SpringBoot入门 (十四) Security安全控制
本文记录在SpringBoot使用SpringSecurity进行安全访问控制。
一 什么是Security
Spring Security是一个能够为基于Spring的企业应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案的安全框架。它提供了一组可以在Spring应用上下文中配置的Bean,充分利用了Spring IoC,DI(控制反转Inversion of Control ,DI:Dependency Injection 依赖注入)和AOP(面向切面编程)功能,为应用系统提供声明式的安全访问控制功能,减少了为企业系统安全控制编写大量重复代码的工作。
目前在我们项目中使用的是RBAC基于角色的权限访问控制(Role-Based Access Control),用户与角色关联,角色与权限相关联,用户通过角色间接的得到权限。关系如下图
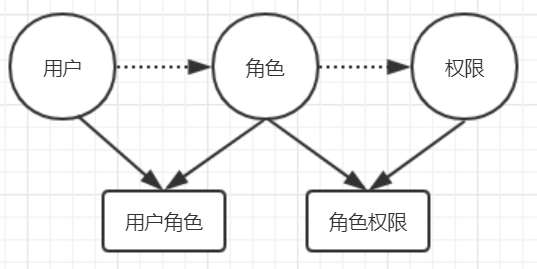
用户:权限的拥有者
角色:一些权限的集合
权限:操作的对象或资源
用户拥有某种角色,从而拥有了对资源的访问操作权限,在访问时SpringSecurity会对所有请求进行拦截,有权限的请求放行,否则拦截。
二 SpringBoot使用SpringSecurity
SpringBoot对SpringSecurity做了支持,要使用的话很方便,只需要引入相应的依赖(spring-boot-starter-security)就可以了。
示例代码主要完成以下功能:
1 系统的首页和登录页面及一些静态资源(CSS,JS),默认所有用户都可以访问;
2 除了第一步的,其他的所有资源路径访问均需要用户通过认证;
3 登录用户在页面只能看到拥有的角色所对应的权限(资源或操作);
修改pom.xml文件,添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
创建配置类,继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,重写一些配置方法
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/static/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().formLogin().loginPage("/login").permitAll()
.successForwardUrl("/main")
.failureUrl("/login")
.and().logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout").permitAll()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login");
} }
@EnableWebSecurity 用来说明开启安全认证
configure(HttpSecurity http) 配置相关访问操作的策略
.antMatchers("/", "/static/**").permitAll() 说明项目根路径/ 及static路径下的静态资源可以被匿名访问
.anyRequest().authenticated() 说明除了可以被匿名访问的资源外,其他所有资源的访问都要经过认证
.formLogin() 说明使用用户自定义的登录,如果不配置的话,会使用SpringSecurity默认提供的登录页面,/login 资源可以被匿名访问,登录成功后访问/main,失败后访问/login
.logout() 退出功能,SpringSecurity默认对/logout做了监控
用户登录就是对当前用户的身份信息做认证,我们需要对相应的方法做重写
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService()).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
指定使用自定义的实现用户认证及授权的userDetailsService和密码的加密器
密码加密器
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
认证与授权
@Bean
@Override
protected UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {
return new UserDetailsService(){
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//此处模拟数据库查询用户
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(2);
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword("$2a$10$GS71hBKk0MaykCWZC/eo2e7Y0Z77zDNCYE06xxAmW37gl850E6I4G");
user.setTelephone("13000000000");
user.setEmail("13000000000@qq.com"); if(user == null) throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User name:"+username+" not fount");
SecurityUser securityUser= new SecurityUser(user);
return securityUser;
}
};
}
/**
* 真正用于登录验证的安全用户(UserDetails)
*/
class SecurityUser extends User implements UserDetails {
/**
* 用户权限
*/
private Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority> permissions;
public Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority> getPermissions() {
return permissions;
}
public void setPermissions(Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority> permissions) {
this.permissions = permissions;
} public SecurityUser(User user){
if(user != null){
this.setUserId(user.getUserId());
this.setUsername(user.getUsername());
this.setPassword(user.getPassword());
this.setEmail(user.getEmail());
this.setTelephone(user.getTelephone());
Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority> gasSet = (Set<SimpleGrantedAuthority>) getAuthorities();
if(gasSet.size()>0){
this.setPermissions(gasSet);
}
}
} /**
* 获取用户权限
* @return
*/
@Override
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
//要返回的用户权限集合
Set<GrantedAuthority> permsSet = new HashSet<GrantedAuthority>();
//模拟数据库查询用户所拥有的角色对应的权限
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/user/add"));
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/user/edit"));
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/user/delete"));
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/user/list")); //区分不同用户拥有不同权限,admin用户加权限
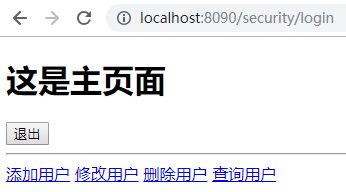
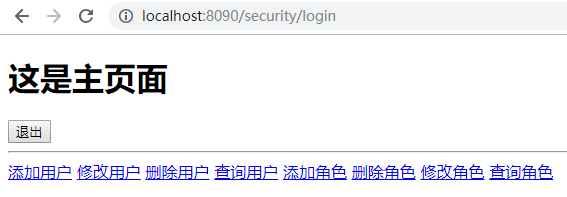
if (this.getUsername().equals("admin")) {
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/role/list"));
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/role/add"));
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/role/edit"));
permsSet.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("/role/delete"));
}
return permsSet;
} @Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
} @Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return true;
} @Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
} @Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}
控制器
@Controller
public class LoginController { /**
* 访问根路径时跳转到index页面
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/")
public String root(){
return "index";
} /**
* 跳转到登录页面
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login(){
return "login";
} /**
* 登录成功后访问
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/main")
public String main(){
return "main";
} }
index页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>index</title>
</head>
<body>
this is index page<br/>
<a th:href="@{/user/login}">登录</a>
</body>
</html>
登录页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>login</title>
</head>
<body>
this is login page
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<input type="text" th:id="username" th:name="username" value="" >
<input type="password" th:id="password" th:name="password" value="">
<input type="submit" th:value="提交" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
main页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="这是主页面">text</h1>
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post"><button th:type="submit" th:text="退出">text</button></form>
<hr/> <th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/user/add')">
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">添加用户</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/user/edit')">
<a th:href="@{/user/edit}">修改用户</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/user/delete')">
<a th:href="@{/user/delete}">删除用户</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/user/list')">
<a th:href="@{/user/list}">查询用户</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/role/add')">
<a th:href="@{/role/add}">添加角色</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/role/delete')">
<a th:href="@{/role/delete}">删除角色</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/role/edit')">
<a th:href="@{/role/edit}">修改角色</a>
</th:block>
<th:block sec:authorize="hasAuthority('/role/list')">
<a th:href="@{/role/list}">查询角色</a>
</th:block>
</body>
</html>
sec:authorize="hasAuthority('')" 说明当用户拥有此权限的时候,操作对用户可见,否则不可见
分别用user用户和admin登录后看到首页信息
SpringBoot入门 (十四) Security安全控制的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot入门(四)——自动配置
本文来自网易云社区 SpringBoot之所以能够快速构建项目,得益于它的2个新特性,一个是起步依赖前面已经介绍过,另外一个则是自动配置.起步依赖用于降低项目依赖的复杂度,自动配置负责减少人工配置的工 ...
- SpringBoot第二十四篇:应用监控之Admin
作者:追梦1819 原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanfei1819/p/11457867.html 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接! 引言 前一章(S ...
- Spring入门(十四):Spring MVC控制器的2种测试方法
作为一名研发人员,不管你愿不愿意对自己的代码进行测试,都得承认测试对于研发质量保证的重要性,这也就是为什么每个公司的技术部都需要质量控制部的原因,因为越早的发现代码的bug,成本越低,比如说,Dev环 ...
- SpringBoot | 第十四章:基于Docker的简单部署
前言 讲解了单元测试,本章节讲讲应用的部署吧.总体而言,在进行自动化部署时,基本都会用上Jenkins+Maven+Docker进行部署.本章节主要讲解使用Maven+Docker进行SpringBo ...
- [WebGL入门]十四,绘制多边形
注意:文章翻译http://wgld.org/.原作者杉本雅広(doxas),文章中假设有我的额外说明,我会加上[lufy:].另外,鄙人webgl研究还不够深入.一些专业词语,假设翻译有误,欢迎大家 ...
- SpringBoot笔记十四:消息队列
目录 什么是消息队列 消息队列的作用 异步通信 应用解耦 流量削峰 RabbitMQ RabbitMQ流程简介 RabbitMQ的三种模式 安装RabbitMQ RabbitMQ交换器路由和队列的创建 ...
- Android入门(十四)内容提供器-实现跨程序共享实例
原文链接:http://www.orlion.ga/661/ 打开SQLite博文中创建的 DatabaseDemo项目,首先将 MyDatabaseHelper中使用 Toast弹出创建数据库成功的 ...
- SpringBoot入门教程(四)MyBatis generator 注解方式和xml方式
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL.存储过程以及高级映射.MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集.MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML ...
- SpringBoot实战(十四)之整合KafKa
本人今天上午参考了不少博文,发现不少博文不是特别好,不是因为依赖冲突问题就是因为版本问题. 于是我结合相关的博文和案例,自己改写了下并参考了下,于是就有了这篇文章.希望能够给大家帮助,少走一些弯路. ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu 开机自启(2B的经历)
上午写了很细致的开机自启说明文档(需打开terminal进行输出认证).睡了一下午,回来楼主说,联想PM要用Ubuntu Server 当服务器,必须用命令行实现.. 连续各种百度谷歌,看了N多文档, ...
- SPRING框架中ModelAndView、Model、ModelMap区别及详细分析
转载内容:http://www.cnblogs.com/google4y/p/3421017.html 1. Model Model 是一个接口, 其实现类为ExtendedModelMap,继承了M ...
- 《mysql必知必会》学习_第八章_20180730_欢
第八章学习LIKE操作符,百分百(%)通配符,下划线(_)通配符 P47 select prod_id,prod_name from products where prod_name LIKE 'je ...
- springJDBC和SpringJDBCTemplate解决方案探究
先来看一个纯JDBC的例子,体会一下springJDBC和SpringJDBCTemplate两者的区别 一个Customer类 package com.mkyong.customer.model; ...
- UIKit Dynamic主题学习笔记
1.重力效果:UIGravityBehavior @IBOutlet weak var frogImage: UIImageView! //创建一个关联到view的动画(必须为全局变量) lazy v ...
- 前端开发 - JavaScript 词法分析
JavaScript代码运行前有一个类似编译的过程即词法分析,词法分析主要有三个步骤: 1.分析函数的参数 2.分析函数的变量声明 3.分析函数的函数声明表达式 具体步骤如下: 函数在运行的瞬间,生成 ...
- TaskCreationOptions.LongRunning 运行比可用线程数更多的任务
最近在学WebSocket,服务端需要监听多个WebSocket客户端发送的消息. 开始的解决方法是每个WebSocket客户端都添加一个线程进行监听,代码如下: /// <summary> ...
- springBoot2 基础语法
请求响应 request对象 request 对象其实是HttpServletRequest 类型, 通过它可以获取请求相关的一切信息, 包含请求信息 . 以及请求参数 ,甚至可以当成往里面存储数据[ ...
- JQuery的页面操作
window.location = "http://www.xxxxxxxx.net" 跳转后有后退功能 其实应该是 window.location.hrefwindow.loca ...
- haproxy监测页面参数简释
Queue Cur: current queued requests //当前的队列请求数量Max:max queued requests //最大的队列请求数量Limit: ...
