STL标准库-算法-常用算法
技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
介绍11种STL标准库的算法,从这11种算法中总结一下算法的基本使用
1.accumulate() 累加
2.for_each() for一段区间 做你指定的行为
3.replace(), replace_if(), replace_copy() 替换函数
4.count(), count_if() 计数
5.find() 查找
6.sort() 排序
7.binary_search()查看元素是否在指定区间
下面的仿函数都没有继承自 binary_function<T,T,bool>, unary_function<T,bool>,但是在实际操作中,声明仿函数一定要继承自binary_function<T,T,bool>,unary_function<T,bool>
下一节内容会介绍为什么要继承自这两个类
一 accumulate(),累加,将指定区域内的value累加起来
源码及参数介绍
//默认累加算法,将传进的__first(begin()迭代器)位置,至__last(end()迭代器),与init求和
template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Tp>
inline _Tp
accumulate(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Tp __init)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_InputIteratorConcept<_InputIterator>)
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last); for (; __first != __last; ++__first)
__init = __init + *__first;
return __init;
} //自定义accumulate 按照指定的要求做”累加”操作
template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Tp, typename _BinaryOperation>
inline _Tp
accumulate(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Tp __init,
_BinaryOperation __binary_op)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_InputIteratorConcept<_InputIterator>)
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last); for (; __first != __last; ++__first)
__init = __binary_op(__init, *__first);
return __init;
}
基本使用
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; namespace wzj000 {
int myfunc(int x, int y) {return x+*y;} struct myclass{
int operator()(int x, int y){return x+*y;}
}; void test_accumulate()
{
int init = ;
int num[] {, , }; cout<<"default accumulate: " << accumulate(num, num+, init)<< endl; //100 + 10 + 20 + 30 默认累加 cout << "using minus: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, minus<int>())<< endl; //100 - 10 - 20 - 30 将累加改为递减 cout << "using custom function: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myfunc)<< endl; // 100 + 2*10 + 2*20 + 2*30 自定义"累加"规则 func cout << "suing custom object: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myclass())<< endl; // 100 + 3*10 + 3*20 + 3*30自定义"累加"规则 仿函数
}
}
测试结果

二 for_each() for一段区间 做你指定的行为
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class Function>
Function for_each(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Function f)
{//参数1 起始点 参数2 终点, 参数3 想要执行的操作
for( ; first != last; ++first)
{
f(*first);
}
return f;
}
基本使用
namespace wzj001 {
void myfunc(int i)
{
cout << " - " << i;
}
struct myclass{
void operator()(int i)
{
cout << " ^ " << i;
}
};
void test_for_each()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myfunc);
cout << endl;
}
void test_for_each_classFunc()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << endl;
}
}
测试结果

三 replace() 替换函数
replace_if()
replace_copy()
源码及参数介绍
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
void replace(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T & old_value, const T& new_value)
{//范围内所有等于old_value者都一new_value取代
for( ; first != last; ++first)
{
if(*first == old_value)
*first = new_value;
}
} template <class Inputerator, class Inputerator, class T>
void replace_if(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Predicate pred, const T& new_value)
{//范围内所有满足pred()为true之元素都以new_value取代
for( ; first != last; ++first)
{
if(pred(*first))
*first = new_value;
}
} template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class T>
Outputerator replace_copy(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Outputerator result, const T & old_value, const T& new_value)
{//范围内所有等于old_value者都以new_value放置新区域
//不符合者原值放入新区域
for( ; first != last; ++first, ++result)
{
*result = *first == old_value ? new_value : *first;
}
}
基本使用
namespace wzj002 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ? true : false;
}
};
void test_replace()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ,);
cout << "replace: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_replace_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass(), );
cout << "replace_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_replace_copy()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
vector<int> myNewVector;
myNewVector.resize();
replace_copy(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myNewVector.begin(), , );
cout << "replace_if_New: ";
for(auto i : myNewVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "replace_if_Old: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
测试结果

四 count() 计数
count_if()
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class T>
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
count(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& value)
{
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
for( ; first != last; ++first)
if(*first == value) //满足要求 值 == value 累计+1
++n;
return n;
} template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class Predicate>
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
count_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Predicate pred)
{
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
for( ; first != last; ++first)
if(pred(*first)) //满足指定要求 累计 +1
++n;
return n;
}
count()和count_if()是全局算法,适用于array,vector,list,forward_list, deque
map,set,unordered_set/map由于是关联式容器,所有有自己的count()和count_if()函数
基本使用
namespace wzj003 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
};
void test_count()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
cout << "count(): "<< count(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) <<endl;
}
void test_count_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , };
cout << "count_if(): " << count_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()) <<endl;
}
}
测试结果

五 find() 查找
find_if()
find()和find_if()是全局算法,适用于array,vector,list,forward_list, deque
map,set,unordered_set/map由于是关联式容器,所有有自己的find()和find_if()函数
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class T>
Inputerator find_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& value)
{
while(first != last && *first != value)
++first;
return first;
} template <class Inputerator, class Predicate>
Inputerator find_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Predicate pred)
{
while(first != last && !pred(*first))
++first;
return first;
}
基本使用
namespace wzj004 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
};
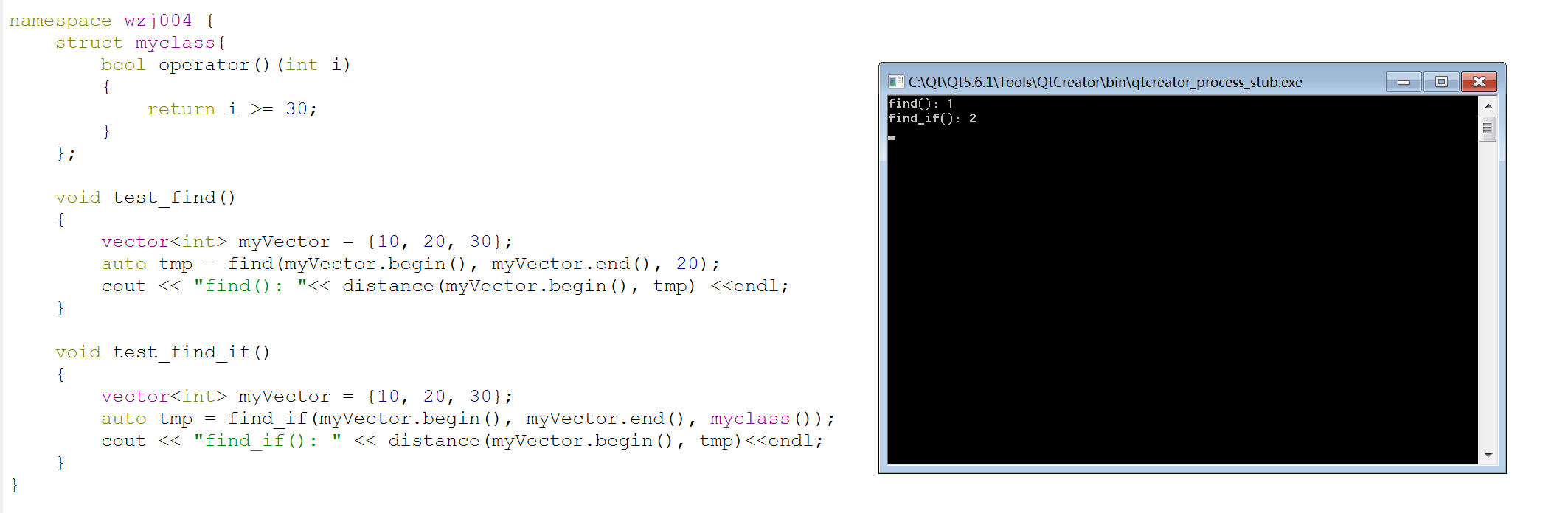
void test_find()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), );
cout << "find(): "<< distance(myVector.begin(), tmp) <<endl;
}
void test_find_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "find_if(): " << distance(myVector.begin(), tmp)<<endl;
}
}
测试结果
六 sort 排序
list和forward_list有成员sort()函数
set/map自动排序
array,vector,deque用全局sort()
namespace wzj005 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;// sort默认降序, 自定义为升序
}
};
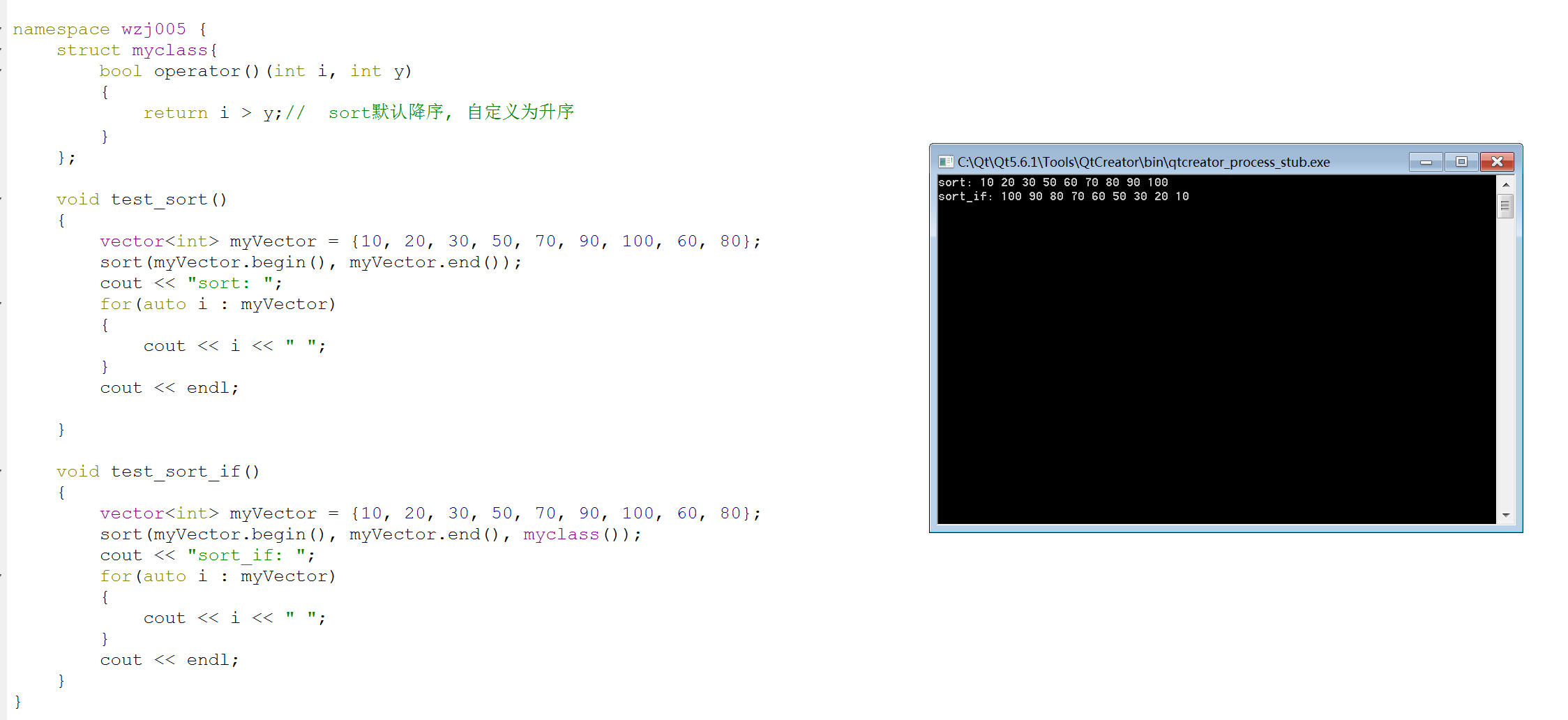
void test_sort()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end());
cout << "sort: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_sort_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "sort_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
测试结果
七 binary_search()查看元素是否在指定区间内
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class T>
bool binary_search(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& val)
{//返回元素是否在指定区间
first = std::lower_bound(first,last,val);
return (first != last && !(val < *first));
}
基本使用
namespace wzj006 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;
}
};
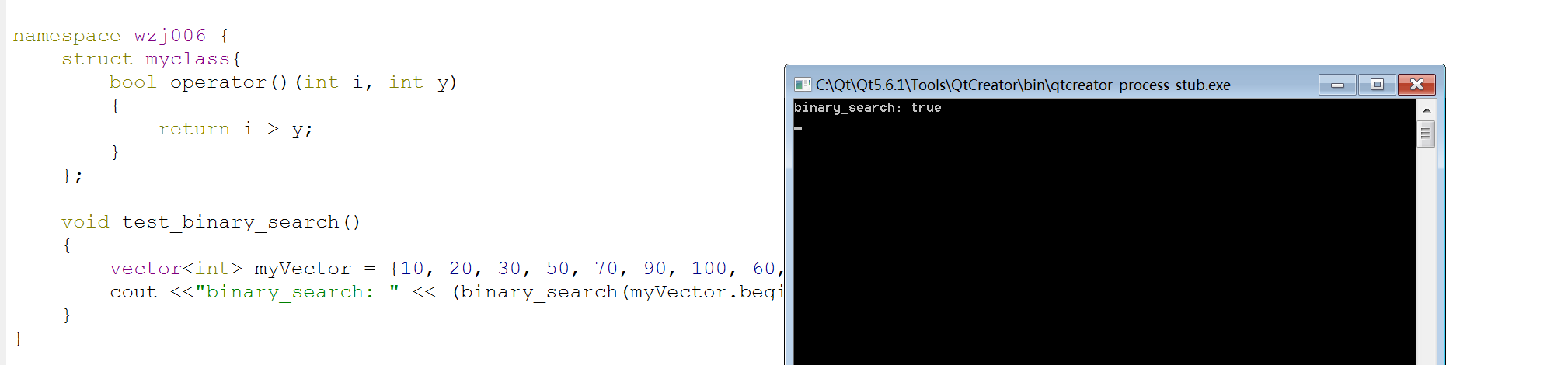
void test_binary_search()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
cout <<"binary_search: " << (binary_search(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) ? "true" : "false") << endl;
}
}
测试结果
全部测试代码
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; namespace wzj000 {
int myfunc(int x, int y) {return x+*y;} struct myclass{
int operator()(int x, int y){return x+*y;}
}; void test_accumulate()
{
int init = ;
int num[] {, , }; cout<<"default accumulate: " << accumulate(num, num+, init)<< endl; //100 + 10 + 20 + 30 默认累加 cout << "using minus: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, minus<int>())<< endl; //100 - 10 - 20 - 30 将累加改为递减 cout << "using custom function: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myfunc)<< endl; // 100 + 2*10 + 2*20 + 2*30 //自定义"累加"规则 func cout << "suing custom object: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myclass())<< endl; // 100 + 3*10 + 3*20 + 3*30//自定义"累加"规则 仿函数
}
} namespace wzj001 {
void myfunc(int i)
{
cout << " - " << i;
} struct myclass{
void operator()(int i)
{
cout << " ^ " << i;
}
}; void test_for_each()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myfunc);
cout << endl;
} void test_for_each_classFunc()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << endl;
}
} namespace wzj002 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ? true : false;
}
}; void test_replace()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ,);
cout << "replace: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} void test_replace_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass(), );
cout << "replace_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} void test_replace_copy()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
vector<int> myNewVector;
myNewVector.resize();
replace_copy(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myNewVector.begin(), , );
cout << "replace_if_New: ";
for(auto i : myNewVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl; cout << "replace_if_Old: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} namespace wzj003 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
}; void test_count()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
cout << "count(): "<< count(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) <<endl;
} void test_count_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , };
cout << "count_if(): " << count_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()) <<endl;
}
} namespace wzj004 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
}; void test_find()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), );
cout << "find(): "<< distance(myVector.begin(), tmp) <<endl;
} void test_find_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "find_if(): " << distance(myVector.begin(), tmp)<<endl;
}
} namespace wzj005 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;// sort默认降序, 自定义为升序
}
}; void test_sort()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end());
cout << "sort: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl; } void test_sort_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "sort_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} namespace wzj006 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;
}
}; void test_binary_search()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
cout <<"binary_search: " << (binary_search(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) ? "true" : "false") << endl;
}
} int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
wzj000::test_accumulate();
wzj001::test_for_each();
wzj001::test_for_each_classFunc();
wzj002::test_replace();
wzj002::test_replace_if();
wzj002::test_replace_copy();
wzj003::test_count();
wzj003::test_count_if();
wzj004::test_find();
wzj004::test_find_if();
wzj005::test_sort();
wzj005::test_sort_if();
wzj006::test_binary_search();
return ;
}
参考侯捷<<STL源码剖析>>
STL标准库-算法-常用算法的更多相关文章
- STL标准库-容器-vector
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. 向量容器vector是一个动态数组,内存连续,它是动态分配内存,且每次扩张的原来的二倍. 他的结构如下 一 定义 vector ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(一)sort
前言: 近来在学习STL标准库,做一份笔记并整理好,方便自己梳理知识.以后查找,也方便他人学习,两全其美,快哉快哉! 这里我会以中国大学慕课上北京大学郭炜老师的<程序设计与算法(一)C语言程序设 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与multiset
技术在于交流.沟通,转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. set与multiset关联容器 结构如下 set是一种关联容器,key即value,value即key.它是自动排序,排序特点依据key se ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(二)二分查找
二.STL中的二分查找算法 1.binary_search 2.lower_bound 3.upper_bound 记得#include<algorithm>! 前言: 在这个笔记中,我把 ...
- stl标准库 iterator_traits
为什么标准库里要有traits? 我们先回忆一下,标准库提供的算法的一些特征: 参数一般包括iterator. 要根据iterator的种类,和iterator包装的元素的类型等信息,来决定使用最优化 ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(五)set
前言: 在这个笔记中,我把大多数代码都加了注释,我的一些想法和注解用蓝色字体标记了出来,重点和需要关注的地方用红色字体标记了出来,这一篇后面主要都是我的记录了,为了防止大片蓝色字体出现,后面就不改蓝色 ...
- STL标准库-容器-deque
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. deque双向开口可进可出的容器 我们知道连续内存的容器不能随意扩充,因为这样容易扩充别人那去 deque却可以,它创造了内存 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与map
STL标准库-容器-set与multiset C++的set https://www.cnblogs.com/LearningTheLoad/p/7456024.html STL标准库-容器-map和 ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(三)multiset
C++STL标准库学习笔记(三)multiset STL中的平衡二叉树数据结构 前言: 在这个笔记中,我把大多数代码都加了注释,我的一些想法和注解用蓝色字体标记了出来,重点和需要关注的地方用红色字体标 ...
随机推荐
- dubbo 实战总结
1,出现重复调用.因为有重试机制,可以改为异步调用或者幂等操作.
- Spring报NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 上述可以看出Ac ...
- Qt5.3.2_Oracle驱动
参考网址:http://blog.csdn.net/sdqyhn/article/details/39855847 ZC: 将编译好的 qsqloci.dll和qsqlocid.dll 放到 目录“E ...
- android开发:Android 中自定义View的应用
大家好我们今天的教程是在Android 教程中自定义View 的学习,对于初学着来说,他们习惯了Android 传统的页面布局方式,如下代码: <?xml version="1.0&q ...
- Oracle 千万级别数据查询优化
说明:平时很少接触到大数据分页,今天有兴趣在数据库插入1000万条数据进行测试,经过查询相关资料得到如下说明:笔者在工作中有一上百万条记录的表,在jsp页面中需对该表进行分页显示,便考虑用rownum ...
- 谈谈Java反射机制
原文出处: locality 写在前面:什么是java反射机制?我们又为什么要学它?当程序运行时,允许改变程序结构或变量类型,这种语言称为动态语言.我们认为java并不是动态语言,但是它却有一个非常突 ...
- 新概念 Lesson 3 Nice to meet you
Nice to meet you. 你好 打招呼: hi,hello 重点: 打招呼和互相介绍.主系表结构 Is Chang-woo Chinese? 昌武是中国人吗? No,he isn't . H ...
- 20170112xlVBA查询SQL
Sub NextSeven_CodeFrame() '应用程序设置 Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = Fal ...
- 『cs231n』线性分类器损失函数
代码部分 SVM损失函数 & SoftMax损失函数: 注意一下softmax损失的用法: SVM损失函数: import numpy as np def L_i(x, y, W): ''' ...
- 诡异的小bug 自动生成font标签包裹span标签中的文字
某天测试自己写的网站的时候突然发现页面上一些文字排版出现了一些奇怪的错乱,在控制台发现错乱的文字被font标签包裹着 ,但是代码中根本没用用到font标签 后来发现是因为自己不小心点了谷歌浏览器地址栏 ...
