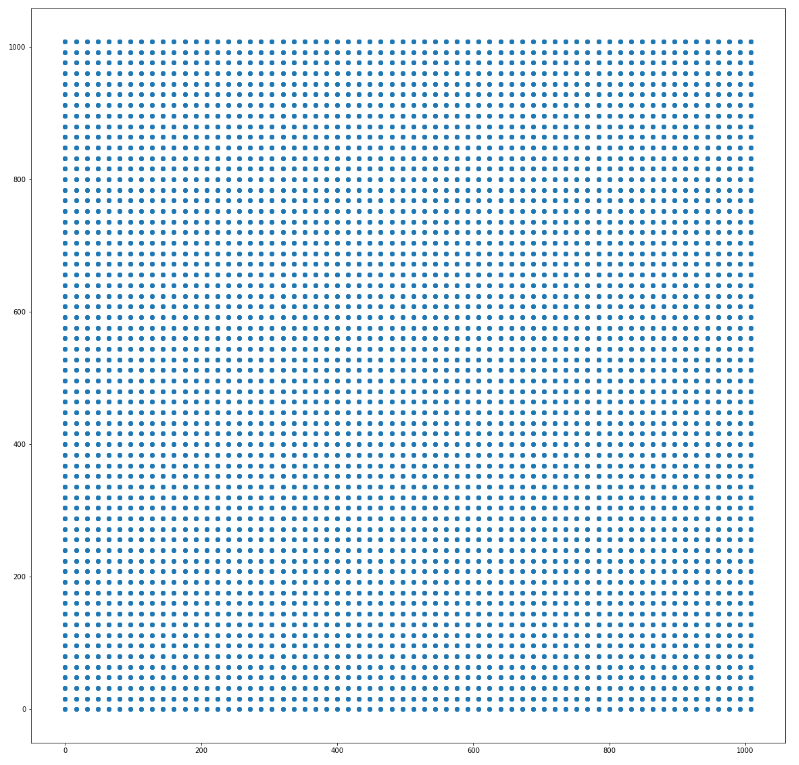
boxes的长宽:
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_RATIOS = [0.5, 1, 2] # 特征层锚框生成参数
self.config.RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512] # 特征层锚框感
最小的框:
heights: 32/sqrt(0.5) = 45.25 width: 32 * sqrt(0.5) = 22.62
height: 32/sqrt(1) = 32 width:32* sqrt(1) = 32
最大的框:
heights: 512/sqrt(2) = 362 widths: 512*sqrt(2) = 724
最后回到get_anchor,调用utils.norm_boxes将锚框坐标化为01之间:
def norm_boxes(boxes, shape):
"""Converts boxes from pixel coordinates to normalized coordinates.
boxes: [N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in pixel coordinates
shape: [..., (height, width)] in pixels Note: In pixel coordinates (y2, x2) is outside the box. But in normalized
coordinates it's inside the box. Returns:
[N, (y1, x1, y2, x2)] in normalized coordinates
"""
h, w = shape
scale = np.array([h - 1, w - 1, h - 1, w - 1])
shift = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
return np.divide((boxes - shift), scale).astype(np.float32)
抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/hellcat/p/9854736.html
Mask rcn nanchor部分理解的更多相关文章
- mask rcnn input数据理解
Array.min() #无参,所有中的最小值 Array.min(0) # axis=0; 每列的最小值 Array.min(1) # axis=1:每行的最小值 字符串在输出时的对齐: S.lju ...
- Mask R-CNN论文理解
摘要: Mask RCNN可以看做是一个通用实例分割架构. Mask RCNN以Faster RCNN原型,增加了一个分支用于分割任务. Mask RCNN比Faster RCNN速度慢一些,达到了5 ...
- 深入理解 Android 之 View 的绘制流程
概述 本篇文章会从源码(基于Android 6.0)角度分析Android中View的绘制流程,侧重于对整体流程的分析,对一些难以理解的点加以重点阐述,目的是把View绘制的整个流程把握好,而对于特定 ...
- [译] 理解数组在 PHP 内部的实现(给PHP开发者的PHP源码-第四部分)
文章来自:http://www.hoohack.me/2016/02/15/understanding-phps-internal-array-implementation-ch 原文:https:/ ...
- 【blade的UI设计】理解前端MVC与分层思想
前言 最近校招要来了,很多大三的同学一定按捺不住心中的焦躁,其中有期待也有彷徨,或许更多的是些许担忧,最近在开始疯狂的复习了吧 这里小钗有几点建议给各位: ① 不要看得太重,关心则乱,太紧张反而表现不 ...
- 利用layer的mask属性实现逐渐揭示的动画效果
github上又看到个不错的动画(https://github.com/rounak/RJImageLoader),如图: 所以就想来自己实现以下 不试不知道,这个动画还真不是看上去那么简单,我自己想 ...
- 理解 OpenStack 高可用(HA)(3):Neutron 分布式虚拟路由(Neutron Distributed Virtual Routing)
本系列会分析OpenStack 的高可用性(HA)概念和解决方案: (1)OpenStack 高可用方案概述 (2)Neutron L3 Agent HA - VRRP (虚拟路由冗余协议) (3)N ...
- Deep learning:四十六(DropConnect简单理解)
和maxout(maxout简单理解)一样,DropConnect也是在ICML2013上发表的,同样也是为了提高Deep Network的泛化能力的,两者都号称是对Dropout(Dropout简单 ...
- Deep learning:四十一(Dropout简单理解)
前言 训练神经网络模型时,如果训练样本较少,为了防止模型过拟合,Dropout可以作为一种trikc供选择.Dropout是hintion最近2年提出的,源于其文章Improving neural n ...
随机推荐
- Python学习之旅(三十七)
Python基础知识(36):访问数据库(Ⅰ) 程序运行的时候,数据都是在内存中的.当程序终止的时候,通常都需要将数据保存到磁盘上,无论是保存到本地磁盘,还是通过网络保存到服务器上,最终都会将数据写入 ...
- python opencv 读取USB摄像头的像素问题
问题描述 每次调用capture读取video的时候,还回的像素都是640x480,不管是笔记本的摄像头还是USB摄像头,明明我的摄像头是支持130万读取的功能的呀. 问题分析 一番查找,关于用ope ...
- String工具类2
1:比较字符串 public static void main(String[] args) { // String去创建对象有多种方式 // 方式1 直接字面值赋值 String s = " ...
- angularjs知识点
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- [Day20]Map接口、可变参数、Collections
1.Map接口-元素成对存在,每个元素由健与值两部分组成,通过键可以找所对应的值 1.1 Map子类 (1)HashMap<K,V>:存储数据所用的哈希表结构,元素的存取数据顺序不能保证一 ...
- kubernetes in action - Volumes
Volume解决Kubernetes的存储的问题 对于Pod使用的存储,抽象为volume,volume伴随着Pod的创建而创建,消失而同时消失,不能单独的创建 这样的好处,是存储的塑胶不会因为某个c ...
- 在linux服务器下JMeter如何执行jmx性能脚本
准备环境:linux平台.jmeter安装包. jdk 一. 安装jdk jdk的安装可以参考以下内容 http://jingyan.baidu.com/article ...
- ACL(Access Control List)
一.ACL的简介 ACL(Access Control List 访问控制列表)是路由器和交换机接口的指令列表,用来控制端口进出的数据包.ACL的定义也是基于每一种被动路由协议的,且适用于所有的被动路 ...
- django集成ansibe实现自动化
动态生成主机列表和相关参数 def create_admin_domain(admin_node): workpath = BASE_DIR + '/tools/ansible/script' hos ...
- 立一个Flag吧
以后在学习上遇到的问题以及解决办法,大部分都要记录在这里了,以备温故知新....就这样吧!
