二、Spring中的@ComponentScan自动扫描组件
在以往采用xml配置的方式中,我们通常需要配置<context:component-scan>标签
比如这样:
<!-- 包扫描、只要标注了@Controller、@Service、@Repository,@Component -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"></context:component-scan>
那在javaConfig的配置方式中,对应于@ComponentScan注解
我们现在就建一个例子 ,来具体演示一下。
我们web工程中,新建一个BookController类,具体如下:
package com.atguigu.controller;
// 省略了包的导入
@Controller
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
}
BookService类
package com.atguigu.service;
@Service
public class BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
public void print(){
System.out.println(bookDao);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BookService [bookDao=" + bookDao + "]";
}
}
最后是BookDao类
package com.atguigu.dao;
//名字默认是类名首字母小写
@Repository
public class BookDao {
private String lable = "1";
public String getLable() {
return lable;
}
public void setLable(String lable) {
this.lable = lable;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BookDao [lable=" + lable + "]";
}
}
以上三个类没什么需要说的,无须关注类的具体内容,只须关注类上的注解,和类所处的包即可。
与上节同样的,我们采用Javaconfig类的方式,还是需要一个配置类。
所以我们新建:MainConfig类,作为我们的配置类
package com.atguigu.config;
//配置类==配置文件
@Configuration //告诉Spring这是一个配置类
@ComponentScan(value="com.atguigu") // 注意这一行。
public class MainConfig {
//给容器中注册一个Bean;类型为返回值的类型,id默认是用方法名作为id
@Bean(name = "person")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("lisi", 20);
}
}
在配置类上加了@ComponentScan注解,这里value="com.atguigu"写成basePackages="com.atguigu"都是指明我们需要扫描的包
我们写个测试方法:
public class IOCTest {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
String[] definitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : definitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
加载配置类,并获取到容器中所有的Bean的名字,然后遍历进行打印
我们看下打印结果
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory // 这几个都是spring容器本身的
mainConfig
bookController
bookDao
bookService
person
我们可以看到将com.atguigu下所有的bean都已经扫描了进来,这里说一下MainConfig这个配置类,也在扫描的包下。它的类上有个注解@Configuration,表示配置类也是一个bean。还有个person是我们在@Bean注解定义的Bean.
接下来我们要对@ComponentScan注解进行详细的讲解。
1.我们有这样一样一个需求:不扫描@Controller注解。
该怎么写呢
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.atguigu",excludeFilters= {@Filter(type=FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes={Controller.class})})
这就表示排除掉了@Controller注解,
看看打印结果:
// 可以看到确实没有bookController类了,它被@Controller注解所修饰,所以被排除在了扫描之外,自然也不没有纳入容器之中
mainConfig
bookDao
bookService
person
2.只扫描@Repository标注的注解
该如何写呢??
@ComponentScan(basePackages="com.atguigu",includeFilters= {@Filter(type=FilterType.ANNOTATION,
classes={Repository.class})},useDefaultFilters=false)
测试方法不变,打印结果:
mainConfig
bookDao
person
可以看到 容器中只有bookDao这一个bean了。
注意:useDefaultFilters=false是禁用掉默认的扫描规则,默认当然是扫描包下的@Controller、@Service、@Repository,@Component这四大金刚咯(其实还包括@Configuration注解),所以禁用掉,就不再扫描了,那么只扫描我们定义的。这点与上面的排除规则不同,注意理解,毕竟排除是从所有扫描中再排除。
让我们再深入一点,嘿嘿
我们来看看 @ComponentScan注解里面能写哪些东西
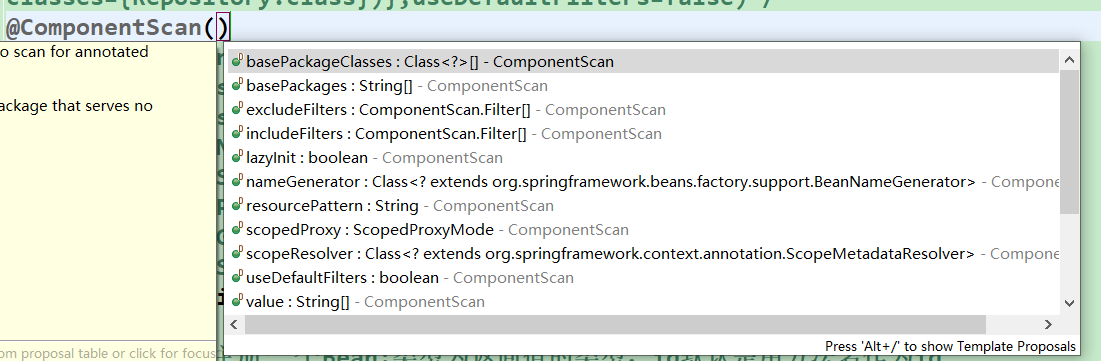
常用的几个注解我们已经讲解过了,
我们主要来看下excludeFilters和includeFilters的写法
在@ComponentScan中,我们拿到这个类的源码看看呗。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan {
boolean useDefaultFilters() default true;
Filter[] includeFilters() default {};
Filter[] excludeFilters() default {};
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({})
@interface Filter {
FilterType type() default FilterType.ANNOTATION; // 过滤的类型,默认是通过注解的类型,
@AliasFor("classes")
Class<?>[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
Class<?>[] classes() default {};
String[] pattern() default {};
}
}
我们发现它们是Filter数组类型,从我们刚刚的写法中也能略窥一二。这个Filter也是一个注解,刚好定义在内部,
也就是说
excludeFilters= {@Filter(type=FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes={Controller.class})}
的意思是说排除掉Controller类型的注解。
那除了通过注解的类型进行排除,还有其他的方式么?
那我们就要去上面这个FilterType.ANNOTATION中的FilterType中一探究竟了。

发现它有五个类型,那我们再举个通过ASSIGNABLE_TYPE的例子
比如这样@Filter(type=FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes={BookService.class}
这就是说通过指定类型,排除掉BookService.class类型,即不扫描,这其实包括了它的子类,父类等。
其他还有一种CUSTOM
也就是自定义过滤规则。不再讲解。
再回来,我们看看@ComponentScan的源码,发现它被@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)注解所修饰,这个注解代表中,我们可以在类上重复加这个注解,定义多个不同的扫描策略。
该睡觉了,又是一个深夜了,晚安!
二、Spring中的@ComponentScan自动扫描组件的更多相关文章
- Spring学习(十四)----- Spring Auto Scanning Components —— 自动扫描组件
一. Spring Auto Scanning Components —— 自动扫描组件 1. Declares Components Manually——手动配置componen ...
- 分布式数据存储 之 Redis(二) —— spring中的缓存抽象
分布式数据存储 之 Redis(二) -- spring中的缓存抽象 一.spring boot 中的 StringRedisTemplate 1.StringRedisTemplate Demo 第 ...
- 关于spring中<context:component-scan base-package="" />写法
1.通配符形式<context:component-scan base-package="com.*" /> 2.全路径 <context:component-s ...
- Spring Boot 自动扫描组件
使用@ComponentScan自动扫描组件 案例准备 1.创建一个配置类,在配置类上添加 @ComponentScan 注解.该注解默认会扫描该类所在的包下所有的配置类,相当于之前的 <con ...
- Spring中@Autowired、@Resource和@Inject注解的使用和区别
在使用Spring进行项目开发的时候,会大量使用到自动装配,那自动装配是什么呢?简单来说:Spring 利用依赖注入(DI)功能,完成SpringIOC容器中各个组件之间的依赖关系赋值管理. 下面介绍 ...
- spring框架应用系列二:component-scan自动扫描注册装配
component-scan自动扫描注册装配 本文系作者原创,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/further-further-further/p/7717331.html ...
- Spring学习笔记之 Spring IOC容器(二) 之注入参数值,自动组件扫描方式,控制Bean实例化方式,使用注解方式
本节主要内容: 1. 给MessageBean注入参数值 2. 测试Spring自动组件扫描方式 3. 如何控制ExampleBean实例化方式 4. 使用注解方式重构Jdb ...
- Spring自动扫描组件
通常情况下,声明所有的Bean类或组件的XML bean配置文件,这样Spring容器可以检测并注册Bean类或组件. 其实,Spring是能够自动扫描,检测和预定义的项目包并实例化bean,不再有繁 ...
- spring中注解注入 context:component-scan 的使用说明
通常情况下我们在创建spring项目的时候在xml配置文件中都会配置这个标签,配置完这个标签后,spring就会去自动扫描base-package对应的路径或者该路径的子包下面的java文件,如果扫描 ...
随机推荐
- oracle 将与本端(name)联系的人取出
本人与其他所有人认识的SQL: 首先新建测试表 create table DIM_IA_TEST6 ( NAME ), OTHERNAME ) ) 插入数据 --如果没有重复的记录,则不用去重使用un ...
- stm32flash的读写特性
在使用stm32自带的flash保存数据时候,如下特点必须知道: 1.必须是先擦除一个扇区,才能写入 2.读数据没有限制 3.写数据必须是2字节,同时写入地址以一定要考虑字节对齐, 4.一般都是在最后 ...
- Mybatis框架-@Param注解
回顾一下上一个小demo中存在的问题,是是根据用户的id修改用户的密码,我们只是修改了用户的密码,结果我们的在写接口方法的时候掺入的参数确实一个User对象,这样让别人看到我们的代码真的是很难读懂啊! ...
- SOA与ESB,微服务与API网关
SOA与ESB,微服务与API网关 SOA: ESB: 微服务: API网关: 参考资料: 1.漫画微服务,http://www.sohu.com/a/221400925_100039689 2.SO ...
- mssql提权
MSSQL的提权:下面是三种方法一种利用xp_cmshell组件,还有一种sp_OACreate组件,COM组件 xp_cmshell组件的开启: 1.sql2005版本以后默认为关闭状态,需要开启命 ...
- LeetCode 1043. Partition Array for Maximum Sum
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-array-for-maximum-sum/ 题目: Given an integer array A, ...
- win7虚拟机安装
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16503045/article/details/81904986 iso下载地址 https://msdn.itellyou.cn/
- GoCN每日新闻(2019-10-23)
GoCN每日新闻(2019-10-23) GoCN每日新闻(2019-10-23) 1. 从0开始,用Go实现Lexer和Parser https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/cFGJX ...
- 【洛谷】P1443 马的遍历
题目:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1443 简单的BFS模板题——因为我写出来了. 分析过程: n*m矩阵,用二维数组 数据不大,二维数组稳了 先把二 ...
- MATLAB关闭科学计数法显示
