003-Spring4 扩展分析-spring类初始化@PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method、ApplicationContext、BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
一、spring类初始化@PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method
InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的子类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法。
示例
<bean id="myInitializingBean" class="com.paic.phssp.springtest.init.MyInitializingBean" init-method="testInit"></bean>
bean
/**
* 继承InitializingBean接口的类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法
*/
//@Component
public class MyInitializingBean implements InitializingBean { public MyInitializingBean() {
System.out.println("1MyInitializingBean....");
} @Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("3ceshi MyInitializingBean>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
} @PostConstruct //功能上近似init-method,但加载时机不同
public void test(){
System.out.println("2PostConstruct >>>>>>>>>>>>");
} public void testInit(){
System.out.println("4ceshi init-method");
}
}
结果:
1MyInitializingBean....
2PostConstruct >>>>>>>>>>>>
3ceshi MyInitializingBean>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
4ceshi init-method
说明:
通过上述输出结果,三者的先后顺序:Constructor > @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method
1.1、 InitializingBean > init-method 执行时机
spring初始化bean过程
002-创建型-03-单例模式(Singleton)【7种】、spring单例及原理 spring 单例
通过查看spring的加载bean的源码类(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory)可看出
如使用getBean方式创建:getBean→doGetBean→createBean→doCreateBean→initializeBean→invokeInitMethods
查看AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.invokeInitMethods
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable { boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
} if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
说明:
1.2、@PostConstruct加载过程
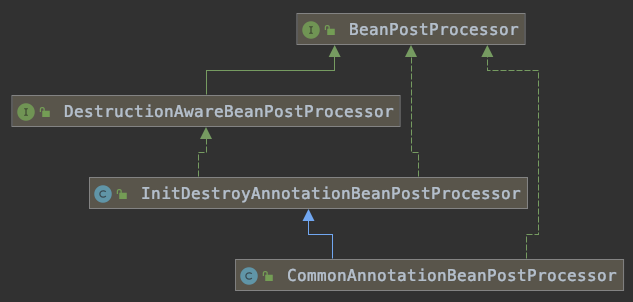
源码:InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
try {
metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);//利用反射,执行注解方法
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex);
}
return bean;
}
findLifecycleMetadata
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {
// Happens after deserialization, during destruction...
return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);
}
return metadata;
}
}
return metadata;
}
buildLifecycleMetadata
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>();
List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
});
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods);
}
判断指定类型注解
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
方法:buildLifecycleMetadata(),判断是否是指定的注解类型,而这个属性,在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class构造方法中被初始化为PostConstruct。
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3);
setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class);
setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class);
ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext");
}
1.3、 @PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method 执行时机
查看AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的InitializingBean 方法
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
查看标红的第一步applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization,第二部是 invokeInitMethods 【先执行了 ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(),进而执行了init-method自定义invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);】
--> 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法 (@PostConstruct在此)
--> 调用bean实例的初始化方法(invokeInitMethods-> InitializingBean->init-method)
--> 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
DisposableBean结束:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaozhuanfeng/p/10415794.html
二、依赖注入ApplicationContext
方法一、@Autowired
创建一个User,内部使用ApplicationContext
@Component
public class User {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public void show() {
System.out.println("User:"+applicationContext.getClass());
}
}
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.lhx.spring.kuozhan");
System.out.println(context.getBean("user"));
// System.out.println(context.getBean("createUser"));
User bean = (User) context.getBean("user");
bean.show();
context.close();
}
方法二、实现ApplicationContextAware接口
@Component
public class Book implements ApplicationContextAware{
private ApplicationContext ApplicationContext; @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.ApplicationContext=applicationContext;
} public void show() {
System.out.println("book:"+ApplicationContext.getClass());
}
}
1)内部原理
接口BeanPostProcessor,内部方法,每一个bean初始化都会被执行
bean初始化属性完毕后,即依赖装配完成之后,postProcessBeforeInitialization
bean初始化在属性设置之后,Bean init之后触发的,postProcessAfterInitialization
作用:回调,返回代理对象等
如在postProcessBeforeInitialization中返回其他代理对象。
构建一个默认实现【两个方法不能返回null】
package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class EchoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("--------------postProcessBeforeInitialization-------------" + "bean" + bean.getClass());
return bean;
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("--------------postProcessBeforeInitialization-------------" + "bean" + bean.getClass());
return bean;
} }
2)示例
User类
@Component
public class User {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Autowired
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
} public void init() {
System.out.println("User init"); } public void show() {
System.out.println("User:" + applicationContext.getClass());
}
}
UserConfig类
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init")
public User createUser() {
return new User();
}
}
调用
System.out.println(context.getBean("user"));
查看日志
User Set属性
--------------postProcessBeforeInitialization-------------beanclass com.lhx.spring.kuozhan.User
User init
--------------postProcessAfterInitialization-------------beanclass com.lhx.spring.kuozhan.User
3)自行实现ApplicationContextAware,这里起名为SpringContextAware,逻辑参考ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
public interface SpringContextAware {
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext);
}
编写ContextBeanPostProcessor
package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class ContextBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof SpringContextAware) {
SpringContextAware sca = (SpringContextAware) bean;
sca.setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
}
return bean;
} @Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return bean;
} }
实际类使用
package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class Dog implements SpringContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
} public void show() {
System.out.println("Dog:" + applicationContext.getClass());
}
}
使用:
context.getBean(Dog.class).show();
4)查看ApplicationContextAware内部实现:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext→GenericApplicationContext→AbstractApplicationContext
找打refresh方法,prepareBeanFactory,
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor内部
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor
方法三、Spring 4.3 新特性,构造方法直接添加,有局限性,与构造方法直接相关
@Component
public class Bank {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
//spring 4.3 提供,与构造方法调用有关
public Bank(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext=applicationContext;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("book:"+applicationContext.getClass());
}
}
二、容器扩展
2.1、BeanFactoryPostProcessor
在beanFactory之后,BeanFactoryPostProcessor容器初始化之后,只初始化一次,先于所有容器以及BeanPostProcessor
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
示例代码扩展2
源码:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext→GenericApplicationContext→AbstractApplicationContext
找打refresh方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
2.2、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
注册一个Bean到Spring容器中,类似标注了@Componment
示例
新建一个Person类
public class Person {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + "]";
}
}
MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现
package com.lhx.spring.kuozhan2; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor { @Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
BeanDefinitionBuilder rootBeanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(Person.class);
rootBeanDefinition.addPropertyValue("name", "admin" + i);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("person" + i, rootBeanDefinition.getBeanDefinition());
} } }
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.lhx.spring.kuozhan2");
System.out.println(context.getBean("person1"));
context.getBeansOfType(Person.class).values().forEach(System.out::println);
context.close();
}
当然在使用
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.lhx.spring.kuozhan2");
使用context也可以注入
context.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
beanDefinition定义可以使用:BeanDefinitionBuilder rootBeanDefinition = BeanDefinitionBuilder.rootBeanDefinition(Person.class);
代码地址:https://github.com/bjlhx15/spring-boot.git
003-Spring4 扩展分析-spring类初始化@PostConstruct > InitializingBean > init-method、ApplicationContext、BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的更多相关文章
- spring bean初始化及销毁你必须要掌握的回调方法
spring bean在初始化和销毁的时候我们可以触发一些自定义的回调操作. 初始化的时候实现的方法 1.通过java提供的@PostConstruct注解: 2.通过实现spring提供的Initi ...
- Spring Boot(七)扩展分析
前面的章节在分析SpringBoot启动过程中,我们发现SpringBoot使用Spring框架提供的SpringFactoriesLoader这个类,实现检索META-INF/spring.fact ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(一):SpringApplication类初始化过程
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 余下的初始化工作
1. 简介 本篇文章是"Spring IOC 容器源码分析"系列文章的最后一篇文章,本篇文章所分析的对象是 initializeBean 方法,该方法用于对已完成属性填充的 bea ...
- 分析java类的初始化契机
分析java类的静态成员变量初始化先于非静态成员变量 依上图中当class字节码文件被jvm虚拟机加载到内存中依次经过 连接 验证:对字节码进行验证 准备:给静态变量分配内存并赋予变量类型各自的默 ...
- JAVA基础加强(张孝祥)_类加载器、分析代理类的作用与原理及AOP概念、分析JVM动态生成的类、实现类似Spring的可配置的AOP框架
1.类加载器 ·简要介绍什么是类加载器,和类加载器的作用 ·Java虚拟机中可以安装多个类加载器,系统默认三个主要类加载器,每个类负责加载特定位置的类:BootStrap,ExtClassLoader ...
- spring框架中@PostConstruct的实现原理
在spring项目经常遇到@PostConstruct注解,首先介绍一下它的用途: 被注解的方法,在对象加载完依赖注入后执行. 此注解是在Java EE5规范中加入的,在Servlet生命周期中有一定 ...
- 🙈羞,Spring Bean 初始化/销毁竟然有这么多姿势
文章来源:http://1t.click/bfHN 一.前言 日常开发过程有时需要在应用启动之后加载某些资源,或者在应用关闭之前释放资源.Spring 框架提供相关功能,围绕 Spring Bean ...
- Spring IOC初始化深度解析
1.前言 本文是基于JAVA配置方法对Spring IOC进行分析,掌握Spring IOC初始化流程对于我们更好的使用Spring.学习Spring还是很有帮助的,本文所使用的的Spring版本为5 ...
随机推荐
- kill命令和killall命令
kill命令用于终止指定的进程(terminate a process),是Unix/Linux下进程管理的常用命令.通常,我们在需要终止某个或某些进程时,先使用ps/pidof/pstree/top ...
- CentOS7.x卸载与安装MySQL5.7的操作过程以及编码格式的修改
一.MySQL5.7的卸载 1.1yum方式查看yum是否安装过mysql cd yum list installed mysql* 如或显示了列表,说明系统中有MySQL 如上显示,我已经安装了my ...
- 异步消息处理机制相关面试问题-handlerThread面试问题详解
handlerThread产生背景: 开启Thread子线程进行耗时操作,多次创建和销毁线程是很耗系统资源的. handlerThread是什么? handler + thread + looper ...
- HNOI 世界树 虚树
//virtual tree /*Huyyt*/ #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a)) #defin ...
- mysql 导入sqlserver数据库
#mysql 导入sqlserver数据库 EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'sjkxb00', @srvproduct=N'MySQL', ...
- 201871010101-陈来弟《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十七周学习总结
实验十七 线程同步控制 实验时间 2018-12-10 第一部分:理论知识 1.多线程并发执行中的问题 ◆多个线程相对执行的顺序是不确定的. ◆线程执行顺序的不确定性会产生执行结果的不确定性. ◆在 ...
- ${filename}用法二:
假设:filename=/dir1/dir2/dir3/my.filename.txt 1.单一符号是最小匹配﹔两个符号是最大匹配. ${filename::}:提取最左边的5个字节:/dir1 ${ ...
- webpack 配置文件说明
var path = require("path"); var webpack = require("webpack"); var HtmlwebpackPlu ...
- 题解 【POJ1157】LITTLE SHOP OF FLOWERS
先把题目意思说一下: 你有F束花,编号为\(1\)~\(F\)(\(1<=F<=100\)),\(V\)个花瓶,编号为\(1\) ~\(V\)(\(1<=V<=100\)), ...
- Babel 转译 class 过程窥探--------引用
// Shape 类function Shape(id, x, y) { this.id = id; this.setLocation(x, y);}// 设置坐标的原型方法Shape.p ...
