python中的字符串学习
# 1.字符串的下标(索引)
# 取字符串中的子串
print('1.字符串的下标(索引)')
str1 = 'PYTHON'
print(str1[0])
print(str1[-4]) # 2.字符串的切片 起始值:终止值:步长
print()
print('2.字符串的切片') print('2.1使用正索引')
str1 = 'PYTHON'
print(str1[::]) # 取全部
print(str1[:]) # 一个冒号是默认步长为1
print(str1[:3]) # 起始值默认为0,包头不包尾
print(str1[2:4]) # 取中间 包头不包尾
print(str1[4:]) # 终止值默认为最大 # 2.2 使用负索引
print()
print('2.2使用负索引')
str1 = 'PYTHON'
print(str1[-3:-1]) # 取中间
print(str1[-4:]) # 取后面
print(str1[:-2]) # 取前面 # 2.3步长
print()
print('2.3步长')
str1 = 'PYTHON'
print(str1[::2])
print(str1[::-1]) # 注意啦,步长为负的时候,起始值默认是-1 # 3.字符串的常用操作
print()
print('3.字符串的常用操作') # 3.1 查找
print()
print('3.1查找') # 3.11 str1.find()
# str1.find(查找的字符串,开始位置,结束位置)
# 找到了,则返回索引值
# 找不到,则返回-1
print()
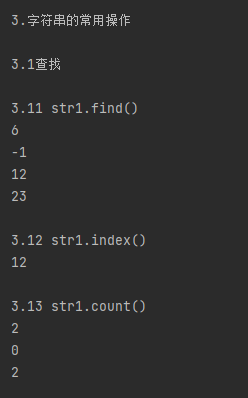
print('3.11 str1.find()')
str1 = 'hello world and Python and Windows'
print(str1.find('world'))
print(str1.find('worlds'))
print(str1.find('and')) # 只找了最开始的and
print(str1.find('and', 13, 50)) # 找到了第二个and # 3.12 str1.index()
# 找到了,则返回索引值
# 找不到,则报错
print()
print('3.12 str1.index()')
print(str1.index('and'))
# print(str1.index('ands')) #会报错 # 3.13 str1.count() 查找字符串出现的次数
print()
print('3.13 str1.count()')
print(str1.count('and'))
print(str1.count('ands')) # 没出现过这个字符串,那就是出现了0次呗
print(str1.count('a')) # 一个字符也是字符串哦 # 3.2.修改
print()
print('3.2 修改')
# 3.21 替换
# str1.replace(旧的,新的,替换的次数)
# 字符串是一个不可变类型
print()
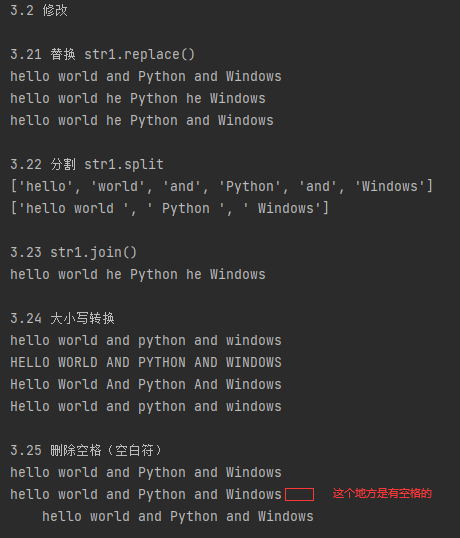
print('3.21 替换 str1.replace()')
str1 = 'hello world and Python and Windows'
str1.replace('and', 'he')
print(str1) # 但这里str1并没有改变
new_str1 = str1.replace('and', 'he') # 替换的次数默认全部
print(new_str1)
new1_str1 = str1.replace('and', 'he', 1) # 只替换了一次
print(new1_str1) # 3.22 分割
# str1.split() 以某个字符进行分割,放回一个列表
# 默认以空格分割,会删去空格
print()
print('3.22 分割 str1.split')
print(str1.split())
print(str1.split('and')) # 以and分割,会删去and,保留空格的! # 3.23 连接
# str1.join(列表) # 正好 连接 分割 后产生的列表
print()
print('3.23 str1.join()')
new_str = 'he'.join(str1.split('and')) # 用'he'连接
print(new_str) # 3.24 大小写转换
print()
print('3.24 大小写转换')
str1 = 'hello world and Python and Windows'
print(str1.lower()) # 所有字母转换为小写
print(str1.upper()) # 所有字母转换为大写
print(str1.title()) # 把每个单词的首个字母大写
print(str1.capitalize()) # 将字符串的第一个单词的首字母转换成大写,其他变成小写 # 3.25 删除空格(空白符)
print()
print('3.25 删除空格(空白符)')
str2 = ' hello world and Python and Windows '
print(str2.strip()) # 删除字符串两边的空格
print(str2.lstrip()) # 只删除字符串左边的空格
print(str2.rstrip()) # 只删除字符串右边的空格 # 3.3 判断
print()
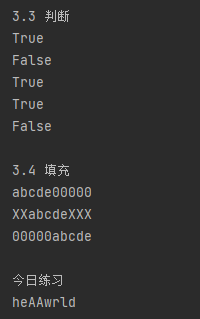
print('3.3 判断')
str1 = 'hello world and Python and Windows'
print(str1.startswith('hello')) # 判断是否以某个字符串开头
print(str1.startswith('hellos'))
print(str1.endswith('Windows')) # 判断是否以某个字符串结尾 str2 = '123'
print(str2.isdigit()) # 判断字符串里面是否全部是数字
print(str2.isalpha()) # 判断字符串里面是否全部是字母 # 3.4 填充
print()
print('3.4 填充')
str2 = 'abcde'
# str2.ljust(填充后字符串的长度,填充的字符) 左填充
# str2.rjust() 右填充
# str2.center() 中间填充
# str2.zfill() 0填充
print(str2.ljust(10, '0')) # 左填充,填充后字符串在左
print(str2.center(10, 'X'))
print(str2.zfill(10)) # 今日练习
# 创建一个字符串'helloworld'
# (1)将l用A替换
# (2)将所有的o删除
# (3)将操作后的字符串结果打印输出
print()
print('今日练习')
str_1 = 'helloworld'
new_str_1 = str_1.replace('l', 'A', 2)
# 字符串是一个不可变类型,
# 所以要用一个新的字符串存储替换后的字符串
print(''.join(new_str_1.split('o')))

python中的字符串学习的更多相关文章
- Python中Unicode字符串
Python中Unicode字符串 字符串还有一个编码问题. 因为计算机只能处理数字,如果要处理文本,就必须先把文本转换为数字才能处理.最早的计算机在设计时采用8个比特(bit)作为一个字节(byte ...
- Python中的字符串处理
Python转义字符 在需要在字符中使用特殊字符时,python用反斜杠(\)转义字符.如下表: 转义字符 描述 \(在行尾时) 续行符 \\ 反斜杠符号 \' 单引号 \" 双引号 \a ...
- python中修改字符串的几种方法
在Python中,字符串是不可变类型,即无法直接修改字符串的某一位字符.因此改变一个字符串的元素需要新建一个新的字符串.常见的修改方法有以下4种. 方法1:将字符串转换成列表后修改值,然后用join组 ...
- python中根据字符串导入模块module
python中根据字符串导入模块module 需要导入importlib,使用其中的import_module方法 import importlib modname = 'datetime' date ...
- python中的字符串
一.在python中,字符串是不可变类型 通过以下代码说明: >>> s = 'hello, world' >>> id(s) 2108634288304 > ...
- 【转】Python中的字符串与字符编码
[转]Python中的字符串与字符编码 本节内容: 前言 相关概念 Python中的默认编码 Python2与Python3中对字符串的支持 字符编码转换 一.前言 Python中的字符编码是个老生常 ...
- python中confIgparser模块学习
python中configparser模块学习 ConfigParser模块在python中用来读取配置文件,配置文件的格式跟windows下的ini配置文件相似,可以包含一个或多个节(section ...
- Python中常见字符串去除空格的方法总结
Python中常见字符串去除空格的方法总结 1:strip()方法,去除字符串开头或者结尾的空格>>> a = " a b c ">>> a.s ...
- Python中的字符串方法
Python中的字符串方法 字符串类即str提供了许多有用的方法来操纵字符串.具体来说,我们将讨论如下的方法. 搜索字符串内的子字符串. 测试字符串. 格式字符串. 转换字符串. 回顾前面的章节,方法 ...
随机推荐
- 【Go实战基础】GO语言是什么,有哪些优势
一.简介 2007年,为了提高在多核.网络机器(networked machines).大型代码库(codebases)的业务场景下的开发效率,Google 首席软件工程师决定创造一种语言那就是 Go ...
- SpringBoot读取.yml配置文件最常见的两种方式-源码及其在nacos的应用
一.前言 我们在开发中会经常遇到一些可能会变的值,比如数据库的密码,一些关键链接的配置等等. 都需要我们写在配置文件中,这样可以把这些配置文件放到nacos上进行管理,修改nacos的配置,咱们发布的 ...
- 万物皆可集成系列:低代码释放用友U8+深度价值(2)—数据拓展应用
在上一篇内容我们介绍了如何利用低代码开发套件实现低代码应用与U8+系统的对接集成,本次给大家带来的是如何将用友U8+系统中的数据进行价值扩展和实际应用. 我们以生产物料齐套分析为例来说明如何利用低代码 ...
- 免杀手法-tcp套字节传递shellcode学习
免杀手法-tcp套字节传递shellcode学习
- scp复制发送文件夹到其他服务器上
简述scp: scp是secure copy的简写,是linux系统下基于ssh登陆进行安全的远程文件拷贝命令. 写法: scp [可选参数] 登录名@地址:源路径 目标路径. 举例:scp -r ...
- 使用.Net对图片进行裁剪、缩放、与加水印
图片的裁剪.缩放.与加水印,是任何系统经常要用到的功能,它们现已集成到IUtility工具中,使用十分简便.(具体代码将在文末给出,支持.NET/.NET Framework/.NET Core) 现 ...
- LibreCAD常用命令
目录 常见命令 常见命令 .text_center { text-align: center } \3cp>.text_left { } 动作命令 命令 绘制直线 相对坐标系 @长度<角度 ...
- noip2018提高组初赛试题
一.单项选择题(共 10 题,每题 2 分,共计 20 分: 每题有且仅有一个正确选项) \2. 下列属于解释执行的程序设计语言是( ). A. C B. C++ C. Pascal D. Pytho ...
- KingbaseES V8R3集群运维案例之---用户自定义表空间管理
案例说明: KingbaseES 数据库支持用户自定义表空间的创建,并建议表空间的文件存储路径配置到数据库的data目录之外.本案例复现了,当用户自定义表空间存储路径配置到data下时,出现的故障问 ...
- bulk collect 在KingbaseES和Oracle的使用方法比较
概述 BULK COLLECT 子句会批量检索结果,即一次性将结果集绑定到一个集合变量中,并从SQL引擎发送到PL/SQL引擎.通常可以在SELECT INTO.FETCH INTO以及RETURNI ...
