Python之操作RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统。他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议。
MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法。应用程序通过读写出入队列的消息(针对应用程序的数据)来通信,而无需专用连接来链接它们。消 息传递指的是程序之间通过在消息中发送数据进行通信,而不是通过直接调用彼此来通信,直接调用通常是用于诸如远程过程调用的技术。排队指的是应用程序通过队列来通信。队列的使用除去了接收和发送应用程序同时执行的要求。
RabbitMQ安装
epel源安装
现在服务器安装epel源,为什么选择epel源呢?强烈推荐大家使用epel源,epel是社区强烈打造的免费开源发行软件包版本库,系统包含大概有1万多个软件包,163和sohu的镜像是没有这么多软件了.
首选确认你的版本号,然后才能选择相应的epel,命令如下
[root@cobbler ~]# cat /etc/issue
CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
Centos6*源安装:
rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
验证是否安装成功,执行如下命令:
[root@cobbler ~]# yum repolist
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, security
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.yun-idc.com
* epel: ftp.riken.jp
* extras: mirrors.yun-idc.com
* updates: mirrors.yun-idc.com
repo id repo name status
base CentOS-6 - Base 6,696
epel Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 6 - x86_64 12,155
extras CentOS-6 - Extras 62
updates CentOS-6 - Updates 263
repolist: 19,176
看到epel,说明安装成功了,可以看到epel有1万2千155个包.有了他你不在需要tar、configure、make等等繁琐的动作了。使用yum即可搞定一切.
还有一个好处,如果你用自动化运维,使用saltstack puppet ansilble 等等统一配置管理时,都一个重要的要求是统一标准化,我们用epel源,直接一条命令就能安装了,不是很爽么?
安装RabbitMQ
安装erlang
$ yum -y install erlang
安装RabbitMQ
$ yum -y install rabbitmq-server
Python中安装API
pip install pika
or
easy_install pika
Python操作RabbitMQ
基本用法
发布者端:
import pika
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.4.193'))
channel=connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='cc') #如果有cc的队列,略过;如果没有,创建cc的队列
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',routing_key='cc',body='hello!world!!!')
print("[x] sent 'hello,world!'")
connection.close()
接收端:
import pika
#创建一个连接对象,对象中绑定了rabbitmq的IP
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.4.193'))
#创建一个频道对象
channel=connection.channel()
#频道中声明指定queue,如果MQ中没有指定queue就创建,如果有,则略过
channel.queue_declare(queue='cc')
#定义回调函数
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print('[x] Recieved %r'%body)
# channel.close()
#no_ack=Fales:表示消费完以后不主动把状态通知rabbitmq,callback:回调函数,queue:指定队列
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue='cc',no_ack=True)
# channel.basic_consume(callback,queue='cc')
print('[*] Waiting for msg')
channel.start_consuming()
acknowledgment 消息不丢失
no-ack = False,如果消费者遇到情况(its channel is closed, connection is closed, or TCP connection is lost)挂掉了,那么,RabbitMQ会重新将该任务添加到队列中。
- 回调函数中的
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag) - basic_comsume中的
no_ack=False
消息接收端应该这么写:
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.4.193'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='cc')
# 定义回调函数
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print('[x] Recieved %r' % body)
# channel.close()
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
# no_ack=Fales:表示消费完以后不主动把状态通知rabbitmq
channel.basic_consume(callback, queue='cc',
no_ack=False)
print('[*] Waiting for msg')
channel.start_consuming()
durable 消息不丢失
消息生产者端发送消息时挂掉了,消费者接消息时挂掉了,以下方法会让RabbitMQ重新将该消息添加到队列中:
- 回调函数中的
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag),消费端需要做的 - basic_comsume中的
no_ack=False,消费端需要做的 - 发布消息端的basic_publish添加参数
properties=pika.BasicProperties(delivery_mode=2),生产者端需要做的
消息生产者端:
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.4.193'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='cc') # 如果有cc的队列,略过;如果没有,创建cc的队列
channel.basic_publish(exchange='',
routing_key='cc',
body='hello!world!!!',
properties=pika.BasicProperties(delivery_mode=2)) #消息持久化
print("[x] sent 'hello,world!'")
connection.close()
消息消费者端:
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.4.193'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='cc')
# 定义回调函数
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print('[x] Recieved %r' % body)
# channel.close()
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
# no_ack=Fales:表示消费完以后不主动把状态通知rabbitmq
channel.basic_consume(callback, queue='cc',
no_ack=True)
print('[*] Waiting for msg')
channel.start_consuming()
消息获取顺序
默认消息队列里的数据是按照顺序被消费者拿走,例如:消费者1去队列中获取 奇数 序列的任务,消费者2去队列中获取 偶数 序列的任务。但有大部分情况下,消息队列后端的消费者服务器的处理能力是不相同的,这就会出现有的服务器闲置时间较长,资源浪费的情况,那么,我们就需要改变默认的消息队列获取顺序!
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1) 表示谁来谁取,不再按照奇偶数排列,这是消费者端需要做的
消费者端如下:
import pika
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.4.193'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.queue_declare(queue='cc')
# 定义回调函数
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print('[x] Recieved %r' % body)
# channel.close()
ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)
channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1) #改变默认获取顺序,谁来谁取
# no_ack=Fales:表示消费完以后不主动把状态通知rabbitmq
channel.basic_consume(callback, queue='cc',
no_ack=True)
print('[*] Waiting for msg')
channel.start_consuming()
发布和订阅
发布订阅和简单的消息队列区别在于,发布订阅会将消息发送给所有的订阅者,而消息队列中的数据被消费一次便消失。所以,RabbitMQ实现发布和订阅时,会为每一个订阅者创建一个队列,而发布者发布消息时,会将消息放置在所有相关队列中。
关键字:exchange type = fanout
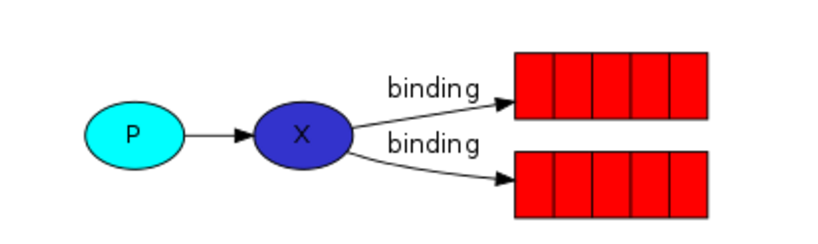
消息生产者:
import pika
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.11.131'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs_fanout',type='fanout')
msg='456'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='logs_fanout',routing_key='',body=msg)
print('开始发送:%s'%msg)
connection.close()
消息消费者:
import pika
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.11.131'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs_fanout',type='fanout')
#随机创建队列
result=channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name=result.method.queue
#绑定相关队列名称
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs_fanout',queue=queue_name)
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print('[x] %r'%body)
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue=queue_name,no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
关键字发送
之前事例,发送消息时明确指定某个队列并向其中发送消息,RabbitMQ还支持根据关键字发送,即:队列绑定关键字,发送者将数据根据关键字发送到消息exchange,exchange根据 关键字 判定应该将数据发送至指定队列。
关键字:exchange type = direct,默认模式也为此模式.
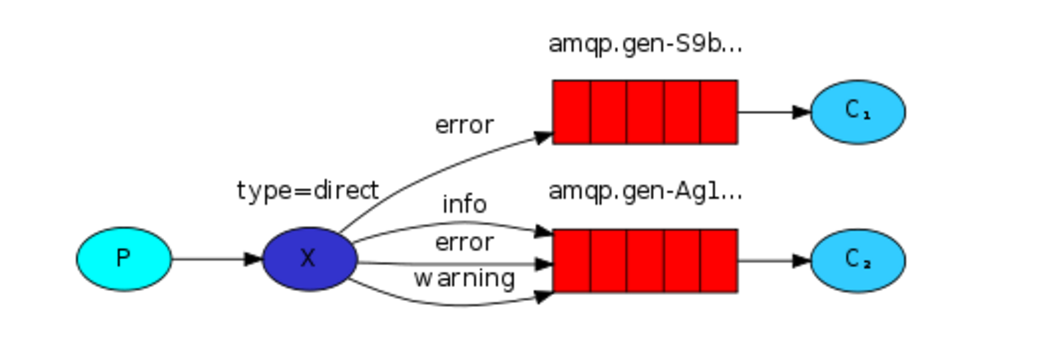
消息生产者端:
import pika
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.11.131'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs_direct_test1',type='direct')
serverity='error'
msg='123'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='logs_direct_test1',routing_key=serverity,body=msg)
print('开始发送:%r:%r'%(serverity,msg))
connection.close()
消息消费者1:
import pika
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.11.131'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs_direct_test1',type='direct')
#随机创建队列
result=channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name=result.method.queue
serverities=['error','info','warning',]
for serverity in serverities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs_direct_test1',queue=queue_name,routing_key=serverity)
print('[***] 开始接受消息!')
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print('[x] %r:%r'%(method.routing_key,body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue=queue_name,no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
消息消费者2:
import pika
connection=pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='192.168.11.131'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='logs_direct_test1',type='direct')
#随机创建队列
result=channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name=result.method.queue
serverities=['error',]
for serverity in serverities:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='logs_direct_test1',queue=queue_name,routing_key=serverity)
print('[***] 开始接受消息!')
def callback(ch,method,properties,body):
print('[x] %r:%r'%(method.routing_key,body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,queue=queue_name,no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
模糊匹配
在topic类型下,可以让队列绑定几个模糊的关键字,之后发送者将数据发送到exchange,exchange将传入”路由值“和 ”关键字“进行匹配,匹配成功,则将数据发送到指定队列。
关键字:exchange type = topic
- 表示只能匹配 一个 单词
- # 表示可以匹配0个或多个单词
发送者路由值 队列中
old.boy.python old.* -- 不匹配
old.boy.python old.# -- 匹配
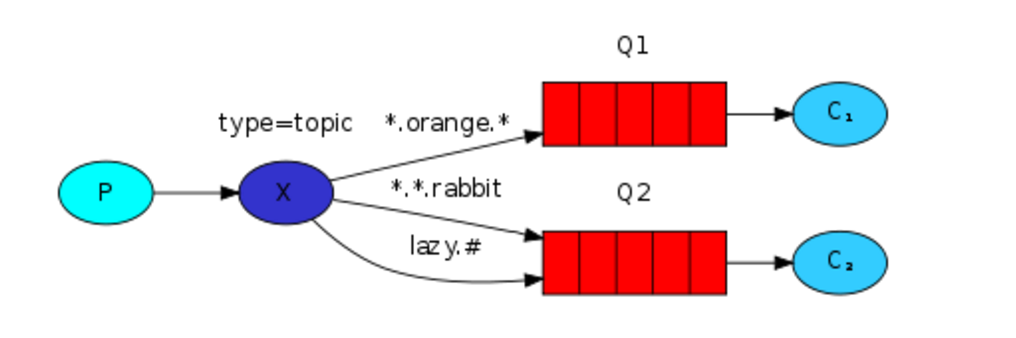
消息生产者:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic')
routing_key = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else 'anonymous.info'
message = ' '.join(sys.argv[2:]) or 'Hello World!'
channel.basic_publish(exchange='topic_logs',
routing_key=routing_key,
body=message)
print(" [x] Sent %r:%r" % (routing_key, message))
connection.close()
消息消费者:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import pika
import sys
connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(
host='localhost'))
channel = connection.channel()
channel.exchange_declare(exchange='topic_logs',
type='topic')
result = channel.queue_declare(exclusive=True)
queue_name = result.method.queue
binding_keys = sys.argv[1:]
if not binding_keys:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s [binding_key]...\n" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
for binding_key in binding_keys:
channel.queue_bind(exchange='topic_logs',
queue=queue_name,
routing_key=binding_key)
print(' [*] Waiting for logs. To exit press CTRL+C')
def callback(ch, method, properties, body):
print(" [x] %r:%r" % (method.routing_key, body))
channel.basic_consume(callback,
queue=queue_name,
no_ack=True)
channel.start_consuming()
Python之操作RabbitMQ的更多相关文章
- Python 【第六章】:Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载.它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提高动态.数据库驱动网站的速度 ...
- Python操作RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ介绍 RabbitMQ是一个由erlang开发的AMQP(Advanced Message Queue )的开源实现的产品,RabbitMQ是一个消息代理,从“生产者”接收消息并传递消 ...
- Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载.它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提高动态.数据库驱动网站的速度 ...
- 十一天 python操作rabbitmq、redis
1.启动rabbimq.mysql 在""运行""里输入services.msc,找到rabbimq.mysql启动即可 2.启动redis 管理员进入cmd, ...
- Python之路【第九篇】:Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
Python之路[第九篇]:Python操作 RabbitMQ.Redis.Memcache.SQLAlchemy Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用 ...
- python - 操作RabbitMQ
python - 操作RabbitMQ 介绍 RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统.他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议.MQ全称为Mess ...
- 文成小盆友python-num12 Redis发布与订阅补充,python操作rabbitMQ
本篇主要内容: redis发布与订阅补充 python操作rabbitMQ 一,redis 发布与订阅补充 如下一个简单的监控模型,通过这个模式所有的收听者都能收听到一份数据. 用代码来实现一个red ...
- Python之路第十二天,高级(4)-Python操作rabbitMQ
rabbitMQ RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统.他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议. MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(M ...
- python操作---RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是一个在AMQP基础上完整的,可复用的企业消息系统.他遵循Mozilla Public License开源协议. MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序 ...
随机推荐
- python excel基本操作
#coding=utf-8 ''' excel基本操作 ''' from openpyxl import Workbook wb=Workbook() ws1=wb.create_sheet('sh1 ...
- Python一些细节
1.python set() dict() 有序问题,不同版本之间的差异,与Java/C++的对比 https://www.cnblogs.com/niuxichuan/p/11608386.html ...
- Procomm Plus 与ASPECT脚本语言在基于远程终端设备上的测试应用
产测 ---------------------------------------------------- 原文:http://www.bixuanzl.com/20180801/1084478. ...
- C#串口图片传输以及对串口缓冲区的简单理解
第一次接触串口,写点东西加深自己对串口的印象: 通过参考一些网上的实例,我明白了串口怎么简单的进行通信交流,但是我所需要的还是图片等大文件在串口中的传输,串口传输是通过二进制位进行单位传输的,所以传输 ...
- Java8-Lock-No.04
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import ...
- 为什么添加了@Aspect 还要加@Component(转)
官方文档中有写: You may register aspect classes as regular beans in your Spring XML configuration, or autod ...
- springboot2.0入门(九)-- springboot使用mybatis-generator自动代码生成
一.配置文件引入 插件引入,引入 <plugin> <groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId> <artifactId& ...
- paramiko多线程远程执行命令
import paramiko import sys import getpass import threading import os def rcmd(host=None, port=22, us ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 72 (Rated for Div. 2) C题
C. The Number Of Good Substrings Problem Description: You are given a binary string s (recall that a ...
- 详解Kafka: 大数据开发最火的核心技术
详解Kafka: 大数据开发最火的核心技术 架构师技术联盟 2019-06-10 09:23:51 本文共3268个字,预计阅读需要9分钟. 广告 大数据时代来临,如果你还不知道Kafka那你就真 ...
