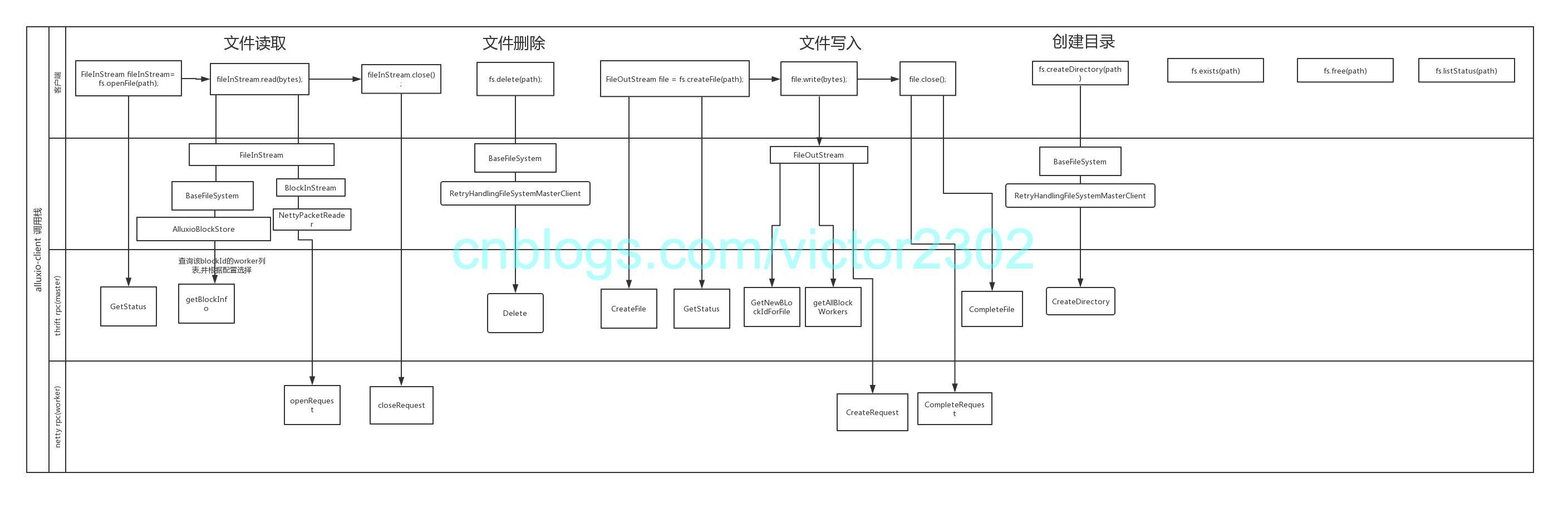
alluxio源码解析-netty部分(2)
netty简介
netty作为alluxio中重要的通讯组件
在常见的客户端上传,下载中,都会有netty的参与
关于这个图,可以看上篇文章的介绍:
https://www.cnblogs.com/victor2302/p/10490253.html
- 解耦ufs和worker缓存的功能
- 解耦 BlockHandler和 ShortCircuitBlockHandler
- 解耦异步上传,同步上传
- 高性能传输
netty客户端部分:
1.固定的处理器:alluxio.network.netty.NettyClient
final Bootstrap boot = new Bootstrap(); boot.group(WORKER_GROUP)
.channel(NettyUtils.getClientChannelClass(!(address instanceof InetSocketAddress)));
boot.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
boot.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
boot.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
if (NettyUtils.USER_CHANNEL_TYPE == ChannelType.EPOLL) {
boot.option(EpollChannelOption.EPOLL_MODE, EpollMode.LEVEL_TRIGGERED);
} // After 10 missed heartbeat attempts and no write activity, the server will close the channel.
final long timeoutMs = Configuration.getMs(PropertyKey.NETWORK_NETTY_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_MS);
final long heartbeatPeriodMs = Math.max(timeoutMs / 10, 1);
boot.handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(RPCMessage.createFrameDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(ENCODER);
pipeline.addLast(DECODER);
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, heartbeatPeriodMs, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new IdleWriteHandler());
}
});
2.临时的处理器:针对通用response注册回调(ShortCircuitBlockHandler 调用)
public static ProtoMessage call(final NettyRPCContext context, ProtoMessage request)
throws IOException {
Channel channel = Preconditions.checkNotNull(context.getChannel());
final Promise<ProtoMessage> promise = channel.eventLoop().newPromise();
channel.pipeline().addLast(new RPCHandler(promise));
channel.writeAndFlush(new RPCProtoMessage(request)).addListener((ChannelFuture future) -> {
if (future.cause() != null) {
future.channel().close();
promise.tryFailure(future.cause());
}
});
ProtoMessage message;
try {
message = promise.get(context.getTimeoutMs(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
CommonUtils.closeChannel(channel);
throw new IOException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
CommonUtils.closeChannel(channel);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (channel.isOpen()) {
channel.pipeline().removeLast();
}
}
if (message.isResponse()) {
CommonUtils.unwrapResponseFrom(message.asResponse(), context.getChannel());
}
return message;
}
3.临时的处理器:针对读写操作注册回调(BlockHandler)
private NettyPacketReader(FileSystemContext context, WorkerNetAddress address,
Protocol.ReadRequest readRequest) throws IOException {
mContext = context;
mAddress = address;
mPosToRead = readRequest.getOffset();
mReadRequest = readRequest; mChannel = mContext.acquireNettyChannel(address);
mChannel.pipeline().addLast(new PacketReadHandler());
mChannel.writeAndFlush(new RPCProtoMessage(new ProtoMessage(mReadRequest)))
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} private NettyPacketWriter(FileSystemContext context, final WorkerNetAddress address, long id,
long length, long packetSize, Protocol.RequestType type, OutStreamOptions options,
Channel channel) {
mContext = context;
mAddress = address;
mLength = length;
Protocol.WriteRequest.Builder builder =
Protocol.WriteRequest.newBuilder().setId(id).setTier(options.getWriteTier()).setType(type);
if (type == Protocol.RequestType.UFS_FILE) {
Protocol.CreateUfsFileOptions ufsFileOptions =
Protocol.CreateUfsFileOptions.newBuilder().setUfsPath(options.getUfsPath())
.setOwner(options.getOwner()).setGroup(options.getGroup())
.setMode(options.getMode().toShort()).setMountId(options.getMountId()).build();
builder.setCreateUfsFileOptions(ufsFileOptions);
}
mPartialRequest = builder.buildPartial();
mPacketSize = packetSize;
mChannel = channel;
mChannel.pipeline().addLast(new PacketWriteResponseHandler());
}
netty服务端:
注册处理器列表:
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
final long timeoutMs = Configuration.getMs(PropertyKey.NETWORK_NETTY_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_MS);
// Decoders & Encoders
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", RPCMessage.createFrameDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("RPCMessageDecoder", new RPCMessageDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("RPCMessageEncoder", new RPCMessageEncoder());
// Idle Event Handlers
pipeline.addLast("idleEventHandler", new IdleStateHandler(timeoutMs, 0, 0,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
pipeline.addLast("idleReadHandler", new IdleReadHandler());
pipeline.addLast("heartbeatHandler", new HeartbeatHandler());
// Block Handlers
pipeline.addLast("blockReadHandler",
new BlockReadHandler(NettyExecutors.BLOCK_READER_EXECUTOR,
mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class), mFileTransferType));
pipeline.addLast("blockWriteHandler", new BlockWriteHandler(
NettyExecutors.BLOCK_WRITER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class),
mWorkerProcess.getUfsManager()));
pipeline.addLast("shortCircuitBlockReadHandler",
new ShortCircuitBlockReadHandler(NettyExecutors.RPC_EXECUTOR,
mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class)));
pipeline.addLast("shortCircuitBlockWriteHandler",
new ShortCircuitBlockWriteHandler(NettyExecutors.RPC_EXECUTOR,
mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class)));
pipeline.addLast("asyncCacheHandler", new AsyncCacheHandler(mRequestManager));
// UFS Handlers
pipeline.addLast("ufsFileWriteHandler", new UfsFileWriteHandler(
NettyExecutors.FILE_WRITER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getUfsManager()));
// Unsupported Message Handler
pipeline.addLast("unsupportedMessageHandler", new UnsupportedMessageHandler());
}
写入或者读取配置
alluxio.client.file.options.CreateFileOptions是FileSystem类createFile的第二个参数,可以选定不同的写入策略
例如:
- MUST_CACHE(只写入Alluxio,必须存储在Alluxio中)
- CACHE_THROUGH(尝试缓存,同步写入到UnderFS)
- THROUGH(无缓存,同步写入到UnderFS)
- ASYNC_THROUGH(异步写入到UnderFS,实现特性)
FileOutStream createFile(AlluxioURI path, CreateFileOptions options)
throws FileAlreadyExistsException, InvalidPathException, IOException, AlluxioException;
而这种写入选项,就是通过在传递netty message时,设置不同的标识,然后在netty中分派到不同的pipeline节点,处理各自的特性的
代码实例:
是否需要写入到ufs,则在UfsFileWriteHandler的acceptMessage方法中进行判断的
alluxio.worker.netty.UfsFileWriteHandler#acceptMessage
protected boolean acceptMessage(Object object) {
if (!super.acceptMessage(object)) {
return false;
}
Protocol.WriteRequest request = ((RPCProtoMessage) object).getMessage().asWriteRequest();
return request.getType() == Protocol.RequestType.UFS_FILE;
}
alluxio源码解析-netty部分(2)的更多相关文章
- Netty 源码解析: Netty 的 ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline和Inbound.Outbound 我想很多读者应该或多或少都有 Netty 中 pipeline 的概念.前面我们说了,使用 Netty 的时候,我们通 ...
- alluxio源码解析-rpc调用概述-client和worker之间的block模块的通讯架构(netty版本)(3)
(1.8版本)client和worker之间的block模块的通讯架构 block作为alluxio文件读取或者存储的最小基本单位,都是通过BlockOutStream和BlockInputtream ...
- alluxio源码解析-层次化存储(4)
层次化存储-特性介绍: https://www.alluxio.org/docs/1.6/cn/Tiered-Storage-on-Alluxio.html 引入分层存储后,Alluxio管理的数据块 ...
- alluxio源码解析-rpc调用概述(1)
alluxio中几种角色以及角色之间的rpc调用: 作为分布式架构的文件缓存系统,rpc调用必不可少 client作为客户端 master提供thrift rpc的服务,管理以下信息: block信息 ...
- Netty 4源码解析:请求处理
Netty 4源码解析:请求处理 通过之前<Netty 4源码解析:服务端启动>的分析,我们知道在最前端"扛压力"的是NioEventLoop.run()方法.我们指定 ...
- Netty 4源码解析:服务端启动
Netty 4源码解析:服务端启动 1.基础知识 1.1 Netty 4示例 因为Netty 5还处于测试版,所以选择了目前比较稳定的Netty 4作为学习对象.而且5.0的变化也不像4.0这么大,好 ...
- netty服务端启动--ServerBootstrap源码解析
netty服务端启动--ServerBootstrap源码解析 前面的第一篇文章中,我以spark中的netty客户端的创建为切入点,分析了netty的客户端引导类Bootstrap的参数设置以及启动 ...
- Netty源码解析—客户端启动
Netty源码解析-客户端启动 Bootstrap示例 public final class EchoClient { static final boolean SSL = System.getPro ...
- Netty源码解析---服务端启动
Netty源码解析---服务端启动 一个简单的服务端代码: public class SimpleServer { public static void main(String[] args) { N ...
随机推荐
- volatile的内存语义与应用
volatile的内存语义 volatile的特性 理解volatile特性的一个好方法是把对volatile变量的单个读/写,堪称是使用同一个锁对这些单个读/写操作做了同步. 锁的happens-b ...
- git简单使用-GitHub
本文描述window下如何使用git工具,操作GitHub远程代码库 一,准备工作: 1,安装git工具,一路默认next安装即可,下载地址 2,注册账号或者创建厂库(已有忽略) 注册账号后,创建仓库 ...
- Design Principles (设计原则)
这是我在2018年4月写的英语演讲稿,可惜没人听得懂(实际上就没几个人在听). 文章的内容是我从此前做过的项目中总结出来的经验,从我们的寝室铃声入手,介绍了可扩展性.兼容性与可复用性等概念,最后提出良 ...
- springboot2.0.4对接redis3.2.12版本哨兵模式
redis 哨兵模式的创建 1. 下载redis3.2.12版本.https://codeload.github.com/antirez/redis/zip/3.2.12 2. 解压后放到/usr/ ...
- kuangbin专题 专题一 简单搜索 非常可乐 HDU - 1495
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-1495 题意:有两个空杯(分别是N升和M升)和一罐满的可乐S升,S = N + M,三个容器可以互相倾倒,如果A倒入B,只有两 ...
- NetCore 获取appsetting.json 文件中的配置
1. using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration public class HomeController : Controller { public IConfi ...
- python笔记(1)--序列(列表 元组 range)
一.序列分类 1.可变序列:list 2.不可变序列:tuple,range 二.序列公共操作方法 1.操作和返回值 其中s和t代表同类型序列:n,i,j,k为整数:x为任意类型. 序号 操作 结果 ...
- Web前端_微信小程序实战开发
微信小程序开发实战教程 一.微信小程序 它是一种混合开发的方式. 是安装在微信中的程序(一个程序最多2M空间). 1.1 注册 1 2 点击立即注册:进入下方页面 3 4 点击小程序进入表单填写页 ...
- android_sdcard读写(一)
现在的android手机其实就是一个小小的掌上电脑,平时电脑有的硬件它估计也有了.这次本人研究下了其中充当手机硬盘的角色,就是sdcard.这是一个保存应用程序的好地方. 老规矩,上代码,学习代码才是 ...
- BI之路学习笔记1--SSIS包的认识和设计
进入了新的公司,开始接触新的方向,内心激动而又兴奋,对于BI以前知道的极少,从今天开始要好好学习了~ BI的概念,功能,强大之处在此先不做赘述,BI之路先要一步一个脚印扎实做起,现在正在看的也是之前好 ...
