Scrapy Architecture overview--官方文档
原文地址:https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/architecture.html
This document describes the architecture of Scrapy and how its components interact.
Overview
The following diagram shows an overview of the Scrapy architecture with its components and an outline of the data flow that takes place inside the system (shown by the red arrows). A brief description of the components is included below with links for more detailed information about them. The data flow is also described below.
Data flow
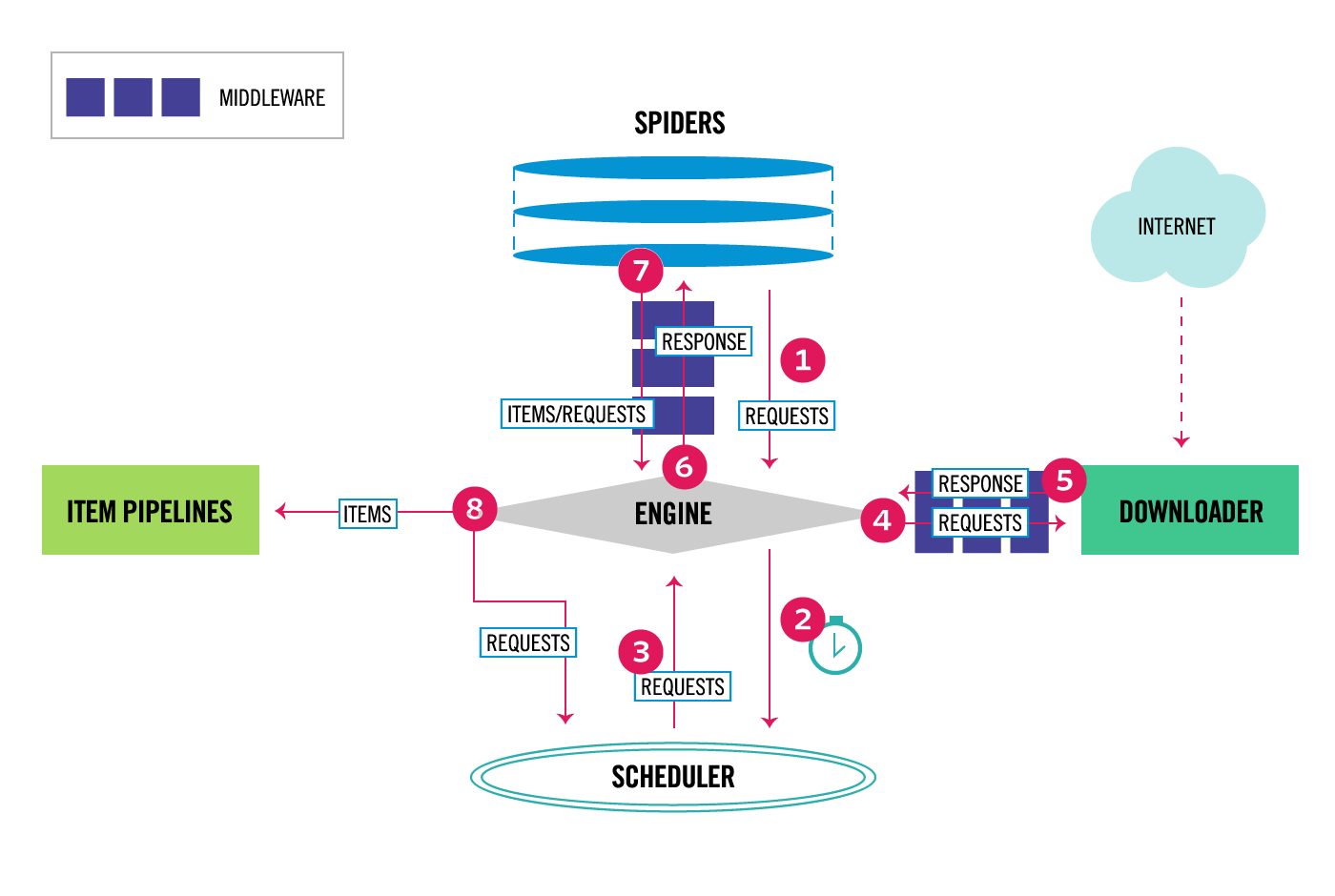
The data flow in Scrapy is controlled by the execution engine, and goes like this:
- The Engine gets the initial Requests to crawl from the Spider.
- The Engine schedules the Requests in the Scheduler and asks for the next Requests to crawl.
- The Scheduler returns the next Requests to the Engine.
- The Engine sends the Requests to the Downloader, passing through the Downloader Middlewares (see
process_request()). - Once the page finishes downloading the Downloader generates a Response (with that page) and sends it to the Engine, passing through the Downloader Middlewares (see
process_response()). - The Engine receives the Response from the Downloader and sends it to the Spider for processing, passing through the Spider Middleware (see
process_spider_input()). - The Spider processes the Response and returns scraped items and new Requests (to follow) to the Engine, passing through the Spider Middleware (see
process_spider_output()). - The Engine sends processed items to Item Pipelines, then send processed Requests to the Scheduler and asks for possible next Requests to crawl.
- The process repeats (from step 1) until there are no more requests from the Scheduler.
Components
Scrapy Engine
The engine is responsible for controlling the data flow between all components of the system, and triggering events when certain actions occur. See the Data Flow section above for more details.
Scheduler
The Scheduler receives requests from the engine and enqueues them for feeding them later (also to the engine) when the engine requests them.
Downloader
The Downloader is responsible for fetching web pages and feeding them to the engine which, in turn, feeds them to the spiders.
Spiders
Spiders are custom classes written by Scrapy users to parse responses and extract items (aka scraped items) from them or additional requests to follow. For more information see Spiders.
Item Pipeline
The Item Pipeline is responsible for processing the items once they have been extracted (or scraped) by the spiders. Typical tasks include cleansing, validation and persistence (like storing the item in a database). For more information see Item Pipeline.
Downloader middlewares
Downloader middlewares are specific hooks that sit between the Engine and the Downloader and process requests when they pass from the Engine to the Downloader, and responses that pass from Downloader to the Engine.
Use a Downloader middleware if you need to do one of the following:
- process a request just before it is sent to the Downloader (i.e. right before Scrapy sends the request to the website);
- change received response before passing it to a spider;
- send a new Request instead of passing received response to a spider;
- pass response to a spider without fetching a web page;
- silently drop some requests.
For more information see Downloader Middleware.
Spider middlewares
Spider middlewares are specific hooks that sit between the Engine and the Spiders and are able to process spider input (responses) and output (items and requests).
Use a Spider middleware if you need to
- post-process output of spider callbacks - change/add/remove requests or items;
- post-process start_requests;
- handle spider exceptions;
- call errback instead of callback for some of the requests based on response content.
For more information see Spider Middleware.
Event-driven networking
Scrapy is written with Twisted, a popular event-driven networking framework for Python. Thus, it’s implemented using a non-blocking (aka asynchronous) code for concurrency.
Scrapy Architecture overview--官方文档的更多相关文章
- hbase官方文档(转)
FROM:http://www.just4e.com/hbase.html Apache HBase™ 参考指南 HBase 官方文档中文版 Copyright © 2012 Apache Soft ...
- HBase官方文档
HBase官方文档 目录 序 1. 入门 1.1. 介绍 1.2. 快速开始 2. Apache HBase (TM)配置 2.1. 基础条件 2.2. HBase 运行模式: 独立和分布式 2.3. ...
- Spark官方文档 - 中文翻译
Spark官方文档 - 中文翻译 Spark版本:1.6.0 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/ 1 概述(Overview) 2 引入Spark(Linki ...
- Spring 4 官方文档学习 Spring与Java EE技术的集成
本部分覆盖了以下内容: Chapter 28, Remoting and web services using Spring -- 使用Spring进行远程和web服务 Chapter 29, Ent ...
- Spark SQL 官方文档-中文翻译
Spark SQL 官方文档-中文翻译 Spark版本:Spark 1.5.2 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/ 1 概述(Overview) 2 Data ...
- 人工智能系统Google开源的TensorFlow官方文档中文版
人工智能系统Google开源的TensorFlow官方文档中文版 2015年11月9日,Google发布人工智能系统TensorFlow并宣布开源,机器学习作为人工智能的一种类型,可以让软件根据大量的 ...
- Google Android官方文档进程与线程(Processes and Threads)翻译
android的多线程在开发中已经有使用过了,想再系统地学习一下,找到了android的官方文档,介绍进程与线程的介绍,试着翻译一下. 原文地址:http://developer.android.co ...
- OGR 官方文档
OGR 官方文档 http://www.gdal.org/ogr/index.html The OGR Simple Features Library is a C++ open source lib ...
- cassandra 3.x官方文档(5)---探测器
写在前面 cassandra3.x官方文档的非官方翻译.翻译内容水平全依赖本人英文水平和对cassandra的理解.所以强烈建议阅读英文版cassandra 3.x 官方文档.此文档一半是翻译,一半是 ...
- Cuda 9.2 CuDnn7.0 官方文档解读
目录 Cuda 9.2 CuDnn7.0 官方文档解读 准备工作(下载) 显卡驱动重装 CUDA安装 系统要求 处理之前安装的cuda文件 下载的deb安装过程 下载的runfile的安装过程 安装完 ...
随机推荐
- Android中图片旋转
Activity_main.xml文件配置 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/androi ...
- XML 之 命名空间详解
最近学xml 遇到了点小问题qaq 找了n多的博客大佬,反复看了半小时终于明白了,可能我太蠢了... 基础的知识就不赘述,直接放“栗子”,切重点: <?xml version="1.0 ...
- html form表单追加input元素后在提交
form.append(input); //input为对象 (设置name和val有效) $("#form1").submit();//提交事件
- 使用jQuery和CSS自定义HTML5 Video 控件 简单适用
Html5 Video是现在html5最流行的功能之一,得到了大多数最新版本的浏览器支持.包括IE9,也是如此.不同的浏览器提供了不同的原生态浏览器视频空间.我们制作自定义视频控件为了在所有的浏览器中 ...
- javase 继承练习
package xuexi; 父级 public class Fu { int num=0; public void eat() { System.out.println("父亲在吃饭&qu ...
- mysql8下载与安装
MySQL各版本的区别 MySQL 8.0.13安装教程(windows 64位) 编码用utf8mb4 Navicat连接mysql出现1862错误
- POJ 3281 Dining[网络流]
Cows are such finicky eaters. Each cow has a preference for certain foods and drinks, and she will c ...
- HDU2147 - kiki's game 【巴什博弈】
Recently kiki has nothing to do. While she is bored, an idea appears in his mind, she just playes th ...
- nyoj2-吝啬的国度
吝啬的国度 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 在一个吝啬的国度里有N个城市,这N个城市间只有N-1条路把这个N个城市连接起来.现在,Tom在第S号城市,他有 ...
- PHP实现并发请求
后端服务开发中经常会有并发请求的需求,比如你需要获取10家供应商的带宽数据(每个都提供不同的url),然后返回一个整合后的数据,你会怎么做呢? 在PHP中,最直观的做法foreach遍历urls,并保 ...
