Gtest:事件
前言
有时候在测试的时候,我们会在测试前做一些初始化活动,和测试后做一些清理工作,gtest提供了多种事件机制,非常方便我们在案例之前或之后做一些操作。总结一下gtest的事件一共有3种:
- 全局的,所有案例执行前后。
- TestSuite级别的,在某一批案例中第一个案例前,最后一个案例执行后。
- TestCase级别的,每个TestCase前后。
接下来按照倒叙3→2→1介绍如何使用事件机制
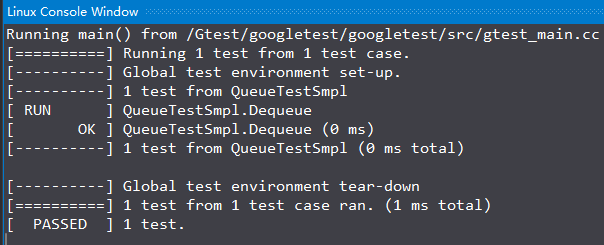
TestCase事件
TestCase事件是挂在每个案例执行前后的,实现方式和上面的几乎一样,不过需要实现的是SetUp方法和TearDown方法:
1. SetUp()方法在每个TestCase之前执行
2. TearDown()方法在每个TestCase之后执行
演示代码(Linux环境)
main.cpp
#include "sample-inl.h"
#include "gtest/gtest.h"
namespace {
class QueueTestSmpl : public testing::Test {
protected: virtual void SetUp() {
//q0_.Enqueue(1);
q1_.Enqueue();
q1_.Enqueue();
q2_.Enqueue();
} virtual void TearDown() {
} static int Double(int n) {
return * n;
} // A helper function for testing Queue::Map().
void MapTester(const Queue<int> * q) {
// Creates a new queue, where each element is twice as big as the
// corresponding one in q.
const Queue<int> * const new_q = q->Map(Double); // Verifies that the new queue has the same size as q.
ASSERT_EQ(q->Size(), new_q->Size()); // Verifies the relationship between the elements of the two queues.
for (const QueueNode<int>*n1 = q->Head(), *n2 = new_q->Head();
n1 != nullptr; n1 = n1->next(), n2 = n2->next()) {
EXPECT_EQ( * n1->element(), n2->element());
} delete new_q;
} // Declares the variables your tests want to use.
Queue<int> q0_;
Queue<int> q1_;
Queue<int> q2_;
}; // Tests Dequeue().
TEST_F(QueueTestSmpl, Dequeue) {
int * n = q0_.Dequeue();
EXPECT_TRUE(n == nullptr); n = q1_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_TRUE(n != nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(, *n);
EXPECT_EQ(1u, q1_.Size());
delete n; n = q1_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_TRUE(n != nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(, *n);
EXPECT_EQ(0u, q1_.Size());
delete n; n = q2_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_TRUE(n != nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(, *n);
EXPECT_EQ(0u, q2_.Size());
delete n;
}
} // namespace
sample-inl.h
#ifndef GTEST_SAMPLES_SAMPLE_INL_H_
#define GTEST_SAMPLES_SAMPLE_INL_H_ #include <stddef.h> template <typename E> // E is the element type
class Queue; template <typename E> // E is the element type
class QueueNode {
friend class Queue<E>; public:
// Gets the element in this node.
const E& element() const { return element_; } // Gets the next node in the queue.
QueueNode* next() { return next_; }
const QueueNode* next() const { return next_; } private:
// Creates a node with a given element value. The next pointer is
// set to NULL.
explicit QueueNode(const E& an_element)
: element_(an_element), next_(nullptr) {} // We disable the default assignment operator and copy c'tor.
const QueueNode& operator = (const QueueNode&);
QueueNode(const QueueNode&); E element_;
QueueNode* next_;
}; template <typename E> // E is the element type.
class Queue {
public:
// Creates an empty queue.
Queue() : head_(nullptr), last_(nullptr), size_() {} // D'tor. Clears the queue.
~Queue() { Clear(); } // Clears the queue.
void Clear() {
if (size_ > ) {
// 1. Deletes every node.
QueueNode<E>* node = head_;
QueueNode<E>* next = node->next();
for (; ;) {
delete node;
node = next;
if (node == nullptr) break;
next = node->next();
} // 2. Resets the member variables.
head_ = last_ = nullptr;
size_ = ;
}
} size_t Size() const { return size_; } QueueNode<E>* Head() { return head_; }
const QueueNode<E>* Head() const { return head_; } QueueNode<E>* Last() { return last_; }
const QueueNode<E>* Last() const { return last_; } void Enqueue(const E& element) {
QueueNode<E>* new_node = new QueueNode<E>(element); if (size_ == ) {
head_ = last_ = new_node;
size_ = ;
}
else {
last_->next_ = new_node;
last_ = new_node;
size_++;
}
} E* Dequeue() {
if (size_ == ) {
return nullptr;
} const QueueNode<E>* const old_head = head_;
head_ = head_->next_;
size_--;
if (size_ == ) {
last_ = nullptr;
} E* element = new E(old_head->element());
delete old_head; return element;
} template <typename F>
Queue* Map(F function) const {
Queue* new_queue = new Queue();
for (const QueueNode<E>* node = head_; node != nullptr;
node = node->next_) {
new_queue->Enqueue(function(node->element()));
} return new_queue;
} private:
QueueNode<E>* head_; // The first node of the queue.
QueueNode<E>* last_; // The last node of the queue.
size_t size_; // The number of elements in the queue. // We disallow copying a queue.
Queue(const Queue&);
const Queue& operator = (const Queue&);
}; #endif // GTEST_SAMPLES_SAMPLE3_INL_H_
TestSuite事件
这个相对来说比较简单,相对上面的实现就是替换成静态的SetUpTestCase,代码
class FooTest : public testing::Test {
protected:
//准备资源
static void SetUpTestCase() {
shared_resource_ = new ;
}
//释放资源
static void TearDownTestCase() {
delete shared_resource_;
shared_resource_ = NULL;
}
// 资源
static T* shared_resource_;
};
全局事件
也是很简单的,就是继承于testing::Environment而已。
class FooEnvironment: public testing::Environment
{
public:
virtual void SetUp()
{
printf("Environment SetUp!\n");
a = 100;
}
virtual void TearDown()
{
printf("Environment TearDown!\n");
}
int a; //共享数据
};
FooEnvironment* foo_env; //对象指针声明
TEST(firstTest, first) //访问共享数据并改变它的值
{
printf("in the firstTest, foo_env->p is %d\n", foo_env->a);
foo_env->a ++;
}
TEST(secondTest, second) //访问共享数据
{
printf("in the secondTest, foo_env->p is %d\n", foo_env->a);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
foo_env = new FooEnvironment;
testing::AddGlobalTestEnvironment(foo_env); //注册
testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);
return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
Gtest:事件的更多相关文章
- JNI详解---从不懂到理解
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/hui12581/article/details/44832651 Chap1:JNI完全手册... 3 Chap2:JNI-百度百科... 11 C ...
- gtest 三种事件机制
前言: 1.首先说明gtest中事件的结构层次: 测试程序:一个测试程序只有一个main函数,也可以说是一个可执行程序是一个测试程序.该级别的事件机制会在程序的开始和结束执行. 测试套件:代表一个测试 ...
- gTest详解
1. 安装使用 1.1 安装 在https://code.google.com/p/googletest/ 下载源码 进入msvc, 注意编译方式, 如果是dll, 选择 gtest-md 编译生成l ...
- 白盒测试之gtest第一个demo
认识gtest工具后,关于它的使用,下面将用一个demo程序演示一下gtest的用法以及成果展示. 一.需要测试的C++代码: #include "myfunction.h" // ...
- gtest框架使用
gtest文档说明: 由于公司单元测试的需要,自己花了大半天时间下载了一个gtest框架,使用了一些测试例子,总览了coderzh的玩转gtest测试框架,又看了几篇gtest博客,写下了以下内容,作 ...
- gtest的安装和测试[good]
一.前言 本篇将介绍一些gtest的基本使用,包括下载,安装,编译,建立我们第一个测试Demo工程,以及编写一个最简单的测试案例. 二.下载 如果不记得网址, 直接在google里搜gtest,第一个 ...
- gtest简短,简单易用
gtest它是一种跨平台的(Liunx.Mac OS X.Windows.Cygwin.Windows CE and Symbian)的C++测试框架.有google该公司宣布. gtest台上为编写 ...
- gtest框架
解析gtest框架运行机制 1.前言 Google test是一款开源的白盒单元测试框架,据说目前在Google内部已在几千个项目中应用了基于该框架的白盒测试. 最近的工作是在搞一个基于gtest ...
- 简单易懂的单元测试框架-gtest(二)
简介 事件机制用于在案例运行前后添加一些操作(相当于挂钩函数).目前,gtest提供了三种等级的事件,分别: 全局级,所有案例执行的前后 TestSuite级,某一个案例集的前后 TestCa ...
随机推荐
- salt远程实现go编译重启
使用salt实现jenkins发版时,远程对go项目编译重启 1.go 版本1.12 使用go mod 2.设置go镜像 GOPROXY="https://goproxy.io" ...
- [数据结构 - 第6章] 树之链式二叉树(C语言实现)
一.什么是二叉树? 1.1 定义 二叉树,是度为二的树,二叉树的每一个节点最多只有二个子节点,且两个子节点有序. 1.2 二叉树的重要特性 (1)二叉树的第 i 层上节点数最多为 2n-1: (2)高 ...
- Java中参数始终是按值传递
Java中参数始终是按值传递. public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int x = 5; change(x); S ...
- Java开发笔记(一百五十)C3P0连接池的用法
JDBC既制定统一标准兼容了多种数据库,又利用预报告堵上了SQL注入漏洞,照理说已经很完善了,可是人算不如天算,它在性能方面不尽如人意.问题出在数据库连接的管理上,按照正常流程,每次操作完数据库,都要 ...
- windows和linux环境下java调用C++代码-JNI技术
最近部门做安卓移动开发的需要调C++的代码,困难重重,最后任务交给了我,查找相关资料,没有一个教程能把不同环境(windows,linux)下怎么调用说明白的,自己在实现的过程中踩了几个坑,在这里总结 ...
- DFS BFS 学习总结
DFS 深度优先搜索 基本思路: if(true) 返回 典型例题: 1.马走日(非常典型) #include<iostream> #include<cstring> usin ...
- C语言 小球撞击反弹
计算法(略) #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int x, y, a, resu; scanf(&quo ...
- Gin上传文件到MongoDB gridfs
目录 上传图片 下载图片 上传图片 func imagePost(c *gin.Context) { image, err := c.FormFile("file") if err ...
- jdbc 简单示例和优缺点
一个使用JDBC的例子: Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //加载驱动 Connection connection = Dri ...
- CDN 访问控制的那些事
网络已经成为生活中必不可少的一部分,无论是清早手机翻看的新闻八卦,还是公交地铁里刷的停不下来的短视频,又或是你闲逛的购物网站,热追的电视剧,都与 CDN 有着密不可分的联系.无论你在互联网上做什么,或 ...
