c++ primer plus 第六章 课后题答案

#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std; int main()
{
char in_put; do
{
cout << "Please enter the letters (enter @ exit):";
cin >> in_put; if (islower(in_put))
cout << "The uppercase of the letter " << in_put << " is " << char (toupper(in_put)) << ".\n";
else if (isupper(in_put))
cout << "The lowercase of the letter " << in_put << " is " << char (tolower(in_put)) << ".\n";
else if (in_put != '@')
cout << "Please enter the letters!\n";
} while (in_put != '@'); cout << "Exit!\n"; system("pause");
}

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = ; int main()
{
double in_put[MAX];
double avg = ;
int sum; cout << "Please enter no more than " << MAX << " digits.\n";
for (int i = ; i < MAX; ++i)
{
cout << "The " << i + << "th digit is: ";
if (cin >> in_put[i])
avg += in_put[i];
else
{
cout << "Not digit! Exit!\n";
sum = i;
break;
}
} avg = avg / sum;
int num_a=, num_b=;
for (int i = ; i < sum; ++i)
{
if (in_put[i] > avg)
num_a += ;
else
num_b += ;
} cout << "The average of these numbers is: " << avg << ".\n"
<< "There are " << num_a << " numbers larger than the average value.\nAnd "
<< num_b << " numbers not larger than the average value.\n"; system("pause");
}

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int show(char); int show(char ch)
{
int flag = ;
cout << "A maple is a ";
switch(ch)
{
case 'c':
cout << "carnivore.\n";
break;
case 'p':
cout << "pianist.\n";
break;
case 't':
cout << "tree.\n";
break;
case 'g':
cout << "game.\n";
break;
default:
cout << "Please enter c,p,t,g :";
flag = ;
}
return flag;
} int main()
{
char ch;
int flag; cout << "Please enter one of the following choices:\n"
<< "c) carnivore\t" << "p) pianist\n"
<< "t) tree\t\t" << "g) game\n"; do
{
cin >> ch;
flag=show(ch);
} while (flag == ); system("pause");
}


#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int strsize = ;
const int MAX = ; struct bop
{
char fullname[strsize];
char title[strsize];
char bopname[strsize];
int preference;
}; int show(char ch, bop mmm[MAX])
{
int flag = ;
switch (ch)
{
case 'a':
for (int i = ; i < MAX; ++i)
{
cout << mmm[i].fullname<<endl;
}
break;
case 'b':
for (int i = ; i < MAX; ++i)
{
cout << mmm[i].title << endl;
}
break;
case 'c':
for (int i = ; i < MAX; ++i)
{
cout << mmm[i].bopname << endl;
}
break;
case 'd':
for (int i = ; i < MAX; ++i)
{
switch(mmm[i].preference)
{
case :cout << mmm[i].fullname << endl;
break;
case :cout << mmm[i].title << endl;
break;
case :cout << mmm[i].bopname << endl;
break;
}
}
break;
case 'q':
flag = ;
break;
default:
cout << "Please enter a,b,c,d,q!\n";
}
return flag;
} int main()
{
bop all_peo[MAX] =
{
{ "QQQ","NiCai","qqq", },
{ "WWW","BuCai","www", },
{ "EEE","CaiBuCai","eee", },
{ "RRR","JiuBuCai","rrr", },
{ "TTT","LaDao","ttt", }
}; char ch;
int flag; cout << "Benevolent Order of Programmers Report\n"
<< "a. display by name\t" << "b. display by title\n"
<< "c. display by bopname\t" << "d. display by preference\n"
<< "q. quit\n"; cout << "Enter your choice:";
cin >> ch; flag = show(ch, all_peo); while (flag == )
{
cout << "Next choice: ";
cin >> ch;
flag=show(ch, all_peo);
}
cout << "Bye!\n"; system("pause");
}
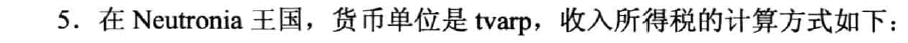

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const float Tax_1 = 0.1;
const float Tax_2 = 0.15;
const float Tax_3 = 0.2;
const int Tax_come1 = ;
const int Tax_come2 = ;
const int Tax_come3 = ; double Tax(double); int main()
{
double income; cout << "Please enter income(enter a negative or non-numeric exit): ";
while (cin >> income)
{
if (income < )
break;
double tax;
tax=Tax(income);
cout << "Income tax: " << tax << "\nNext enter: ";
}
cout << "Bye!\n"; system("pause");
} double Tax(double income)
{
double tax;
double num1 = income - Tax_come3;
double num2 = income - Tax_come2;
double num3 = income - Tax_come1;
if (num1 > )
tax =(Tax_come2 - Tax_come1)*Tax_1 + (Tax_come3 - Tax_come2)*Tax_2 + num1 * Tax_3;
else
{
if (num2 > )
tax =(Tax_come2 - Tax_come1)*Tax_1 + num2 *Tax_2;
else
{
if (num3 > )
tax = num3 * Tax_1;
else
tax = ;
}
} return tax;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std; struct potron
{
string name;
double money;
}; int main()
{
int num;
cout << "Please enter the number of donors: ";
cin >> num; potron *potrons = new potron[num];
for (int i = ; i < num; ++i)
{
cout << "Please enter the " << i + << "th donor name:";
cin.ignore();
getline(cin,potrons[i].name);
cout << "Please enter the number of " << i + << "th donor contributions:";
cin >> potrons[i].money;
} int flag1 = , flag2 = ;
cout << "Grand Potrons\n";
for (int i = ; i < num; ++i)
{
if (potrons[i].money > )
{
cout << potrons[i].name << " : " << potrons[i].money << endl;
flag1 = ;
}
}
if (flag1 == )
cout << "None!\n"; cout << "Potrons\n";
for (int i = ; i < num; ++i)
{
if (!(potrons[i].money > ))
{
cout << potrons[i].name << " : " << potrons[i].money << endl;
flag2 = ;
}
}
if (flag2 == )
cout << "None!\n"; system("pause");
}

#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = ; int main()
{
char words[MAX][];
char ch;
int num_y = , num_f = , num_o = ; cout << "Enter words (q to quit):\n";
for (int i = ; i < MAX; ++i)
{
cin >> words[i];
ch = words[i][];
if (ch == 'q')
break;
if (isalpha(ch))
{
switch (ch)
{
case 'a':;
case 'e':;
case 'i':;
case 'o':;
case 'u':
num_y += ;
break;
default:
num_f += ;
break;
}
}
else
num_o += ;
} cout << num_y << " beginning with vowels\n";
cout << num_f << " beginning with consonants\n";
cout << num_o << " others\n";
system("pause");
}

#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = ; int main()
{
char filename[SIZE];
ifstream infile;
cout << "Enter name of data file: ";
cin.getline(filename, SIZE);
infile.open(filename);
if (!infile.is_open())
{
cout << "Could not open the file " << filename << endl;
cout << "Program terminating.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} int count=;
char ch; infile >> ch;
while (infile.good())
{
++count;
// ch= infile.get();//读取空白字符
infile >> ch;//不读取空白字符
} cout << "The number of characters in the file is: " << count << endl; system("pause");
}

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = ; struct potron
{
string name;
double money;
}; int main()
{
char filename[SIZE];
ifstream infile;
cout << "Enter name of data file: ";
cin.getline(filename, SIZE);
infile.open(filename);
if (!infile.is_open())
{
cout << "Could not open the file " << filename << endl;
cout << "Program terminating.\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} int num;
infile >> num; potron *potrons = new potron[num];
for (int i = ; i < num; ++i)
{
infile.ignore();
getline(infile, potrons[i].name);
infile >> potrons[i].money;
} int flag1 = , flag2 = ;
cout << "Grand Potrons\n";
for (int i = ; i < num; ++i)
{
if (potrons[i].money > )
{
cout << potrons[i].name << " : " << potrons[i].money << endl;
flag1 = ;
}
}
if (flag1 == )
cout << "None!\n"; cout << "Potrons\n";
for (int i = ; i < num; ++i)
{
if (!(potrons[i].money > ))
{
cout << potrons[i].name << " : " << potrons[i].money << endl;
flag2 = ;
}
}
if (flag2 == )
cout << "None!\n"; system("pause");
}
c++ primer plus 第六章 课后题答案的更多相关文章
- c++ primer plus 第七章 课后题答案
#include <iostream> using namespace std; double HAR_AVG(double, double); void TEST(bool); int ...
- c++ primer plus 第五章 课后题答案
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { ; cout << "Please enter two n ...
- c++ primer plus 第四章 课后题答案
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string first_name; ...
- c++ primer plus 第三章 课后题答案
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { ; int shen_gao; cout <<"Please ...
- python 核心编程第六章课后题自己做的答案
6–6. 字符串.创建一个 string.strip()的替代函数:接受一个字符串,去掉它前面和后面的 空格(如果使用 string.*strip()函数那本练习就没有意义了) 'Take a str ...
- c++ primer plus 第二章 课后题答案
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { cout << "My name is Jiantong C ...
- python核心编程第5章课后题答案
5-8Geometry import math def sqcube(): s = float(raw_input('enter length of one side: ')) print 'the ...
- python核心编程第4章课后题答案(第二版75页)
4-1Python objects All Python objects have three attributes:type,ID,and value. All are readonly with ...
- python核心编程第3章课后题答案(第二版55页)
3-4Statements Ues ; 3-5Statements Use\(unless part of a comma-separated sequence in which case \ is ...
随机推荐
- dxf cad dwg 文件读写,支持跨平台移植 库
http://www.pudn.com/Download/item/id/3096684.html 联合开发网 --->绘图程序
- 利用lodop打印控件轻松实现批量打印 (转载http://www.thinkphp.cn/topic/13085.html)
最近在做一个打印程序,要实现批量打印功能,在网上找了很多天,也在tp官网咨询大牛们,对大家的的提议我一一进行了研究,总结如下: 要实现批量打印可以有两个办法: 一是利用专业的报表程序,能实现十分复杂的 ...
- csv到mysql数据库如何分割
这两天修改一个取XML文件存入到CSV,然后再存入到mysql的bug,bug是XML文件里面有个name字段,存入CSV文件里面的时候我们用“|”,来分割字段.但是name里面有时候也有 ...
- Maven的常用功能
一.jar包管理(仓库) 最佳实践: 1:排除依赖 pom中依赖了某个第三方API,此API又依赖其它API,有可能出问题.(必须申明排除该第三方依赖) Spring-core又隐式的依赖了commo ...
- Perl的子程序(二)
在Perl中可以自己创建子程序(Subroutine): 关键字sub,子程序名以及用花括号封闭起来的代码块. sub marine { ... } 子程序名与标量的命名空间是不同的两个部分. 子程 ...
- typed.js
实现效果,文字逐个输出. 实例代码: <script> $(function(){ $("#head-title").typed({ strings: ["为 ...
- 20154312 曾林 Exp5_MSF基础应用
--目录-- MSF渗透测试-CVE-2017-11882 1.基础内容回答 2.实践过程记录 2.1.主动攻击实践-ms08_067 2.2.针对浏览器的攻击-ms10_046 2.3.针对客户端的 ...
- Linux服务器配置---ssh配置
Ssh配置 通过配置文件,我们可以有效的管理ssh 1.空闲时间关闭连接 1)修改配置文件“/etc/ssh/sshd_config”,设置clientAliveInterval和client ...
- Linux基础命令---service
service service可以控制系统服务(打开.关闭.重启).service在尽可能可预测的环境中运行SystemV init脚本,删除大多数环境变量并将当前工作目录设置为根目录.脚本参数位于“ ...
- QPropertyAnimation 几行代码快速制作流畅的动画效果
QPropertyAnimation Class 官方英文文档[点击前往] QPropertyAnimation Class 中文译文文档[点击前往] 简介 QPropertyAnimation ...
