Spring源码阅读 之 配置的加载(希望有喜欢源码的朋友一起交流)
想写Spring的源码方面的东西想了好久了,之前花了一段时间学习了SpringCloud,现在总算对SpringCloud有了一个大概的了解,从今天开始好好读一篇Spring的源码,结合书本跟网上的一些资料,希望能坚持下去,完成这一系列的文章,给自己加油!!!!
版本是基于5.1.X的,大家在阅读的时候请注意,不过因为是Spring的一些基础流程,估计版本间差异也不会太大
关于配置的加载主要可以分为两种:
- 注解式配置的加载
- XML配置加载
注解配置相对于XML更加简单,其过程主要在于注解的解析,而XML配置是用xml文件格式保存配置,其中就涉及到了文件的读取,读取后要进行标签的解析,稍显复杂。我们这篇文章主要就是来讲清楚Spring读取配置文件的过程,对于后面的XML标签的解析或者说是注解的解析其实都是差不多的,在后面的文章中,我会慢慢介绍
我们先看一段代码:
/**
* @author dmz
* @date Create in 20:49 2019/7/20
*/
public class Spring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建一个基于XML的Spring应用的上下文
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
}
}
很简单,目的就是跟踪一个基于XML的Spring应用是如何被加载的,我们一步步点进去看源码可以发现:
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
// 这个构造函数暂时不说
super(parent);
// 这个方法主要是为了设置这个应用需要使用的Spring的配置文件
// 主要是对配置文件的路径进行一些处理
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// 这是Spring的核心方法
refresh();
}
}
Spring的源码很大,我们需要一点点啃,这篇文章目的只是分析配置的读取,所以只分析跟配置相关的代码,在这里也提醒大家,阅读源码时不要被细枝末节牵绊的太深,抓住自己需要分析的主线,然后不断探究,能做到这样就是极好的!!!
我们接着说代码:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 为容器的刷新做准备
prepareRefresh();
// 主要分析这个代码
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 省略后面的代码
.......
}
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 刷新BeanFactory
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 如果当前容器的BeanFactory已经经过初始化,进行清空
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 我们主要需要关注的方法
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// 我们可以看到,在这一步,创建了一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader,构造参数是一个DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// 对这个reader的成员变量进行赋值
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// 提供给子类使用,让子类能自定义BeanDefinitionReader
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
// 最后调用loadBeanDefinitions
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
我们将注意力放到loadBeanDefinitions这个方法上,从方法名称上我们可以知道,这个方法一定读取了配置文件,跟踪其代码最后会到org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions方法,我们看下这个方法的具体实现:
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
// 我们之前给定的是一个application.xml,所以会进这个方法
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
继续跟踪,进入org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 获取一个资源加载器
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
// 这里获取到的资源加载器是一个org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,而所有的applicationContext都实现了ResourcePatternResolver接口
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
try {
// 呼~,终于到这个加载资源的方法了,这个方法会根据不同location,选择对应的resourceLoader加载配置文件
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
......省略部分代码......
在我们的示例中,最终会调用org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader的getResource方法
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) {
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
我们可以看到,这个方法会根据一些匹配规则,比如说localtion是否以“/”开头,是否是一个FileURL等等分别创建
ClassPathResource,FileUrlResource,UrlResource等,我们可以看一下它的类图:
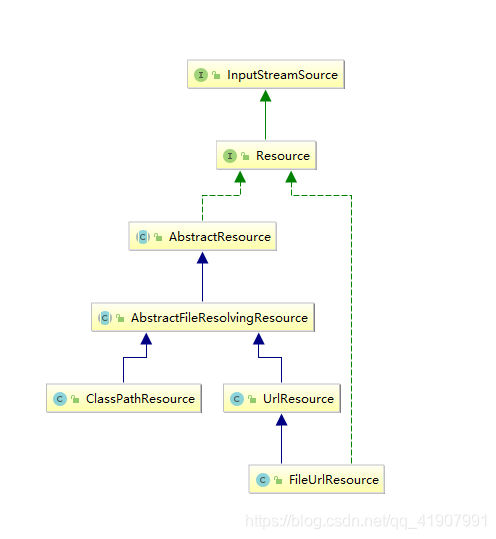
在java中,将不同来源的资源抽象成URL,通过注册不同的handler(URLStramHandler)来处理不同来源的资源的读取逻辑,一般hanlder使用不同前缀(协议,Protocol)来识别,如“file”,"http:"等,然而URL没有默认定义相对Classpath或者ServletContext等资源的hanlder,虽然可以注册自己的URLStream来解析特定的URL前缀,比如“classpath:”,然后这需要了解URL的实现机制,而且URL也没有提供基本的方法,如检查当前资源是否存在,检查当前资源是否可读等,因而Spring对其内部使用到的资源实现了自己的抽象结构:Resource接口封装底层资源
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* 顶层接口,返回资源对应的输入流
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 是否存在
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 是否可读
*/
default boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
/**
* 是否打开
*/
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
/**
* 是否是一个file,如果是的话,getFile()一定能正常返回
*/
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
/**
* 返回资源对应的URL
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源对应的URI
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源对应的文件
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回一个根据当前资源转变的可读的nio中的ReadableByteChannel
*/
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
/**
* 返回资源的字节长度
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回上一次修改的时间戳
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 基于当前资源,创建一个相对资源
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源的文件名(不带路径),没有文件名则返回null
*/
@Nullable
String getFilename();
/**
* 返回资源描述
*/
String getDescription();
}
绝大部分情况下,我们都是直接在resoures直接创建配置文件,所以大部分情况,我们使用的都是ClassPathResource,我们不妨看一下它对这些方法的实现,加深我们对这些接口的理解
@Override
// 可以发现,就是通过类加载器获取对应资源,最终的实现还是会依赖于我们jdk中的URL类
// 最后通过URL返回一个流
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if (this.clazz != null) {
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else if (this.classLoader != null) {
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
}
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
// 判断这个ClassPathResource对应的路径能否被解析成一个java中的URL,如果能则存在
public boolean exists() {
return (resolveURL() != null);
}
.......
经过上面的分析我们已经知道了Spring怎么加载一个配置文件,我们可以总结如下:
- 创建一个
XmlBeanDefinitionReader - 获取对应的
ResourceLoader资源加载器 - 根据location的不同匹配模式,采用不同的ResourceLoader进行资源的加载
- Spring封装了java中的URL类,自定义了一套资源加载策略
- 最后返回一个Spring中的Resource对象
码字不易,希望能找几个同学一起学习源码,后续会一直更新这个系列,有喜欢的朋友加个收藏,点个赞吧!!!谢啦~
Spring源码阅读 之 配置的加载(希望有喜欢源码的朋友一起交流)的更多相关文章
- Spring源码阅读 之 配置的读取,解析
在上文中我们已经知道了Spring如何从我们给定的位置加载到配置文件,并将文件包装成一个Resource对象.这篇文章我们将要探讨的就是,如何从这个Resouce对象中加载到我们的容器?加载到容器后又 ...
- 【Spring源码分析】非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(下篇)
doCreateBean方法 上文[Spring源码分析]非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上篇),分析了单例的Bean初始化流程,并跟踪代码进入了主流程,看到了Bean是如何被实例化出来的.先贴一下 ...
- 【Spring源码分析】非懒加载的单例Bean初始化前后的一些操作
前言 之前两篇文章[Spring源码分析]非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上篇)和[Spring源码分析]非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(下篇)比较详细地分析了非懒加载的单例Bean的初始化过程, ...
- Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化前后的一些操作
之前两篇文章Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上)和Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(下)比较详细地分析了非懒加载的单例Bean的初始化过程,整个流程始于A ...
- Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(下)
上文Spring源码分析:非懒加载的单例Bean初始化过程(上),分析了单例的Bean初始化流程,并跟踪代码进入了主流程,看到了Bean是如何被实例化出来的.先贴一下AbstractAutowireC ...
- spring源码学习之bean的加载(一)
对XML文件的解析基本上已经大致的走了一遍,虽然没有能吸收多少,但是脑子中总是有些印象的,接下来看下spring中的bean的加载,这个比xml解析复杂的多.这个加载,在我们使用的时候基本上是:Bea ...
- wemall app商城源码Android之ListView异步加载网络图片(优化缓存机制)
wemall-mobile是基于WeMall的android app商城,只需要在原商城目录下上传接口文件即可完成服务端的配置,客户端可定制修改.本文分享wemall app商城源码Android之L ...
- Android 图片加载框架Glide4.0源码完全解析(二)
写在之前 上一篇博文写的是Android 图片加载框架Glide4.0源码完全解析(一),主要分析了Glide4.0源码中的with方法和load方法,原本打算是一起发布的,但是由于into方法复杂性 ...
- 自己动手实现springboot运行时执行java源码(运行时编译、加载、注册bean、调用)
看来断点.单步调试还不够硬核,根本没多少人看,这次再来个硬核的.依然是由于apaas平台越来越流行了,如果apaas平台选择了java语言作为平台内的业务代码,那么不仅仅面临着IDE外的断点.单步调试 ...
随机推荐
- 如何正确管理HBase的连接,从原理到实战
本文将介绍HBase的客户端连接实现,并说明如何正确管理HBase的连接. 最近在搭建一个HBase的可视化管理平台,搭建完成后发现不管什么查询都很慢,甚至于使用api去listTable都要好几秒. ...
- MySQL 5.7.18 zip 文件安装过程
安装最新MySQL:5.7.18 1.下载路径 https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/ 有账号登陆下载, 没有账号:no thanks;just start my ...
- 排序算法代码实现-Java
前言 为了准备面试,从2月开始将排序算法认认真真得刷了一遍,通过看书看视频,实践打代码,还有一部分的leetcode题,自己感觉也有点进步,将笔记记录总结发出来. 冒泡排序 该排序就是一种像泡泡浮到水 ...
- Java 基础讲解
Hello,老同学们,又见面啦,新同学们,你们好哦! 在看完本人的<数据结构与算法>专栏的博文的老同学,恭喜你们在学习本专栏时,你们将会发现好多知识点都讲解过,都易于理解,那么,没看过的同 ...
- SpringBoot集成MyBatis底层原理及简易实现
MyBatis是可以说是目前最主流的Spring持久层框架了,本文主要探讨SpringBoot集成MyBatis的底层原理.完整代码可移步Github. 如何使用MyBatis 一般情况下,我们在Sp ...
- 使用JAVA API编程实现简易Habse操作
使用JAVA API编程实现下面内容: 1.创建<王者荣耀>游戏玩家信息表gamer,包含列族personalInfo(个人信息).recordInfo(战绩信息).assetsInfo( ...
- C#多线程(14):任务基础②
目录 判断任务状态 再说父子任务 组合任务/延续任务 复杂的延续任务 并行(异步)处理任务 并行(同步)处理任务 并行任务的 Task.WhenAny 并行任务状态 循环中值变化问题 定时任务 Tas ...
- 二维vector的使用
和数组一样,数组有二维的数组,vector也有二维的vector.下面就介绍一下二维vector的使用方法. 一般声明初始化二维vector有三种方法 (1) vector< vector< ...
- PHP 新特性:如何善用接口与Trait
首先! 接口也可以继承,通过使用 extends 操作符. 案例: <?php interface a { public function foo(); } interface b extend ...
- Ubuntu 修改 hosts 文件
sudo vi /etc/hosts sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
