算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-006归并排序(Mergesort)
一、
1.特点
(1)merge-sort : to sort an array, divide it into two halves, sort the two halves (recursively), and then merge the results. As you will see, one of mergesort’s most attractive properties is that it guarantees to sort any array of N items in time proportional to N log N. Its prime disadvantage is that it uses extra space proportional to N.
(2)
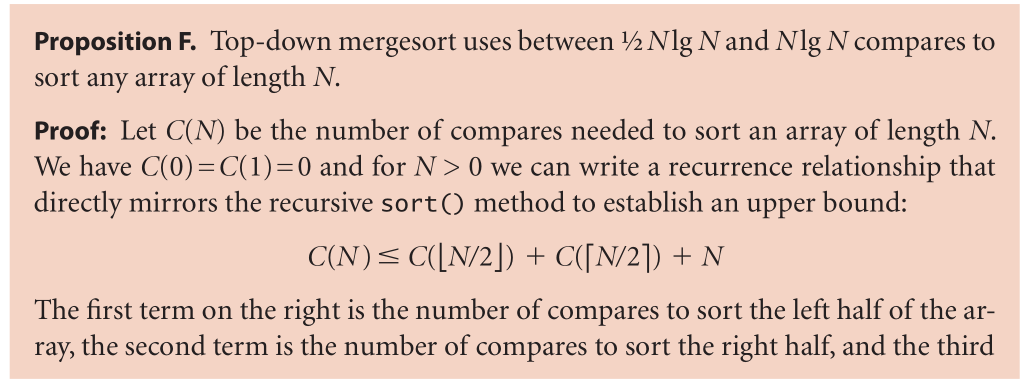
(3)

(4)
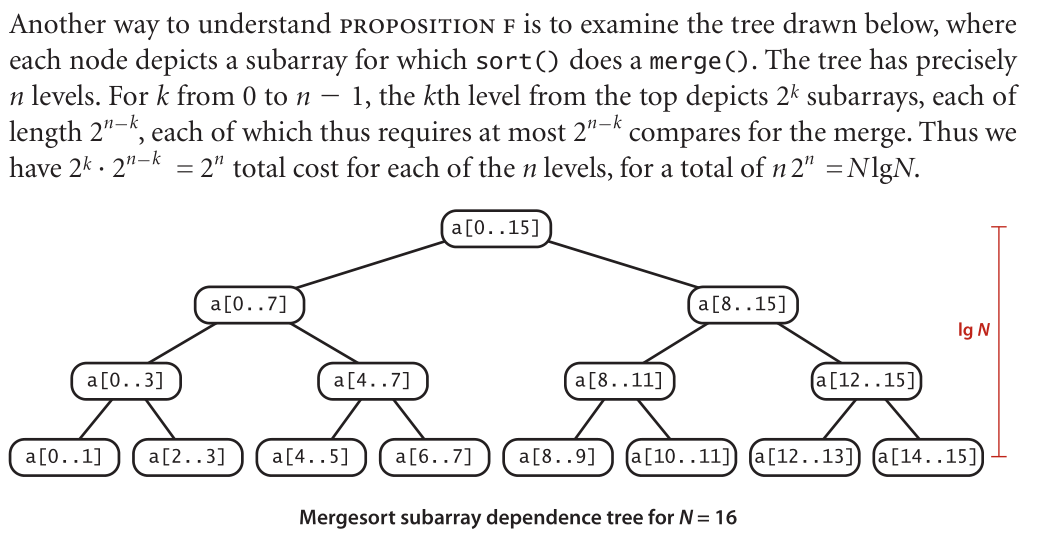
(5)

2.缺点
■ Mergesort is not optimal with respect to space usage.
■ The worst case may not be likely in practice.
■ Operations other than compares (such as array accesses) may be important.
■ One can sort certain data without using any compares.
Thus, we shall be considering several other sorting methods in this book.
3.介绍



二、
1.代码
package algorithms.mergesort22; import algorithms.util.StdIn;
import algorithms.util.StdOut; /******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Merge.java
* Execution: java Merge < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdOut.java StdIn.java
* Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort/tiny.txt
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort/words3.txt
*
* Sorts a sequence of strings from standard input using mergesort.
*
* % more tiny.txt
* S O R T E X A M P L E
*
* % java Merge < tiny.txt
* A E E L M O P R S T X [ one string per line ]
*
* % more words3.txt
* bed bug dad yes zoo ... all bad yet
*
* % java Merge < words3.txt
* all bad bed bug dad ... yes yet zoo [ one string per line ]
*
******************************************************************************/ /**
* The <tt>Merge</tt> class provides static methods for sorting an
* array using mergesort.
* <p>
* For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/22mergesort">Section 2.2</a> of
* <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
* For an optimized version, see {@link MergeX}.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class Merge { // This class should not be instantiated.
private Merge() { } // stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 ..hi] using aux[lo .. hi]
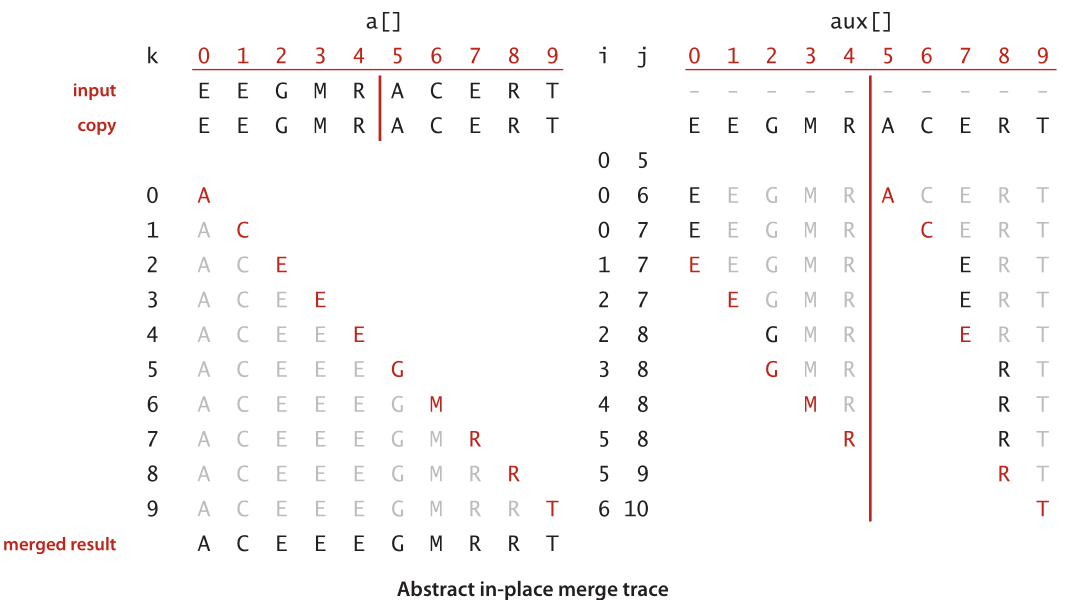
private static void merge(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
// precondition: a[lo .. mid] and a[mid+1 .. hi] are sorted subarrays
assert isSorted(a, lo, mid);
assert isSorted(a, mid+1, hi); // copy to aux[]
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
aux[k] = a[k];
} // merge back to a[]
int i = lo, j = mid+1;
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++];
else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++];
else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++];
else a[k] = aux[i++];
} // postcondition: a[lo .. hi] is sorted
assert isSorted(a, lo, hi);
} // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi]
private static void sort(Comparable[] a, Comparable[] aux, int lo, int hi) {
if (hi <= lo) return;
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
sort(a, aux, lo, mid);
sort(a, aux, mid + 1, hi);
merge(a, aux, lo, mid, hi);
} /**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order.
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
Comparable[] aux = new Comparable[a.length];
sort(a, aux, 0, a.length-1);
assert isSorted(a);
} /***************************************************************************
* Helper sorting functions.
***************************************************************************/ // is v < w ?
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
} // exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(Object[] a, int i, int j) {
Object swap = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = swap;
} /***************************************************************************
* Check if array is sorted - useful for debugging.
***************************************************************************/
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
return isSorted(a, 0, a.length - 1);
} private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++)
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
} /***************************************************************************
* Index mergesort.
***************************************************************************/
// stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 .. hi] using aux[lo .. hi]
private static void merge(Comparable[] a, int[] index, int[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { // copy to aux[]
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
aux[k] = index[k];
} // merge back to a[]
int i = lo, j = mid+1;
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
if (i > mid) index[k] = aux[j++];
else if (j > hi) index[k] = aux[i++];
else if (less(a[aux[j]], a[aux[i]])) index[k] = aux[j++];
else index[k] = aux[i++];
}
} /**
* Returns a permutation that gives the elements in the array in ascending order.
* @param a the array
* @return a permutation <tt>p[]</tt> such that <tt>a[p[0]]</tt>, <tt>a[p[1]]</tt>,
* ..., <tt>a[p[N-1]]</tt> are in ascending order
*/
public static int[] indexSort(Comparable[] a) {
int N = a.length;
int[] index = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
index[i] = i; int[] aux = new int[N];
sort(a, index, aux, 0, N-1);
return index;
} // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi]
private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int[] index, int[] aux, int lo, int hi) {
if (hi <= lo) return;
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
sort(a, index, aux, lo, mid);
sort(a, index, aux, mid + 1, hi);
merge(a, index, aux, lo, mid, hi);
} // print array to standard output
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
} /**
* Reads in a sequence of strings from standard input; mergesorts them;
* and prints them to standard output in ascending order.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
Integer[] a = {3,1,2,5,4};
Merge.sort(a);
show(a);
}
}
2.可视化
package algorithms.mergesort22; import algorithms.util.StdDraw;
import algorithms.util.StdRandom; /******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac MergeBars.java
* Execution: java MergeBars M N
* Dependencies: StdDraw.java
*
* Sort N random real numbers between 0 and 1 (with M disintct values)
* using mergesort with cutoff to insertion sort.
*
* Visualize the results by ploting bars with heights proportional
* to the values.
*
* % java MergeBars 1000 96
*
* Comments
* --------
* - suggest removing the 10% default StdDraw border
* - if image is too large, it may not display properly but you can
* still save it to a file
*
******************************************************************************/ public class MergeBars {
private static final int VERTICAL = 70;
private static final int CUTOFF = 12; private static int numberOfRows;
private static int row = 0; // stably merge a[lo .. mid] with a[mid+1 .. hi] using aux[lo .. hi]
public static void merge(double[] a, double[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { // copy to aux[]
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
aux[k] = a[k];
} // merge back to a[]
int i = lo, j = mid+1;
for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) {
if (i > mid) a[k] = aux[j++];
else if (j > hi) a[k] = aux[i++];
else if (less(aux[j], aux[i])) a[k] = aux[j++];
else a[k] = aux[i++];
}
} // mergesort a[lo..hi] using auxiliary array aux[lo..hi]
private static void sort(double[] a, double[] aux, int lo, int hi) {
int N = hi - lo + 1;
if (N <= CUTOFF) {
insertionSort(a, lo, hi);
show(a, lo, hi);
return;
}
if (hi <= lo) return;
int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
sort(a, aux, lo, mid);
sort(a, aux, mid + 1, hi);
merge(a, aux, lo, mid, hi);
show(a, lo, hi);
} public static void sort(double[] a) {
double[] aux = new double[a.length];
sort(a, aux, 0, a.length-1);
} // sort from a[lo] to a[hi] using insertion sort
private static void insertionSort(double[] a, int lo, int hi) {
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++)
for (int j = i; j > lo && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--)
exch(a, j, j-1);
} private static boolean less(double v, double w) {
return v < w;
} private static void exch(double[] a, int i, int j) {
double t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
} // draw one row of trace
private static void show(double[] a, int lo, int hi) {
double y = numberOfRows - row - 1;
for (int k = 0; k < a.length; k++) {
if (k < lo) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.LIGHT_GRAY);
else if (k > hi) StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.LIGHT_GRAY);
else StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLACK);
StdDraw.filledRectangle(k, y + a[k]*.25, .25, a[k]*.25);
}
row++;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
int M = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int N = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
if (args.length == 3) {
long seed = Long.parseLong(args[2]);
StdRandom.setSeed(seed);
}
double[] a = new double[N];
double[] b = new double[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
a[i] = (1 + StdRandom.uniform(M)) / (double) M;
b[i] = a[i];
} // precompute the number of rows
StdDraw.show(0);
numberOfRows = 0;
sort(b);
numberOfRows = row;
row = 0;
StdDraw.clear(); StdDraw.setCanvasSize(800, numberOfRows*VERTICAL);
StdDraw.show(0);
StdDraw.square(.5, .5, .5);
StdDraw.setXscale(-1, N);
StdDraw.setYscale(-0.5, numberOfRows);
StdDraw.show(0);
sort(a);
StdDraw.show(0);
}
}
算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-006归并排序(Mergesort)的更多相关文章
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-001选择排序法(Selection sort)
一.介绍 1.算法的时间和空间间复杂度 2.特点 Running time is insensitive to input. The process of finding the smallest i ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-007归并排序(自下而上)
一. 1. 2. 3. 二.代码 package algorithms.mergesort22; import algorithms.util.StdIn; import algorithms.uti ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-005插入排序的改进版
package algorithms.elementary21; import algorithms.util.StdIn; import algorithms.util.StdOut; /***** ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-004希尔排序法(Shell Sort)
一.介绍 1.希尔排序的思路:希尔排序是插入排序的改进.当输入的数据,顺序是很乱时,插入排序会产生大量的交换元素的操作,比如array[n]的最小的元素在最后,则要经过n-1次交换才能排到第一位,因为 ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-002插入排序法(Insertion sort)
一.介绍 1.时间和空间复杂度 运行过程 2.特点: (1)对于已排序或接近排好的数据,速度很快 (2)对于部分排好序的输入,速度快 二.代码 package algorithms.elementar ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-008排序算法的复杂度(比较次数的上下限)
一. 1. 2.
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-003比较算法及算法的可视化
一.介绍 1. 2. 二.代码 1. package algorithms.elementary21; /*********************************************** ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-001递归
一. 方法可以调用自己(如果你对递归概念感到奇怪,请完成练习 1.1.16 到练习 1.1.22).例如,下面给出了 BinarySearch 的 rank() 方法的另一种实现.我们会经常使用递归, ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-1.3Bags, Queues, and Stacks-001可变在小的
1. package algorithms.stacks13; /******************************************************************* ...
随机推荐
- OOP思想应该怎样来理解?
https://blog.csdn.net/qq157962718/article/details/50990154 https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaosongluffy/p/5 ...
- spark 稠密向量和稀疏向量
Spark mlib的本地向量有两种: DenseVctor :稠密向量 其创建方式 Vector.dense(数据) SparseVector :稀疏向量 其创建方式有两种: 方法一 ...
- Agc019_C Fountain Walk
传送门 题目大意 给定网格图上起点和终点每个格子是长为$100$米的正方形,你可以沿着线走. 平面上还有若干个关键点,以每个关键点为圆心,$10$为半径画圆,表示不能进入圆内的线,但是可以从圆周上走, ...
- Arc083_F Collecting Balls
传送门 题目大意 给定$N$,在$(1,0),(2,0)......(N,0)$和$(0,1),(0,2)...(0,N)$上都有$1$个机器人,同时给定$2N$个坐标$(x,y),x,y\in[1, ...
- Spring MVC配置文件的三个常用配置详解
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/benwu/articles/5162614.html Spring MVC项目中通常会有二个配置文件,sprng-servlet.xml和appl ...
- ACM学习历程—SNNUOJ1215 矩阵2(二分 && dfs)
http://219.244.176.199/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1215 这是这次微软和百度实习面试的一道题,题目大意就是:有一个n*m的矩阵,已知它每一行都是不严 ...
- 2017.10.3北京清北综合强化班DAY3
括号序列(bracket) Time Limit:1000ms Memory Limit:128MB 题目描述 LYK有一个括号序列,但这个序列不一定合法. 一个合法的括号序列如下: ()是合法的 ...
- python 修改文件内容
python 修改文件内容 一.修改原文件方式 1 def alter(file,old_str,new_str): 2 """ 3 替换文件中的字符串 4 :param ...
- walle部署系统的使用
在项目开发的时候要管理各种开发 测试 线上环境的代码 部署 回滚等操作 这里可以使用walle walle官网:http://www.walle-web.io/ 学习安装:https://blog.c ...
- 断路器之一:Hystrix 使用与分析
一:为什么需要Hystrix? 在大中型分布式系统中,通常系统很多依赖(HTTP,hession,Netty,Dubbo等),如下图: 在高并发访问下,这些依赖的稳定性与否对系统的影响非常大,但是依赖 ...
