树及其衍生算法(Trees and tree algorithms)
1,二叉树(Binary tree)
二叉树:每一个节点最多两个子节点,如下图所示:

相关概念:节点Node,路径path,根节点root,边edge,子节点 children,父节点parent,兄弟节点sibling, 子树subtree,叶子节点leaf node, 度level,树高hight
节点Node:
路径path:从一个节点到拧一个节点间的边
根节点root,
边edge:节点间的连线
子节点 children,
父节点parent,
兄弟节点sibling,
子树subtree,
叶子节点leaf node,
度level:从当前节点到根节点的路径中边的数量
高度 hight:树中所有节点的最大level
二叉树可以通过多级列表的形式实现,多级列表形式如下,根节点r,有两个子节点a , b,且a, b节点没有子节点。
mytree =[ r,
[ a, [ ], [ ] ], [ b, [ ], [ ] ]
]
python实现代码如下:
#coding:utf-8 #多级列表实现
def binaryTree(r):
return [r,[],[]] #root[]为根节点,root[1]左子树,root[2]右子树 def insertLeftTree(root,newbranch):
t = root.pop(1)
if len(t)>1:
root.insert(1, [newbranch, t, []])
else:
root.insert(1,[newbranch, [], []])
return root def insertRightTree(root,newbranch):
t = root.pop(2)
if len(t)>1:
root.insert(2, [newbranch, [], t])
else:
root.insert(2,[newbranch, [], []])
return root
def getRootVal(root):
return root[0] def setRootVal(root,val):
root[0]= val def getLeftChildren(root):
return root[1] def getRightChildren(root):
return root[2] r = binaryTree(3)
insertLeftTree(r,4)
insertLeftTree(r,5)
insertRightTree(r,6)
insertRightTree(r,7)
l = getLeftChildren(r)
print(l) setRootVal(l,9)
print(r)
insertLeftTree(l,11)
print(r)
print(getRightChildren(getRightChildren(r)))
多级列表形式
二叉树可以通过节点的形式实现,如下所示:

python实现代码如下:
class BinaryTree(object):
def __init__(self,value):
self.key = value
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None def insertLeft(self,newNode):
if self.leftChild != None:
temp = BinaryTree(newNode)
temp.leftChild = self.leftChild
self.leftChild = temp
else:
self.leftChild = BinaryTree(newNode) def insertRight(self,newNode):
if self.rightChild != None:
temp = BinaryTree(newNode)
temp.rightChild= self.rightChild
self.rightChild = temp
else:
self.rightChild = BinaryTree(newNode) def getRootVal(self):
return self.key def setRootVal(self,value):
self.key = value def getLeftChild(self):
return self.leftChild def getRightChild(self):
return self.rightChild
节点形式
2,二叉树的应用
2.1 解析树(parse tree)
解析树常用于表示真实世界的结构表示,如句子和数学表达式。如下图是((7+3)*(5-2))的解析树表示,根据解析树的层级结构,从下往上计算,能很好的代替括号的表达式中括号的作用
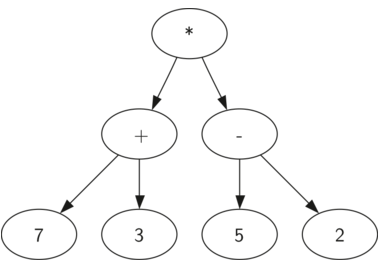
将一个全括号数学表达式转化为解析树的过程如下:
遍历表达式:
1,若碰到“(”,为当前节点插入左节点,并移动到左节点
2,若碰到 + ,- ,* , /,设置当前节点的值为该符号,并为当前节点插入右节点,并移动到右节点
3,若碰到数字,设置当前节点的值为该数字,并移动到其父节点
4,若碰到“)”,移动到当前节点的父节点
python实现代码如下:(Stack 参见数据结构之栈)
from stackDemo import Stack #参见数据结构之栈 def buildParseTree(expstr):
explist = expstr.split()
s = Stack()
t = BinaryTree('')
s.push(t)
current = t
for token in explist:
#token = token.strip()
if token =='(':
current.insertLeft('')
s.push(current)
current = current.getLeftChild()
elif token in ['*','/','+','-']:
current.setRootVal(token)
current.insertRight('')
s.push(current)
current = current.getRightChild()
elif token not in ['(','*','/','+','-',')']:
current.setRootVal(token)
current = s.pop()
elif token==')':
current = s.pop()
else:
raise ValueError
return t t = buildParseTree("( ( 10 + 5 ) * 3 )")
构造解析树
计算解析树:数学表达式转化为解析树后,可以对其进行计算,python代码如下:
import operator
def evaluate(parseTree):
operators={'+':operator.add,'-':operator.sub,'*':operator.mul,'/':operator.div }
rootval = parseTree.getRootVal()
left = parseTree.getLeftChild()
right = parseTree.getRightChild() if left and right:
fn = operators[rootval]
return fn(evaluate(left),evaluate(right))
else:
return parseTree.getRootVal()
计算解析树
中序遍历解析树,可以将其还原为全括号数学表达式,python代码如下:
#解析树转换为全括号数学表达式
def printexp(tree):
val = ''
if tree:
val = '('+printexp(tree.getLeftChild())
val = val +str(tree.getRootVal())
val = val +printexp(tree.getRightChild())+')'
if tree.getLeftChild()==None and tree.getRightChild()==None:
val = val.strip('()')
return val t = buildParseTree("( ( 10 + 5 ) * 3 )")
exp = printexp(t)
print exp
3,树的遍历
树的遍历包括前序遍历(preorder),中序遍历(inorder)和后序遍历(postorder).
前序遍历:先访问根节点,再访问左子树,最后访问右子树(递归),python代码实现如下:
def preorder(tree):
if tree:
print tree.getRootVal()
preorder(tree.getLeftChild())
preorder(tree.getRightChild()) #定义在类中的前序遍历
# def preorder(self):
# print self.key
# if self.leftChild:
# self.leftChild.preorder()
# if self.rightChild:
# self.rightChild.preorder()
preorder
中序遍历:先访问左子树,再访问根节点,最后访问右子树(递归),python代码实现如下:
#中序遍历inorder
def inorder(tree):
if tree:
preorder(tree.getLeftChild())
print tree.getRootVal()
preorder(tree.getRightChild())
后续遍历:先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问根节点,python代码实现如下:
def postorder(tree):
if tree :
postorder(tree.getLeftChild())
postorder(tree.getRightChild())
print(tree.getRootVal())
树的层次遍历,树的深度,前序遍历和中序遍历构建树,判断两棵树是否相同:
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, data, leftchild=None, rightchild=None):
self.data = data
self.leftchild = leftchild
self.rightchild = rightchild
def preorder(self):
print self.data
if self.leftchild:
self.leftchild.preorder()
if self.rightchild:
self.rightchild.preorder()
def midorder(self):
if self.leftchild:
self.leftchild.preorder()
print self.data
if self.rightchild:
self.rightchild.preorder()
t1 = TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode()),TreeNode()),TreeNode(,TreeNode(),TreeNode())) # #层次遍历
def lookup(root):
row=[root]
while row:
print [x.data for x in row]
temp=[]
for item in row:
if item.leftchild:
temp.append(item.leftchild)
if item.rightchild:
temp.append(item.rightchild)
row = temp
lookup(t1) #树的深度
def get_height(root):
if root ==None:
return
return max(get_height(root.leftchild),get_height(root.rightchild))+
print(get_height(t1)) #根据前序遍历和中序遍历构建树
pre=[,,,,,,,] # t1.preorder()
mid=[,,,,,,,] # t1.midorder()
def build(pre,mid):
if not pre:
return None
node = TreeNode(pre[])
index = mid.index(pre[])
node.leftchild = build(pre[:index+],mid[:index])
node.rightchild = build(pre[index+:],mid[index+:])
return node
tt = build(pre,mid)
tt.preorder() #判断两棵树是否相同
t1 = TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode()),TreeNode()),TreeNode(,TreeNode(),TreeNode()))
t2 = TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode()),TreeNode()),TreeNode(,TreeNode(),TreeNode()))
t3 = TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode()),TreeNode()),TreeNode(,TreeNode(),TreeNode()))
def is_same_tree(t1,t2):
if t1==None and t2==None:
return True
elif t1 and t2:
return is_same_tree(t1.leftchild,t2.leftchild) and t1.data==t2.data and is_same_tree(t1.rightchild,t2.rightchild)
else:
return False
print(is_same_tree(t1,t2))
print(is_same_tree(t1,t3))
morris 遍历:上面的前中后序遍历方法都使用了递归,需要额外的空间,morris 遍历为非递归,空间复杂度为O(1), 当二叉树数据量庞大时更加适用
Morris遍历算法的步骤如下:(中序遍历)
1, 根据当前节点,找到其前序节点,如果前序节点的右孩子是空,那么把前序节点的右孩子指向当前节点,然后进入当前节点的左孩子。
2, 如果当前节点的左孩子为空,打印当前节点,然后进入右孩子。
3,如果当前节点的前序节点其右孩子指向了它本身,那么把前序节点的右孩子设置为空,打印当前节点,然后进入右孩子。
前序节点:给定某个节点,在中序遍历中,直接排在它前面的节点,我们称之为该节点的前序节点
前序节点寻找算法:
如果该节点有左孩子,那么从左孩子开始,沿着左孩子的右孩子指针一直向下走到底,得到的节点就是它的前序节点
如果左孩子的右节点指针是空,那么左孩子就是当前节点的前序节点
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, data, leftchild=None, rightchild=None):
self.data = data
self.leftchild = leftchild
self.rightchild = rightchild
def preorder(self):
print self.data
if self.leftchild:
self.leftchild.preorder()
if self.rightchild:
self.rightchild.preorder()
def midorder(self):
if self.leftchild:
self.leftchild.midorder()
print self.data
if self.rightchild:
self.rightchild.midorder()
t1 = TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode(,TreeNode()),TreeNode()),TreeNode(,TreeNode(),TreeNode())) #morris遍历
def morris(root):
if root==None:
return None
cur=root
while cur!=None:
if cur.leftchild==None:
print cur.data
cur = cur.rightchild
else:
pre = get_predecessor(cur)
if pre.rightchild==None:
pre.rightchild=cur
cur = cur.leftchild
elif(pre.rightchild==cur):
pre.rightchild=None
print cur.data
cur = cur.rightchild
def get_predecessor(node):
pre = node
if pre.leftchild!=None:
pre = pre.leftchild
while pre.rightchild!=None and pre.rightchild!=node:
pre = pre.rightchild
return pre
t1.midorder()
print("="*)
morris(t1)
morris遍历(中序)
4,优先队列和二叉堆(priority queue and binary heap)
优先队列:优先队列和队列类似,enqueue操作能加入元素到队列末尾,dequeue操作能移除队列首位元素,不同的是优先队列的元素具有优先级,首位元素具有最高或最小优先级,因此当进行enqueue操作时,还需要根据元素的优先级将其移动到适合的位置。优先队列一般利用二叉堆来实现,其enqueue和dequeue的复杂度都为O(logn)。(也可以用list来实现,但list的插入复杂度为O(n),再进行排序的复杂度为O(n logn))
二叉堆:二叉堆是一颗完全二叉树,当父节点的键值总是大于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最大堆,当父节点的键值总是小于或等于任何一个子节点的键值时为最小堆。(完全二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的节点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点;满二叉树:除叶子结点外的所有结点均有两个子结点。节点数达到最大值。所有叶子结点必须在同一层上)
最小堆示例及操作如下:(父节点的值总是小于或等于子节点)
BinaryHeap() #创建空的二叉堆
insert(k) #插入新元素
findMin() #返回最小值,不删除
delMin() #返回最小值,并删除
isEmpty()
size()
buildHeap(list) #通过list创建二叉堆
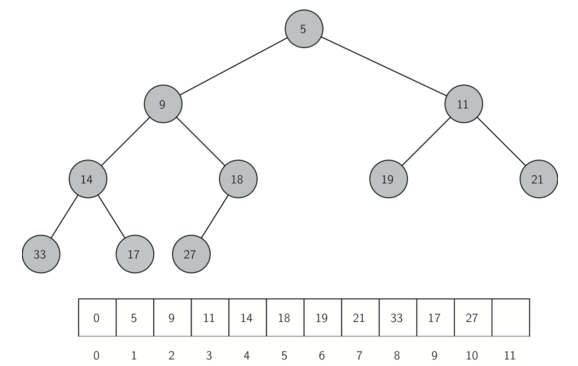
对于完全二叉树,若根节点的序号为p,则左右节点的序号应该为2p和2p+1,结合上图可以发现,可以用一个队列(首位元素为0)来表示二叉堆的结构。最小堆的python实现代码如下:(heaplist中第一个元素为0,不会用到,只是为了保证二叉堆的序列从1开始,方便进行除和乘2p,2p+1)
#coding:utf-8 class BinaryHeap(object):
def __init__(self):
self.heapList=[0]
self.size = 0 #将元素加到完全二叉树末尾,然后再根据其大小调整其位置
def insert(self,k):
self.heapList.append(k)
self.size = self.size+1
self._percUp(self.size) # 如果当前节点比父节点小,和父节点交换位置,一直向上重复该过程
def _percUp(self,size):
i = size
while i>0:
if self.heapList[i]<self.heapList[i//2]:
temp = self.heapList[i]
self.heapList[i] = self.heapList[i//2]
self.heapList[i//2] = temp
i=i//2 # 将根元素返回,并将最末尾元素移动到根元素保持完全二叉树结构不变,再根据大小,将新的根元素向下移动到合适的位置
def delMin(self):
temp = self.heapList[1]
self.heapList[1]=self.heapList[self.size]
self.size = self.size-1
self.heapList.pop()
self._percDown(1)
return temp # 如果当前节点比最小子节点大,和该子节点交换位置,一直向下重复该过程
def _percDown(self,i):
while (2*i)<=self.size:
mc = self._minChild(i)
if self.heapList[i]>self.heapList[mc]:
temp = self.heapList[i]
self.heapList[i]=self.heapList[mc]
self.heapList[mc] =temp
i = mc #返回左右子节点中较小子节点的位置
def _minChild(self,i):
if (2*i+1)>self.size:
return 2*i
else:
if self.heapList[2*i] < self.heapList[2*i+1]:
return 2*i
else:
return 2*i+1 #通过一个list建立二叉堆
def buildHeap(self,list):
i = len(list)//2
self.heapList = [0]+list[:]
self.size = len(list)
while i>0:
self._percDown(i)
i = i-1
insert()插入过程示例图如下:将元素加到完全二叉树末尾,然后再根据其大小调整其位置
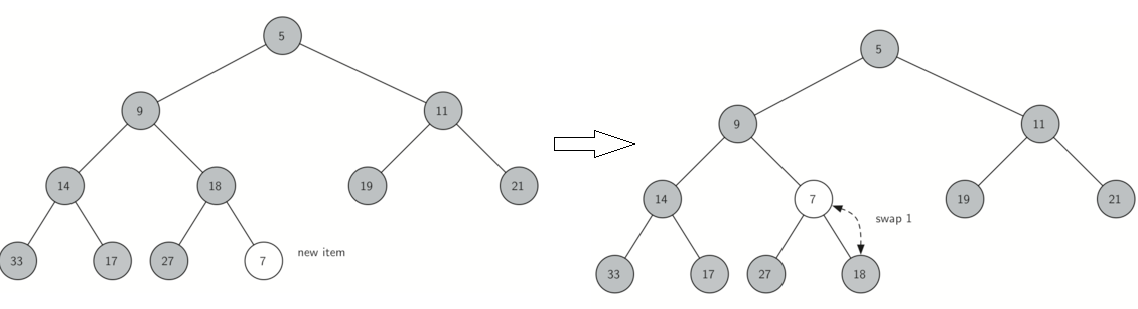
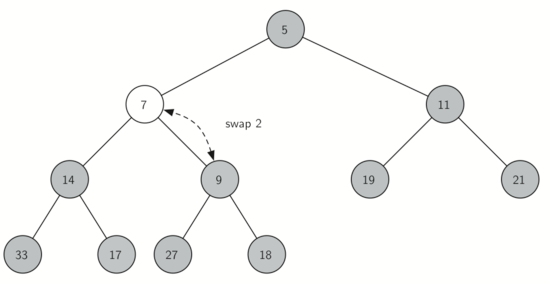
delMin()操作过程示例如下:将根元素返回,并将最末尾元素移动到根元素保持完全二叉树结构不变,再根据大小,将新的根元素向下移动到合适的位置
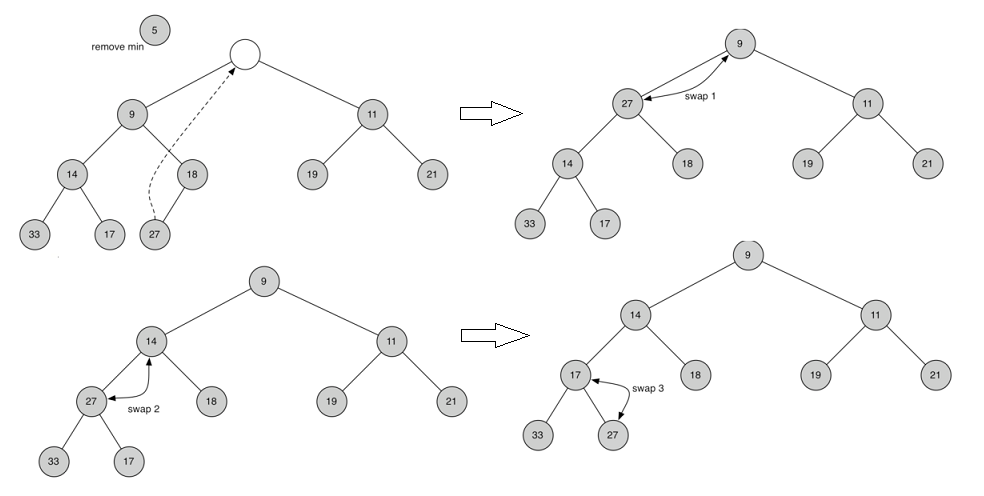
insert和delMin的复杂度都为O(log n), buildHeap的复杂度为O(n),利用二叉堆对list进行排序,复杂度为O(n log n),代码如下:
#通过list构造二叉堆,然后不断将堆顶元素返回,就得到排序好的list
alist = [54,26,93,17,98,77,31,44,55,20]
h = BinaryHeap()
h.buildHeap(alist)
s=[]
while h.size>0:
s.append(h.delMin())
print s
#堆排序
def build_min_heap(alist):
size = len(alist)
hq = []+alist
i = len(alist)//
while i>:
movedown(hq,i,size)
i = i-
return hq
def movedown(hq,i,size):
while (*i)<=size:
small = *i
if *i+<=size and hq[*i]>hq[*i+]:
small = *i+
if hq[i]>hq[small]:
hq[i],hq[small] = hq[small],hq[i]
i = small def heappop(hq):
temp = hq[]
hq[]=hq[-]
hq.pop()
movedown(hq,,len(hq)-)
return temp alist = [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]
q = build_min_heap(alist)
t = []
for i in range(len(alist)):
t.append(heappop(q))
print t
堆排序
#coding:utf- #堆排序
def build_max_heap(alist):
length = len(alist)
for i in range(length/,-,-):
heapify(alist,i,length) def heapify(alist,i,length):
left = *i+
right = *i+
largest = i
if left<length and alist[left]>alist[largest]:
largest = left
if right<length and alist[right]>alist[largest]:
largest = right
if largest!=i:
swap(alist,i,largest)
heapify(alist,largest,length)
def swap(alist,i,j):
alist[i],alist[j] = alist[j],alist[i] def heapsort(alist):
length = len(alist)
build_max_heap(alist)
for i in range(len(alist)-,,-):
swap(alist,,i)
length = length-
heapify(alist,,length)
return alist
alist = [,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,]
print(heapsort(alist))
最大堆排序列表
5,二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, bst)
二叉搜索树:左节点的值,总是小于其父节点的值,右节点的值总是大于其父节点的值(bst property)。如下图所示:
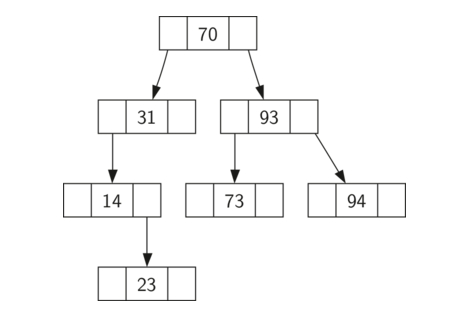
利用python实现二叉搜索树代码如下:
#二叉查找树
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self,value,leftchild=None,rightchild=None,parent=None):
self.value = value
self.leftchild = leftchild
self.rightchild = rightchild
self.parent = parent def is_leaf(self):
return not self.leftchild and not self.rightchild def is_leftchild(self):
return self.parent.leftchild==self def is_rightchild(self):
return self.parent.rightchild==self def has_both_children(self):
return self.leftchild and self.rightchild def has_left_child(self):
return self.leftchild def has_right_child(self):
return self.rightchild def delete(self):
if self.is_leftchild():
self.parent.leftchild=None
elif self.is_rightchild():
self.parent.rightchild=None class BinarySearchTree(object):
def __init__(self,node=None):
self.root=node
self.size = def length(self):
return self.szie def insert(self,value):
if self.root==None:
self.root = TreeNode(value)
else:
self._insert(self.root,value)
def _insert(self,node,value):
if node.value>value:
if node.leftchild:
self._insert(node.leftchild,value)
else:
temp = TreeNode(value)
node.leftchild=temp
temp.parent = node
elif node.value<value:
if node.rightchild:
self._insert(node.rightchild,value)
else:
temp = TreeNode(value)
node.rightchild=temp
temp.parent = node
else:
print("%s已经存在"%value) def search(self,value):
if self.root==None:
return None
else:
return self._search(self.root,value) def _search(self,node,value):
if node==None:
return None
if node.value>value:
return self._search(node.leftchild,value)
elif node.value<value:
return self._search(node.rightchild,value)
else:
return node def delete(self,value):
node = self._search(self.root,value)
if node==None:
return None
if node.is_leaf(): #删除节点为叶子结点
node.delete()
elif node.has_both_children(): #删除节点有两个孩子
successor = self.find_min(node)
node.value = successor.value
if successor.is_leaf():
successor.delete()
else: #successor 只可能有一个右节点
if successor.is_leftchild():
successor.parent.leftchild = successor.rightchild
elif successor.is_rightchild():
successor.parent.rightchild = successor.rightchild
successor.rightchild.parent = successor.parent
else: #删除节点只有一个孩子
if node.has_left_child():
if node.is_leftchild():
node.parent.leftchild=node.leftchild
node.leftchild.parent=node.parent
elif node.is_rightchild:
node.parent.rightchild = node.leftchild
node.leftchild.parent = node.parent
elif node.has_right_child():
if node.is_leftchild():
node.parent.leftchild = node.rightchild
node.rightchild.parent = node.parent
elif node.is_rightchild():
node.parent.rightchild = node.rightchild
node.rightchild.parent = node.parent def find_min(self,node):
cur = node.rightchild
while cur.leftchild: #右子树的最小值
cur = cur.leftchild
return cur def traverse(self):
row=[self.root]
while row:
print([i.value for i in row])
temp=[]
for node in row:
if node.leftchild:
temp.append(node.leftchild)
if node.rightchild:
temp.append(node.rightchild)
row = temp if __name__=='__main__':
root = BinarySearchTree()
root.insert()
root.insert()
root.insert()
root.insert()
root.insert()
root.insert()
root.insert()
root.traverse()
root.insert()
root.insert()
print(root.search())
print(root.search())
print("*"*)
root.traverse()
# print("delete leaf")
# root.delete()
# root.traverse()
# print("delete node with one child")
# root.delete()
# root.traverse()
print("delete node with two children")
root.delete()
root.traverse()
二叉查找树
上述代码中,进行节点删除时注意有三种情况:
删除节点为叶子结点:直接删除节点,然后将其父节点的左子节点或右子节点设为None
删除节点有一个孩子节点:利用子节点代替删除节点原来的位置
删除节点有两个孩子节点:找到删除节点的后继节点(其左子树的最右边节点,或者是其右子树的最左边节点),利用后继节点代替该节点的位置
利用二叉搜索树可以实现map(字典),常用操作如下:
Map() # 创建字典
put(key,val) # 字典中插入数据
get(key) # 取键值
del # 删除
len() # 求长度
in # 是否存在
python实现map代码如下:
#coding:utf-8 class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self,key, value, leftChild=None,rightChild=None,parent=None):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.leftChild = leftChild
self.rightChild = rightChild
self.parent = parent
self.balanceFactor =0 def hasLeftChild(self):
return self.leftChild def hasRightChild(self):
return self.rightChild def isLeftChild(self):
return self.parent and self.parent.leftChild==self def isRightChild(self):
return self.parent and self.parent.rightChild==self def isRoot(self):
return not self.parent def isLeaf(self):
return not (self.leftChild or self.rightChild) def hasAnyChildren(self):
return self.leftChild or self.rightChild def hasBothChildren(self):
return self.leftChild and self.rightChild def replaceNodeData(self,key,value,lc=None,rc=None):
self.key=key
self.value = value
self.leftChild = lc
self.rightChild = rc
if self.hasLeftChild():
self.leftChild.parent = self
if self.hasRightChild():
self.rightChild = self def __iter__(self):
if self:
if self.hasLeftChild():
for elem in self.leftChild: #调用self.leftChiLd.__iter__(),所以此处是递归的
yield elem
yield self.key, self.value, self.balanceFactor
if self.hasRightChild():
for elem in self.rightChild: #调用self.rightChiLd.__iter__()
yield elem def findSuccessor(self): #寻找继承
succ = None
if self.hasRightChild():
succ = self.rightChild._findMin()
else:
if self.parent:
if self.isLeftChild():
succ = self.parent
else:
self.parent.rightChild = None
succ = self.parent.findSuccessor()
self.parent.rightChild = self
return succ def _findMin(self):
current = self
while current.hasLeftChild():
current = current.leftChild
return current def spliceOut(self):
if self.isLeaf():
if self.isLeftChild():
self.parent.leftChild=None
else:
self.parent.rightChild=None
elif self.hasAnyChildren():
if self.hasLeftChild():
if self.isLeftChild():
self.parent.leftChild = self.leftChild
else:
self.parent.rightChild = self.leftChild
self.leftChild.parent = self.parent
else:
if self.isLeftChild():
self.parent.leftChild = self.rightChild
else:
self.parent.rightChild = self.rightChild
self.rightChild.parent = self.parent class BinarySearchTree(object): def __init__(self):
self.root = None
self.size = 0 def length(self):
return self.size def __len__(self):
return self.size def __iter__(self):
return self.root.__iter__() #加入元素
def put(self,key,value):
if self.root:
self._put(key,value,self.root)
else:
self.root = TreeNode(key,value)
self.size = self.size+1 def _put(self,key,value,currentNode):
if currentNode.key<key:
if currentNode.hasRightChild():
self._put(key,value,currentNode.rightChild)
else:
currentNode.rightChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode)
elif currentNode.key>key:
if currentNode.hasLeftChild():
self._put(key,value,currentNode.leftChild)
else:
currentNode.leftChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode)
else:
currentNode.replaceNodeData(key,value) def __setitem__(self, key, value):
self.put(key,value) #获取元素值
def get(self,key):
if self.root:
node = self._get(key,self.root)
if node:
return node.value
else:
return None
else:
return None def _get(self,key,currentNode):
if not currentNode:
return None
if currentNode.key==key:
return currentNode
elif currentNode.key<key:
return self._get(key,currentNode.rightChild) #rightChild可能不存在
else:
return self._get(key,currentNode.leftChild) #leftChild可能不存在 # def _get(self,key,currentNode):
# if currentNode.key == key:
# return currentNode
# elif currentNode.key<key:
# if currentNode.hasRightChild():
# return self._get(key,currentNode.rightChild)
# else:
# return None
# else:
# if currentNode.hasLeftChild():
# return self._get(key,currentNode.leftChild)
# else:
# return None def __getitem__(self, key):
return self.get(key) def __contains__(self, key): #实现 in 操作
if self._get(key,self.root):
return True
else:
return False def delete(self,key):
if self.size>1:
node = self._get(key,self.root)
if node:
self._del(node)
self.size = self.size - 1
else:
raise KeyError('Error, key not in tree')
elif self.size==1 and self.root.key==key:
self.root = None
self.size = self.size - 1
else:
raise KeyError('Error, key not in tree') def _del(self,currentNode):
if currentNode.isLeaf():
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.leftChild = None
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.rightChild = None
elif currentNode.hasBothChildren():
successor = currentNode.findSuccessor() #此处successor为其右子树的最小值,即最左边的值
successor.spliceOut()
currentNode.key = successor.key
currentNode.value = successor.value
elif currentNode.hasAnyChildren():
if currentNode.hasLeftChild():
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.leftChild
currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.leftChild
currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent
else: # currentNode has no parent (is root)
currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.leftChild.key,
currentNode.leftChild.value,
currentNode.leftChild.leftChild,
currentNode.leftChild.rightChild)
elif currentNode.hasRightChild():
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.rightChild
currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.rightChild
currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent
else: # currentNode has no parent (is root)
currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.rightChild.key,
currentNode.rightChild.value,
currentNode.rightChild.leftChild,
currentNode.rightChild.rightChild) def __delitem__(self, key):
self.delete(key)
if __name__ == '__main__':
mytree = BinarySearchTree()
mytree[8]="red"
mytree[4]="blue"
mytree[6]="yellow"
mytree[5]="at"
mytree[9]="cat"
mytree[11]="mat" print(mytree[6])
print(mytree[5])
for x in mytree:
print x del mytree[6]
print '-'*12
for x in mytree:
print x
在上述代码中最复杂的为删除操作,删除节点时有三种情况:节点为叶子节点,节点有两个子节点,节点有一个子节点。当节点有两个子节点时,对其删除时,应该用其右子树的最小值来代替其位置(即右子树中最左边的值)。
对于map进行复杂度分析,可以发现put,get取决于tree的高度,当节点随机分配时复杂度为O(log n),但当节点分布不平衡时,复杂度会变成O(n),如下图所示:
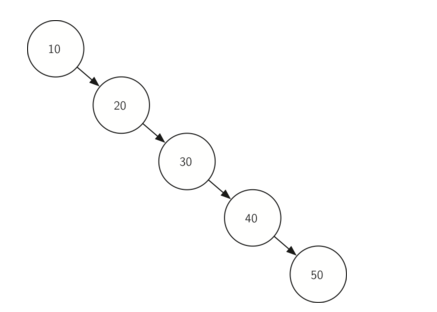
6, 平衡二叉搜索树 (Balanced binary search tree, AVL tree)
平衡二叉搜索树:又称为AVL Tree,取名于发明者G.M. Adelson-Velskii 和E.M. Landis,在二叉搜索树的基础上引入平衡因子(balance factor),每次插入和删除节点时都保持树平衡,从而避免上面出现的搜索二叉树复杂度会变成O(n)。一个节点的balance factor的计算公式如下,即该节点的左子树高度减去右子树高度。
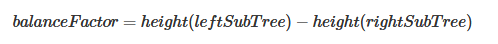
当树所有节点的平衡因子为-1,0,1时,该树为平衡树,平衡因子大于1或小于-1时,树不平衡需要调整,下图为一颗树的各个节点的平衡因子。(1时树left-heavy,0时完全平衡,-1时right-heavy)
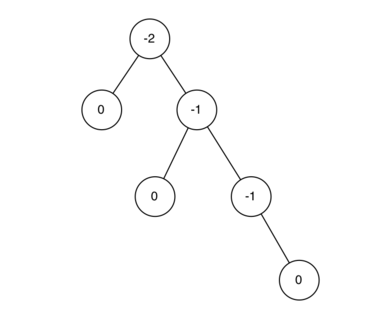
相比于二叉搜索树,AVL树的put和delete操作后,需要对节点的平衡因子进行更新,如果某个节点不平衡时,需要进行平衡处理,主要分为左旋转和右旋转。
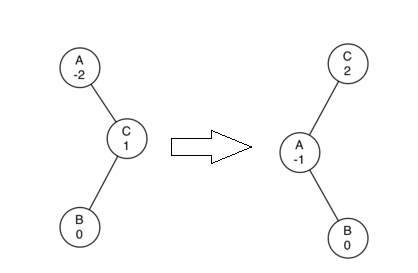
左旋转:如图,节点A的平衡因子为-2(right heavy),不平衡,对其进行左旋转,即以A为旋转点,AB边逆时针旋转。
详细操作为:1,A的右节点B作为新的子树根节点
2,A成为B的左节点,如果B有左节点时,将其左节点变为A的右节点(A的右节点原来为B,所以A的右节点现在为空)

右旋转:如图,节点E的平衡因子为2(left heavy),不平衡,对其进行右旋转,即以E为旋转点,EC边顺时针旋转。
详细操作为:1,E的左节点C作为新的子树根节点
2,E成为C的右节点,如果C有右节点时,将其右节点变为E的左节点(E的左节点原来为C,所以E的左节点现在为空)
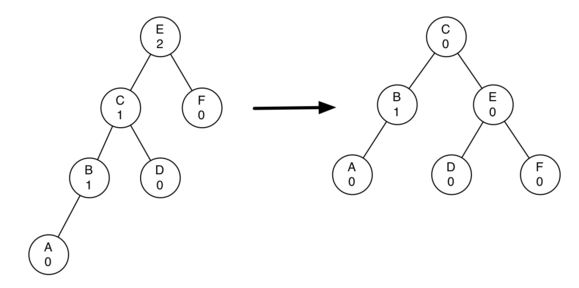
特殊情况:当出现下面的情况时,如图所示,A依旧为right heavy,但若进行左旋转,又会出现left heavy,无法完成平衡操作。 所以在进行左旋转和右旋转前需要进行一步判断,具体操作如下:
1,如果某节点需要进行左旋转平衡时(right heavy),检查其右子节点的平衡因子,若右子节点为left heavy,先对右子节点右旋转,然后对该节点左旋转
2,如果某节点需要进行右旋转平衡时(left heavy),检查其左子节点的平衡因子,若左子节点为right heavy,先对左子节点左旋转,然后对该节点右旋转
AVL tree用python实现的代码如下:
#coding:utf-8 from binarySearchTree import TreeNode, BinarySearchTree # class AVLTreeNode(TreeNode):
#
# def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
# self.balanceFactor = 0
# super(AVLTreeNode,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs) class AVLTree(BinarySearchTree): def _put(self,key,value,currentNode):
if currentNode.key<key:
if currentNode.hasRightChild():
self._put(key,value,currentNode.rightChild)
else:
currentNode.rightChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode)
self.updateBalance(currentNode.rightChild)
elif currentNode.key>key:
if currentNode.hasLeftChild():
self._put(key,value,currentNode.leftChild)
else:
currentNode.leftChild=TreeNode(key,value,parent=currentNode)
self.updateBalance(currentNode.leftChild)
else:
currentNode.replaceNodeData(key,value) def _del(self,currentNode):
if currentNode.isLeaf():
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.leftChild = None
currentNode.parent.balanceFactor -=1
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.rightChild = None
currentNode.parent.balanceFactor += 1
if currentNode.parent.balanceFactor>1 or currentNode.parent.balanceFactor<-1:
self.reblance(currentNode.parent)
elif currentNode.hasBothChildren():
successor = currentNode.findSuccessor() #此处successor为其右子树的最小值,即最左边的值
# 先更新parent的balanceFactor
if successor.isLeftChild():
successor.parent.balanceFactor -= 1
elif successor.isRightChild():
successor.parent.balanceFactor += 1
successor.spliceOut()
currentNode.key = successor.key
currentNode.value = successor.value # 删除后,再判断是否需要再平衡,然后进行再平衡操作
if successor.parent.balanceFactor>1 or successor.parent.balanceFactor<-1:
self.reblance(successor.parent)
elif currentNode.hasAnyChildren(): #先更新parent的balanceFactor
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.balanceFactor -= 1
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.balanceFactor += 1 if currentNode.hasLeftChild():
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.leftChild
currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.leftChild
currentNode.leftChild.parent = currentNode.parent
else: # currentNode has no parent (is root)
currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.leftChild.key,
currentNode.leftChild.value,
currentNode.leftChild.leftChild,
currentNode.leftChild.rightChild)
elif currentNode.hasRightChild():
if currentNode.isLeftChild():
currentNode.parent.leftChild = currentNode.rightChild
currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent
elif currentNode.isRightChild():
currentNode.parent.rightChild = currentNode.rightChild
currentNode.rightChild.parent = currentNode.parent
else: # currentNode has no parent (is root)
currentNode.replaceNodeData(currentNode.rightChild.key,
currentNode.rightChild.value,
currentNode.rightChild.leftChild,
currentNode.rightChild.rightChild)
#删除后,再判断是否需要再平衡,然后进行再平衡操作
if currentNode.parent!=None: #不是根节点
if currentNode.parent.balanceFactor>1 or currentNode.parent.balanceFactor<-1:
self.reblance(currentNode.parent) def updateBalance(self,node):
if node.balanceFactor>1 or node.balanceFactor<-1:
self.reblance(node)
return
if node.parent!=None:
if node.isLeftChild():
node.parent.balanceFactor +=1
elif node.isRightChild():
node.parent.balanceFactor -=1
if node.parent.balanceFactor!=0:
self.updateBalance(node.parent) def reblance(self,node):
if node.balanceFactor>1:
if node.leftChild.balanceFactor<0:
self.rotateLeft(node.leftChild)
self.rotateRight(node)
elif node.balanceFactor<-1:
if node.rightChild.balanceFactor>0:
self.rotateRight(node.rightChild)
self.rotateLeft(node) def rotateLeft(self,node):
newroot = node.rightChild
node.rightChild = newroot.leftChild
if newroot.hasLeftChild():
newroot.leftChild.parent = node
newroot.parent = node.parent
if node.parent!=None:
if node.isLeftChild():
node.parent.leftChild = newroot
elif node.isRightChild():
node.parent.rightChild = newroot
else:
self.root = newroot
newroot.leftChild = node
node.parent = newroot
node.balanceFactor = node.balanceFactor+1-min(newroot.balanceFactor,0)
newroot.balanceFactor = newroot.balanceFactor+1+max(node.balanceFactor,0) def rotateRight(self,node):
newroot = node.leftChild
node.leftChild = newroot.rightChild
if newroot.rightChild!=None:
newroot.rightChild.parent = node
newroot.parent = node.parent
if node.parent!=None:
if node.isLeftChild():
node.parent.leftChild = newroot
elif node.isRightChild():
node.parent.rightChild = newroot
else:
self.root = newroot
newroot.rightChild = node
node.parent = newroot
node.balanceFactor = node.balanceFactor-1-max(newroot.balanceFactor,0)
newroot.balanceFactor = newroot.balanceFactor-1+min(node.balanceFactor,0) if __name__ == '__main__': mytree = AVLTree()
mytree[8]="red"
mytree[4]="blue" mytree[6]="yellow" mytree[5]="at" mytree[9]="cat" mytree[11]="mat" print(mytree[6])
print(mytree[5]) print '-'*12
print ('key','value','balanceFactor')
for x in mytree:
print x
print 'root:',mytree.root.key del mytree[6]
print '-'*12
print ('key','value','balanceFactor')
for x in mytree:
print x
print 'root:',mytree.root.key
AVL Tree继承了二叉搜索树,对其插入和删除方法进行了重写,另外对TreeNode增加了balanceFactor属性。再进行左旋转和右旋转时,对于balanceFactor的需要计算一下,如图的左旋转过程中,D成为了新的根节点,只有B和D的平衡因子发生了变化,需要对其进行更新。(右旋转和左旋转类似)
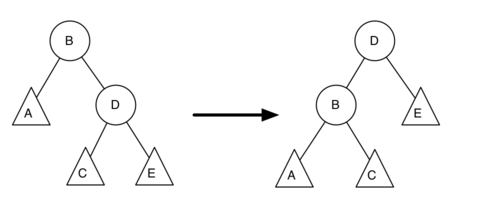
B的平衡因子计算过程如下:(newBal(B)为左旋转后B的平衡因子,oldBal(B)为原来的节点B的平衡因子,h为节点的高度)
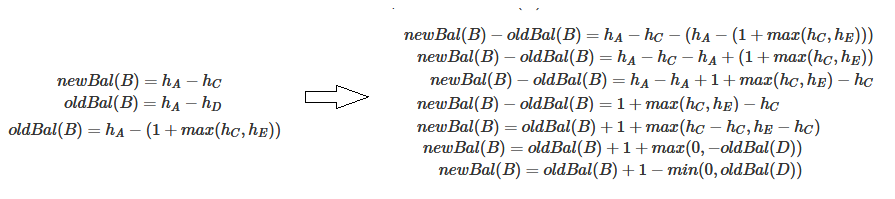
D的平衡因子计算过程如下:
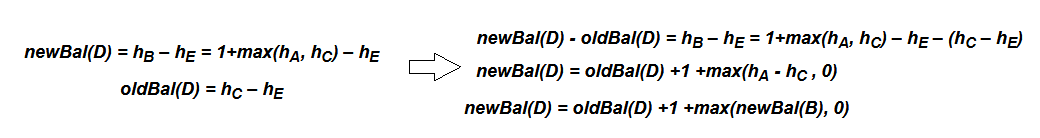
由于AVL Tree总是保持平衡,其put和get操作的复杂度能保持为O(log n)
7.总结
到目前为止,对于map(字典)数据结构,用二叉搜索树和AVL树实现了,也用有序列表和哈希表实现过,对应操作的复杂度如下:
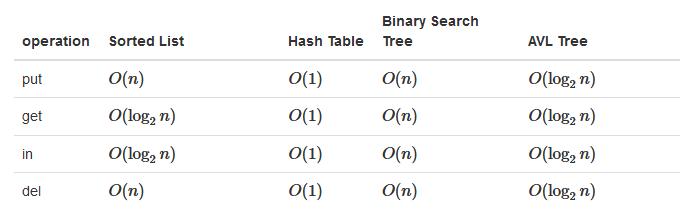
8. 其他树形结构
8.1 哈夫曼树及哈夫曼编码
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/mcgrady/p/3329825.html
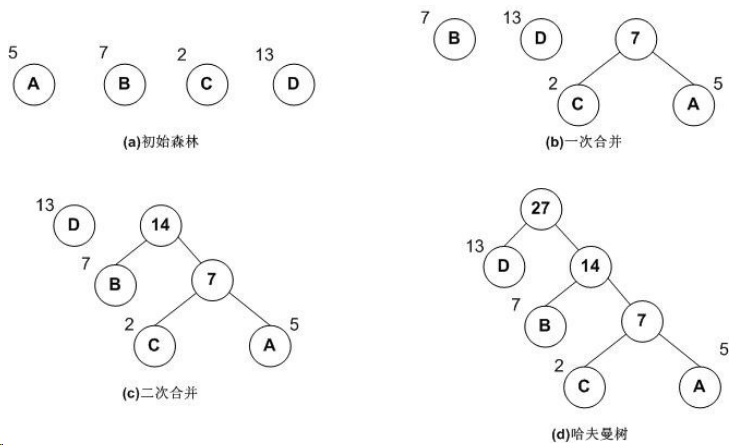
哈夫曼树:哈夫曼树是一种带权路径长度最短的二叉树,也称为最优二叉树。 (权:叶子节点的权重;路径:根节点到叶子节点经过的线段)
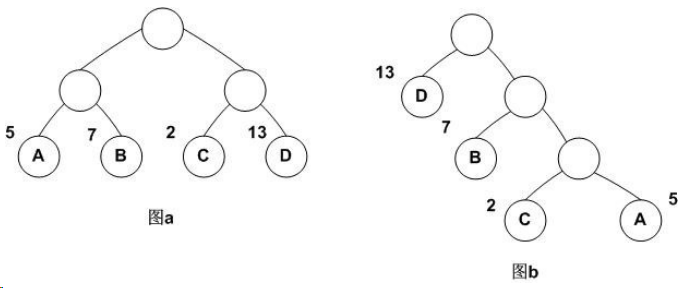
下图中的带权路径长度分别为:
图a: WPL=5*2+7*2+2*2+13*2=54
图b: WPL=5*3+2*3+7*2+13*1=48
可见,图b的带权路径长度较小,我们可以证明图b就是哈夫曼树(也称为最优二叉树)。
构建哈夫曼树步骤:
1,将所有左,右子树都为空的作为根节点。
2,在森林中选出两棵根节点的权值最小的树作为一棵新树的左,右子树,且置新树的附加根节点的权值为其左,右子树上根节点的权值之和。注意,左子树的权值应小于右子树的权值。
3,从森林中删除这两棵树,同时把新树加入到森林中。
4,重复2,3步骤,直到森林中只有一棵树为止,此树便是哈夫曼树。
下面是构建哈夫曼树的图解过程:
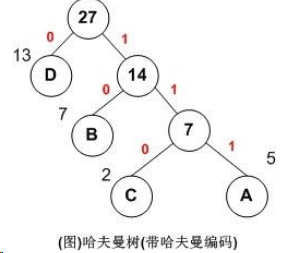
哈夫曼编码:利用哈夫曼树求得的用于通信的二进制编码称为哈夫曼编码。树中从根到每个叶子节点都有一条路径,对路径上的各分支约定指向左子树的分支表示”0”码,指向右子树的分支表示“1”码,取每条路径上的“0”或“1”的序列作为各个叶子节点对应的字符编码,即是哈夫曼编码。
上图A,B,C,D对应的哈夫曼编码分别为:111,10,110,0。 用图说明如下:
利用哈夫曼树编码字符窜和解码: 首先统计字符窜中每个字符出现的频率,以字符频率为权重建立哈夫曼树,得到每个字符的哈夫曼码,最后对字符窜编码。下面代码利用哈夫曼树对字符窜进行了编码和解码
#哈夫曼树节点
class HaffmanNode(object): def __init__(self,value=None,weight=None,leftchild=None,rightchild=None): #value为统计字符,weight为字符出现频率
self.value = value
self.weight = weight
self.leftchild=leftchild
self.rightchild = rightchild def is_leaf(self): #判断是否为叶子节点
return not self.leftchild and not self.rightchild def __lt__(self,other): #用于两个对象间大小比较
return self.weight<other.weight #根据哈夫曼树获得哈夫曼码
def get_haffman_code(root,code,code_dict1,code_dict2):
if root.is_leaf():
code_dict1[root.value]=code #进行编码时使用
code_dict2[code]=root.value #进行解码时使用
else:
get_haffman_code(root.leftchild, code+'',code_dict1,code_dict2)
get_haffman_code(root.rightchild, code+'',code_dict1,code_dict2) #根据字符频率构建哈夫曼树
import heapq
def build_haffman_tree(weight_dict):
hp=[]
for value,weight in weight_dict.items(): #value为字符,weight为字符出现频率
heapq.heappush(hp,HaffmanNode(value,weight))
while len(hp)>:
left = heapq.heappop(hp)
right = heapq.heappop(hp)
parent = HaffmanNode(weight=left.weight+right.weight,leftchild=left,rightchild=right)
heapq.heappush(hp,parent)
return hp[] #剩下最后元素即为haffman tree weight_dict = {}
code_dict1={}
code_dict2={}
#对字符窜astr进行哈夫曼编码
def haff_encode(astr):
for i in astr:
if i not in weight_dict:
weight_dict[i]=
else:
weight_dict[i]+=
haffman_tree = build_haffman_tree(weight_dict)
get_haffman_code(haffman_tree,'',code_dict1,code_dict2)
encoded_astr = ''
for i in astr:
encoded_astr+=code_dict1[i]
return encoded_astr #解码哈夫曼编码后的字符窜
def haff_decode(encoded_astr,code_dict2):
code = ''
astr=''
for i in encoded_astr:
code = code+i
if code in code_dict2:
astr+=code_dict2[code]
code=''
return astr astr="This is my big fancy house"
encoded_astr=haff_encode(astr)
print(encoded_astr)
decoded_astr = haff_decode(encoded_astr,code_dict2)
print(decoded_astr)
编码和解码字符串
利用哈夫曼树压缩文件和解压缩:
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/4cbbfed4160b
https://github.com/gg-z/huffman_coding
https://gist.github.com/Arianxx/603dc688a4b68f207ada2c4534758637
8.2 Trie树(字典树)
Trie树:又称字典树或前缀树,储存单词字符,方便用来进行词频统计和前缀匹配。Trie tree如图所示: 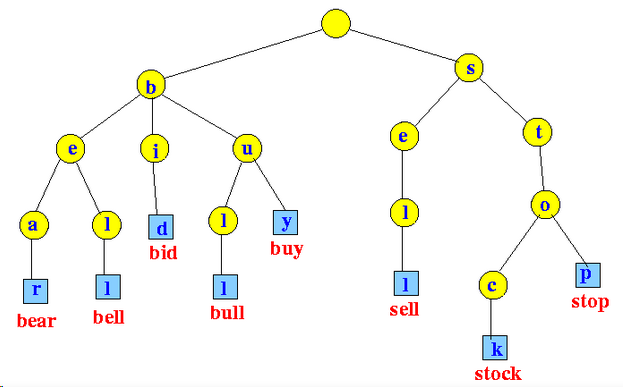
Trie树的特点:
除根节点外每个节点都包含字符
从根节点到叶子节点路径上的字符组成一个完成单词,
多个单词的共同路径节点即为公共前缀
Trie作用:
节约储存内存;
前缀匹配时,搜索更快,时间复杂度为O(n), (n为单词的长度)
下面代码用python实现了一个简单Trie Tree
#Trie树,字典树
class TrieNode(object):
def __init__(self,char):
self.char = char
self.child=[]
self.is_leaf = False #是否是叶子节点,即是否为一个完整单词的最后一个字母
self.counter = #多少单词有这个共同前缀 class TrieTree(object):
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode(None) #将一个单词加入到Trie树中
def add_trie_word(self,word):
root = self.root
for char in word:
found = False
for node in root.child:
if node.char==char:
node.counter+=
root = node
found = True
break
if not found:
temp = TrieNode(char)
root.child.append(temp)
root = temp
root.is_leaf=True #查找某个单词前缀是否在Trie树,并返回有多少个单词有这个共同前缀
def search_trie_prefix(self,prefix):
root = self.root
if not root.child:
return False,
for char in prefix:
found=False
for node in root.child:
if node.char==char:
root=node
found=True
break
if not found:
return False,
return True,root.counter trie_tree = TrieTree()
trie_tree.add_trie_word("hammer")
trie_tree.add_trie_word("ham")
trie_tree.add_trie_word("had")
print(trie_tree.search_trie_prefix("ha"))
print(trie_tree.search_trie_prefix("ham"))
print(trie_tree.search_trie_prefix("had"))
print(trie_tree.search_trie_prefix("b"))
Trie tree
Trie tree参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/11/25/2788268.html
https://towardsdatascience.com/implementing-a-trie-data-structure-in-python-in-less-than-100-lines-of-code-a877ea23c1a1
参考:http://interactivepython.org/runestone/static/pythonds/Trees/toctree.html
树及其衍生算法(Trees and tree algorithms)的更多相关文章
- [数据结构]——二叉树(Binary Tree)、二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)及其衍生算法
二叉树(Binary Tree)是最简单的树形数据结构,然而却十分精妙.其衍生出各种算法,以致于占据了数据结构的半壁江山.STL中大名顶顶的关联容器--集合(set).映射(map)便是使用二叉树实现 ...
- 笔试算法题(58):二分查找树性能分析(Binary Search Tree Performance Analysis)
议题:二分查找树性能分析(Binary Search Tree Performance Analysis) 分析: 二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree,BST)是一颗典型的二叉树,同时任 ...
- 将百分制转换为5分制的算法 Binary Search Tree ordered binary tree sorted binary tree Huffman Tree
1.二叉搜索树:去一个陌生的城市问路到目的地: for each node, all elements in its left subtree are less-or-equal to the nod ...
- 【机器学习实战 第九章】树回归 CART算法的原理与实现 - python3
本文来自<机器学习实战>(Peter Harrington)第九章"树回归"部分,代码使用python3.5,并在jupyter notebook环境中测试通过,推荐c ...
- JavaScript 排序算法(JavaScript sorting algorithms)
JavaScrip 排序算法(JavaScript Sorting Algorithms) 基础构造函数 以下几种排序算法做为方法放在构造函数里. function ArrayList () { va ...
- 树状数组(Binary Indexed Tree,BIT)
树状数组(Binary Indexed Tree) 前面几篇文章我们分享的都是关于区间求和问题的几种解决方案,同时也介绍了线段树这样的数据结构,我们从中可以体会到合理解决方案带来的便利,对于大部分区间 ...
- 【数据结构与算法】k-d tree算法
k-d tree算法 k-d树(k-dimensional树的简称),是一种分割k维数据空间的数据结构.主要应用于多维空间关键数据的搜索(如:范围搜索和最近邻搜索). 应用背景 SIFT算法中做特征点 ...
- 树状数组(Binary Indexed Tree)
树状数组(Binary Indexed Tree,BIT) 是能够完成下述操作的数据结构. 给一个初始值全为 0 的数列 a1, a2, ..., an (1)给定 i,计算 a1+a2+...+ai ...
- 图及其衍生算法(Graphs and graph algorithms)
1. 图的相关概念 树是一种特殊的图,相比树,图更能用来表示现实世界中的的实体,如路线图,网络节点图,课程体系图等,一旦能用图来描述实体,能模拟和解决一些非常复杂的任务.图的相关概念和词汇如下: 顶点 ...
随机推荐
- ES5中一些重要的拓展
1.对象的拓展 ①Object.create(obj, {age:{value:18, writable:true, configurable:true, enumerable:true}); 以指定 ...
- tomcat 的配置文件server.xml 几个端口的作用
tomcat中server.xml配置文件中几个port的作用和区别 在tomcat的server.xml中有这么几个port,很多人虽然一直在使用tomcat,但是却不知道这几个port各有什么作用 ...
- python读取ubuntu系统磁盘挂载情况
磁盘挂载 利用df -h 的命令 此功能主要实现了python 命令行执行函数进行解析df 返回的数据 代码如下 : # liunx 系统获取 磁盘挂载的情况 代码 #!/usr/bin/pyt ...
- 如何使用jMeter发送两个逻辑上相关的HTTP请求
在前一篇文章使用jMeter构造大量并发的随机HTTP请求里我通过jMeter构造了大量的HTTP GET并发请求,对服务器产生了大量读操作. 现在我有另一个需求场景:假设我开发了一个创建Servic ...
- Spring Cloud(十)高可用的分布式配置中心 Spring Cloud Config 中使用 Refresh
上一篇文章讲了SpringCloudConfig 集成Git仓库,配和 Eureka 注册中心一起使用,但是我们会发现,修改了Git仓库的配置后,需要重启服务,才可以得到最新的配置,这一篇我们尝试使用 ...
- spring 整合mongodb报NoSuchMethodError错误
刚开始通过网上查到相关的资料进行了一些配置,参考链接:http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1454374782167.html maven的dependenci ...
- Oralce问题之Oracle ORA-28001:某用户密码过期
解决办法: (1).通过CMD打开命令行窗口,以sysdba连接数据库 SqlPlus / as sysdba (2).通过查询dba_user检查哪些用户过期 Sql>Select UserN ...
- 解读>/dev/null 2>&1
背景 我们经常能在shell脚本中发现>/dev/null 2>&1这样的语句.以前的我并没有去深入地理解这段命令的作用,照搬照用,今天开始去解读>/dev/null 2&g ...
- Codeforces Round #589 (Div. 2) B. Filling the Grid
链接: https://codeforces.com/contest/1228/problem/B 题意: Suppose there is a h×w grid consisting of empt ...
- ORM高阶补充:only, defer,select_related
Queryset官方文档:https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/ref/models/querysets/ 1.需求1:只取某n列 1.方法1:values 2 ...
