Netty 异步模型
简介
- Netty中的 I/O 操作是异步的, 包括 Bind、Write、Connect 等操作会简单的返回一个ChannelFuture。
- 调用者不能立刻获得结果, 而是通过Future-Listener 机制, 用户可以方便的主动获取或者通过通知机制获得IO操作结果。
- Netty的异步模型是建立在future和callback之上的。callback就是回调。
- Future的核心思想是: 假设一个方法func(), 其计算过程可能很耗时, 等待func()返回不合适。那么就可以在调用func()的时候, 立马返回一个Future, 后续可以通过Future去监控方法func()的处理过程(即: Future-Listener机制)
Future说明
- 表示异步的结果, 可以通过它提供的方法来检测执行是否完成, 比如检索计算等。
- ChannelFuture是一个继承了Future类的接口, public interface ChannelFuture extends Future {}。可以添加监听器, 当监听的事件发生时, 就会通知到监听器。
ChannelFuture类注释
/**
* The result of an asynchronous {@link Channel} I/O operation.
* 异步I/O操作的执行结果
* <p>
* All I/O operations in Netty are asynchronous.
* Netty中的所有 I/O操作都是异步的
* It means any I/O calls will return immediately with no guarantee that the
* requested I/O operation has been completed at the end of the call.
* 这意味着 任意 I/O 调用都会直接返回, 但是不能保证请求的I/O 操作在被调用前能够完成。
*
* Instead, you will be returned with a {@link ChannelFuture} instance which gives
* you the information about the result or status of the I/O operation.
* 但是, 会有一个能提供该I/O操作的结果或状态的ChannelFuture类实例被返回。
* <p>
*
* A {@link ChannelFuture} is either <em>uncompleted</em> or <em>completed</em>.
* channelFuture的状态可以是未完成的也可以是完成的。
*
* When an I/O operation begins, a new future object is created.
* 当一个 I/O 操作开始, 一个新的对象被创建。
*
* The new future is uncompleted initially - it is neither succeeded, failed, nor
* cancelled because the I/O operation is not finished yet.
* 新的future一开始是未完成状态, 它不是成功的, 失败的, 或取消的, 因为 I/O 操作并没有完成。
*
* If the I/O operation is finished either successfully, with failure, or by
* cancellation, the future is marked as completed with more specific information,
* such as the cause of the failure.
* 如果 I/O 操作是成功完成的, 失败的 或是 被取消状态, future就被标记为带有特定信息的完成状
* 态, 比如导致失败的原因。
*
* Please note that even failure and cancellation belong to the completed state.
* 请记住, 即使是 失败 和 取消 都是完成状态
* <pre>
* +---------------------------+
* | Completed successfully |
* +---------------------------+
* +----> isDone() = true |
* +--------------------------+ | | isSuccess() = true |
* | Uncompleted | | +===========================+
* +--------------------------+ | | Completed with failure |
* | isDone() = false | | +---------------------------+
* | isSuccess() = false |----+----> isDone() = true |
* | isCancelled() = false | | | cause() = non-null |
* | cause() = null | | +===========================+
* +--------------------------+ | | Completed by cancellation |
* | +---------------------------+
* +----> isDone() = true |
* | isCancelled() = true |
* +---------------------------+
* </pre>
*
* Various methods are provided to let you check if the I/O operation has been
* completed, wait for the completion, and retrieve the result of the I/O
* operation.
* 有许多方法提供给你来检查 此I/O 操作是否完成, 在等待完成, 并取回 I/O 操作的结果。
* It also allows you to add {@link ChannelFutureListener}s so you
* can get notified when the I/O operation is completed.
* 它还允许你添加 ChannelFuture监听器, 所以你能够在I/O 操作完成时被通知。
*
* <h3>Prefer {@link #addListener(GenericFutureListener)} to {@link #await()}</h3>
*
* It is recommended to prefer {@link #addListener(GenericFutureListener)} to
* {@link #await()} wherever possible to get notified when an I/O operation is
* done and to do any follow-up tasks.
* 当一个 I/O 操作被完成 并且 有接下来的任务要做时, 推荐使用 addListener(添加监听器)而不是
* await() 方法, 因为使用监听器的方式可以被通知。
* <p>
* {@link #addListener(GenericFutureListener)} is non-blocking.
* addListener 方法是非阻塞的
*
* It simply adds the specified {@link ChannelFutureListener} to the {@link
* ChannelFuture}, and I/O thread will notify the listeners when the I/O operation
* associated with the future is done.
* 它仅仅添加了特定的ChannelFutureListener到ChannelFuture中, 并且 I/O 线程会在 与future
* 相关联的 I/O 操作完成时通知监听器。
*
* {@link ChannelFutureListener} yields the best performance and resource
* utilization because it does not block at all, but it could be tricky to implement
* a sequential logic if you are not used to event-driven programming.
* 由于本身不阻塞, ChannelFutureListener(监听器) 能提供最好的效用 和 最好的资源利用率, 但
* 是如果内没有习惯于事件启动编程模型, 实现一系列逻辑时可能会比较tricky。
*
* <p>
* By contrast, {@link #await()} is a blocking operation.
* 相比较之下, await() 方法是一个阻塞操作。
* Once called, the caller thread blocks until the operation is done.
* 一旦被调用, 在操作结束之前, 调用者线程会一直阻塞。
* It is easier to implement a sequential logic with {@link #await()}, but the
* caller thread blocks unnecessarily until the I/O operation is done and there's
* relatively expensive cost of inter-thread notification.
* 以await() 方法实现一系列的逻辑会相对简单, 但是调用者线程在I/O操作间有不必要的阻塞 以及
* 线程内部通信代价很高。
* Moreover, there's a chance of dead lock in a particular circumstance, which is
* described below.
* 此外, 在特殊情况下, 还有可能会产生死锁, 描述如下。
*
* <h3>Do not call {@link #await()} inside {@link ChannelHandler}</h3>
* 不要在 ChannelHandler 中调用 await() 方法
* <p>
* The event handler methods in {@link ChannelHandler} are usually called by
* an I/O thread.
* ChannelHandler中的事件处理方法通常是由 I/O 线程调用的。
*
* If {@link #await()} is called by an event handler method, which is called by the
* I/O thread, the I/O operation it is waiting for might never complete because
* {@link #await()} can block the I/O operation it is waiting for, which is a dead
* lock.
* 如果 await() 方法是被一个事件处理方法以 I/O 线程的形式调用的, 该 I/O 操作会因为await()
* 方法阻塞了此 正在被等待的 I/O 操作, 从而导致死锁。
* <pre>
* // BAD - NEVER DO THIS 千万别做以下操作
* {@code @Override}
* public void channelRead({@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx, Object msg) {
* {@link ChannelFuture} future = ctx.channel().close();
* future.awaitUninterruptibly();
* // Perform post-closure operation
* // ...
* }
*
* // GOOD 好的操作
* {@code @Override}
* public void channelRead({@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx, Object msg) {
* {@link ChannelFuture} future = ctx.channel().close();
* future.addListener(new {@link ChannelFutureListener}() {
* public void operationComplete({@link ChannelFuture} future) {
* // Perform post-closure operation
* // ...
* }
* });
* }
* </pre>
* <p>
* In spite of the disadvantages mentioned above, there are certainly the cases
* where it is more convenient to call {@link #await()}.
* 尽管await()方法的缺点已经在上列出, 还是肯定会有使用它跟方便的情况
* In such a case, please make sure you do not call {@link #await()} in an I/O
* thread.
* 在此情况下, 请确保你没有在I/O线程中调用await()
* Otherwise, {@link BlockingOperationException} will be raised to prevent a dead
* lock.
* 此外 BlockingOperationException(阻塞操作异常) 会被抛出来预防死锁
*
* <h3>Do not confuse I/O timeout and await timeout</h3>
* 不要将 I/O 超时 和 await 超时 弄混
*
* The timeout value you specify with {@link #await(long)},
* {@link #await(long, TimeUnit)}, {@link #awaitUninterruptibly(long)}, or
* {@link #awaitUninterruptibly(long, TimeUnit)} are not related with I/O
* timeout at all.
* 你使用 await(long), await(long, TimeUnit), awaitUninterruptibly(long) 或
* awaitUninterruptibly(long, TimeUnit)方法时的延时与 I/O 延迟无关。
*
* If an I/O operation times out, the future will be marked as
* 'completed with failure,' as depicted in the diagram above.
* 如果 I/O 操作延时, 该future 会被标记为 完成且失败, 就像途中描述的那样。
*
* For example, connect timeout should be configured via a transport-specific
* option:
* 比如, 连接事件应当通过特定的传输选项配置
* <pre>
* // BAD - NEVER DO THIS 不要做以下操作
* {@link Bootstrap} b = ...;
* {@link ChannelFuture} f = b.connect(...);
* f.awaitUninterruptibly(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
* if (f.isCancelled()) {
* // Connection attempt cancelled by user
* // 连接请求被用户取消
* } else if (!f.isSuccess()) {
* // You might get a NullPointerException here because the future
* // might not be completed yet.
* // 你可能会得到一个空指针, 因为该future没有被完成。
* f.cause().printStackTrace();
* } else {
* // Connection established successfully
* // 连接建立成功
* }
*
* // GOOD 好的操作
* {@link Bootstrap} b = ...;
* // Configure the connect timeout option.
* <b>b.option({@link ChannelOption}.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 10000);</b>
* {@link ChannelFuture} f = b.connect(...);
* f.awaitUninterruptibly();
*
* // Now we are sure the future is completed.
* // 此时我们可以确认该future已完成
* assert f.isDone();
*
* if (f.isCancelled()) {
* // Connection attempt cancelled by user
* // 连接请求被用户取消
* } else if (!f.isSuccess()) {
* f.cause().printStackTrace();
* } else {
* // Connection established successfully
* // 成功建立连接
* }
* </pre>
*/
工作原理示意图
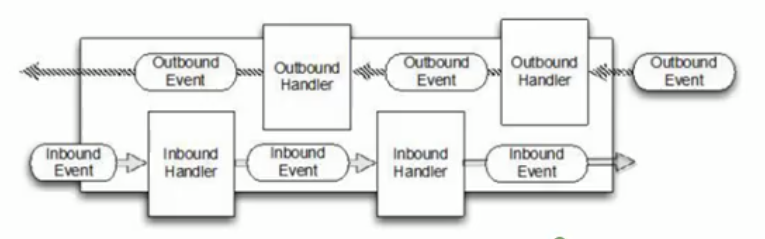
- inBound: 入栈
- outBound: 出栈
- 说明:
- 在使用Netty进行编程时, 拦截操作和转换出入栈数据只需要提供callback 或 利用future即可。
- 这使得链式操作简单、高效, 并有利于编写可重用的、通用的代码。
- Netty 框架的目标就是让你的业务逻辑从网络基础应用编码中分离出来。
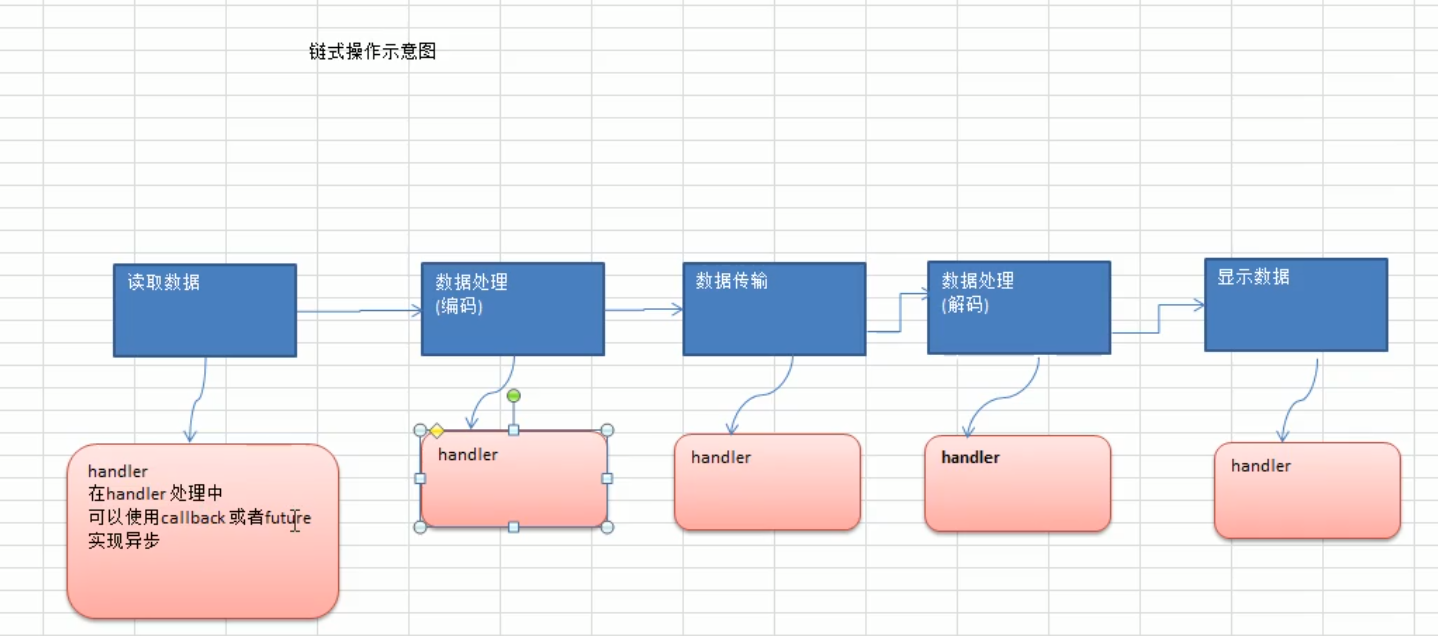
Future-Listener机制
- 当Future对象刚刚创建时, 处于非完成状态, 调用者可以通过返回的ChannelFuture来获取操作执行的状态, 注册监听函数来执行完成后的操作。
- 常见操作
- 通过 isDone 方法来判断当前操作是否完成;
- 通过 isSuccess 方法来判断已完成的当前操作是否成功;
- 通过 getCause 方法来获取已完成的当前操作失败的原因;
- 通过 isCancelled 方法来判断已完成的当前操作是否被取消;
- 通过 addListener 方法来注册监听器, 当操作已完成(isDone 方法返回完成), 将会通知指定的监听器; 如果 Future 对象已完成, 则通知指定的监听器
Netty 异步模型的更多相关文章
- 结合异步模型,再次总结Netty多线程编码最佳实践
更多技术分享可关注我 前言 本文重点总结Netty多线程的一些编码最佳实践和注意事项,并且顺便对Netty的线程调度模型,和异步模型做了一个汇总.原文:结合异步模型,再次总结Netty多线程编码最 ...
- eventloop & actor模式 & Java线程模型演进 & Netty线程模型 总结
eventloop的基本概念可以参考:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/10/event_loop.html Eventloop指的是独立于主线程的一条线程,专门 ...
- Netty线程模型
一.Reactor模型 1.单线程模型 Reactor单线程模型,指的是所有的IO操作都在同一个NIO线程上面完成,NIO线程的职责如下: 1)作为NIO服务端,接收客户端的TCP连接: 2)作为NI ...
- Netty系列之Netty线程模型
Reference: http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/netty-threading-model 1. 背景 1.1. Java线程模型的演进 1.1.1. 单线程 ...
- 彻底搞懂 netty 线程模型
编者注:Netty是Java领域有名的开源网络库,特点是高性能和高扩展性,因此很多流行的框架都是基于它来构建的,比如我们熟知的Dubbo.Rocketmq.Hadoop等.本文就netty线程模型展开 ...
- Netty源码死磕一(netty线程模型及EventLoop机制)
引言 好久没有写博客了,近期准备把Netty源码啃一遍.在这之前本想直接看源码,但是看到后面发现其实效率不高, 有些概念还是有必要回头再细啃的,特别是其线程模型以及EventLoop的概念. 当然在开 ...
- .NET - 基于事件的异步模型
注:这是大概四年前写的文章了.而且我离开.net领域也有四年多了.本来不想再发表,但是这实际上是Active Object模式在.net中的一种重要实现方法,因此我把它掏出来发布一下.如果该模型有新的 ...
- Task C# 多线程和异步模型 TPL模型
Task,异步,多线程简单总结 1,如何把一个异步封装为Task异步 Task.Factory.FromAsync 对老的一些异步模型封装为Task TaskCompletionSource 更通用, ...
- libgo协程库:网络性能完爆ASIO异步模型(-O3测试)
在purecpp社区的github组织中有一个协程库:https://github.com/yyzybb537/libgo 近日有用户找到我,想要了解一下libgo库在网络方面的性能,于是选取已入选标 ...
随机推荐
- Servlet+Spring+Mybatis初试
1.导入相关的jar包 druid mybatis mybatis-spring pageHelper mysql驱动包 spring-context-support spring-aspect sp ...
- ApacheDbUtilsUpdate
ApacheDbUtilsUpdate package p1; import com.DataSourceUtil; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRu ...
- 第1节 Scala基础语法:14、15、list集合练习
package cn.itcast.collect /** *作业题 */object ListTest { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //创建一 ...
- electron-edge-js 环境搭建
确保nodejs环境 为 10.X (因为edge的编译需要node对应版本的支持,太新的node不包含对应edge的编译) 1.创建工程2.使用npm init初始化程序信息3.使用npm ins ...
- Hot Module Replacement [热模块替换]
安装了webpack-dev-server后 , 配置 "start": "webpack-dev-server" 然后运行 npm start 会开起一个we ...
- C++11并发编程1------并发介绍
也许有人会觉得多线程和并发难用,复杂,还会让代码出现各种各样的问题,不过,其实它是一个强有力的工具,能让程序充分利用硬件资源,让程序运行得更快. 何谓并发: 两个或更多独立得活动同时发生.计算机中就是 ...
- vbs操作IE对象
Dim fso,filepath,i 'Dim ExcelBook,ExcelSheet,MyExcelBook,MyExcelSheet Dim ie Set ie=WScript.CreateOb ...
- hdu 1541 Stars 统计<=x的数有几个
Stars Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- 第1节 kafka消息队列:3、4、kafka的安装以及命令行的管理使用
6.kafka的安装 5.1三台机器安装zookeeper 注意:安装zookeeper之前一定要确保三台机器时钟同步 */1 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate us.pool.nt ...
- vue2 Excel导出数据 js-xlsx的使用
vue2 Excel导出数据 js-xlsx的使用 https://www.jianshu.com/p/ea115a8e9107 小世界最温暖 关注 2018.11.19 16:08 字数 280 阅 ...
